Abstract
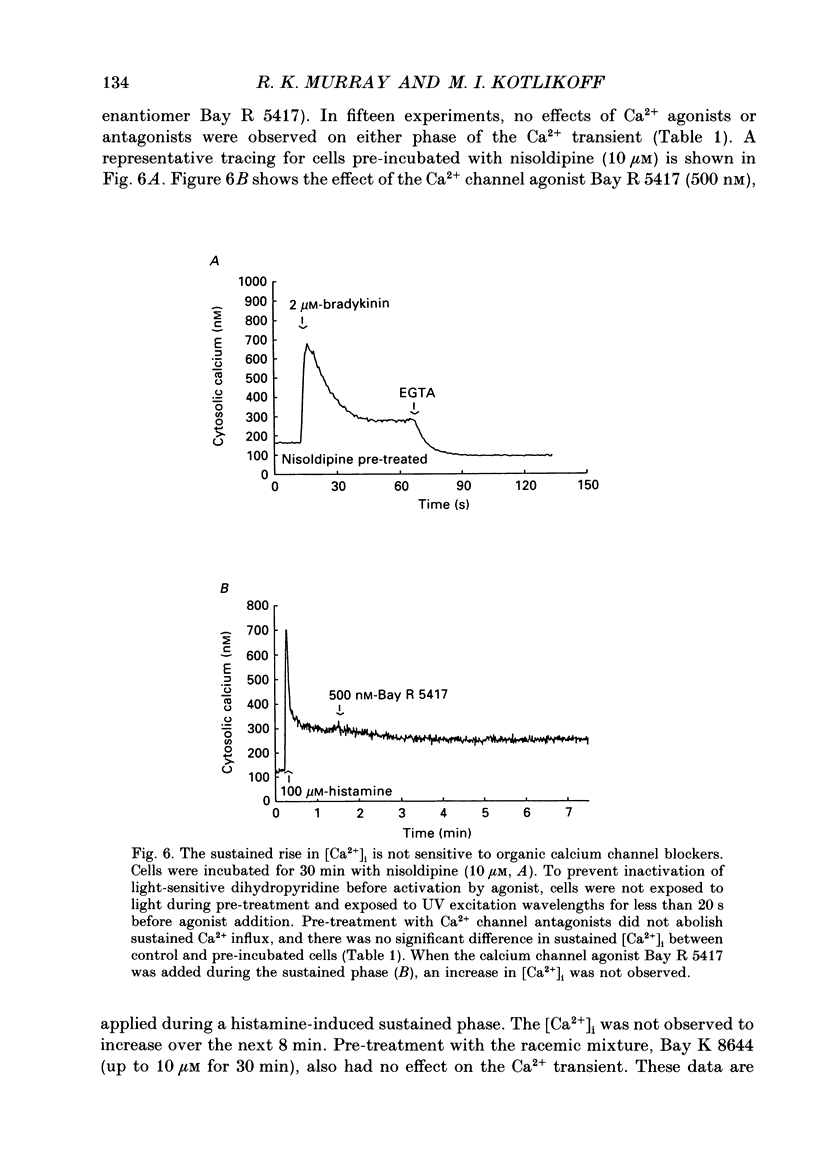
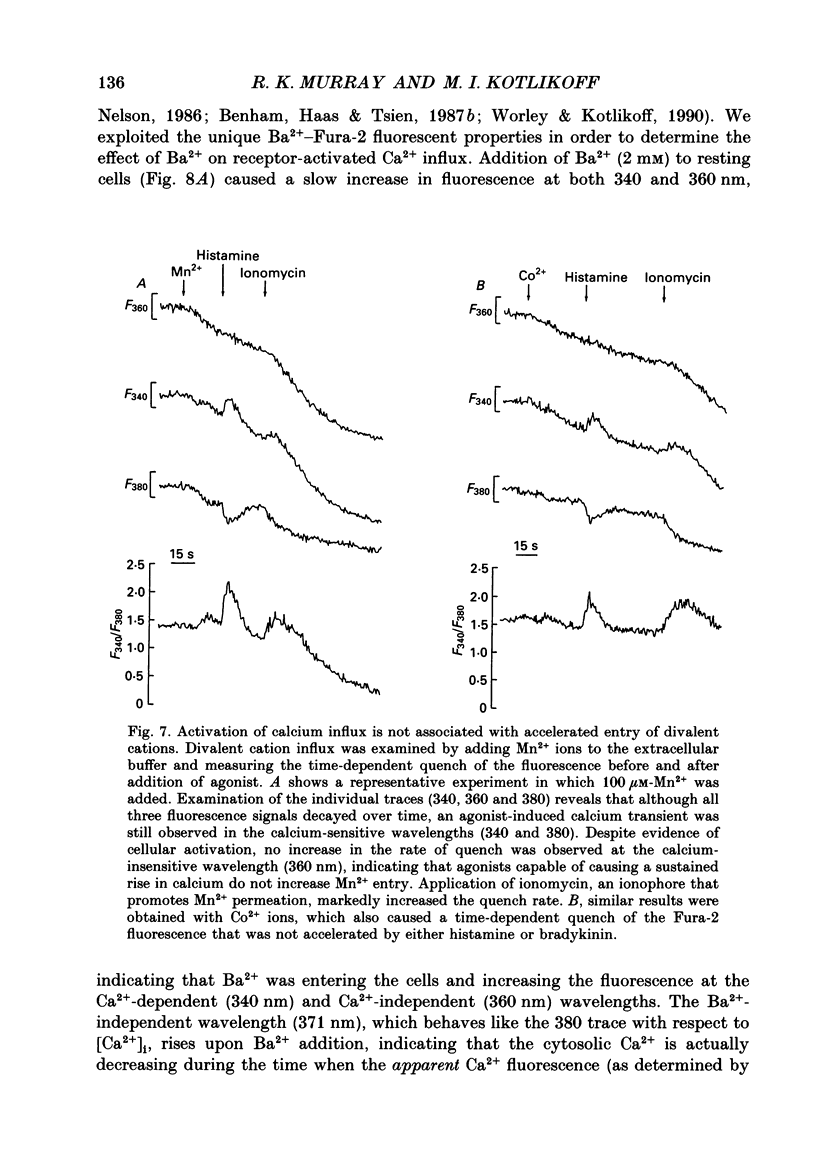
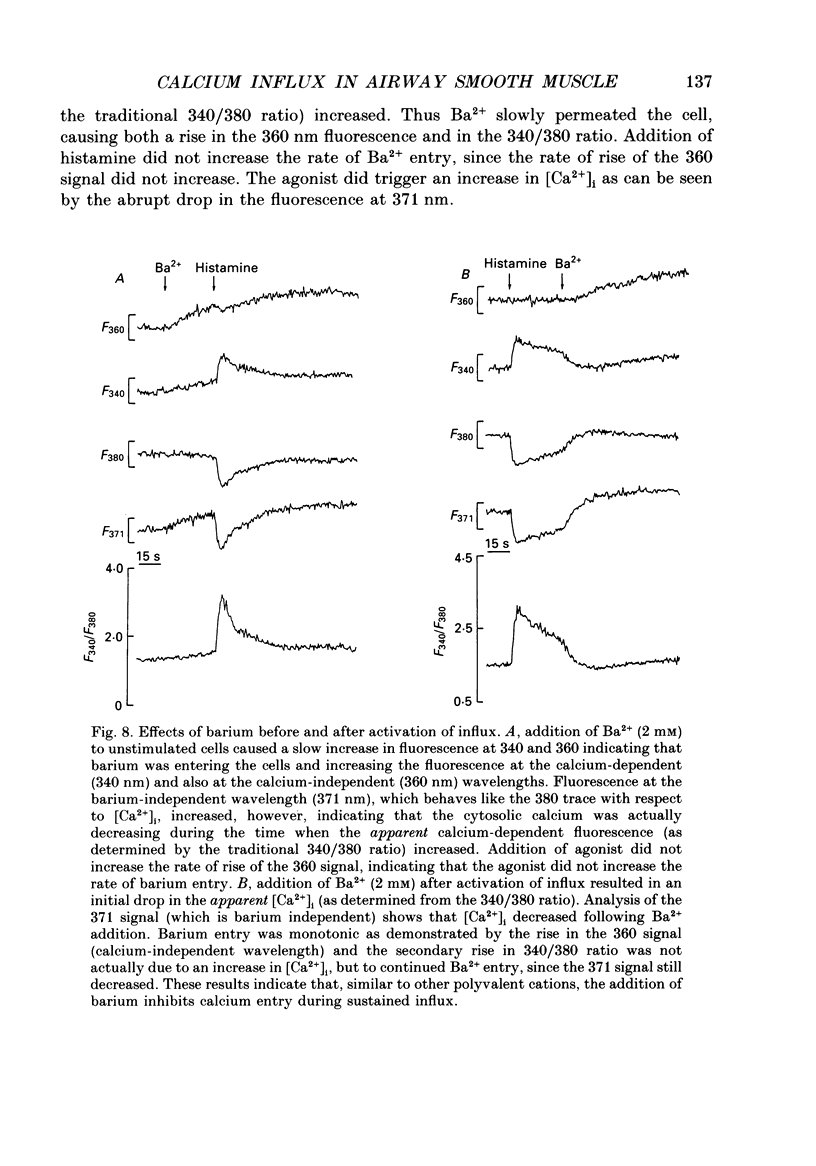
1. Fluorescence measurements of intracellular calcium concentrations ([Ca2+]i) were made on cultured human airway smooth muscle cells using the dye Fura-2. The response to either histamine (100 microM) or bradykinin (1 microM) was biphasic, with a transient increase in [Ca2+]i followed by a sustained [Ca2+]i increase lasting many minutes. The average steady-state (plateau) [Ca2+]i following agonist activation was 267 +/- 5 nM, whereas the average basal [Ca2+]i was 148 +/- 4 nM. 2. The sustained rise in [Ca2+]i required the continued presence of either histamine or bradykinin and was dependent on extracellular Ca2+. The magnitude of the transient rise in [Ca2+]i was not dependent on extracellular Ca2+. Sustained, receptor-activated rises in [Ca2+]i were rapidly abolished by chelation of extracellular Ca2+, or addition of non-permeant polyvalent cations, whereas these agents had minor effects in the absence of agonist. These data indicate that the sustained increase in [Ca2+]i was dependent on receptor-activated Ca2+ influx. 3. Receptor-activated Ca2+ influx was not affected by treatment with organic Ca2+ channel antagonists (nifedipine (10 microM), nisoldipine (10 microM) or diltiazem (10 microM] or agonists (Bay K 8644 (500 nM to 10 microM) or Bay R 5417 (500 nM]. The magnitude of the sustained rise was also not affected by pre-treatment with ouabain (100 microM) indicating little involvement of Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange in the influx mechanism. 4. Receptor-activated Ca2+ influx could be completely inhibited by several polyvalent cations (Co2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, -Cd2+ or La3+). Quantitative estimates of the potency of block were obtained for Ni2+ and La3+. These measurements indicate that the pKi for Ni2+ was 3.6 and for La3+ was 3.5. 