Abstract
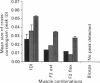
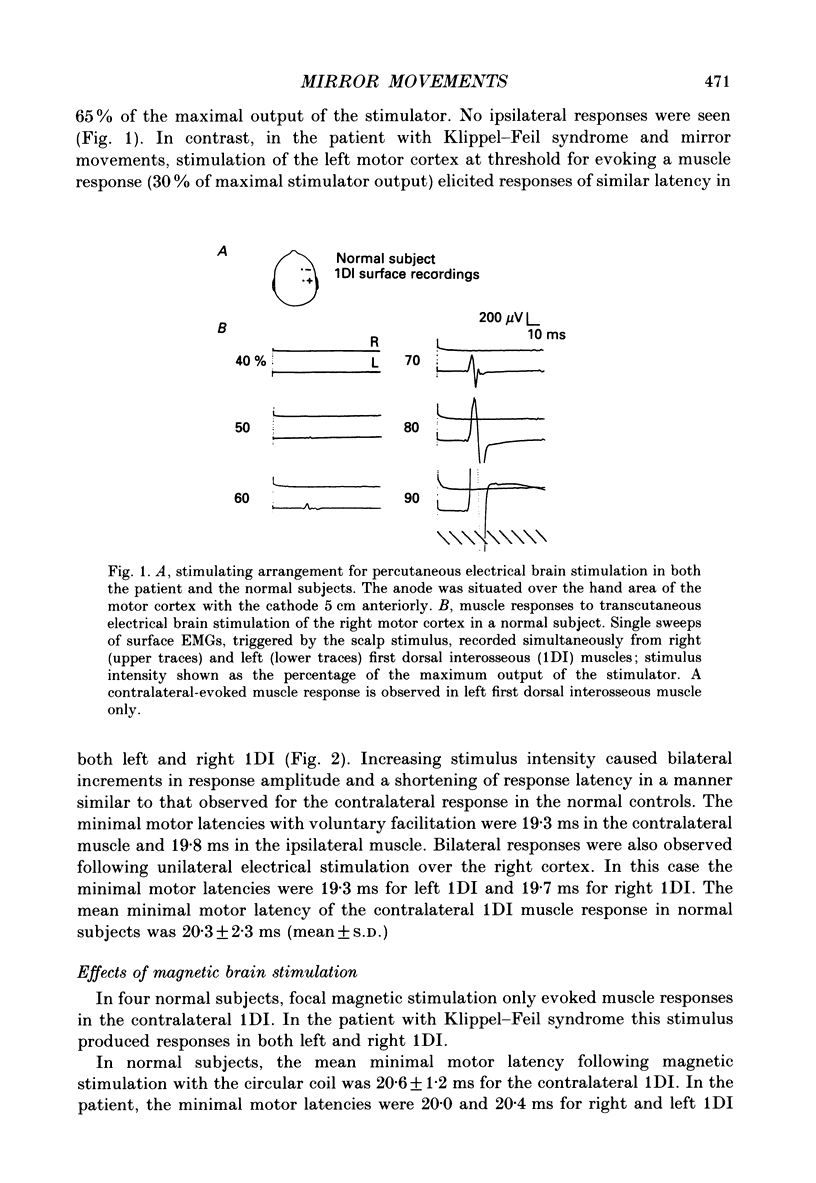
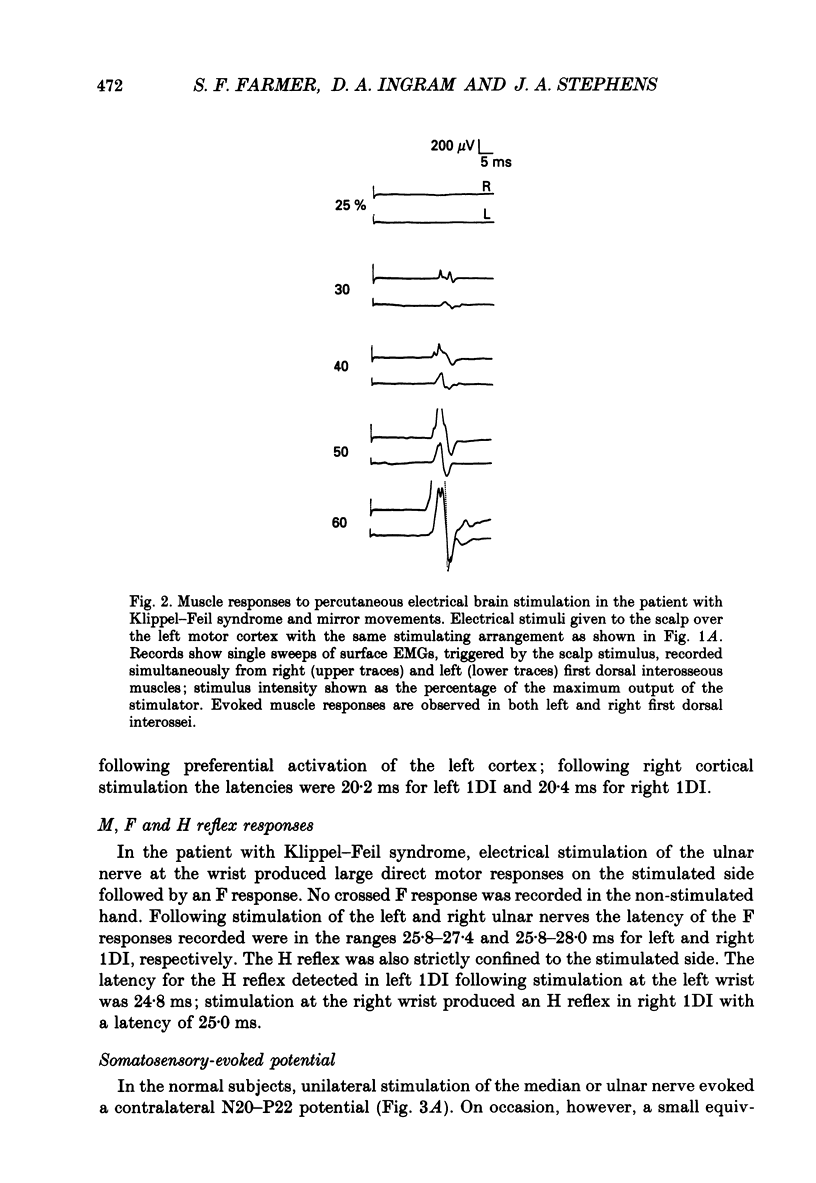
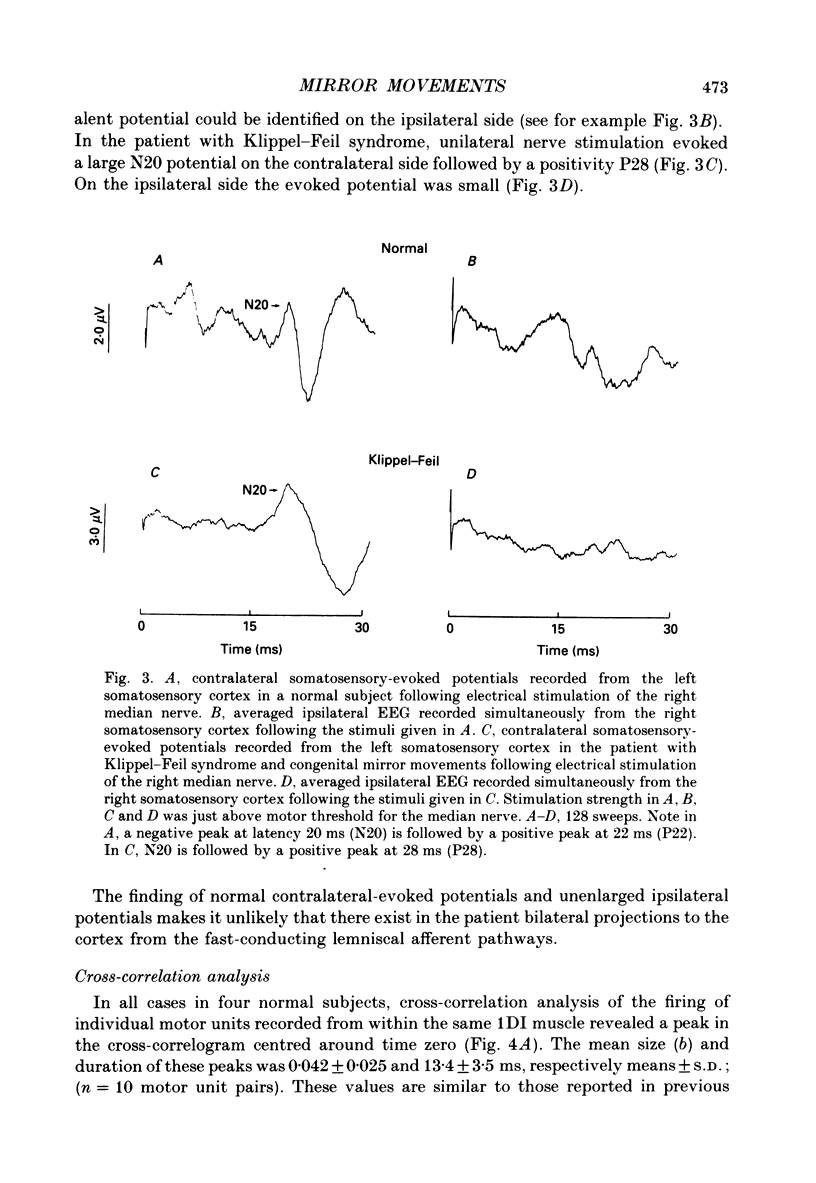
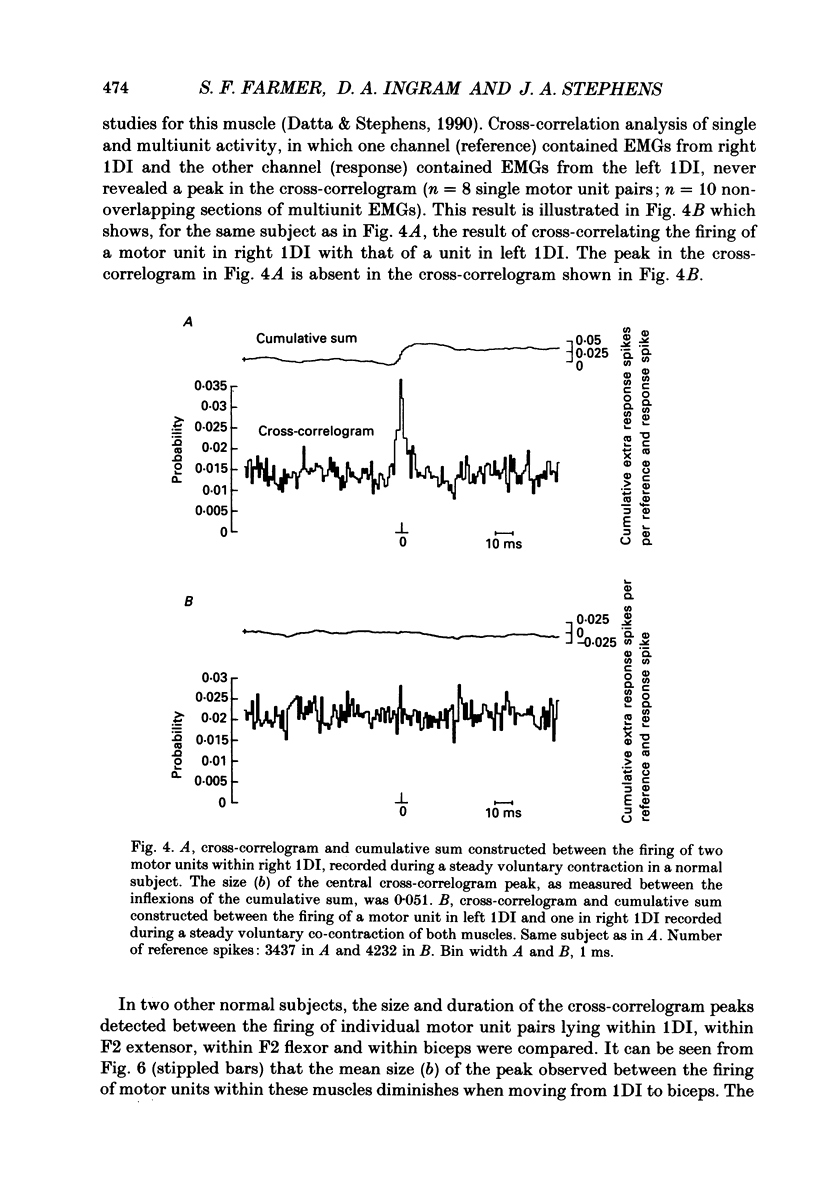
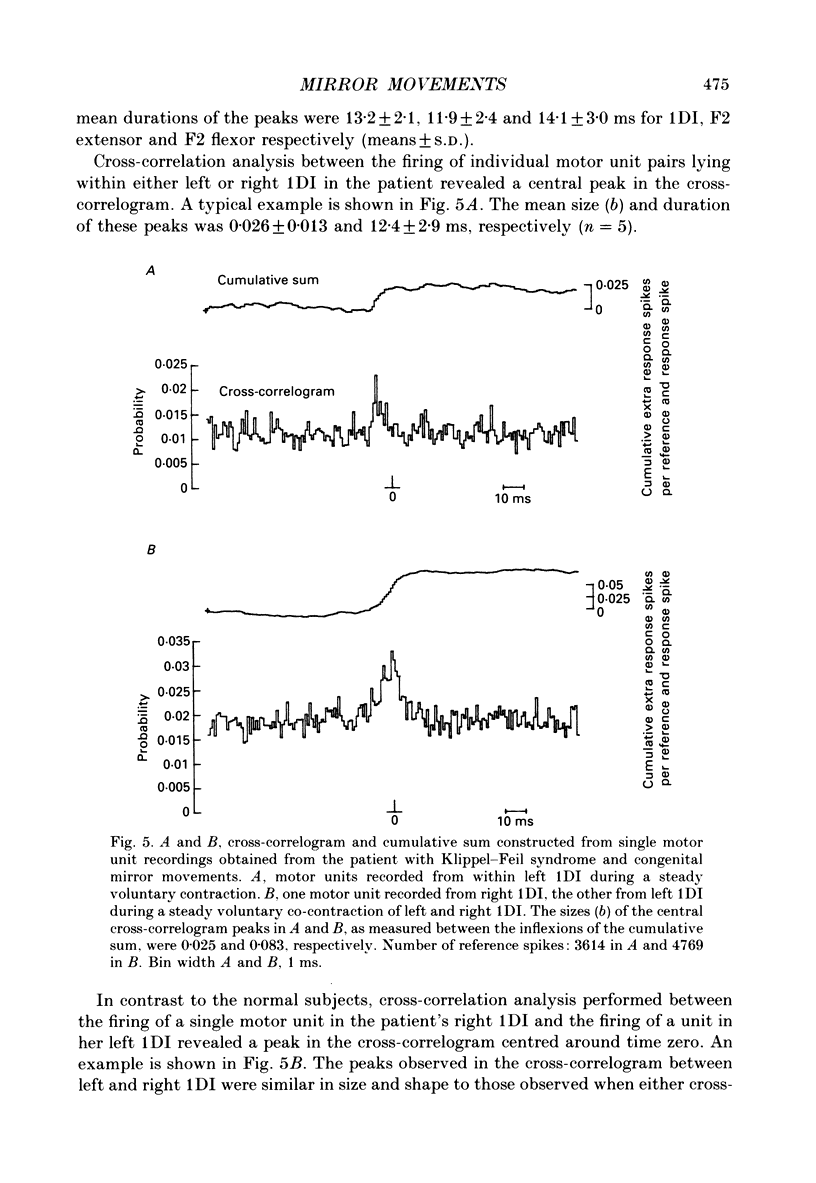
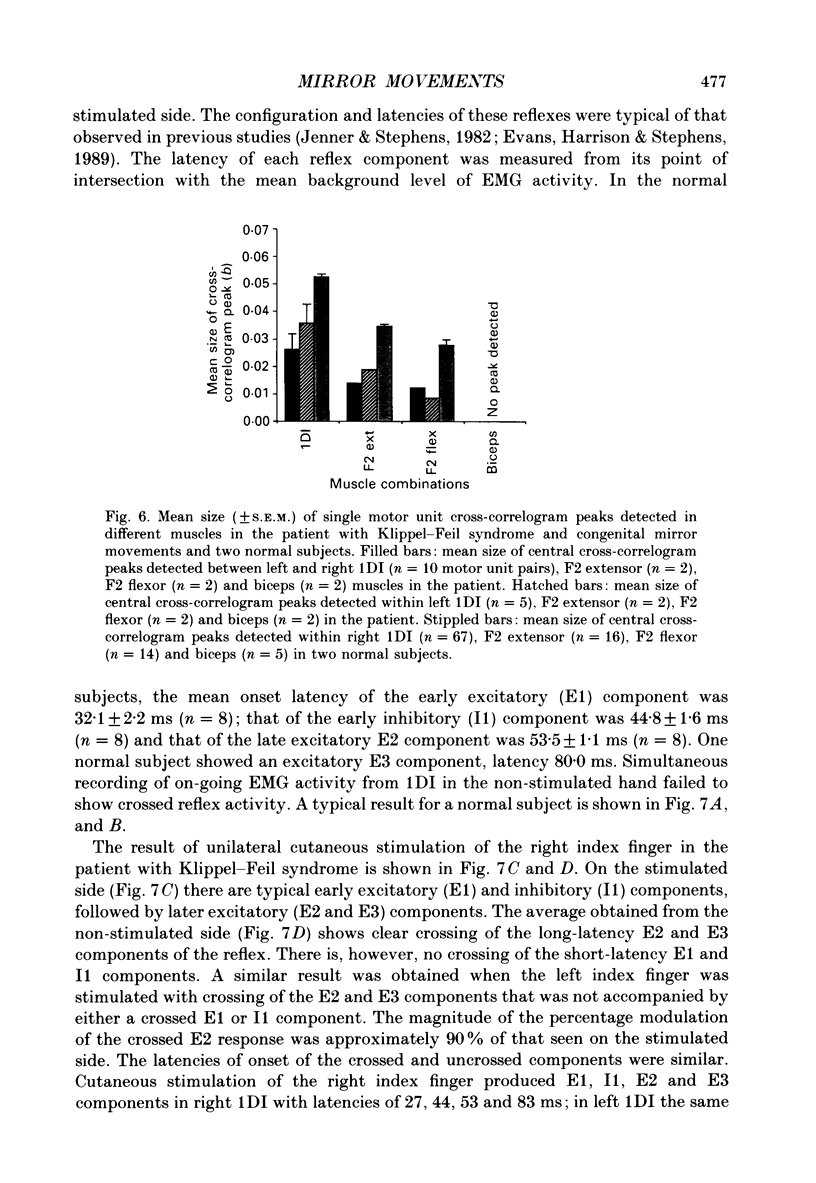
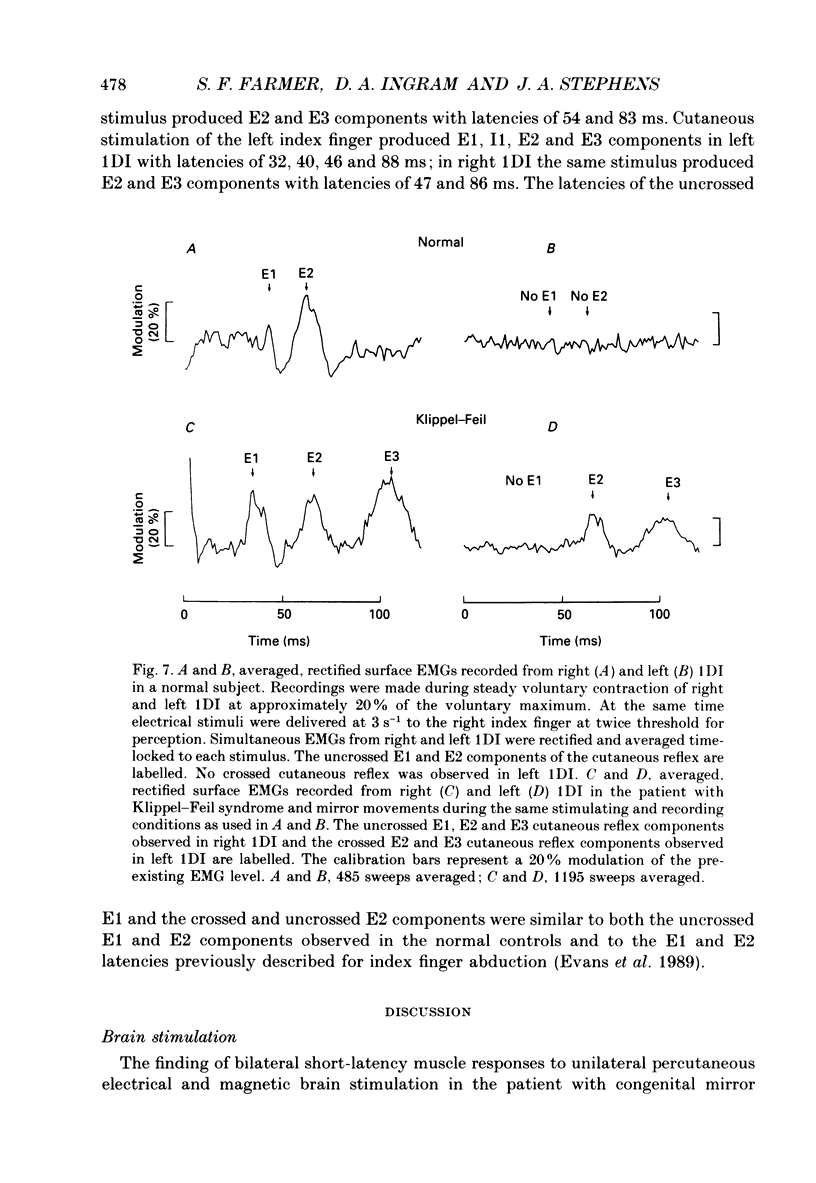
1. Electromyographic (EMG) recordings have been made from upper limb muscles in a patient with well-defined congenital mirror movements occurring in association with Klippel-Feil syndrome and the results compared to those obtained in normal control subjects. 2. In the patient, liminal percutaneous electrical or magnetic brain stimulation applied over either hemisphere elicited bilateral and symmetrical short-latency muscle responses in relaxed intrinsic hand muscles. In the normal subjects unilateral brain stimulation only elicited contralateral muscle responses. 3. F response and H reflex studies for the patient's ulnar-supplied intrinsic hand muscles were normal. No crossed responses were recorded in the homologous muscles of the contralateral hand. 4. Scalp-recorded somatosensory-evoked responses following ulnar or median nerve stimulation were of normal latency and distribution in the patient. 