Abstract
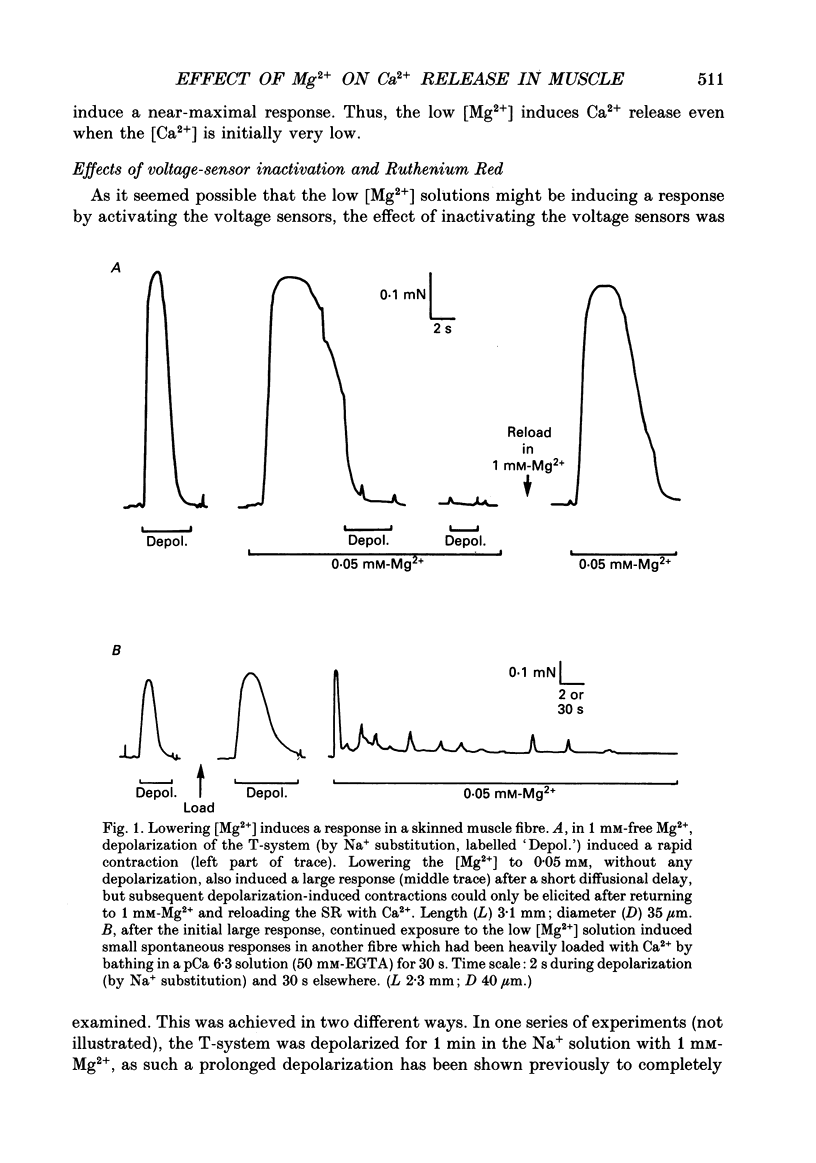
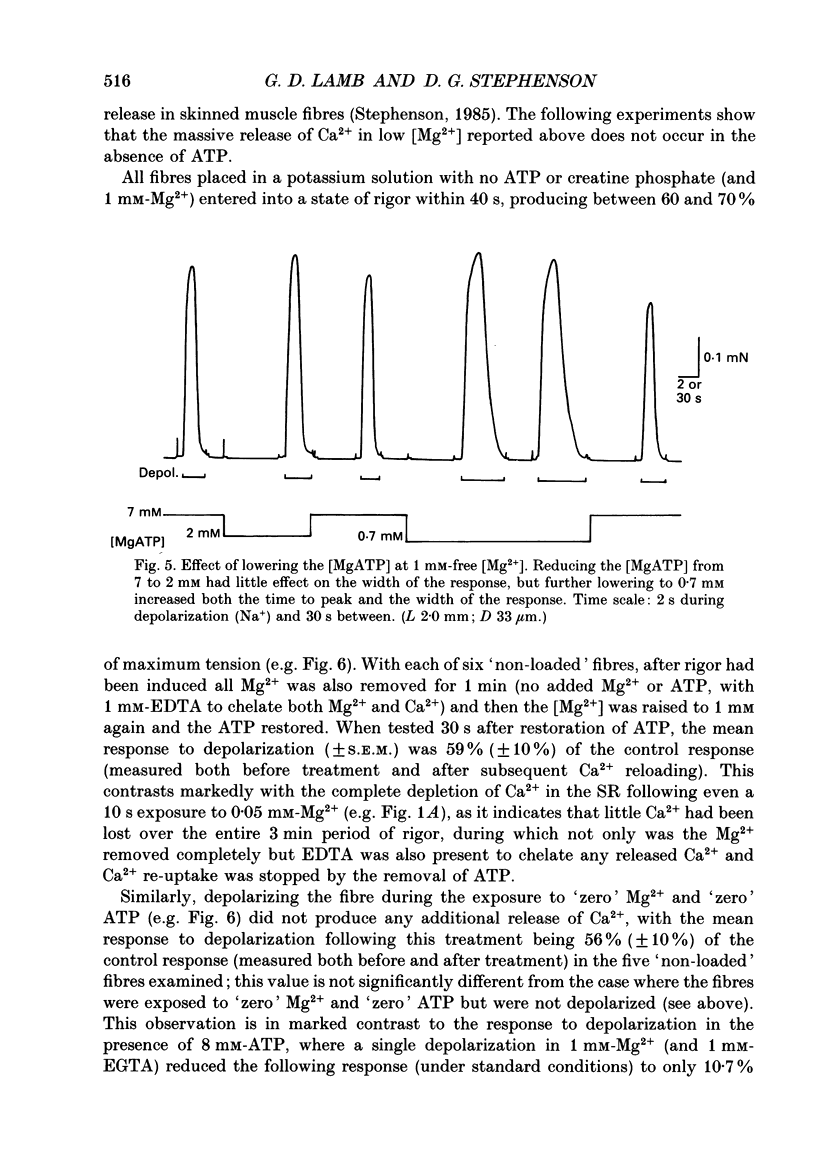
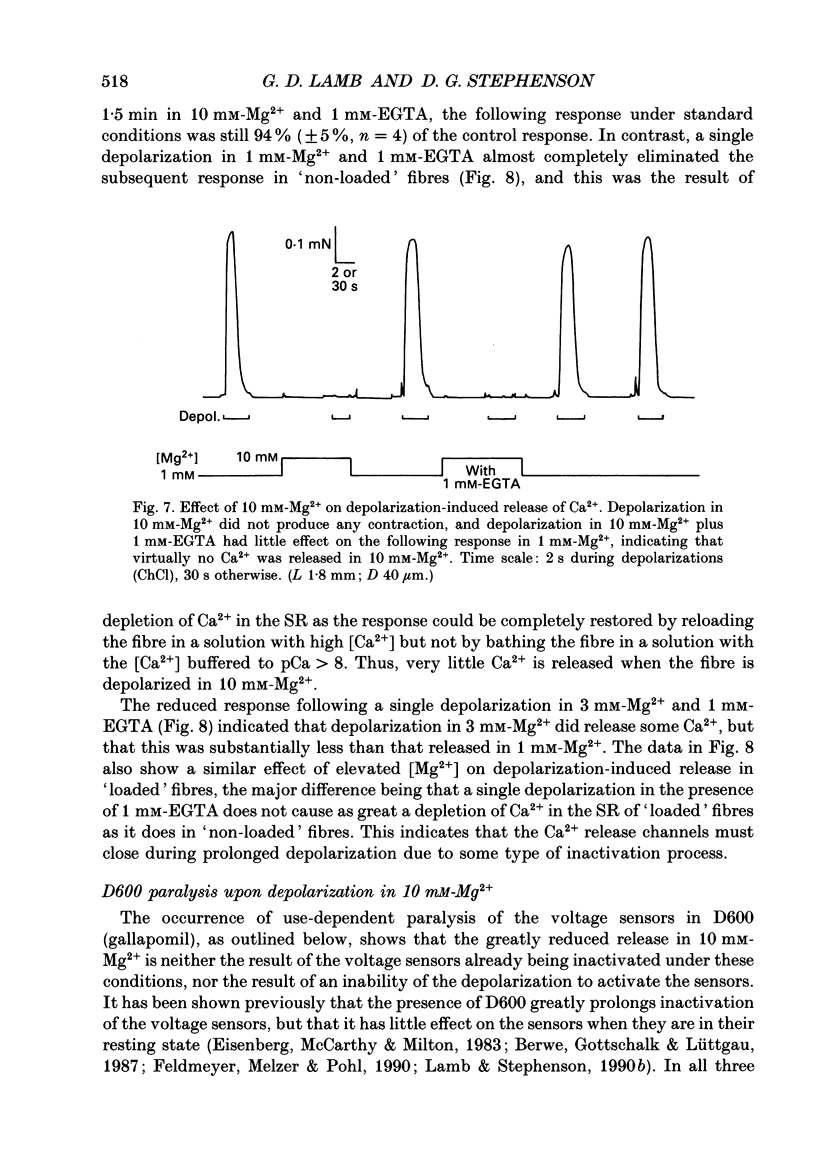
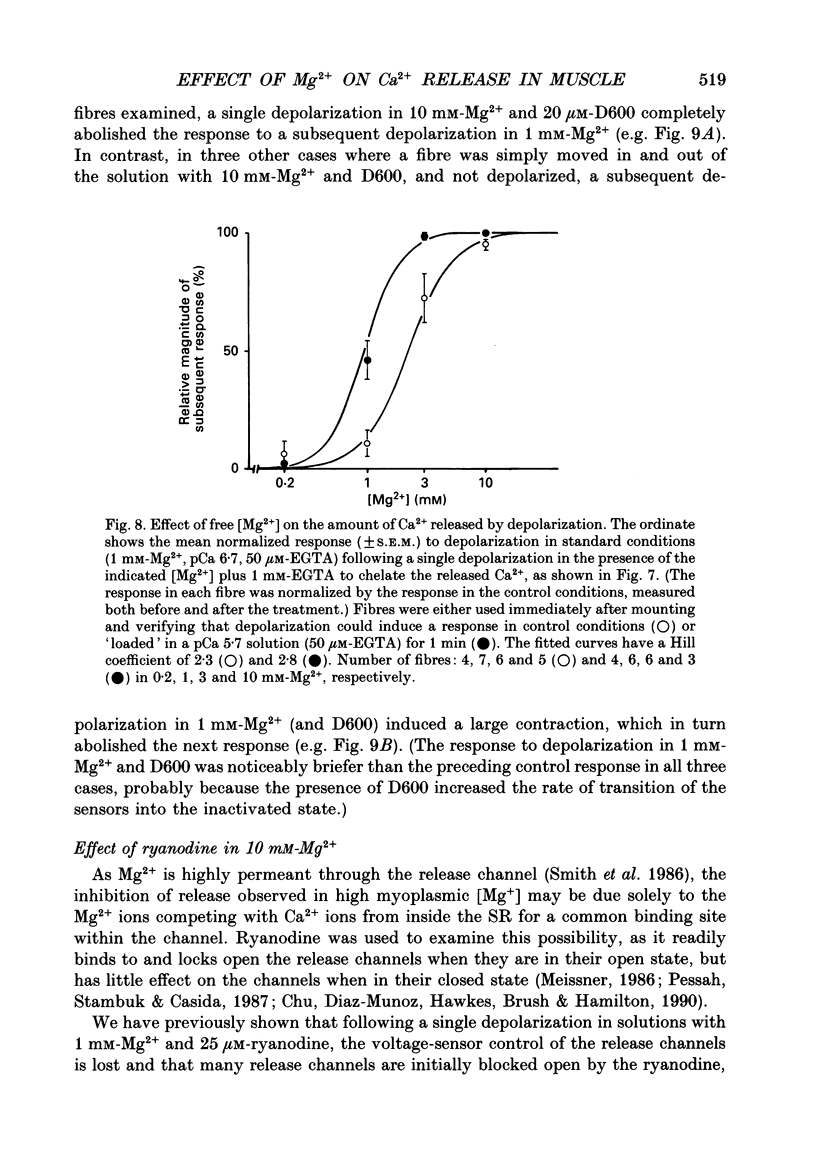
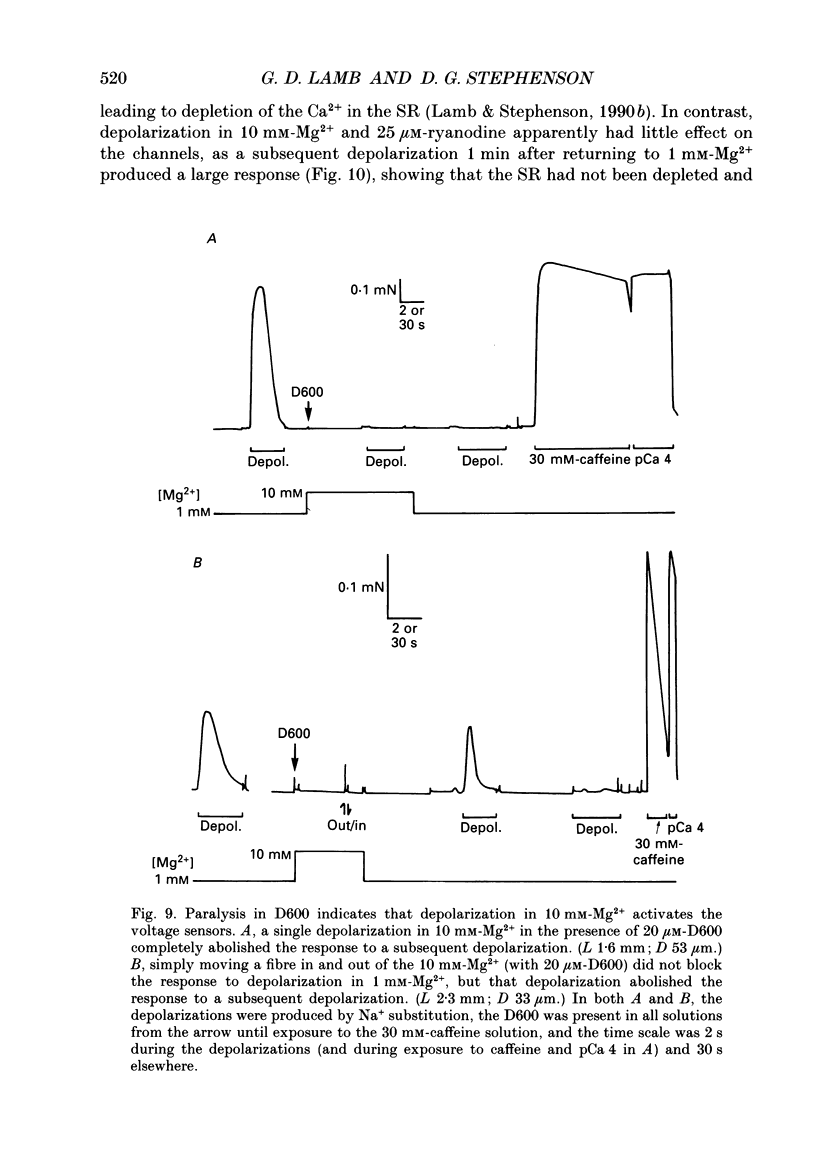
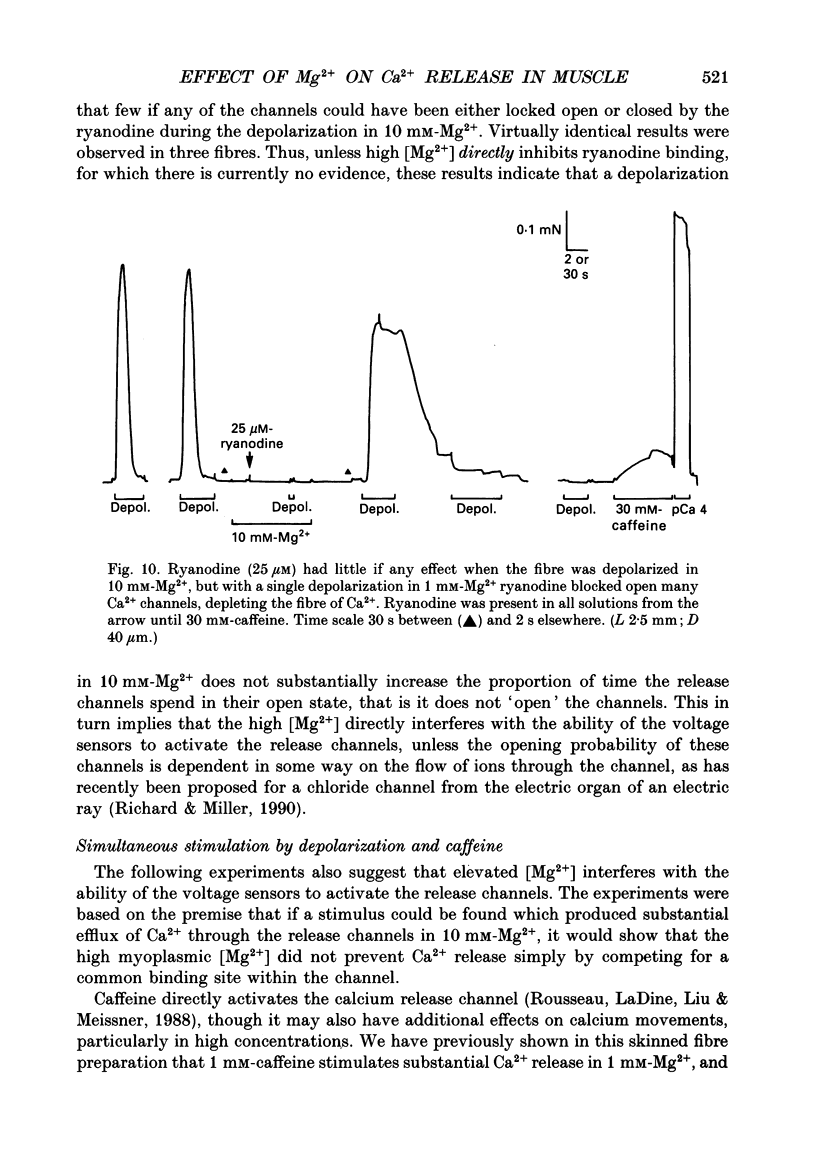
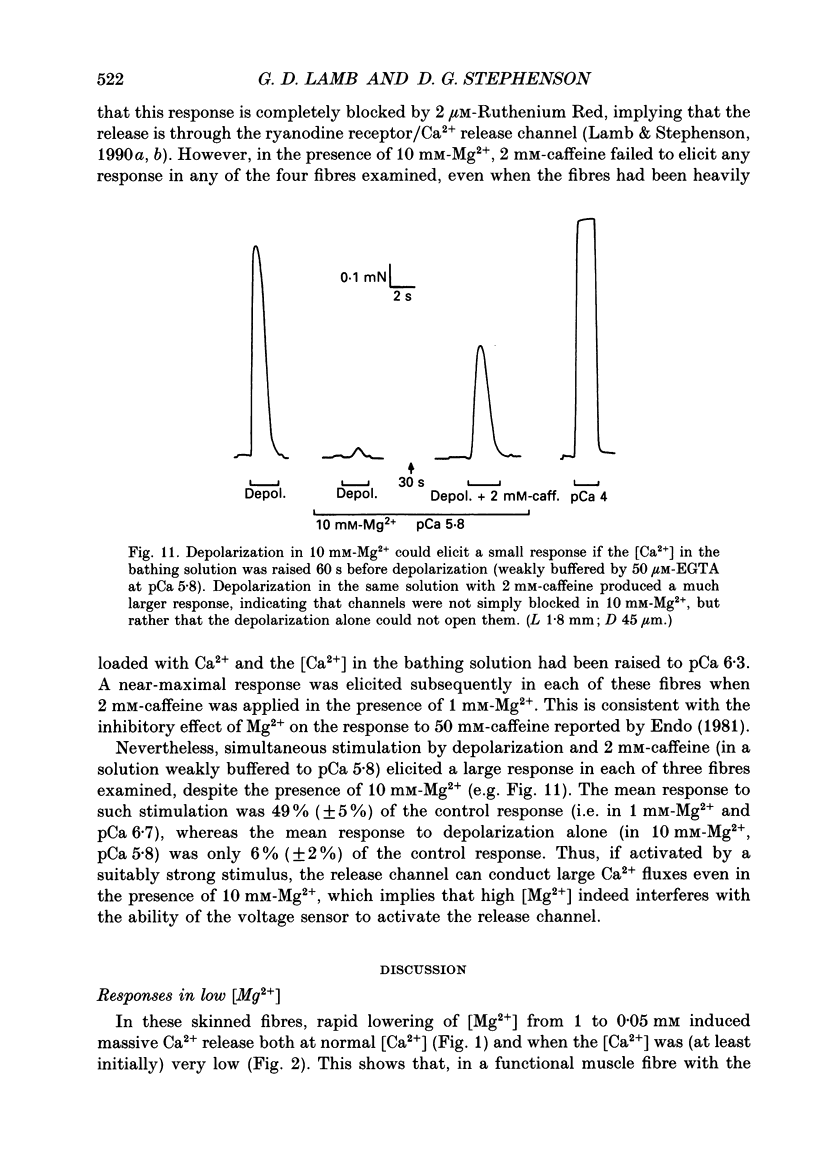
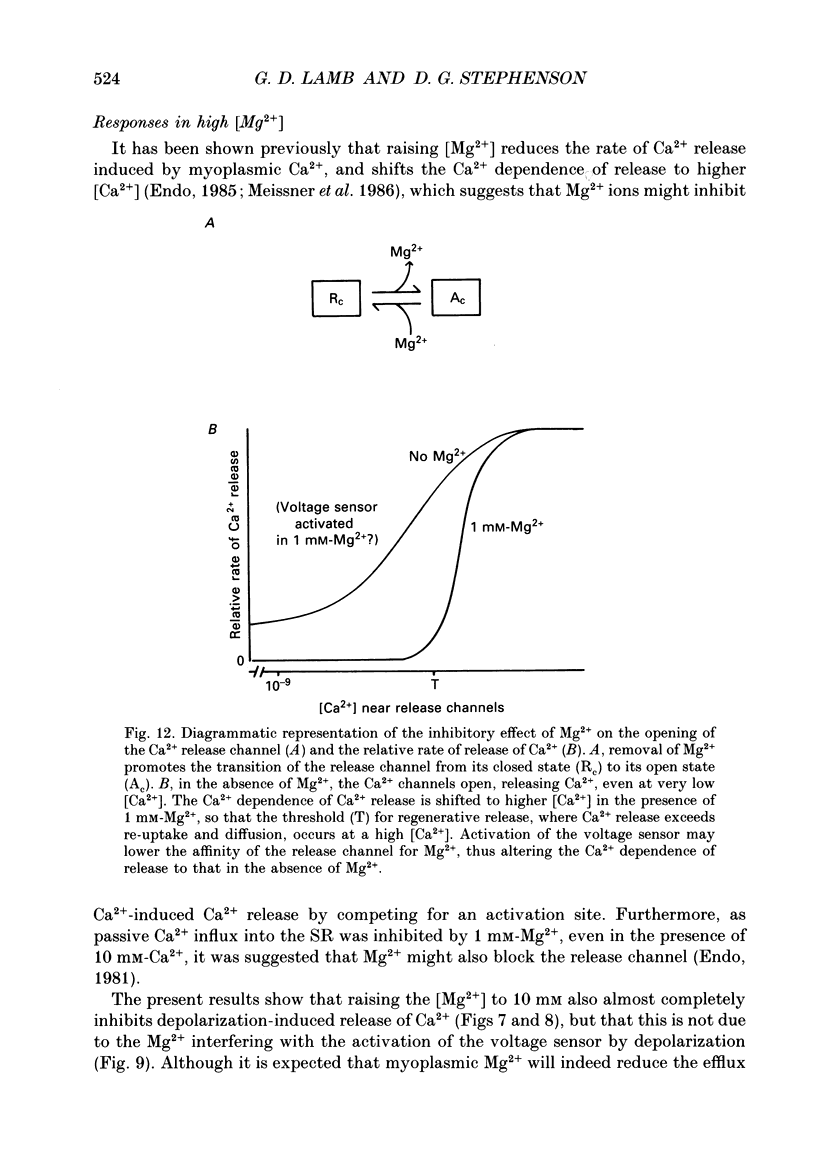
1. The effect of myoplasmic Mg2+ on Ca2+ release was examined in mechanically skinned skeletal muscle fibres, in which the normal voltage-sensor control of Ca2+ release is preserved. The voltage sensors could be activated by depolarizing the transverse tubular (T-) system by lowering the [K+] in the bathing solution. 2. Fibres spontaneously contracted when the free [Mg2+] was decreased from 1 to 0.05 mM, with no depolarization or change of total ATP, [Ca2+] or pH (pCa 6.7, 50 microM-EGTA). After such a 'low-Mg2+ response' the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) was depleted of Ca2+ and neither depolarization nor caffeine (2 mM) could induce a response, unless the [Mg2+] was raised and the SR reloaded with Ca2+. Exposure to 0.05 mM-Mg2+ at low [Ca2+] (2 mM-free EGTA, pCa greater than 8.7) also induced Ca2+ release and depleted the SR. 3. The response to low [Mg2+] was