Abstract
1. Human soleus muscles were fatigued under ischaemic conditions by intermittent stimulation at 15 Hz. When maximal voluntary plantarflexion was then attempted, the loss of torque was found to be associated with a reduction in voluntary EMG activity. 2. The decrease in EMG activity could not have been due to 'exhaustion' of descending motor drive in the central nervous system since fatigue had been induced by electrical stimulation of peripheral nerve fibres. Similarly, the decrease could not be explained by changes at the neuromuscular junction or muscle fibre membrane, since changes in the M wave (evoked muscle compound action potential) were relatively modest. 3. When the excitability of the soleus motoneurones was tested during fatigue, using the H (Hoffmann) reflex, it was found to be significantly reduced. Control experiments with ischaemia or electrical stimulation, but without fatigue, failed to demonstrate any significant effects on reflex excitability. 4. The findings in this study favour the concept of reflex inhibition of alpha-motoneurones during fatigue.
Full text
PDF

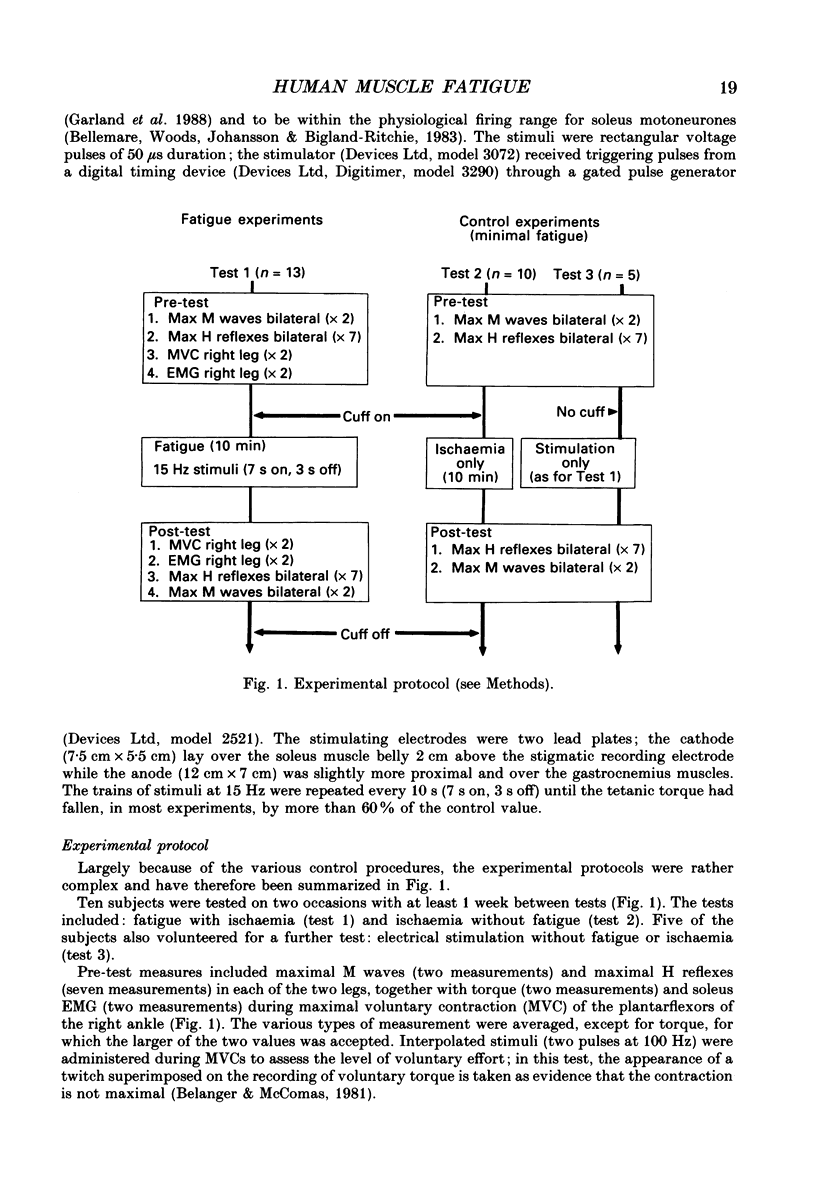

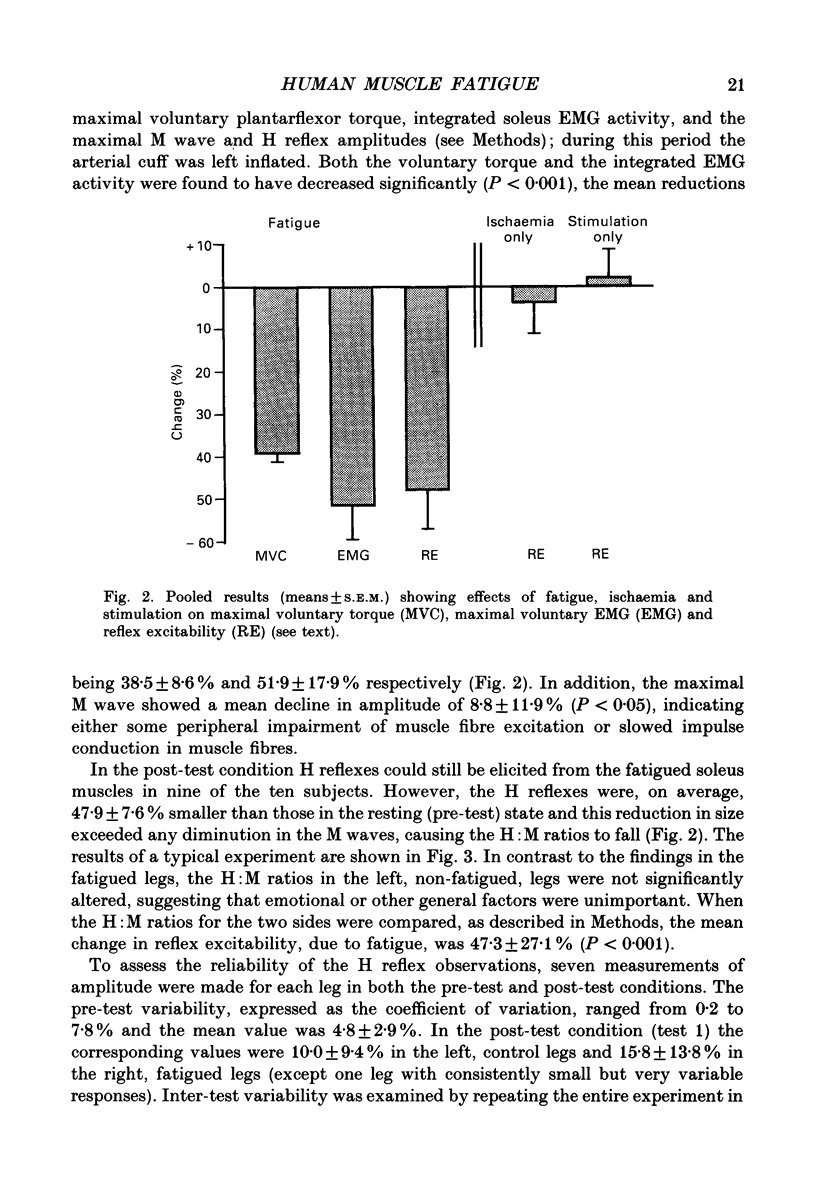
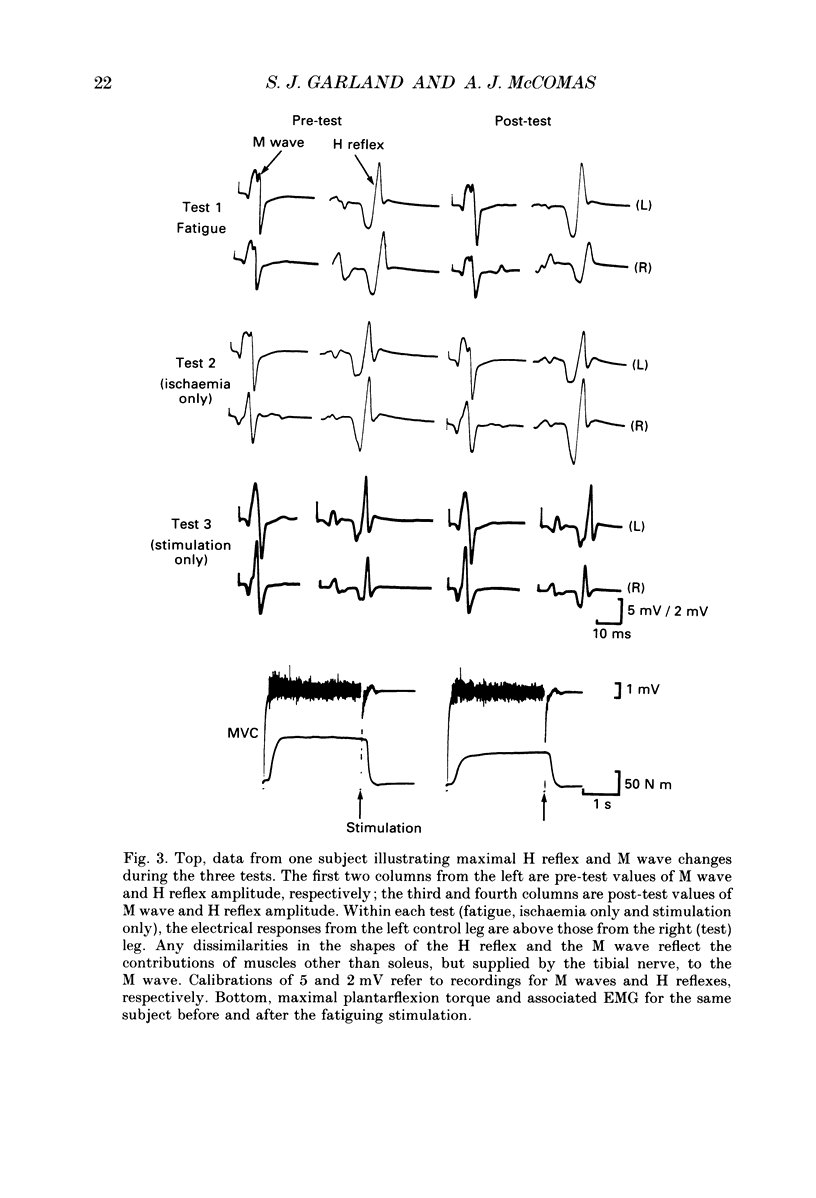
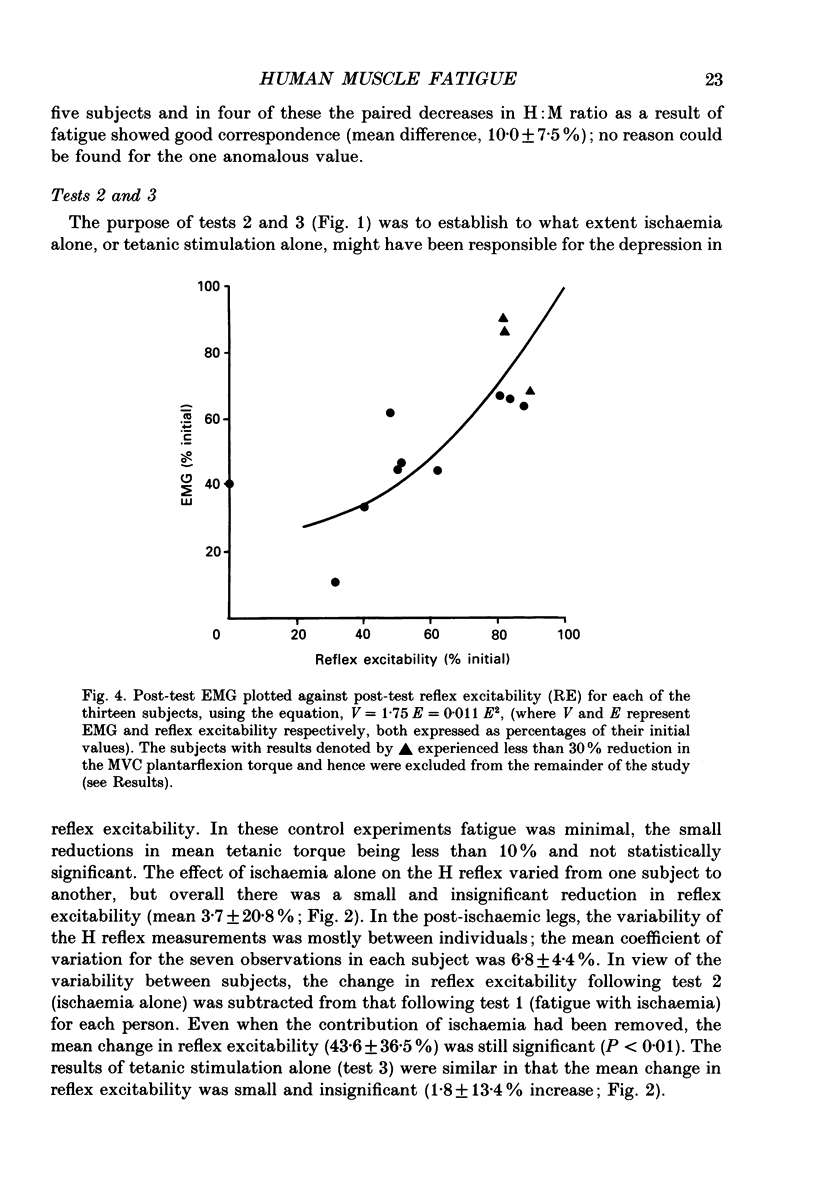




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGEL R. W., HOFMANN W. W. THE H REFLEX IN NORMAL, SPASTIC, AND RIGID SUBJECTS. Arch Neurol. 1963 Jun;9:591–596. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1963.00460060021002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belanger A. Y., McComas A. J. Extent of motor unit activation during effort. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Nov;51(5):1131–1135. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.5.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Woods J. J., Johansson R., Bigland-Ritchie B. Motor-unit discharge rates in maximal voluntary contractions of three human muscles. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Dec;50(6):1380–1392. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.6.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigland-Ritchie B. R., Dawson N. J., Johansson R. S., Lippold O. C. Reflex origin for the slowing of motoneurone firing rates in fatigue of human voluntary contractions. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:451–459. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulbulian R., Darabos B. L. Motor neuron excitability: the Hoffmann reflex following exercise of low and high intensity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1986 Dec;18(6):697–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussel B., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Inhibition of human motoneurons, probably of Renshaw origin, elicited by an orthodromic motor discharge. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):319–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenna P., Schieppati M., de Curtis M. Long-latency, nonreciprocal reflex responses of antagonistic hind limb muscles after cutaneous nerve stimulation in the cat. Exp Neurol. 1982 Apr;76(1):58–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(82)90101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwaide P. J., Crenna P., Fleron M. H. Cutaneous nerve stimulation and motoneuronal excitability: I, soleus and tibialis anterior excitability after ipsilateral and contralateral sural nerve stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Aug;44(8):699–707. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.8.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eke-Okoro S. T. The H-reflex studied in the presence of alcohol, aspirin, caffeine, force and fatigue. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1982 Dec;22(7):579–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoka R. M., Hutton R. S., Eldred E. Changes in excitability of tendon tap and Hoffmann reflexes following voluntary contractions. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980 Jun;48(6):664–672. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(80)90423-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland S. J., Garner S. H., McComas A. J. Reduced voluntary electromyographic activity after fatiguing stimulation of human muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:547–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGBARTH K. E. Spinal withdrawal reflexes in the human lower limbs. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960 Aug;23:222–227. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.23.3.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukulka C. G., Moore M. A., Russell A. G. Changes in human alpha-motoneuron excitability during sustained maximum isometric contractions. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Aug 4;68(3):327–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90511-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER R. F., MAWDSLEY C. STUDIES IN MAN AND CAT OF THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE H WAVE. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1965 Jun;28:201–211. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.28.3.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh E., Sale D., McComas A. J., Quinlan J. Influence of joint position on ankle dorsiflexion in humans. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Jul;51(1):160–167. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.1.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinck H. M. Facilitation and inhibition of the human H reflex as a function of the amplitude of the control reflex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;48(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(80)90305-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Giannini D., Milner-Brown H. S., Layzer R. B., Koretsky A. P., Hooper D., Weiner M. W. Effects of fatiguing exercise on high-energy phosphates, force, and EMG: evidence for three phases of recovery. Muscle Nerve. 1987 Nov-Dec;10(9):810–821. doi: 10.1002/mus.880100906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin C., Katz R., Mazieres L., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Comparison of soleus H reflex facilitation at the onset of soleus contractions produced voluntarily and during the stance phase of human gait. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Nov 16;33(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schieppati M., Crenna P. From activity to rest: gating of excitatory autogenetic afferences from the relaxing muscle in man. Exp Brain Res. 1984;56(3):448–457. doi: 10.1007/BF00237985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schieppati M. The Hoffmann reflex: a means of assessing spinal reflex excitability and its descending control in man. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(4):345–376. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton A. R., McComas A. J., Sica R. E. Potentiation of "late" responses evoked in muscles during effort. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Dec;34(6):699–711. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.6.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrier M. C. Alterations in H reflex magnitude by variations in baseline EMG excitability. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1985 Jun;60(6):492–499. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(85)91109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. J., Furbush F., Bigland-Ritchie B. Evidence for a fatigue-induced reflex inhibition of motoneuron firing rates. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Jul;58(1):125–137. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