5. In the patient, cross-correlation analysis of on-going single and multiunit needle EMGs recorded between muscles of left and right hands revealed a central peak in the cross-correlogram. No cross-correlogram peaks were found between left- and right-hand muscles in normal subjects. The magnitude and time course of the central peaks in the cross-correlograms constructed between the firing of motor units on opposite sides of the body in the patient were similar to those found in cross-correlograms constructed between the firing of motor units from muscles on the same side of the body in the patient and in normal subjects. 6. The magnitude of cross-correlogram peaks detected within a muscle and those detected between left and right homologous muscles showed a gradient in which the largest peaks were found in the intrinsic hand and forearm extensor muscles. The smallest peaks were observed in the forearm flexor muscles. No peaks were detected between left and right biceps brachii muscles. In intrinsic hand muscles, the size of the cross-correlogram peak detected between the EMGs of homologous muscle pairs was greater than that found for non-homologous muscle pairs. 7. Cutaneous reflex responses were recorded from first dorsal interosseous muscle following unilateral electrical stimulation of the digital nerves of the index finger. In the patient, this produced an early excitatory (E1) response on the stimulated side. Later excitatory (E2 and E3) responses, of approximately equal size and latency, were distributed bilaterally. In the normal subjects, reflex responses were confined to the stimulated side.