5. Both Mn2+ and Co2+ ions caused a time-dependent quench of intracellular Fura-2; however, permeation of neither ion was increased following receptor activation, indicating that the influx pathway is not permeable to these cations. 6. Fura-2 was used to monitor the rate of Ba2+ entry into airway smooth muscle cells by monitoring the Ca(2+)-Fura-2 and Ba(2+)-Fura-2 isosbestic points as well as the 340 and 380 nm signals. Cell activation did not increase the rate of Ba2+ entry indicating that the Ca2+ influx pathway was poorly permeant to Ba2+ ions. Ba2+ (2 mM) was able to inhibit Ca2+ entry as shown by its effects on the Ba(2+)-independent, Ca(2+)-dependent wavelength (371 nm). 7. The voltage dependence of Ca2+ influx was examined before and after agonist-induced activation. The effect of KCl-induced depolarization prior to cell activation was to cause a slight increase in [Ca2+]i.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


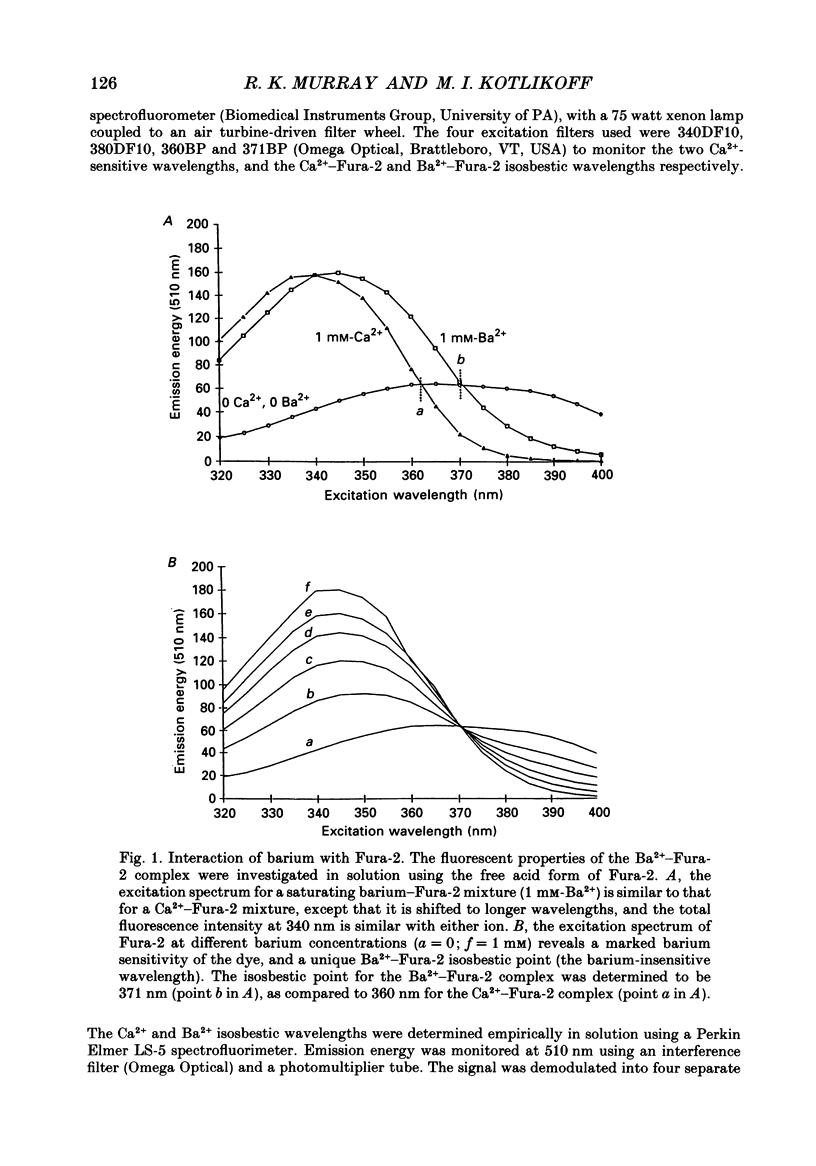

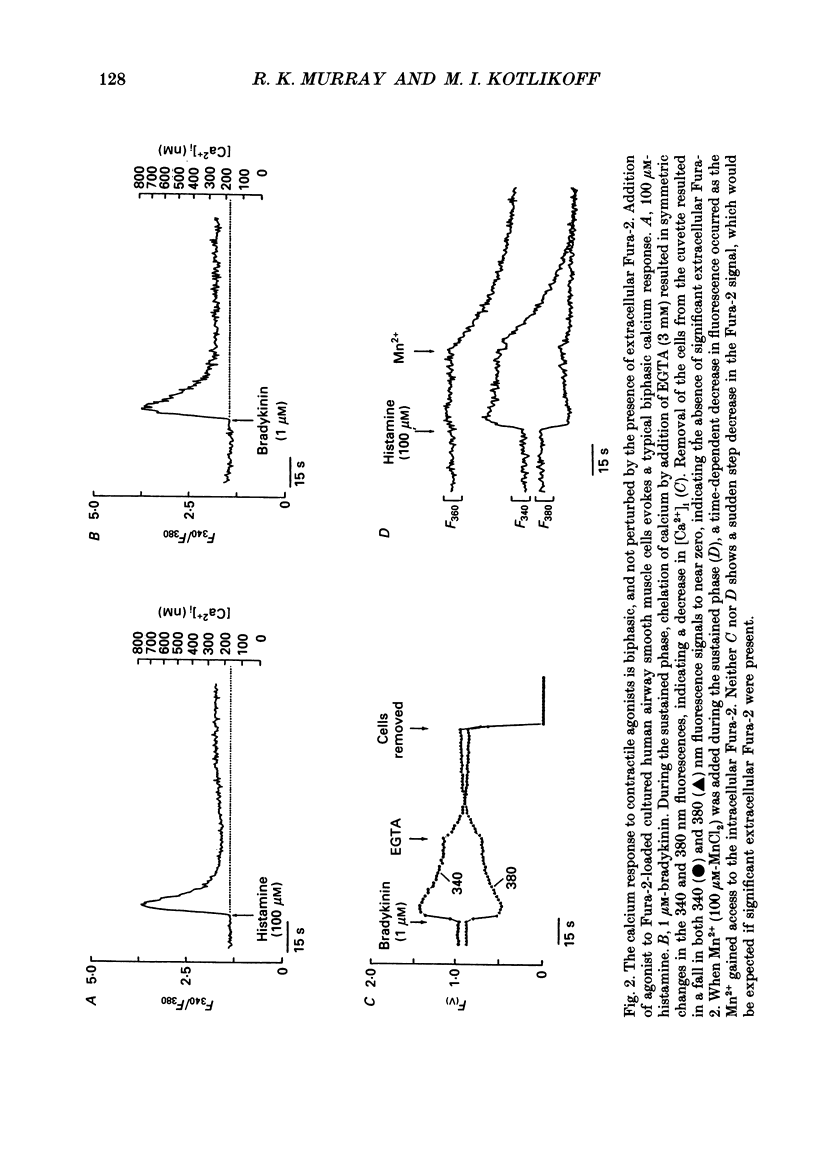

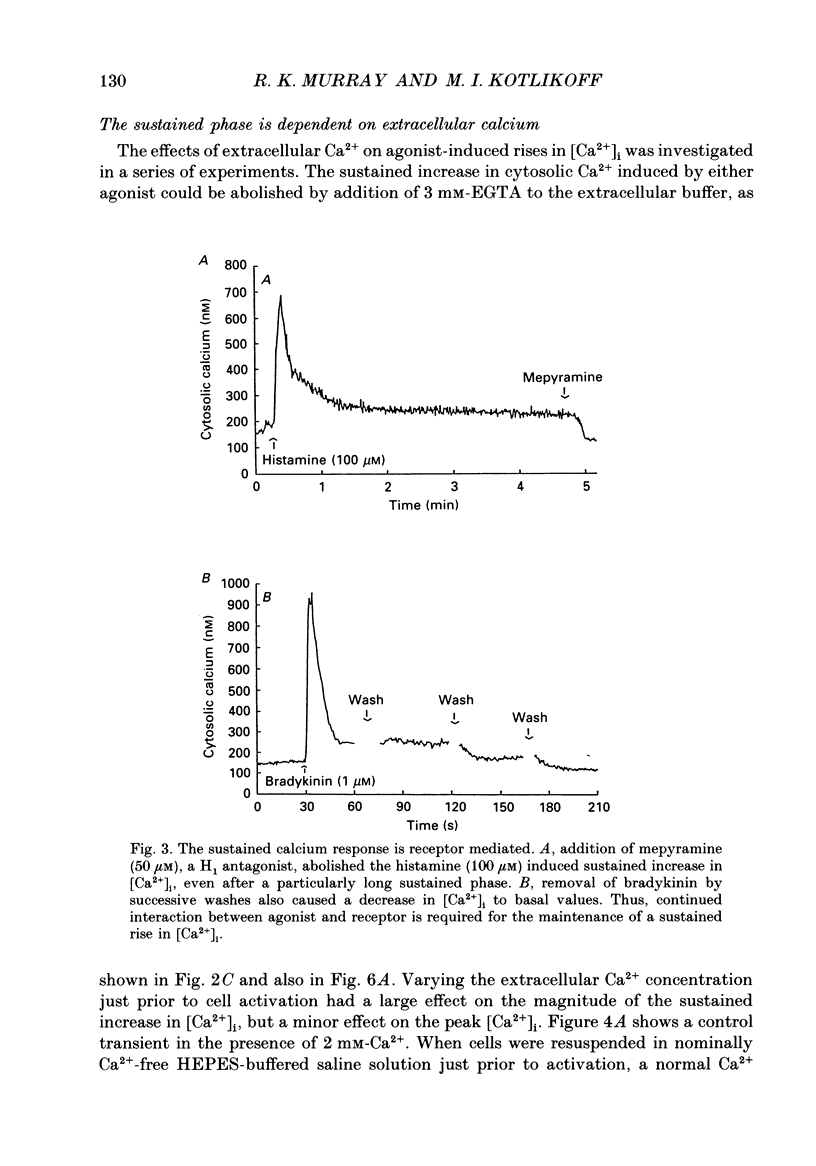
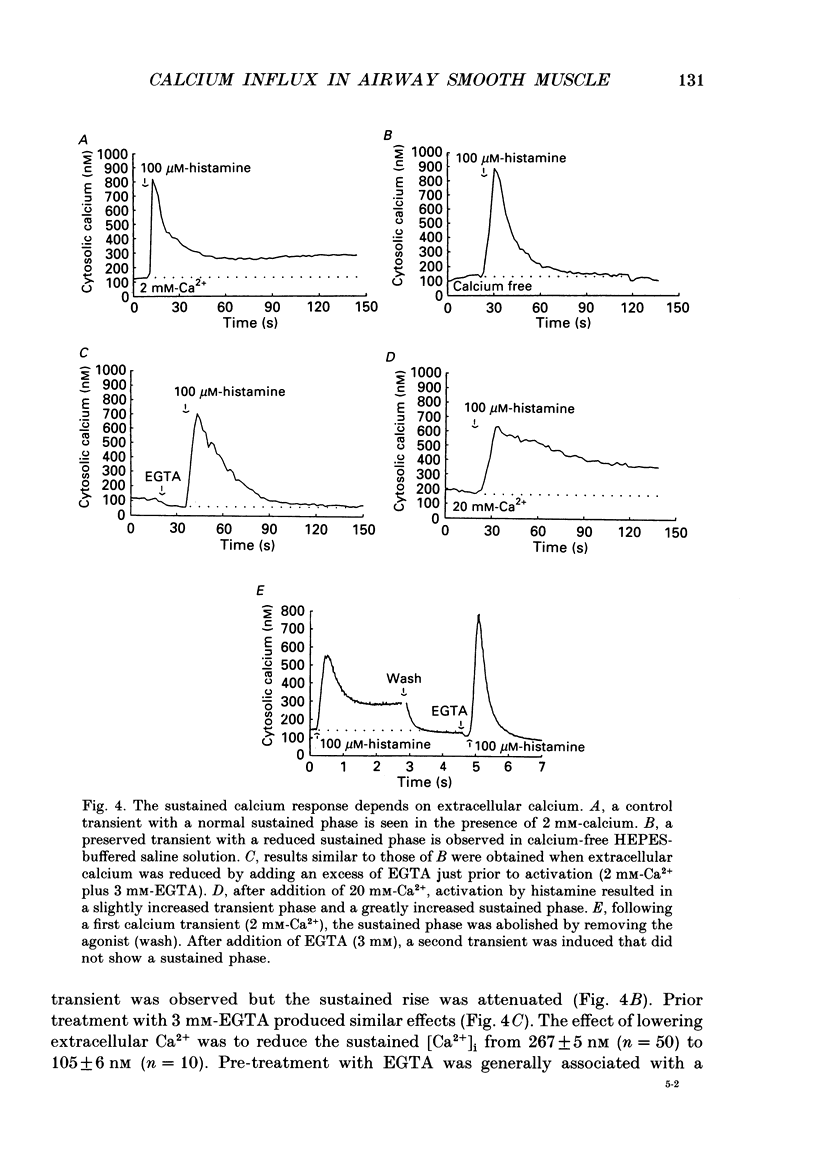

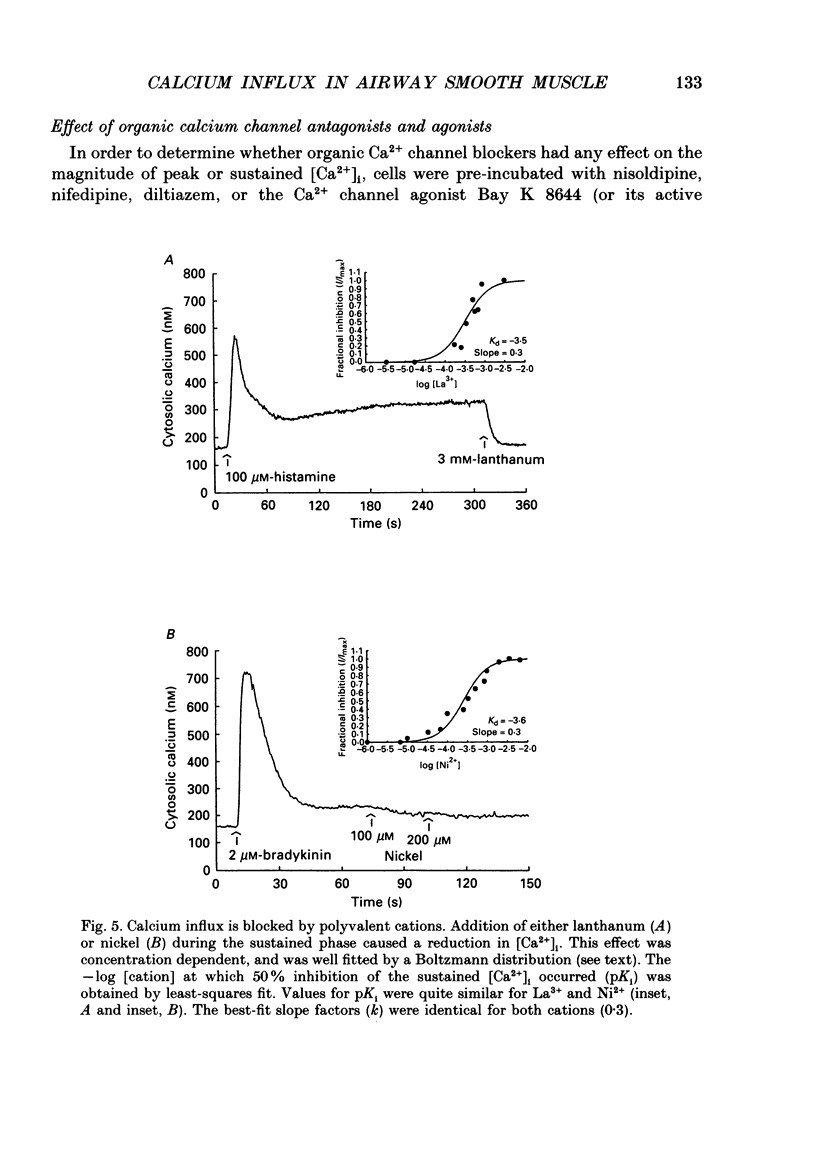







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed F., Foster R. W., Small R. C. Some effects of nifedipine in guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;84(4):861–869. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb17380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson T., Dahlgren C., Pozzan T., Stendahl O., Lew P. D. Characterization of fMet-Leu-Phe receptor-mediated Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane of human neutrophils. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;30(5):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C. B., Cunningham M., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Coburn R. F. Pharmacomechanical coupling in smooth muscle may involve phosphatidylinositol metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6899–6903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. L., Singer J. J., Walsh J. V., Jr, Fay F. S. Regulation of calcium concentration in voltage-clamped smooth muscle cells. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):211–214. doi: 10.1126/science.2704996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D. ATP-activated channels gate calcium entry in single smooth muscle cells dissociated from rabbit ear artery. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:689–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Byrne N. G., Large W. A. Action of externally applied adenosine triphosphate on single smooth muscle cells dispersed from rabbit ear artery. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:473–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):606–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerrina J., Advenier C., Renier A., Floch A., Duroux P. Effects of diltiazem and other Ca2+ antagonists on guinea-pig tracheal muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct 28;94(3-4):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90413-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilvers E. R., Challiss R. A., Barnes P. J., Nahorski S. R. Mass changes of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in trachealis muscle following agonist stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 30;164(3):587–590. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn R. F. Electromechanical coupling in canine trachealis muscle: acetylcholine contractions. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):C177–C184. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.3.C177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colden-Stanfield M., Schilling W. P., Ritchie A. K., Eskin S. G., Navarro L. T., Kunze D. L. Bradykinin-induced increases in cytosolic calcium and ionic currents in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1987 Nov;61(5):632–640. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.5.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo T. T., Morgan K. G. Calcium-force relationships as detected with aequorin in two different vascular smooth muscles of the ferret. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:269–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J. M., Miles P. R. Role of depolarization in acetylcholine-induced contractions of dog trachealis muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Apr;201(1):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J. M., Miles P. R. The sources of calcium for acetylcholine-induced contractions of dog tracheal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Nov;207(2):340–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerthoffer W. T., Murphey K. A., Gunst S. J. Aequorin luminescence, myosin phosphorylation, and active stress in tracheal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):C1062–C1068. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.6.C1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara N., Irisawa H., Kameyama M. Contribution of two types of calcium currents to the pacemaker potentials of rabbit sino-atrial node cells. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:233–253. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Jacob R., Merritt J. E. Evidence that agonists stimulate bivalent-cation influx into human endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):179–184. doi: 10.1042/bj2550179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Agonists stimulate divalent cation channels in the plasma membrane of human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80703-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Receptor-mediated Ca2+ entry: diversity of function and mechanism. