Abstract
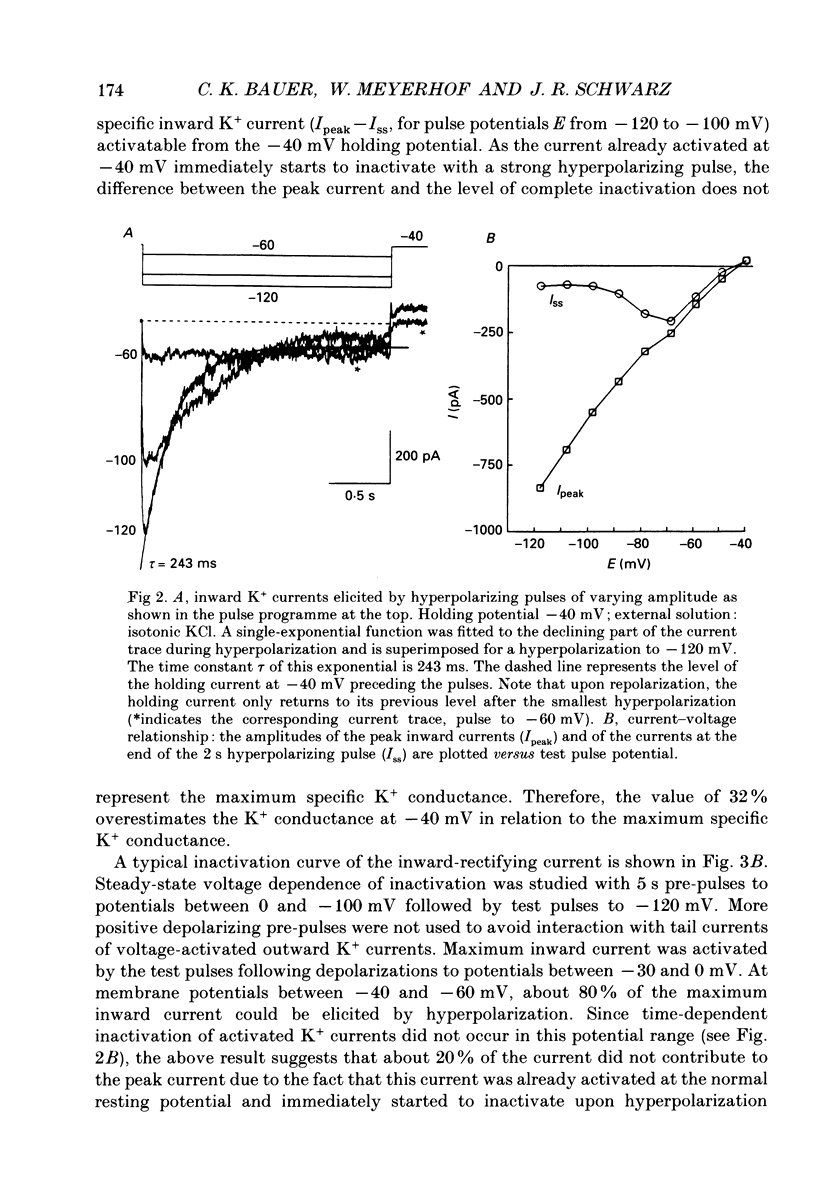
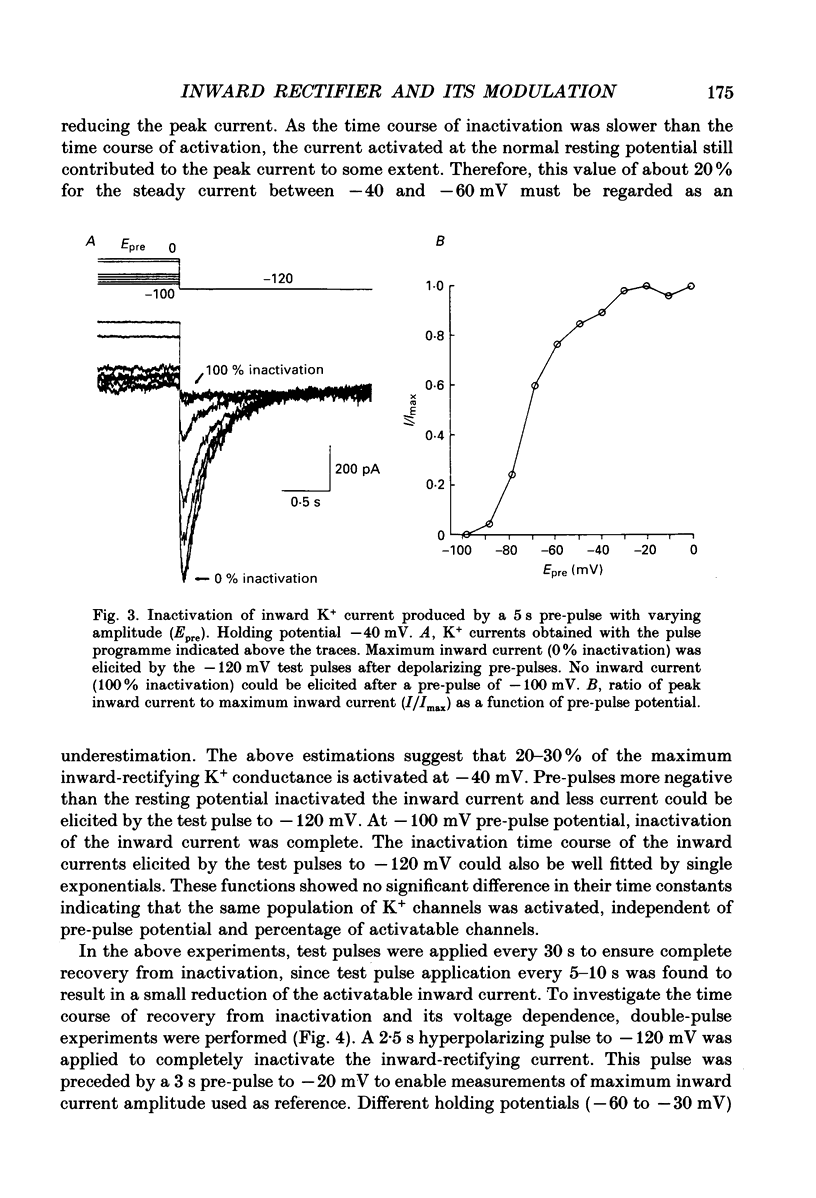
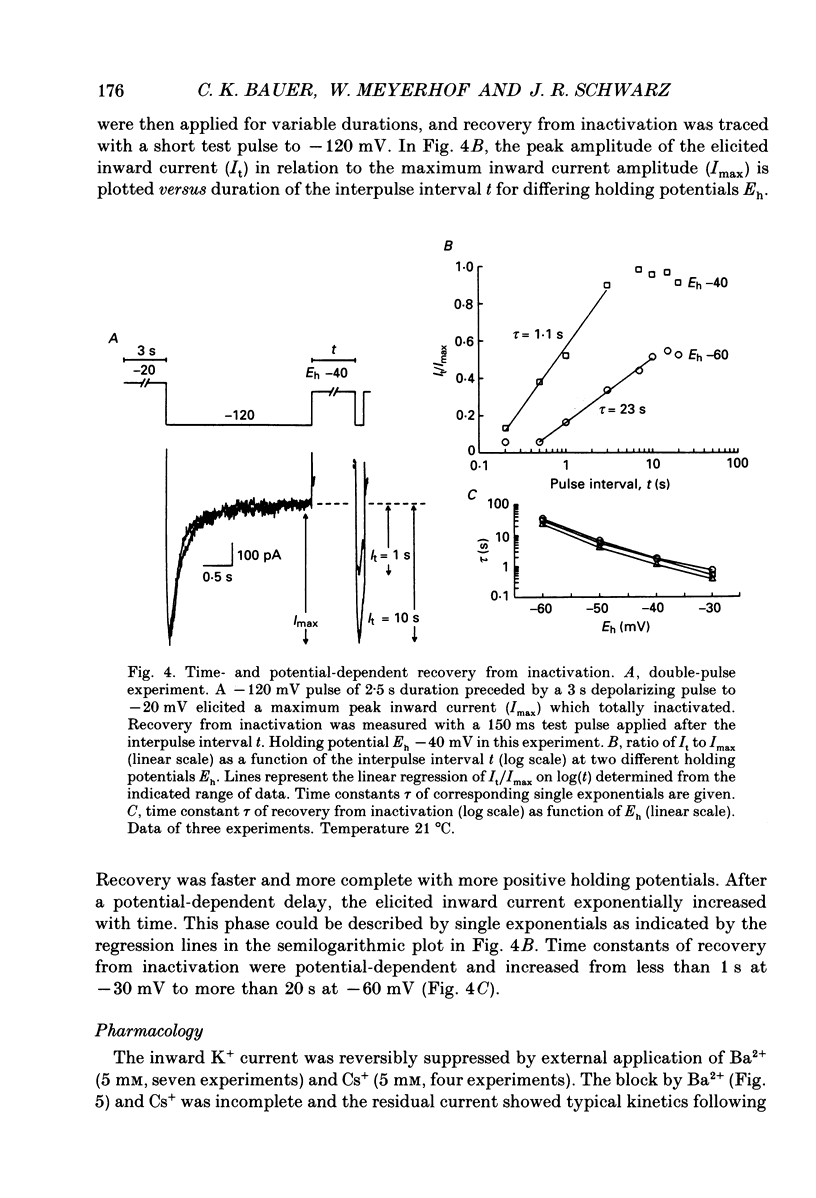
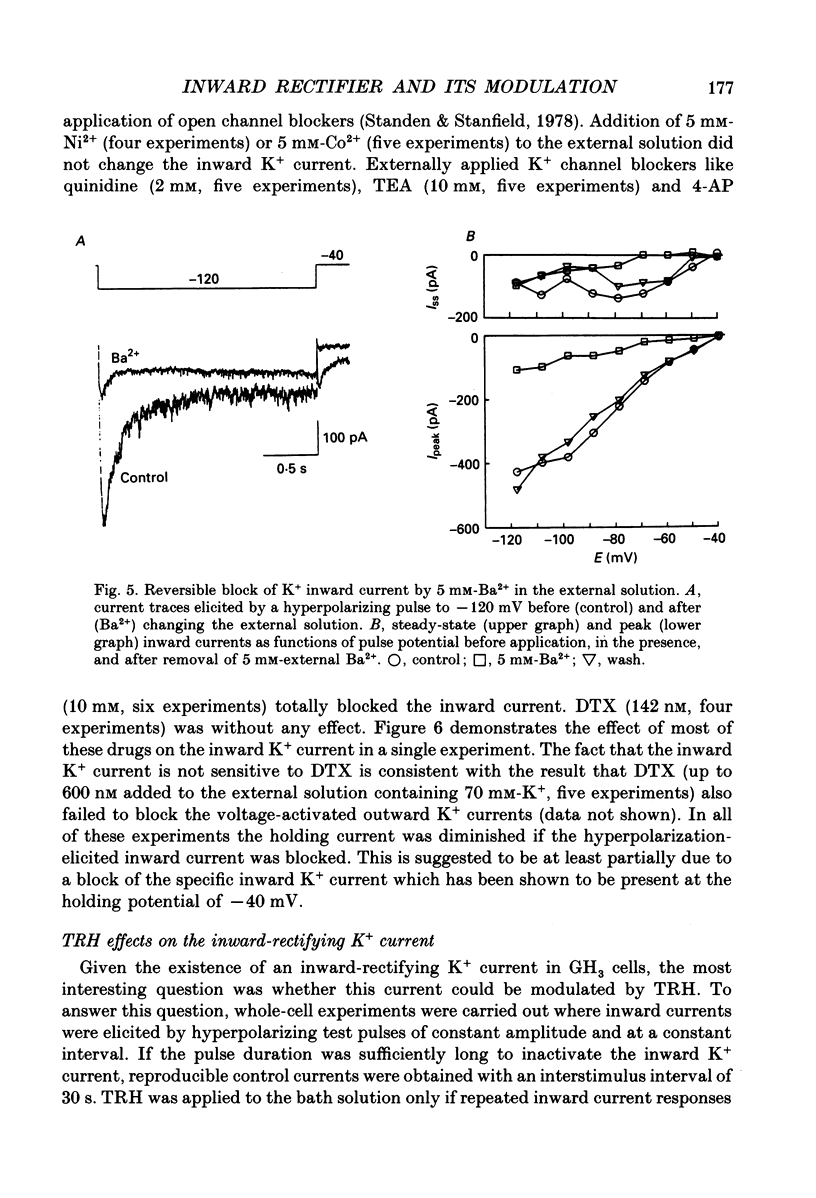
1. Voltage-dependent K+ currents were recorded in cultured tumour-derived anterior pituitary cells of the rat (GH3 cells) with the patch clamp technique. An inward-rectifying current is described which is found to be carried by K+. 2. In isotonic KCl, whole-cell inward K+ currents were elicited by hyperpolarizing pulses from a holding potential of -40 mV. These inward K+ currents showed time- and voltage-dependent inactivation at potentials more negative