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amassian V. E., Cracco R. Q. Human cerebral cortical responses to contralateral transcranial stimulation. Neurosurgery. 1987 Jan;20(1):148–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHARD C. G., BOHM E. Cortical representation and functional significance of the corticomotoneuronal system. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1954 Oct;72(4):473–502. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1954.02330040075006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird P. A., Robinson G. C., Buckler W. S. Klippel-Feil syndrome. A study of mirror movement detected by electromyography. Am J Dis Child. 1967 May;113(5):546–551. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1967.02090200078006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccia M. R., McComas A. J., Upton A. R., Blogg T. Cutaneous reflexes in small muscles of the hand. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;36(6):960–977. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.6.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. K., Stephens J. A. Synchronization of motor unit activity during voluntary contraction in man. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:397–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey N. J., Ellaway P. H., Stein R. B. Statistical limits for detecting change in the cumulative sum derivative of the peristimulus time histogram. J Neurosci Methods. 1986 Aug;17(2-3):153–166. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(86)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. L., Harrison L. M., Stephens J. A. Task-dependent changes in cutaneous reflexes recorded from various muscles controlling finger movement in man. J Physiol. 1989 Nov;418:1–12. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Cheney P. D. Functional relations between primate motor cortex cells and muscles: fixed and flexible. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;132:98–117. doi: 10.1002/9780470513545.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Cheney P. D. Postspike facilitation of forelimb muscle activity by primate corticomotoneuronal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Oct;44(4):751–772. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.44.4.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget R., Boghen D., Attig E., Lamarre Y. Electromyographic studies of congenital mirror movements. Neurology. 1986 Oct;36(10):1316–1322. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.10.1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos A. P., Kettner R. E., Schwartz A. B. Primate motor cortex and free arm movements to visual targets in three-dimensional space. II. Coding of the direction of movement by a neuronal population. J Neurosci. 