unaffected by inactivation of the voltage sensors, but was completely blocked by 2 microM-Ruthenium Red indicating that it involved Ca2+ efflux through the normal Ca2+ release channels. 4. In the absence of ATP (and creatine phosphate), complete removal of Mg2+ (i.e. no added Mg2+ with 1 mM-EDTA) did not induce Ca2+ release. Depolarization in the absence of Mg2+ and ATP also did not induce Ca2+ release. 5. Depolarization in 10 mM-Mg2+ (pCa 6.7, 50 microM-EGTA, 8 mM-total ATP) did not produce any response. In the presence of 1 mM-EGTA to chelate most of the released Ca2+, depolarizations in 10 mM-Mg2+ did not noticeably deplete the SR of Ca2+, whereas a single depolarization in 1 mM-Mg2+ (and 1 mM-EGTA) resulted in marked depletion. Depolarization in the presence of D600 and 10 mM-Mg2+ produced use-dependent 'paralysis', indicating that depolarization in 10 mM-Mg2+ did indeed activate the voltage sensors. 6. Depolarization in the presence of 10 mM-Mg2+ and 25 microM-ryanodine neither interfered with the normal voltage control of Ca2+ release nor caused depletion of the Ca2+ in the SR even after returning to 1 mM-Mg2+ for 1 min, indicating that few if any of the release channels had been opened by the depolarization.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
