Abstract
1. A patch of plasma membrane was excised, in the inside-out configuration, from the outer segment tip of a catfish cone and recorded electrically with a patch pipette. A solution of 118 mM-NaCl was present on both sides of the membrane. 2. With the solution outside the pipette containing a low concentration (typically several micromoles per litre) of cyclic GMP and the membrane potential held at a non-zero level, brief steps of current indicative of the openings of single ion channels could be detected. There was no sign of desensitization to the ligand over a period of tens of seconds. 3. The prominent openings were associated with a conductance near 50 pS and an open-time constant of 0.5 ms or less. There was also an indication of sub-state openings. 4. The conductance of the large openings appeared to be invariant between -50 mV and +50 mV. However, the macroscopic current-voltage relation measured at a saturating concentration of cyclic GMP showed a slight upward curvature, which we attribute to a voltage dependence in the open probability of the fully liganded channel. 5. The relation between mean current and cyclic GMP concentration had an average Hill coefficient of about 2.4. The Hill coefficient was not affected by membrane voltage, but the conductance was activated by cyclic GMP slightly more readily at depolarizations; this could be adequately explained by a higher open probability of the fully liganded channel at positive voltages. 6. In several experiments, the membrane patch apparently contained a single cyclic GMP-activated channel, in that the measured current never rose above that for a single channel even at high concentrations of cyclic GMP. In these cases, a high concentration of the ligand simply engaged the channel in a literally continuous burst of openings, with an open probability of 0.8-0.9 at between -30 mV and +30 mV. The amplitude distribution of the burst under these conditions could be described by a beta distribution, consistent with the channel switching predominantly between a single closed state and a single open state when fully liganded. 