than -60 mV. Inactivation was faster and more complete at larger hyperpolarizations. Recovery from inactivation was also time- and voltage-dependent. It was faster and more complete with more positive potentials. Time course of inactivation and of recovery from inactivation could be fitted by single exponentials. 3. Two results showed that a steady inward K+ current is present at -40 mV. The holding current at -40 mV was reduced following complete inactivation of the inward K+ current during strong hyperpolarizing pulses, and the amplitude of maximum inward K+ current elicited by hyperpolarization increased after depolarizing pre-pulses of 5 s. The resting conductance was estimated to be 20-30% of the maximum inward-rectifying conductance. 4. The inward K+ current was drastically reduced by Cs+ and Ba2+, but not by Ni2+ and Co2+. Quinidine, 4-aminopyridine and tetraethylammonium chloride blocked the current. In contrast, dendrotoxin was without effect. 5. Thyrotrophin-releasing hormone (TRH) which induces biphasic secretion of prolactin in GH3 cells consistently reduced the inward K+ current in the presence of internal Ca2+. This reduction was abolished if the pipette solution contained guanosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) (GDP beta S; 400 microM), confirming the involvement of G-proteins in the signal transduction pathway. 6. TRH shifted the voltage-dependence of inward K+ current inactivation to less negative potentials resulting in pronounced K+ current inactivation in the range of the resting potential of these cells (-40 to -60 mV). 7. In intact cells, closing of K+ channels would result in a depolarization. The existence of an inward-rectifying K+ current in GH3 cells which is able to be reduced by TRH could readily explain the TRH-induced increase in action potential firing underlying the sustained second phase of secretion.
