Abstract
1. The cardiovascular responses, together with the effects on medullary sympathoexcitatory (vasomotor) neurones of the rostral ventrolateral medulla, of area postrema stimulation have been studied in vivo. 2. Electrical (10 Hz) or chemical stimulation using microinjections of L-glutamate of the area postrema produced a vasodepressor response and an inhibition of the medullary sympathoexcitatory neurones in the nucleus reticularis rostroventrolateralis (RVL), while similar stimulation in the adjacent nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) caused increases in arterial pressure. 3. Single-pulse stimulation of the area postrema revealed at least three influences on the activity of RVL vasomotor neurones, one being excitatory and two inhibitory. 4. The inhibitions evoked in the medullary vasomotor neurones on area postrema stimulation were blocked by ionophoretic application of bicuculline, a GABAA receptor antagonist, without altering the excitatory input to the same neurones. Bilateral microinjections of bicuculline into the RVL in regions where the vasomotor neurones had been identified totally eliminated the vasodepression due to area postrema stimulation. 5. These data support a role for the area postrema in cardiovascular control. It is concluded that the area postrema exerts its action on cardiovascular control in part via GABAergic inhibition of the 'vasomotor' neurones in the nucleus reticularis rostroventrolateralis.
Full text
PDF








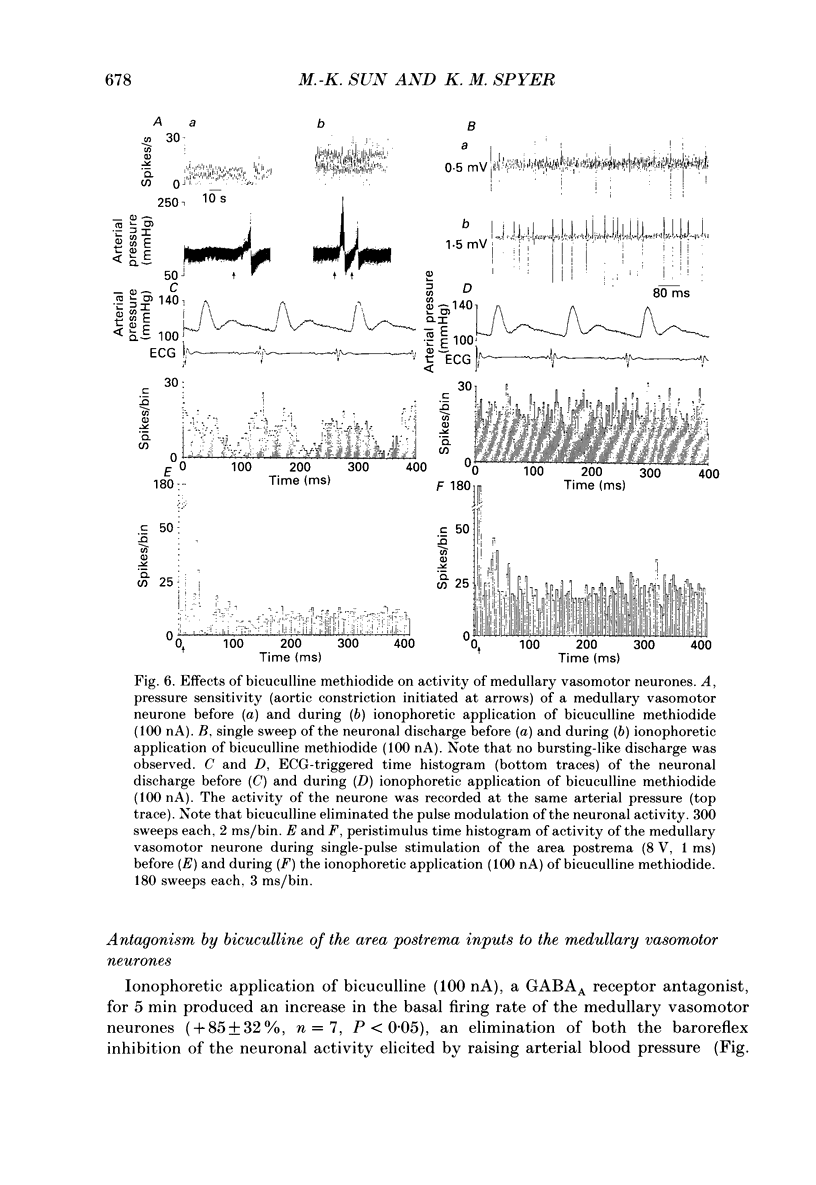
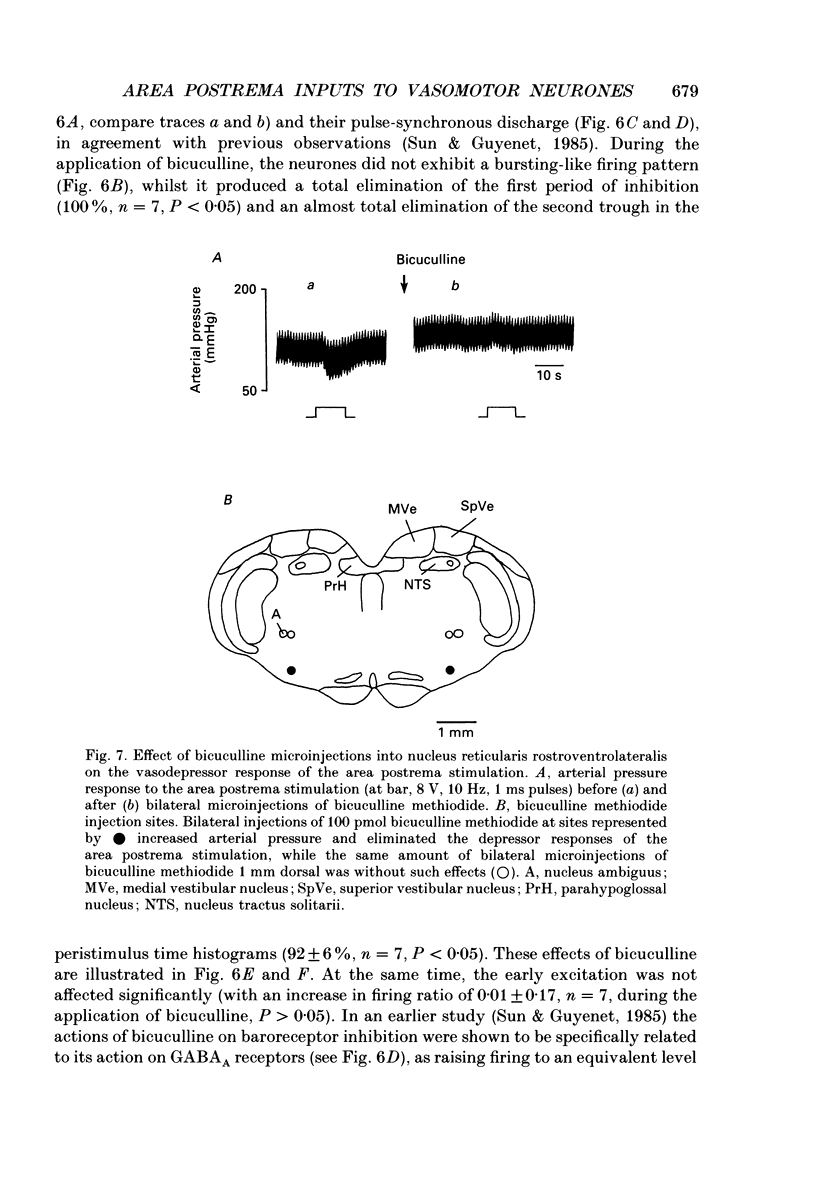





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrezik J. A., Chan-Palay V., Palay S. L. The nucleus paragigantocellularis lateralis in the rat. Demonstration of afferents by the retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1981;161(4):373–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00316049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Applegate R. J., Hasser E. M., Bishop V. S. Vagal cold block in area postrema-lesioned dogs: interaction of vasopressin and sympathetic nervous system. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 2):H135–H141. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.1.H135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes K. L., Ferrario C. M., Conomy J. P. Comparison of the hemodynamic changes produced by electrical stimulation of the area postrema and nucleus tractus solitarii in the dog. Circ Res. 1979 Jul;45(1):136–143. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.1.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi C., Gutkowska J., Ballak M., Thibault G., Garcia R., Genest J., Cantin M. Radioautographic localization of 125I-atrial natriuretic factor binding sites in the brain. Neuroendocrinology. 1986;44(3):365–372. doi: 10.1159/000124670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. L., Guyenet P. G. Electrophysiological study of cardiovascular neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla in rats. Circ Res. 1985 Mar;56(3):359–369. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casto R., Phillips M. I. Cardiovascular actions of microinjections of angiotensin II in the brain stem of rats. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 2):R811–R816. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.5.R811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A. V., Marcus P. Area postrema stimulation induced cardiovascular changes in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 2):R855–R860. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1988.255.5.R855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink G. D., Bruner C. A., Mangiapane M. L. Area postrema is critical for angiotensin-induced hypertension in rats. Hypertension. 1987 Apr;9(4):355–361. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti P. J., Dias Souza J., Taveira Da Silva A. M., Quest J. A., Gillis R. A. Chemical stimulation of the area postrema induces cardiorespiratory changes in the cat. Brain Res. 1985 Oct 28;346(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasser E. M., Nelson D. O., Haywood J. R., Bishop V. S. Inhibition of renal sympathetic nervous activity by area postrema stimulation in rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 2):H91–H99. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.1.H91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joy M. D., Lowe R. D. Evidence that the area postrema mediates the central cardiovascular response to angiotensin II. Nature. 1970 Dec 26;228(5278):1303–1304. doi: 10.1038/2281303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiapane M. L., Skoog K. M., Rittenhouse P., Blair M. L., Sladek C. D. Lesion of the area postrema region attenuates hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circ Res. 1989 Jan;64(1):129–135. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn F. A., Quirion R., Saavedra J. M., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Autoradiographic localization of angiotensin II receptors in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. F., Spyer K. M. Brain stem regions mediating the cardiovascular responses elicited from the posterior cerebellar cortex in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:533–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M. V., Winkler B. S. Strong Pasteur effect in rabbit corneal endothelium preserves fluid transport under anaerobic conditions. J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:81–93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Ruggiero D. A., Joh T. H., Park D. H., Reis D. J. Rostral ventrolateral medulla: selective projections to the thoracic autonomic cell column from the region containing C1 adrenaline neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Sep 10;228(2):168–185. doi: 10.1002/cne.902280204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero D. A., Meeley M. P., Anwar M., Reis D. J. Newly identified GABAergic neurons in regions of the ventrolateral medulla which regulate blood pressure. Brain Res. 1985 Jul 22;339(1):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90640-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R. E., Miselis R. R. The central neural connections of the area postrema of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Apr 15;234(3):344–364. doi: 10.1002/cne.902340306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Guyenet P. G. Arterial baroreceptor and vagal inputs to sympathoexcitatory neurons in rat medulla. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 2):R699–R709. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.252.4.R699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Guyenet P. G. Effect of clonidine and gamma-aminobutyric acid on the discharges of medullo-spinal sympathoexcitatory neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 12;368(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Guyenet P. G. Effects of vasopressin and other neuropeptides on rostral medullary sympathoexcitatory neurons 'in vitro'. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 17;492(1-2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90909-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Guyenet P. G. GABA-mediated baroreceptor inhibition of reticulospinal neurons. Am J Physiol. 1985 Dec;249(6 Pt 2):R672–R680. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1985.249.6.R672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Guyenet P. G. Hypothalamic glutamatergic input to medullary sympathoexcitatory neurons in rats. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 2):R798–R810. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.251.4.R798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Guyenet P. G. Medullospinal sympathoexcitatory neurons in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 2):R910–R917. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.5.R910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Hackett J. T., Guyenet P. G. Sympathoexcitatory neurons of rostral ventrolateral medulla exhibit pacemaker properties in the presence of a glutamate-receptor antagonist. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 12;438(1-2):23–40. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Young B. S., Hackett J. T., Guyenet P. G. Reticulospinal pacemaker neurons of the rat rostral ventrolateral medulla with putative sympathoexcitatory function: an intracellular study in vitro. Brain Res. 1988 Mar 1;442(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91508-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Young B. S., Hackett J. T., Guyenet P. G. Rostral ventrolateral medullary neurons with intrinsic pacemaker properties are not catecholaminergic. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 7;451(1-2):345–349. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90781-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker D. C., Saper C. B., Ruggiero D. A., Reis D. J. Organization of central adrenergic pathways: I. Relationships of ventrolateral medullary projections to the hypothalamus and spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1987 May 22;259(4):591–603. doi: 10.1002/cne.902590408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Undesser K. P., Hasser E. M., Haywood J. R., Johnson A. K., Bishop V. S. Interactions of vasopressin with the area postrema in arterial baroreflex function in conscious rabbits. Circ Res. 1985 Mar;56(3):410–417. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.3.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISLOCKI G. B., LEDUC E. H. Vital staining of the hematoencephalic barrier by silver nitrate and trypan blue, and cytological comparisons of the neurohypophysis, pineal body, area postrema, intercolumnar tubercle and supraoptic crest. J Comp Neurol. 1952 Jun;96(3):371–413. doi: 10.1002/cne.900960302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylitalo P., Karppanen H., Paasonen M. K. Is the area postrema a control center of blood pressure? Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):58–59. doi: 10.1038/247058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kooy D., Koda L. Y. Organization of the projections of a circumventricular organ: the area postrema in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Sep 20;219(3):328–338. doi: 10.1002/cne.902190307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