7. Estimates of channel density on the cone membrane ranged from about 2 to 130 microns -2, with an average of 20 microns -2. This observed density is about ten times lower than the density of the homologous channel on rod membrane, being roughly in inverse relation to the tenfold larger surface membrane area of the cone outer segment.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




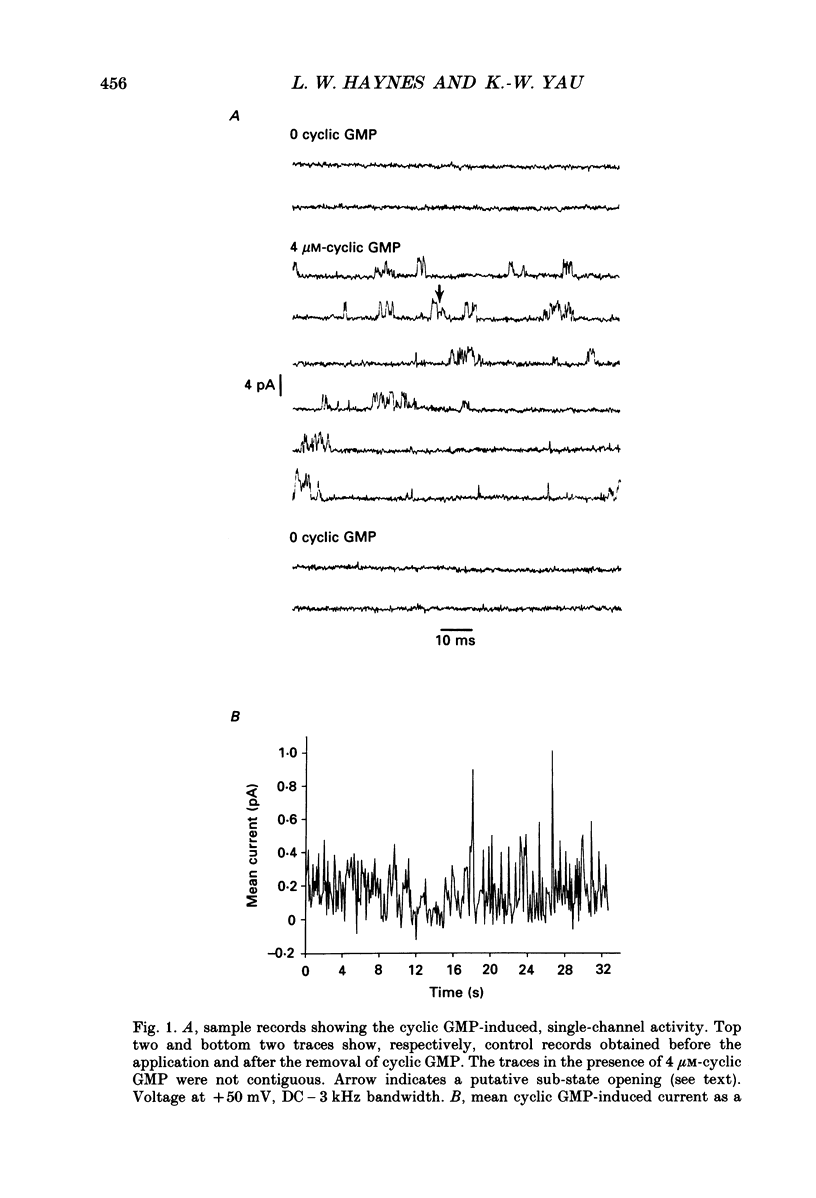

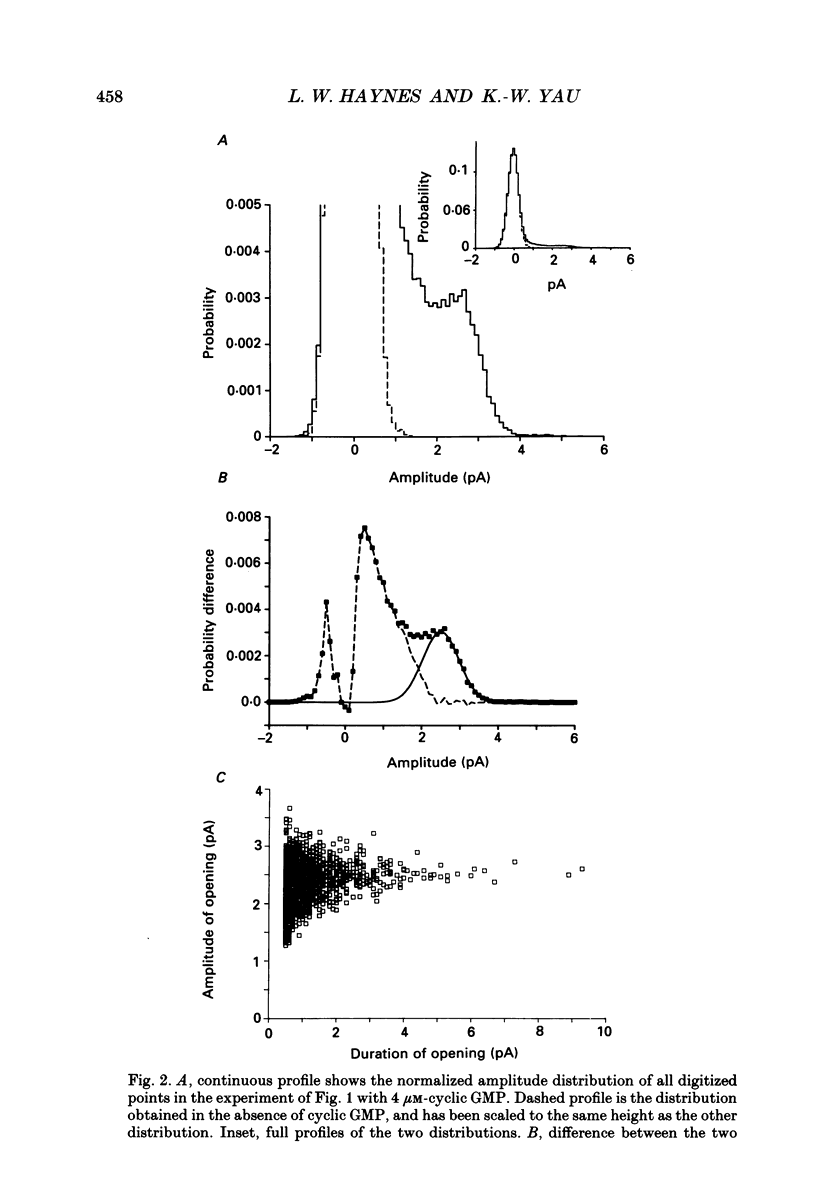

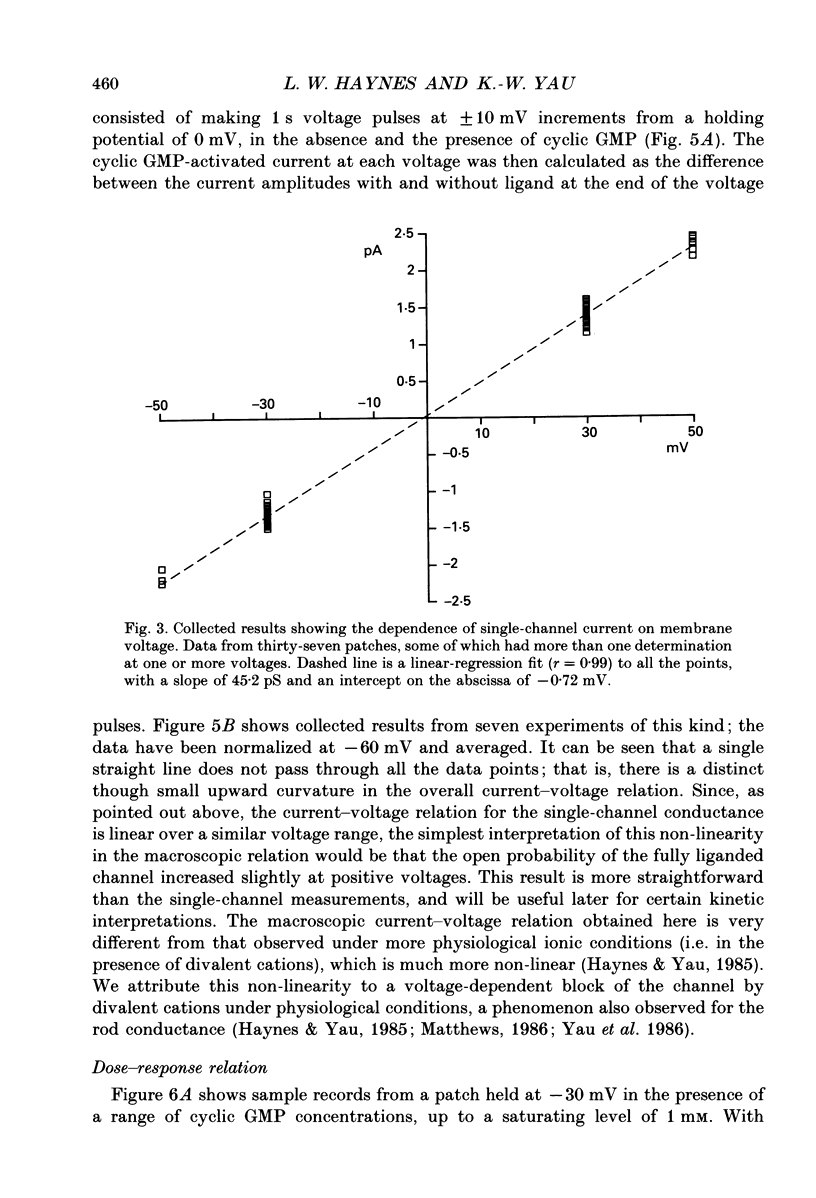
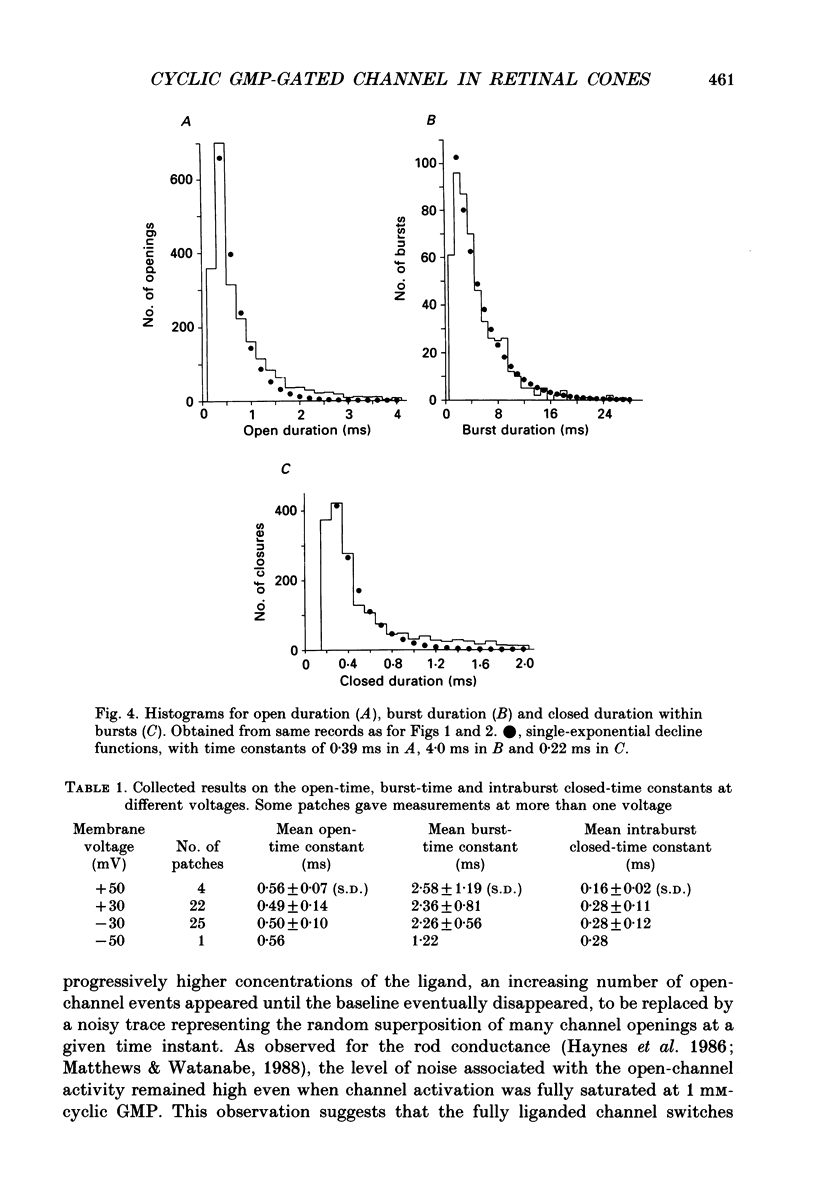
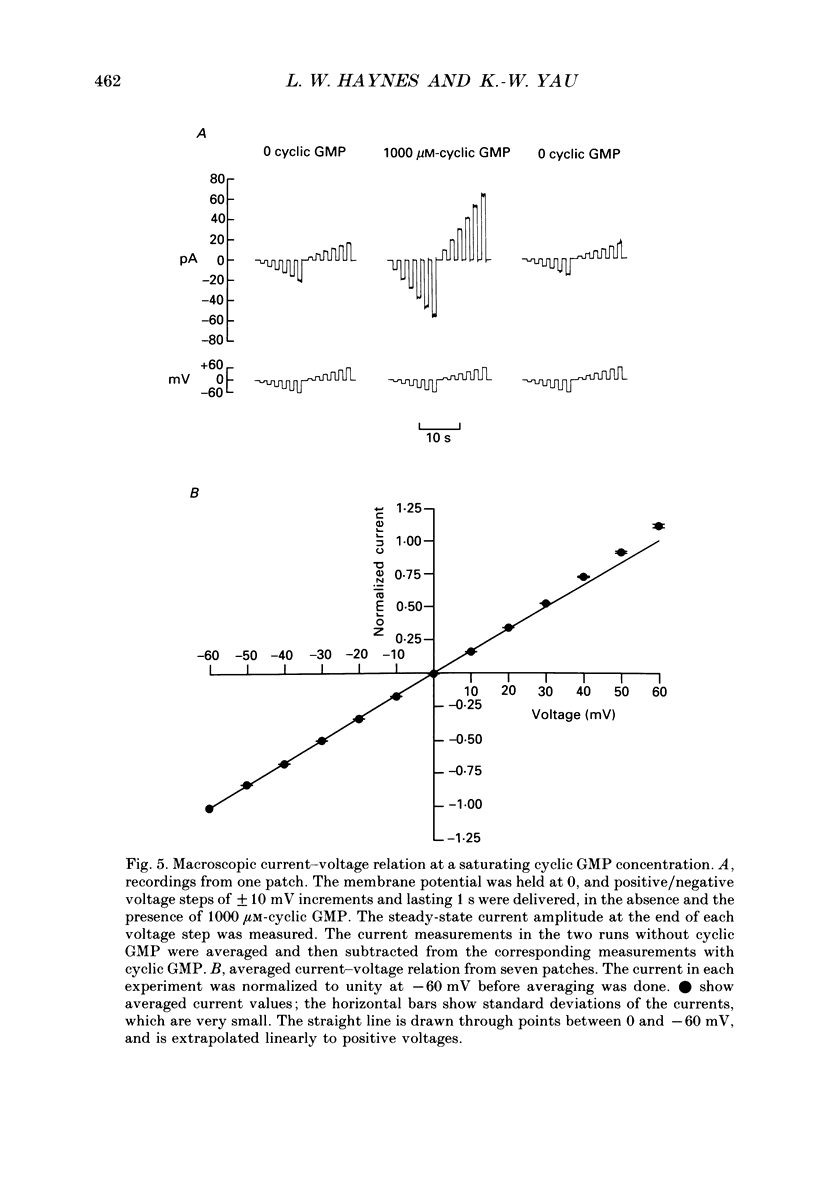
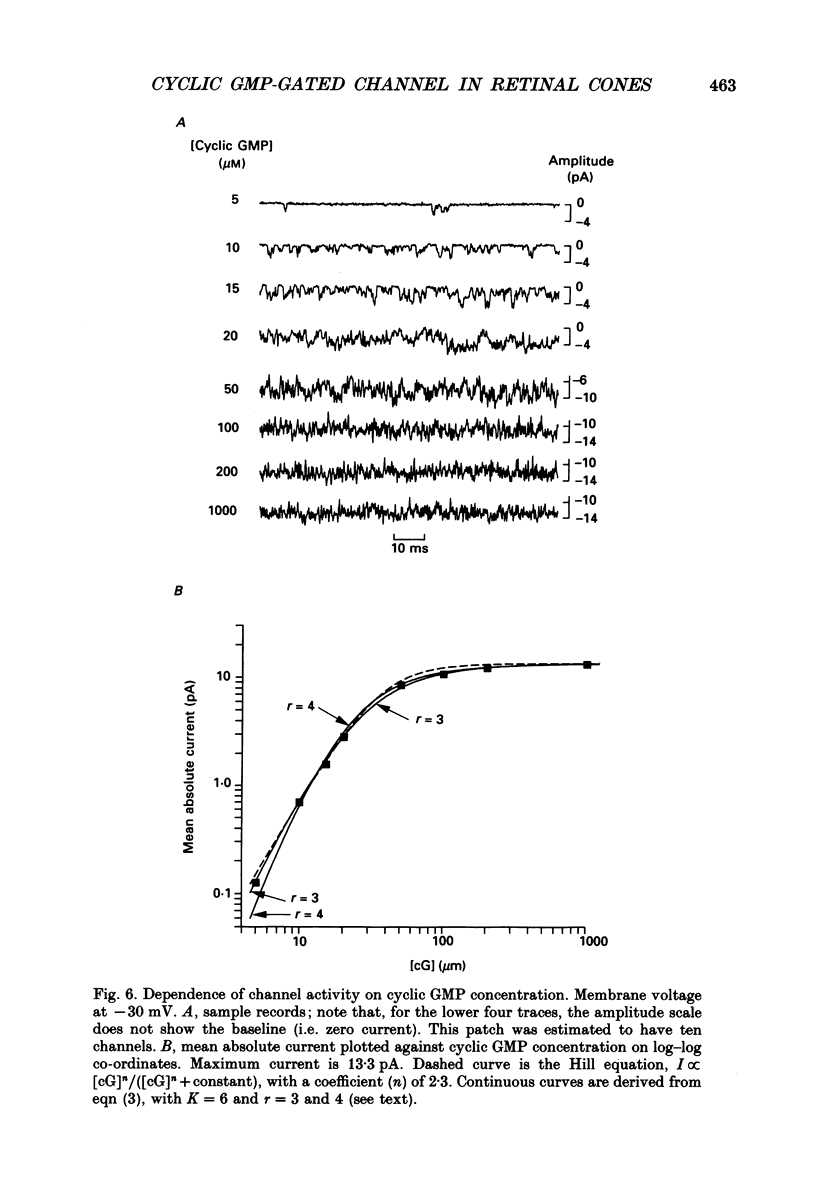

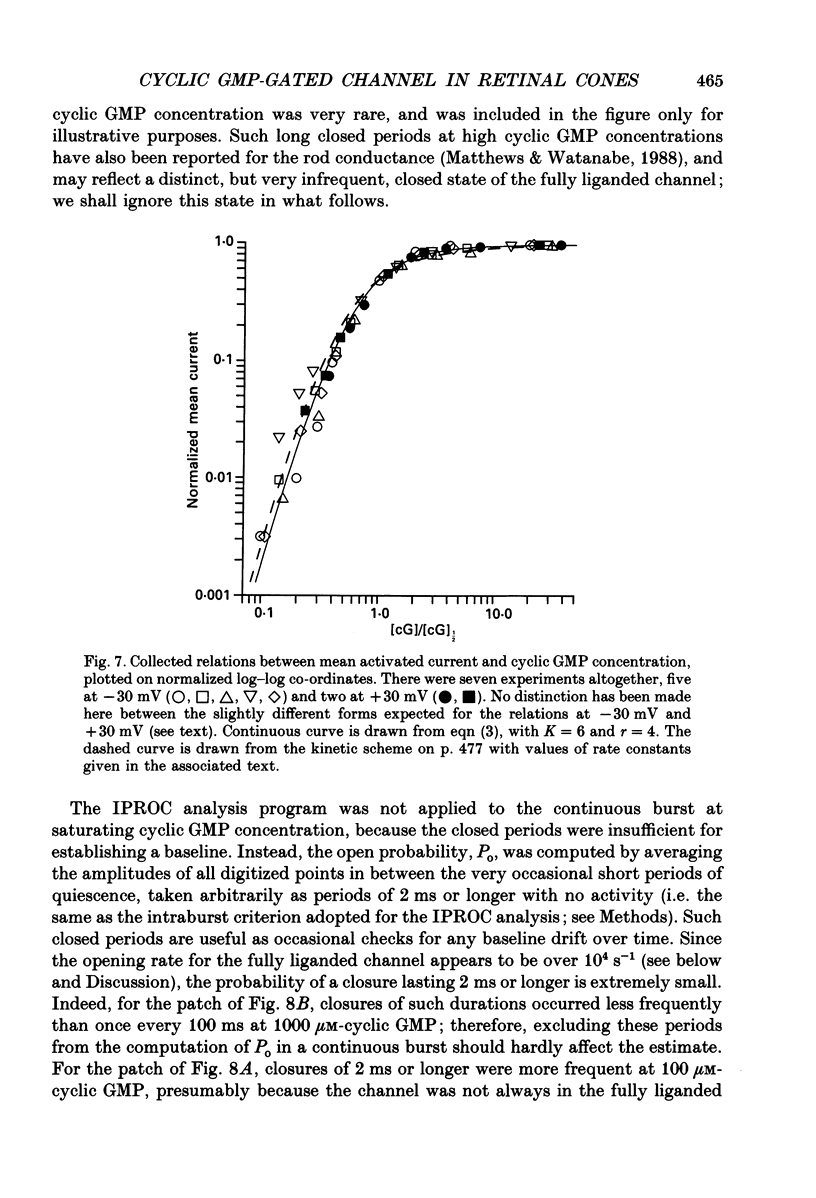
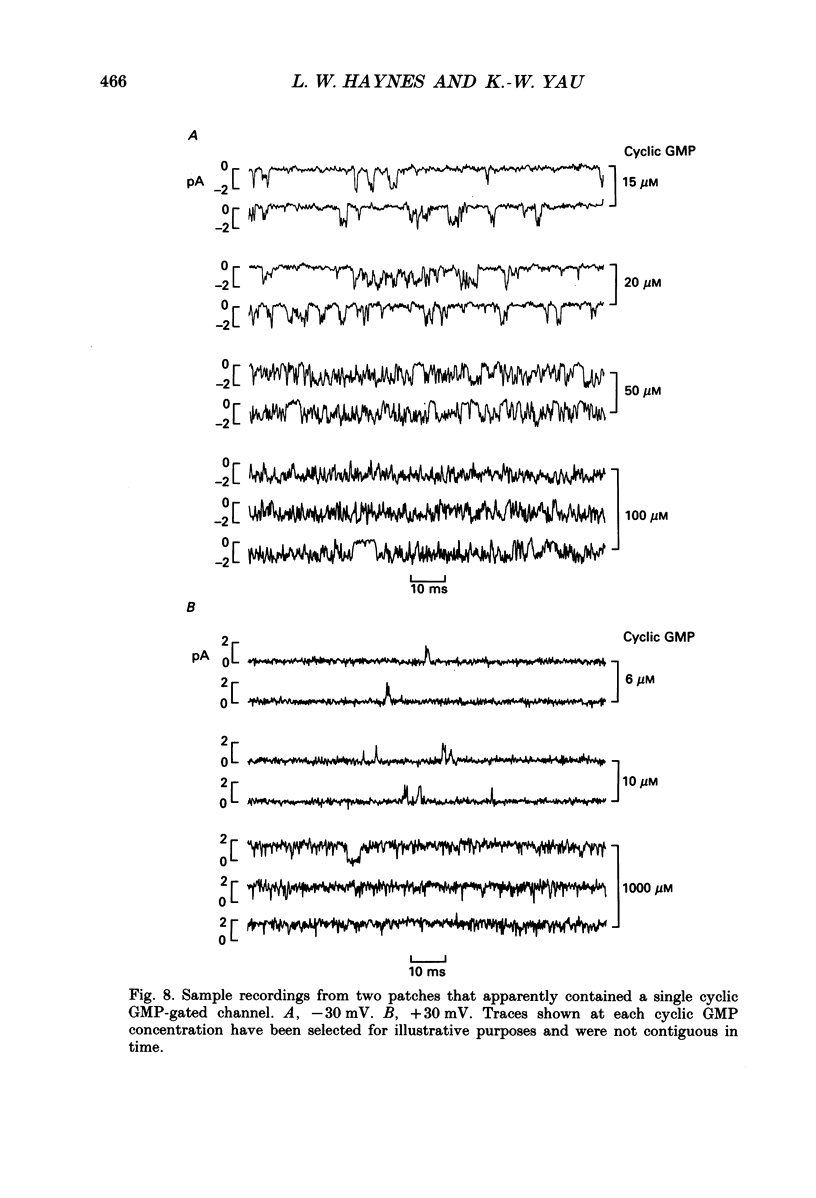


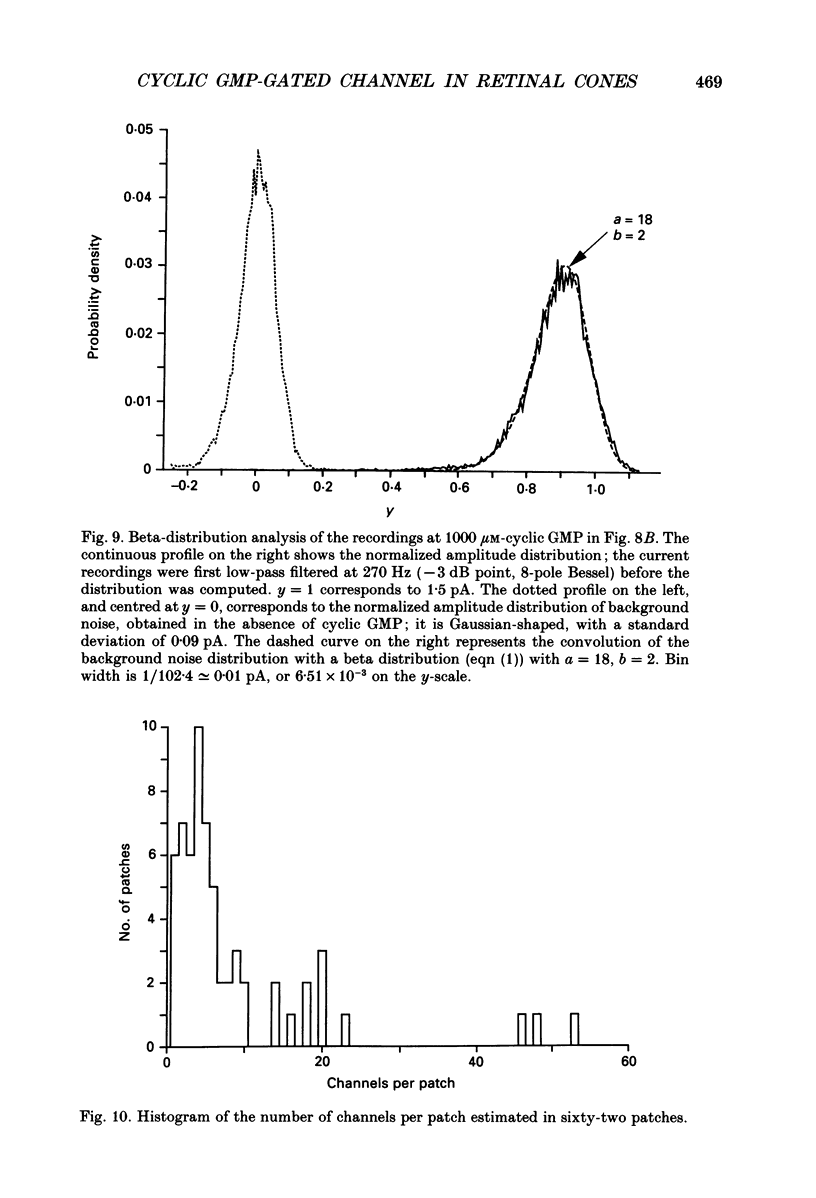


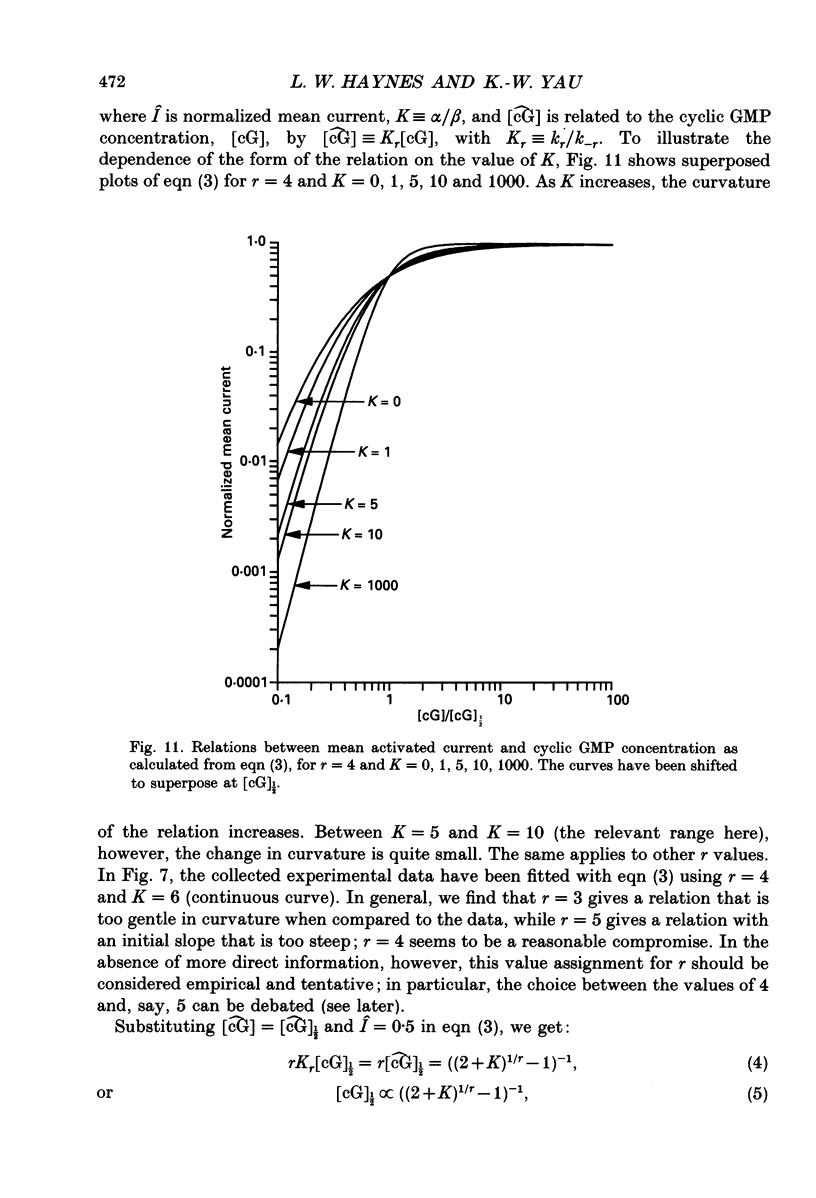

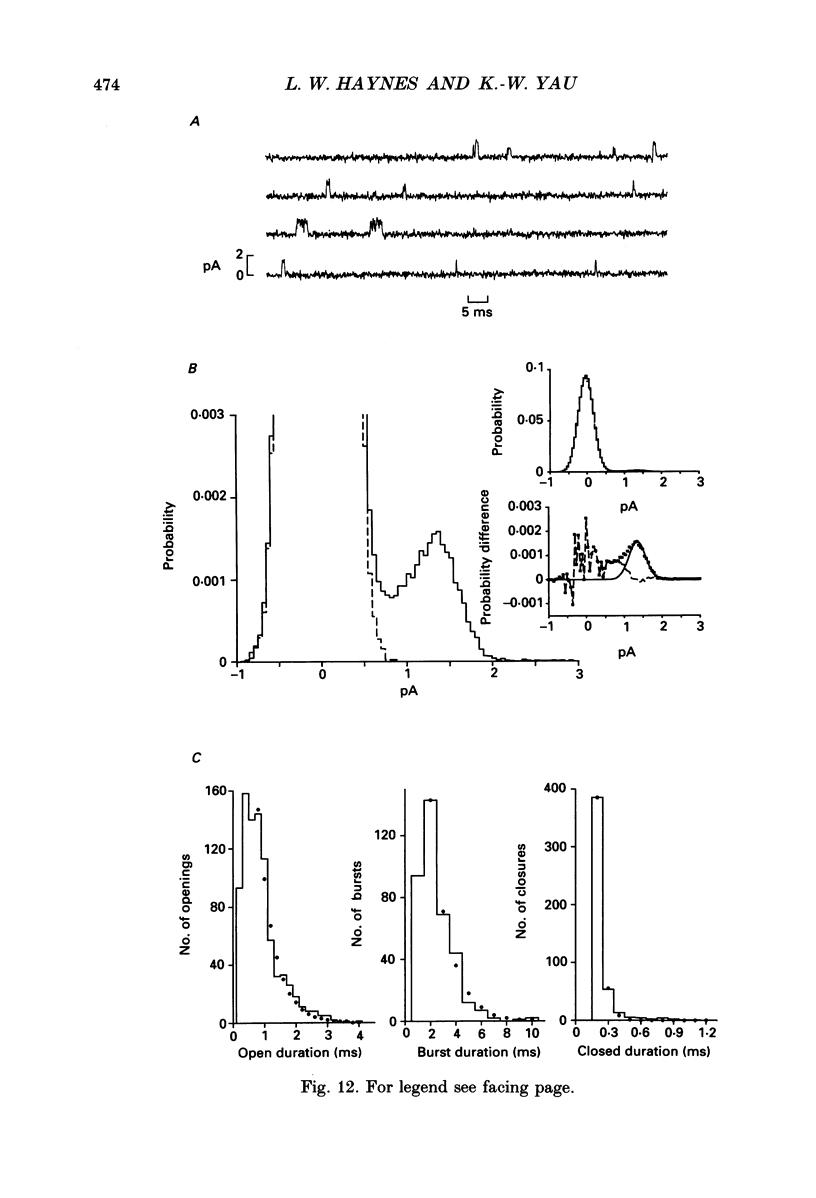

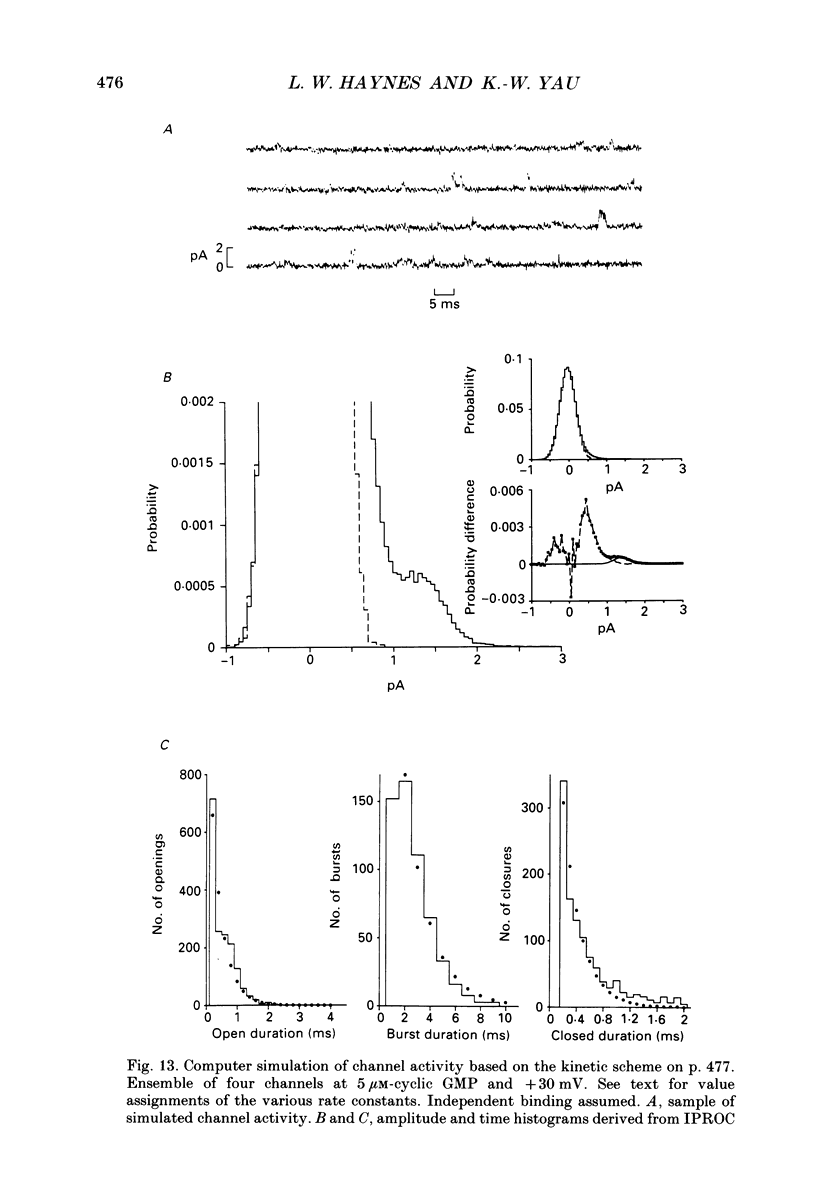





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN P. K., GIBBONS I. R., WALD G. THE VISUAL CELLS AND VISUAL PIGMENT OF THE MUDPUPPY, NECTURUS. J Cell Biol. 1963 Oct;19:79–106. doi: 10.1083/jcb.19.