Full text
PDF




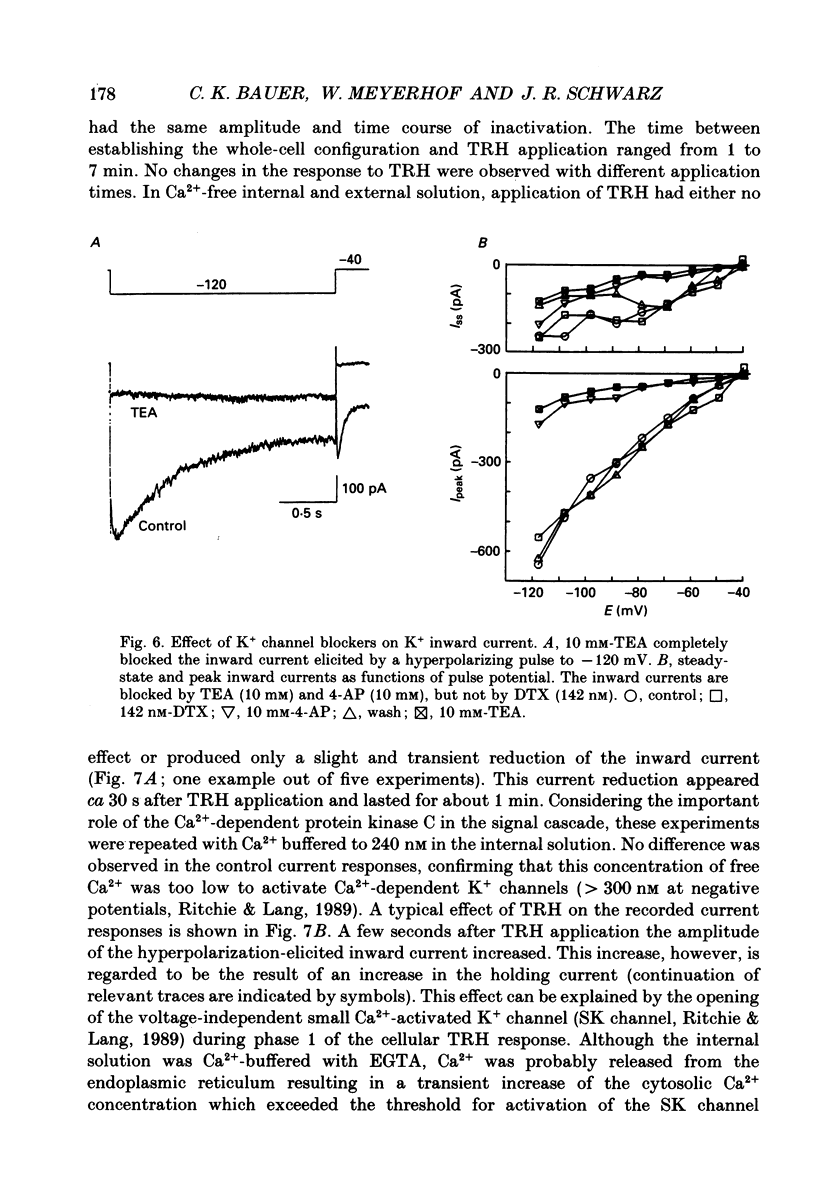
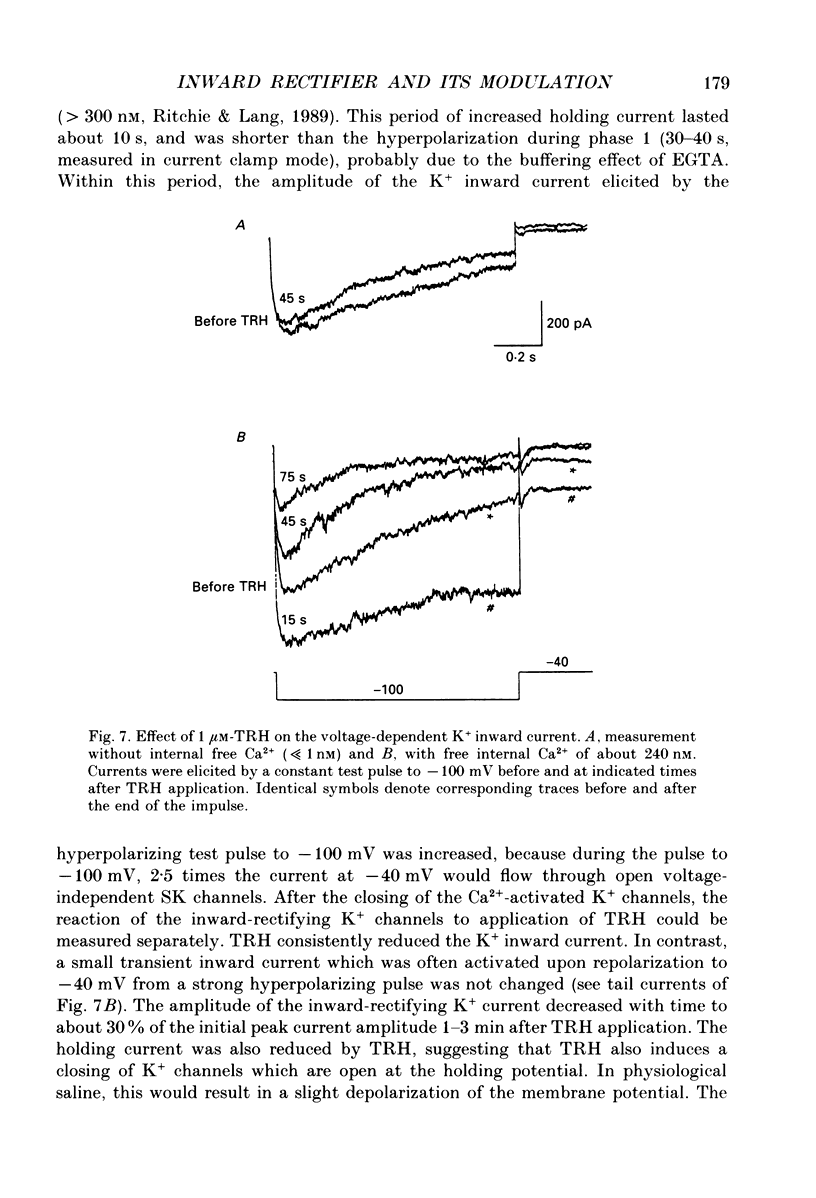


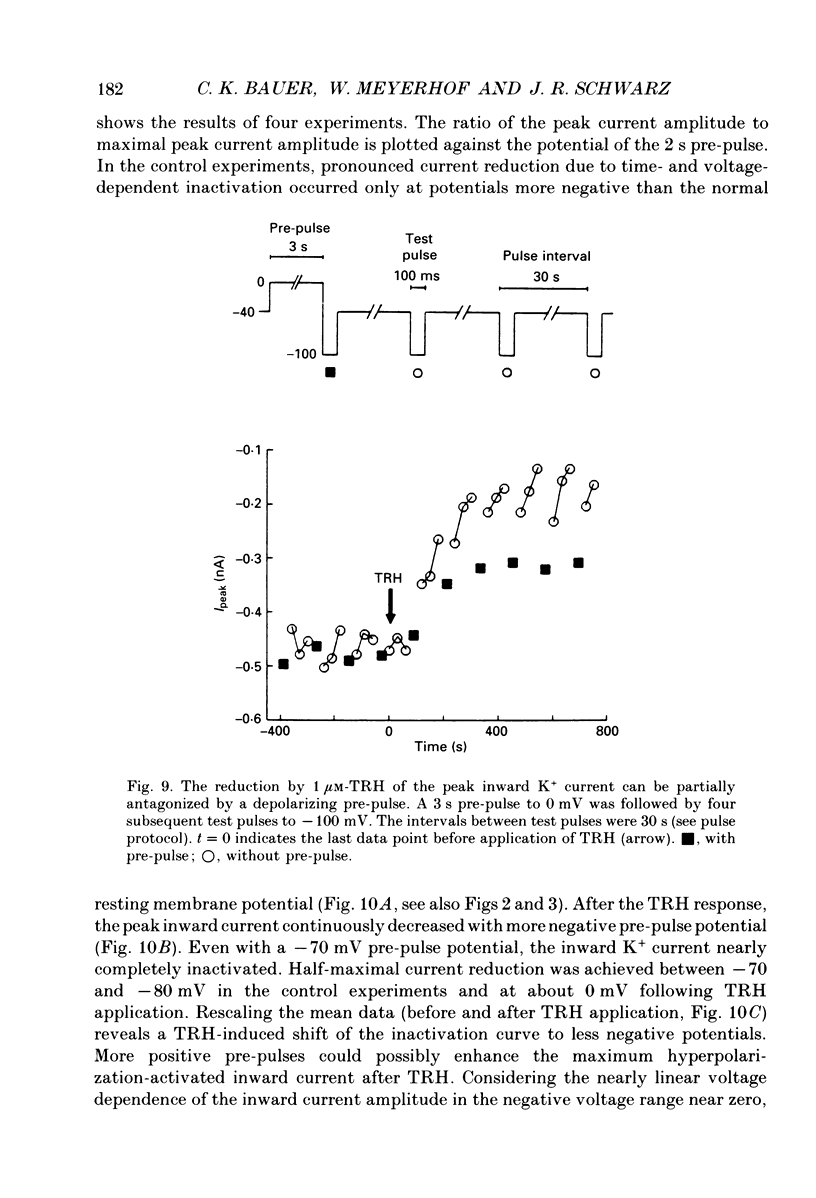







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abercrombie R. F., Masukawa L. M., Sjodin R. A., Livengood D. Uptake and release of 45Ca by Myxicola axoplasm. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Oct;78(4):413–429. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Slow changes in potassium permeability in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):645–668. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beretta L., Boutterin M. C., Drouva S. V., Sobel A. Phosphorylation of a group of proteins related to the physiological, multihormonal regulations of the various cell types in the anterior pituitary gland. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1358–1364. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjøro T., Ostberg B. C., Sand O., Gordeladze J., Iversen J. G., Torjesen P. A., Gautvik K. M., Haug E. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and peptide with N-terminal histidine and C-terminal isoleucine increase prolactin secretion in cultured rat pituitary cells (GH4C1) via a cAMP-dependent mechanism which involves transient elevation of intracellular Ca2+. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Feb;49(2-3):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd R. S., Wallis M. Effects of pretreatment with tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate on regulation of growth hormone and prolactin secretion from ovine anterior pituitary cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81436-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubinsky J. M., Oxford G. S. Dual modulation of K channels by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in clonal pituitary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4282–4286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufy B., Jaken S., Barker J. L. Intracellular Ca2+-dependent protein kinase C activation mimics delayed effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone on clonal pituitary cell excitability. Endocrinology. 1987 Aug;121(2):793–802. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-2-793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufy B., Mollard P., Dufy-Barbe L., Manciet G., Guerin J., Roger P. The electrophysiological effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone are similar in human TSH- and prolactin-secreting pituitary cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Dec;67(6):1178–1185. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-6-1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French M. B., Moor B. C., Lussier B. T., Kraicer J. Protein kinase C is not essential for growth hormone (GH)-releasing factor-induced GH release from rat somatotrophs. Endocrinology. 