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jan;10(1):8–10. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Hirata M., Ito Y. A role for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in the initiation of agonist-induced contractions of dog tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):191–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09449.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himpens B., Matthijs G., Somlyo A. V., Butler T. M., Somlyo A. P. Cytoplasmic free calcium, myosin light chain phosphorylation, and force in phasic and tonic smooth muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Dec;92(6):713–729. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.6.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Ikebe M., Kargacin G. J., Hartshorne D. J., Kemp B. E., Fay F. S. Effects of modulators of myosin light-chain kinase activity in single smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):164–167. doi: 10.1038/338164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. The function of myosin and myosin light chain kinase phosphorylation in smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:593–620. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. T. Excitation and contraction in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):263–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlikoff M. I. Calcium currents in isolated canine airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 1):C793–C801. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.6.C793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlikoff M. I., Murray R. K., Reynolds E. E. Histamine-induced calcium release and phorbol antagonism in cultured airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):C561–C566. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.4.C561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marthan R., Martin C., Amédée T., Mironneau J. Calcium channel currents in isolated smooth muscle cells from human bronchus. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Apr;66(4):1706–1714. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.4.1706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J. Platelets and parotid acinar cells have different mechanisms for agonist-stimulated divalent cation entry. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6161–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Rink T. J. Regulation of cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded rat parotid acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17362–17369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Vascular smooth muscle: the first recorded Ca2+ transients. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):75–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00584972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. K., Bennett C. F., Fluharty S. J., Kotlikoff M. I. Mechanism of phorbol ester inhibition of histamine-induced IP3 formation in cultured airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):L209–L216. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.4.L209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T., Tsunoo A., Yoshii M. Characterization of two types of calcium channels in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:231–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Standen N. B., Brayden J. E., Worley J. F., 3rd Noradrenaline contracts arteries by activating voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):382–385. doi: 10.1038/336382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panettieri R. A., Murray R. K., DePalo L. R., Yadvish P. A., Kotlikoff M. I. A human airway smooth muscle cell line that retains physiological responsiveness. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):C329–C335. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.2.C329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Matthews G., Neher E. Regulation of calcium influx by second messengers in rat mast cells. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):499–504. doi: 10.1038/334499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard K., Ashley C. C. Evidence for Na+/Ca2+ exchange in isolated smooth muscle cells: a fura-2 study. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Nov;410(4-5):401–407. doi: 10.1007/BF00586517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Receptor-mediated calcium entry in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated with ADP and thrombin. Dual-wavelengths studies with Mn2+. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 15;258(3):923–926. doi: 10.1042/bj2580923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling W. P., Rajan L., Strobl-Jager E. Characterization of the bradykinin-stimulated calcium influx pathway of cultured vascular endothelial cells. Saturability, selectivity, and kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12838–12848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P. Excitation-contraction coupling and the ultrastructure of smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1985 Oct;57(4):497–507. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.4.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. A., Stull J. T. Calcium dependence of myosin light chain phosphorylation in smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14456–14462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Breemen C., Aaronson P., Loutzenhiser R. Sodium-calcium interactions in mammalian smooth muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1978 Jun;30(2):167–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallnöfer A., Cauvin C., Lategan T. W., Rüegg U. T. Differential blockade of agonist- and depolarization-induced 45Ca2+ influx in smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):C607–C611. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.4.C607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley J. F., 3rd, Deitmer J. W., Nelson M. T. Single nisoldipine-sensitive calcium channels in smooth muscle cells isolated from rabbit mesenteric artery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5746–5750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley J. F., 3rd, Kotlikoff M. I. Dihydropyridine-sensitive single calcium channels in airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):L468–L480. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.259.6.L468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi S., Becker P. L., Fay F. S. Relationship between force and Ca2+ concentration in smooth muscle as revealed by measurements on single cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4109–4113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi D. T., Green J., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Properties of the depolarization-activated calcium and barium entry in osteoblast-like cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):197–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Breemen C., Saida K. Cellular mechanisms regulating [Ca2+]i smooth muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:315–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