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Macleish P. R., Schwartz E. A. A voltage-clamp study of the light response in solitary rods of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:1–26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Nunn B. J. Electrical properties of the light-sensitive conductance of rods of the salamander Ambystoma tigrinum. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:115–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodoia R. D., Detwiler P. B. Patch-clamp recordings of the light-sensitive dark noise in retinal rods from the lizard and frog. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:183–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbs W. H., Barkdoll A. E., 3rd, Pugh E. N., Jr Cyclic GMP increases photocurrent and light sensitivity of retinal cones. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):64–66. doi: 10.1038/317064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesenko E. E., Kolesnikov S. S., Lyubarsky A. L. Induction by cyclic GMP of cationic conductance in plasma membrane of retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):310–313. doi: 10.1038/313310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P., Attwell D. Kinetics of light-sensitive channels in vertebrate photoreceptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jan 22;223(1232):379–388. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Cook N. J., Kaupp U. B. cGMP-dependent channel protein from photoreceptor membranes: single-channel activity of the purified and reconstituted protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):94–98. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes L. W., Kay A. R., Yau K. W. Single cyclic GMP-activated channel activity in excised patches of rod outer segment membrane. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):66–70. doi: 10.1038/321066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes L., Yau K. W. Cyclic GMP-sensitive conductance in outer segment membrane of catfish cones. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):61–64. doi: 10.1038/317061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B. Dependence of acetylcholine receptor channel kinetics on agonist concentration in cultured mouse muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:555–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen J. W., Zimmerman A. L., Stryer L., Baylor D. A. Gating kinetics of the cyclic-GMP-activated channel of retinal rods: flash photolysis and voltage-jump studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1287–1291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. W., Kaupp U. B. Cyclic GMP directly regulates a cation conductance in membranes of bovine rods by a cooperative mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6788–6800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews G. Comparison of the light-sensitive and cyclic GMP-sensitive conductances of the rod photoreceptor: noise characteristics. J Neurosci. 1986 Sep;6(9):2521–2526. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-09-02521.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews G., Watanabe S. Activation of single ion channels from toad retinal rod inner segments by cyclic GMP: concentration dependence. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:389–405. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews G., Watanabe S. Properties of ion channels closed by light and opened by guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate in toad retinal rods. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:691–715. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani K., Yau K. W. Calcium and magnesium fluxes across the plasma membrane of the toad rod outer segment. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:695–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani K., Yau K. W. Sodium-dependent calcium extrusion and sensitivity regulation in retinal cones of the salamander. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:525–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs F., Neil J., Barkakati N. The automated analysis of data from single ionic channels. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Dec;395(4):331–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00580798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J. C., Eccleston J. F., Furman R. E. Photoreceptor channel activation by nucleotide derivatives. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2776–2784. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Baylor D. A. Cyclic GMP-activated conductance of retinal photoreceptor cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:289–327. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Light-suppressible, cyclic GMP-sensitive conductance in the plasma membrane of a truncated rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):252–255. doi: 10.1038/317252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Ionic permeation and blockade in Ca2+-activated K+ channels of bovine chromaffin cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Aug;84(2):157–186. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman A. L., Baylor D. A. Cyclic GMP-sensitive conductance of retinal rods consists of aqueous pores. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):70–72. doi: 10.1038/321070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman A. L., Yamanaka G., Eckstein F., Baylor D. A., Stryer L. Interaction of hydrolysis-resistant analogs of cyclic GMP with the phosphodiesterase and light-sensitive channel of retinal rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8813–8817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