1989 May;124(5):2235–2244. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-5-2235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon C. M., Oxford G. S., Allen A. C., McCarthy K. D., Morell P. Diacylglycerol modulates action potential frequency in GH3 pituitary cells: correlative biochemical and electrophysiological studies. Brain Res. 1989 Feb 13;479(2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91622-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C. Mechanism of thyrotropin releasing hormone stimulation of pituitary hormone secretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:515–526. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.002503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C. Role of inositol lipid second messengers in regulation of secretion: studies of thyrotropin-releasing hormone action in pituitary cells. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1989;44:1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordeladze J. O., Björo T., Torjesen P. A., Ostberg B. C., Haug E., Gautvik K. M. Protein kinase C stimulates adenylate cyclase activity in prolactin-secreting rat adenoma (GH4C1) pituicytes by inactivating the inhibitory GTP-binding protein Gi. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 1;183(2):397–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordeladze J. O., Bjøro T., Ostberg B. C., Sand O., Torjesen P., Haug E., Gautvik K. M. Phorbol esters and thyroliberin have distinct actions regarding stimulation of prolactin secretion and activation of adenylate cyclase in rat pituitary tumour cells (GH4C1 cells). Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Aug 15;37(16):3133–3138. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90311-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Moody W., Patlak J. Blocking effects of barium and hydrogen ions on the potassium current during anomalous rectification in the starfish egg. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:167–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Rosenthal N. P. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomalous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):621–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund B., Dufy B., Barker L. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide alters GH3/B6 pituitary cell excitability. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):173–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00582311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram C. D., Bicknell R. J., Mason W. T. Intracellular recordings from bovine anterior pituitary cells: modulation of spontaneous activity by regulators of prolactin secretion. Endocrinology. 1986 Dec;119(6):2508–2518. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-6-2508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara K., Mitsuiye T., Noma A., Takano M. The Mg2+ block and intrinsic gating underlying inward rectification of the K+ current in guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:297–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. G., Ritchie A. K. Large and small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in the GH3 anterior pituitary cell line. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Dec;410(6):614–622. doi: 10.1007/BF00581321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingle C. J., Sombati S., Freeman M. E. Membrane currents in identified lactotrophs of rat anterior pituitary. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):2995–3005. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-02995.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Armstrong C. M. Na and Ca channels in a transformed line of anterior pituitary cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):371–394. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Schultz G., Rosenthal W. Secretion-stimulating and secretion-inhibiting hormones stimulate high-affinity pertussis-toxin-sensitive GTPases in membranes of a pituitary cell line. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):283–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori H. Inactivation kinetics and steady-state current noise in the anomalous rectifier of tunicate egg cell membranes. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:77–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostberg B. C., Sand O., Bjøro T., Haug E. The phorbol ester TPA induces hormone release and electrical activity in clonal rat pituitary cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Apr;126(4):517–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Wagoner P. K. The inactivating K+ current in GH3 pituitary cells and its modification by chemical reagents. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:587–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa S., Sand O. Electrophysiology of excitable endocrine cells. Physiol Rev. 1986 Oct;66(4):887–952. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.4.887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappone P. A., Lucero M. T. Pandinus imperator scorpion venom blocks voltage-gated potassium channels in GH3 cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jun;91(6):817–833. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.6.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogawski M. A., Inoue K., Suzuki S., Barker J. L. A slow calcium-dependent chloride conductance in clonal anterior pituitary cells. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Jun;59(6):1854–1870. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.6.1854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Hescheler J., Hinsch K. D., Spicher K., Trautwein W., Schultz G. Cyclic AMP-independent, dual regulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ currents by LHRH and somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1627–1633. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02989.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):729–749. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Trube G. Voltage-dependent inactivation of inward-rectifying single-channel currents in the guinea-pig heart cell membrane. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:659–683. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. A potential- and time-dependent blockade of inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibres by barium and strontium ions. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:169–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R., Nakajima Y., Yamaguchi K. Substance P raises neuronal membrane excitability by reducing inward rectification. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):498–501. doi: 10.1038/315498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Yasumura Y., Levine L., Sato G. H., Parker M. L. Establishment of clonal strains of rat pituitary tumor cells that secrete growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):342–352. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarroel A., Marrion N. V., Lopez H., Adams P. R. Bradykinin inhibits a potassium M-like current in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 11;255(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima Y., Akita Y., Saito T. Effects of cholera toxin on the coupling of thyrotropin-releasing hormone to a guanine nucleotide-binding protein in cultured GH3 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;33(6):592–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita N., Shibuya N., Ogata E. Hyperpolarization of the membrane potential caused by somatostatin in dissociated human pituitary adenoma cells that secrete growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6198–6202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita N., Shibuya N., Ogata E. Requirement of GTP on somatostatin-induced K+ current in human pituitary tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4924–4928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Sekura R. D., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Reconstitution of somatostatin and muscarinic receptor mediated stimulation of K+ channels by isolated GK protein in clonal rat anterior pituitary cell membranes. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Apr;1(4):283–289. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-4-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