1988 Aug;8(8):2928–2937. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-08-02928.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenner J. R., Stephens J. A. Cutaneous reflex responses and their central nervous pathways studied in man. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:405–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner R. E., Schwartz A. B., Georgopoulos A. P. Primate motor cortex and free arm movements to visual targets in three-dimensional space. III. Positional gradients and population coding of movement direction from various movement origins. J Neurosci. 1988 Aug;8(8):2938–2947. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-08-02938.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A., Stagg D., Westgaard R. H. The spatial distribution of synchronization of intercostal motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:137–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. The synaptic connexions to intercostal motoneurones as revealed by the average common excitation potential. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:103–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A., Tuck D. L., Westgaard R. H. Variations in the time course of the synchronization of intercostal motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:105–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU C. N., CHAMBERS W. W. AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE CORTICO-SPINAL SYSTEM IN THE MONKEY (MACACA MULATTA). THE SPINAL PATHWAYS AND PRETERMINAL DISTRIBUTION OF DEGENERATING FIBERS FOLLOWING DISCRETE LESIONS OF THE PRE- AND POSTCENTRAL GYRI AND BULBAR PYRAMID. J Comp Neurol. 1964 Oct;123:257–283. doi: 10.1002/cne.901230209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon R. The output map of the primate motor cortex. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Nov;11(11):501–506. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott J. F., Marshall J. M. Effects of hypoxia upon contractions evoked in isolated rabbit pulmonary artery by potassium and noradrenaline. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:15–28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunami K., Hamada I. Effects of stimulation of corpus callosum on precentral neuron activity in the awake monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Oct;52(4):676–691. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.52.4.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Stimulation of the cerebral cortex in the intact human subject. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):227–227. doi: 10.1038/285227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schott G. D., Wyke M. A. Congenital mirror movements. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Jul;44(7):586–599. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.7.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. B., Kettner R. E., Georgopoulos A. P. Primate motor cortex and free arm movements to visual targets in three-dimensional space. I. Relations between single cell discharge and direction of movement. J Neurosci. 1988 Aug;8(8):2913–2927. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-08-02913.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears T. A., Stagg D. Short-term synchronization of intercostal motoneurone activity. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(3):357–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. S., Fetz E. E. Effects of synchrony between primate corticomotoneuronal cells on post-spike facilitation of muscles and motor units. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jan 2;96(1):76–81. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90246-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. D., Weaver L. C. Multi- and single-fibre mesenteric and renal sympathetic responses to chemical stimulation of intestinal receptors in cats. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:155–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]