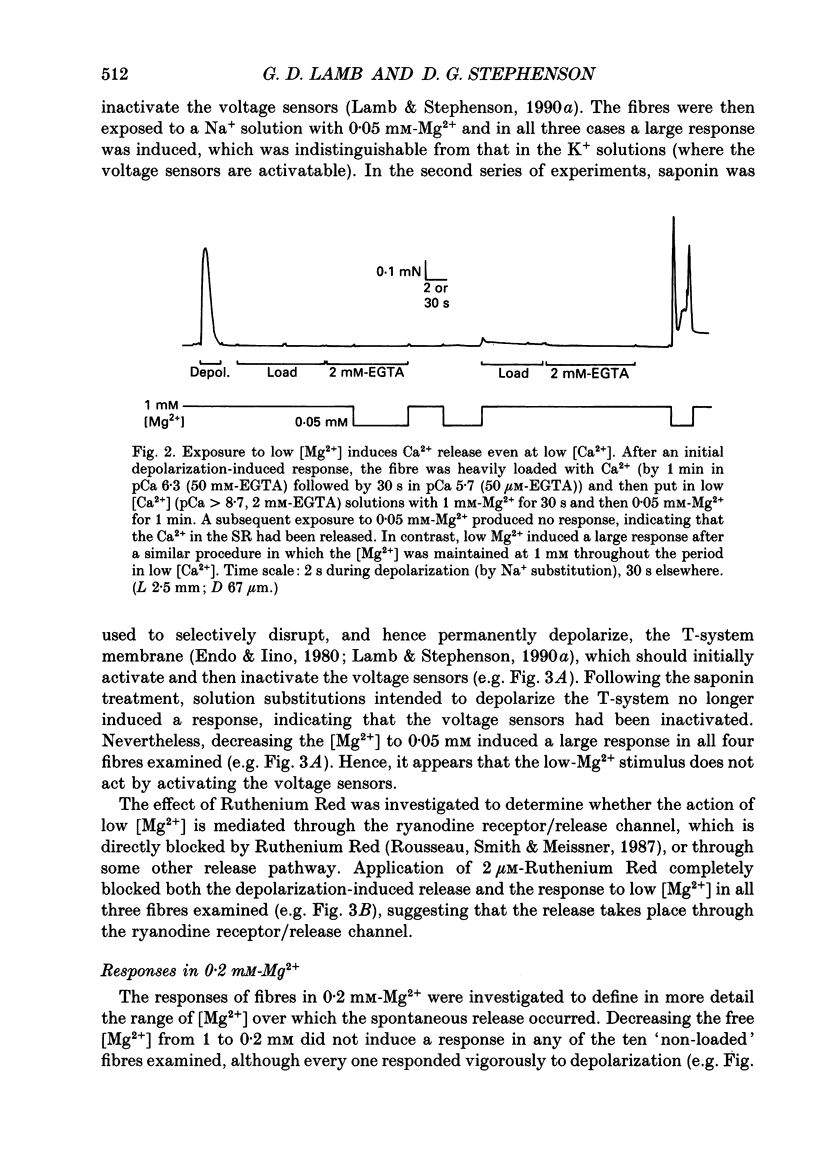
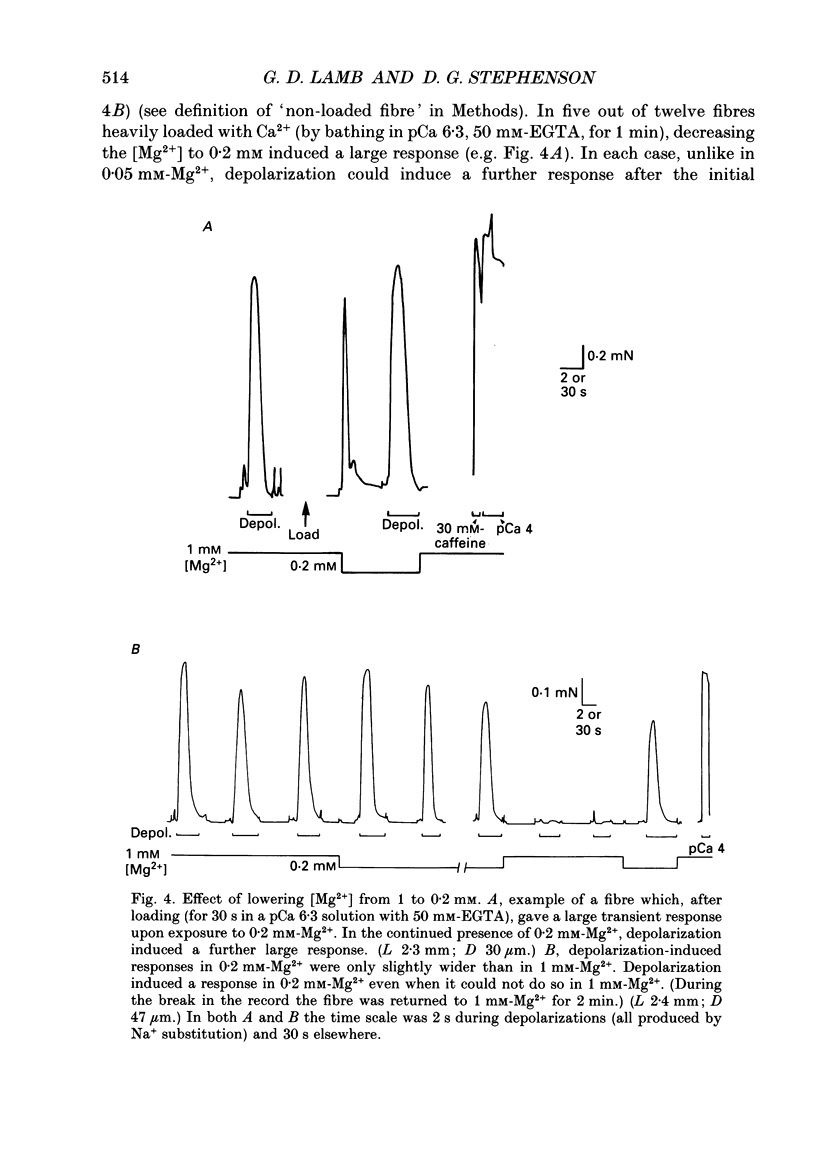
Full text
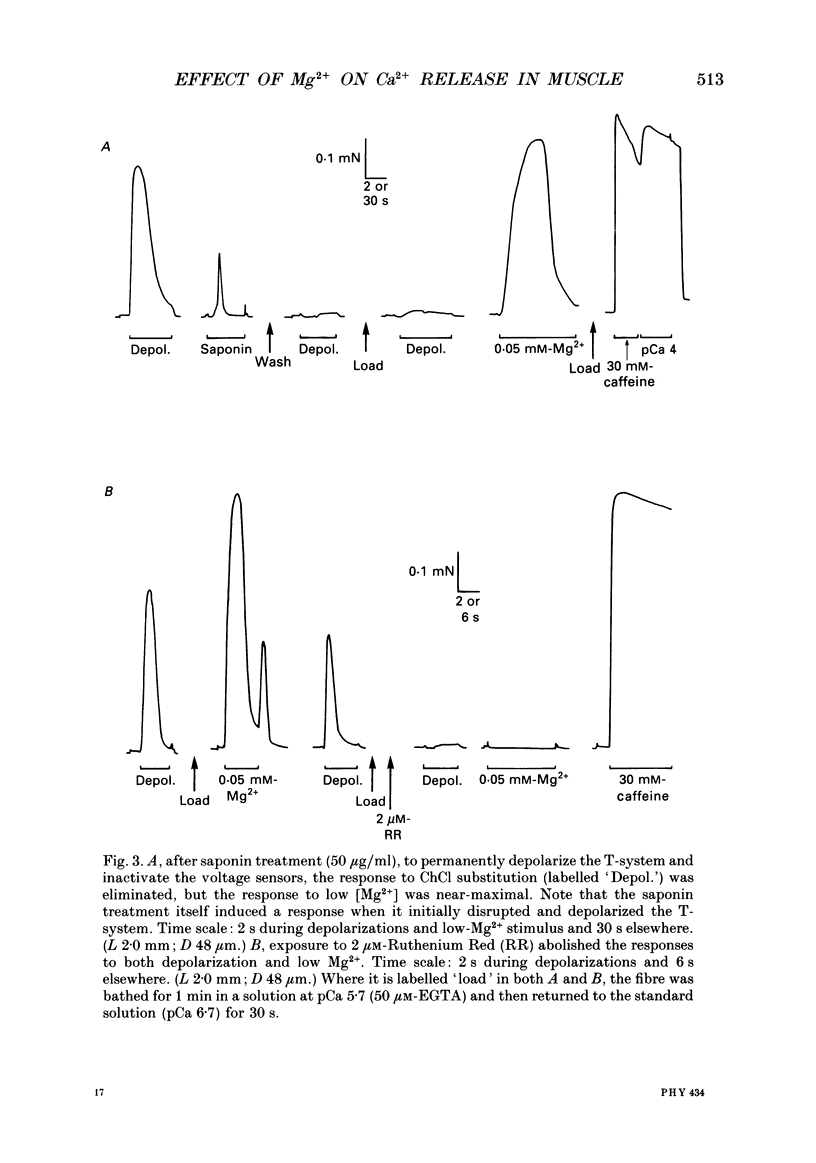
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berwe D., Gottschalk G., Lüttgau H. C. Effects of the calcium antagonist gallopamil (D600) upon excitation-contraction coupling in toe muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:693–707. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C., Fernandez de Bolaños P. Membrane potential, contractile activation and relaxation rates in voltage clamped short muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:175–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu A., Díaz-Muñoz M., Hawkes M. J., Brush K., Hamilton S. L. Ryanodine as a probe for the functional state of the skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release channel. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 May;37(5):735–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., McCarthy R. T., Milton R. L. Paralysis of frog skeletal muscle fibres by the calcium antagonist D-600. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:495–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Iino M. Specific perforation of muscle cell membranes with preserved SR functions by saponin treatment. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1980 Mar;1(1):89–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00711927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C1–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmeyer D., Melzer W., Pohl B. Effects of gallopamil on calcium release and intramembrane charge movements in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1990 Feb;421:343–362. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink R. H., Stephenson D. G., Williams D. A. Potassium and ionic strength effects on the isometric force of skinned twitch muscle fibres of the rat and toad. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:317–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Inui M. Biochemistry and biophysics of excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:333–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. H., Mandveno A. Computer modeling of Ca2+ pump function of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jan;67(1):244–284. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.1.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemoto N., Ronjat M., Mészáros L. G., Koshita M. Postulated role of calsequestrin in the regulation of calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 8;28(16):6764–6771. doi: 10.1021/bi00442a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacapère J. J., Bennett N., Dupont Y., Guillain F. pH and magnesium dependence of ATP binding to sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Evidence that the catalytic ATP-binding site consists of two domains. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):348–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D., Stephenson D. G. Calcium release in skinned muscle fibres of the toad by transverse tubule depolarization or by direct stimulation. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:495–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D., Stephenson D. G. Control of calcium release and the effect of ryanodine in skinned muscle fibres of the toad. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:519–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. N. Mechanisms of Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1240–1320. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Darling E., Eveleth J. Kinetics of rapid Ca2+ release by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Effects of Ca2+, Mg2+, and adenine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):236–244. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Rousseau E., Lai F. A., Liu Q. Y., Anderson K. A. Biochemical characterization of the Ca2+ release channel of skeletal and cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Mol Cell Biochem. 1988 Jul-Aug;82(1-2):59–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00242517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Ryanodine activation and inhibition of the Ca2+ release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6300–6306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Schneider M. F., Simon B. J., Szucs G. Intramembrane charge movement and calcium release in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:481–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G., Thieleczek R. Calcium and strontium concentration changes within skinned muscle preparations following a change in the external bathing solution. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:241–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessah I. N., Stambuk R. A., Casida J. E. Ca2+-activated ryanodine binding: mechanisms of sensitivity and intensity modulation by Mg2+, caffeine, and adenine nucleotides. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;31(3):232–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard E. A., Miller C. Steady-state coupling of ion-channel conformations to a transmembrane ion gradient. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1208–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.2156338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Ladine J., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Activation of the Ca2+ release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum by caffeine and related compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Nov 15;267(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Meissner G. Ryanodine modifies conductance and gating behavior of single Ca2+ release channel. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C364–C368. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation by Ca2+ and ATP and modulation by Mg2+. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Nov;88(5):573–588. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Williams D. A. Calcium-activated force responses in fast- and slow-twitch skinned muscle fibres of the rat at different temperatures. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:281–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. W. Ca2+ dependence of stimulated 45Ca efflux in skinned muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Apr;77(4):419–443. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.4.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. W. Excitation of skinned muscle fibers by imposed ion gradients. II. Influence of quercetin and ATP removal on the Ca2+-insensitive component of stimulated 45Ca efflux. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Dec;86(6):833–852. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.6.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. W., Podolsky R. J. Regulation by magnesium of intracellular calcium movement in skinned muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jan;69(1):1–16. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Yamamoto T., Tonomura Y. Molecular mechanism of active calcium transport by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1978 Jan;58(1):1–79. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


