Abstract
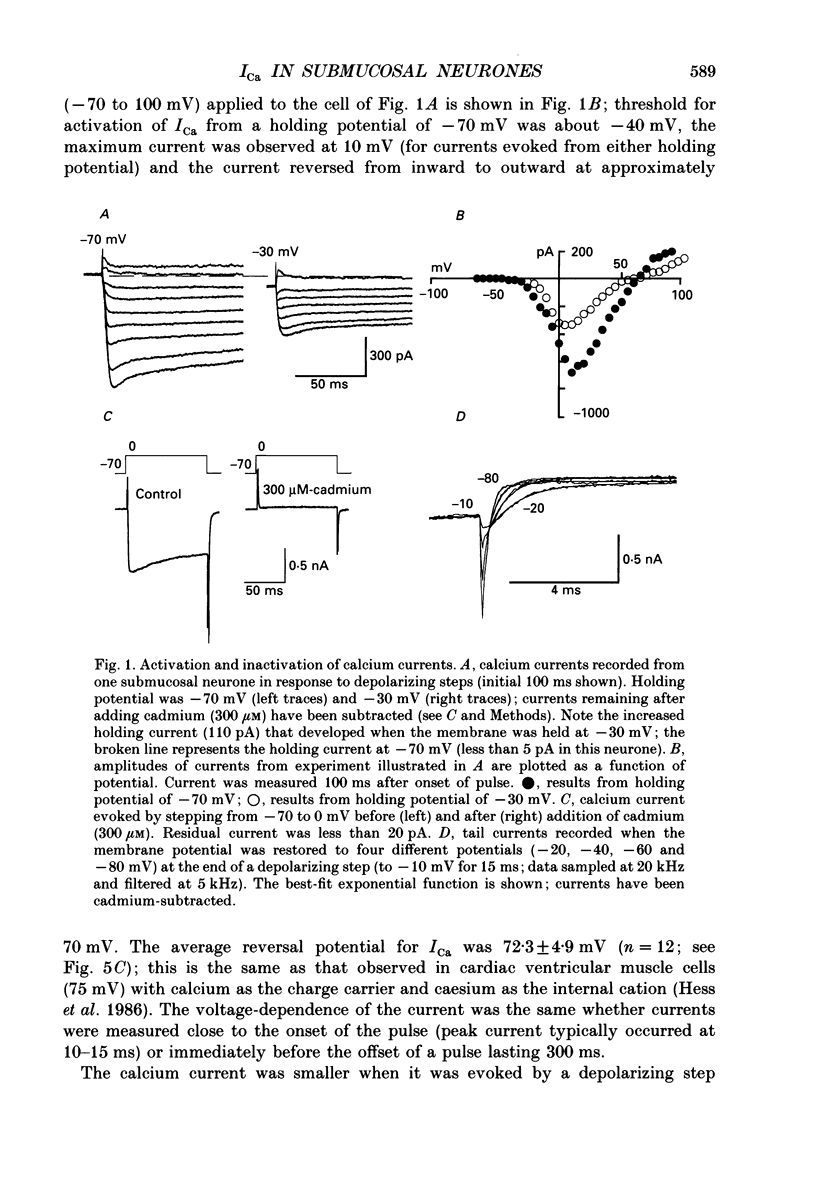
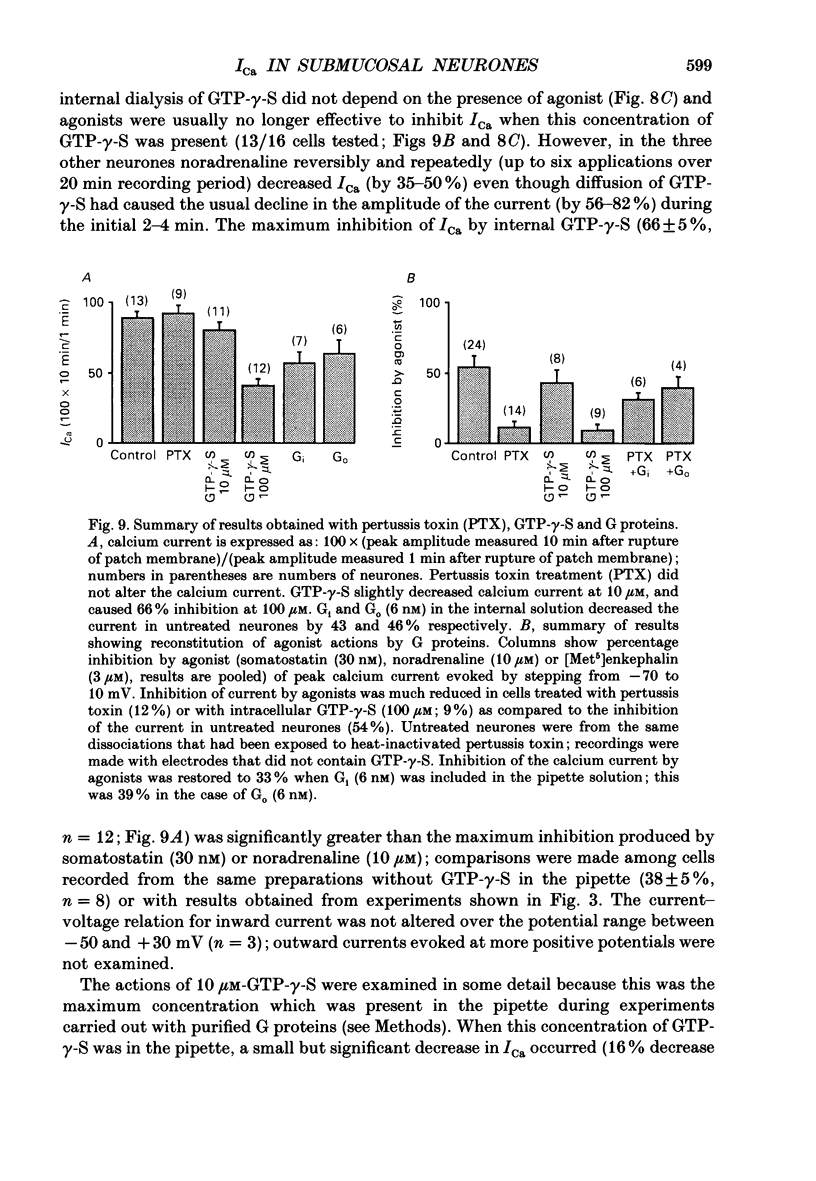
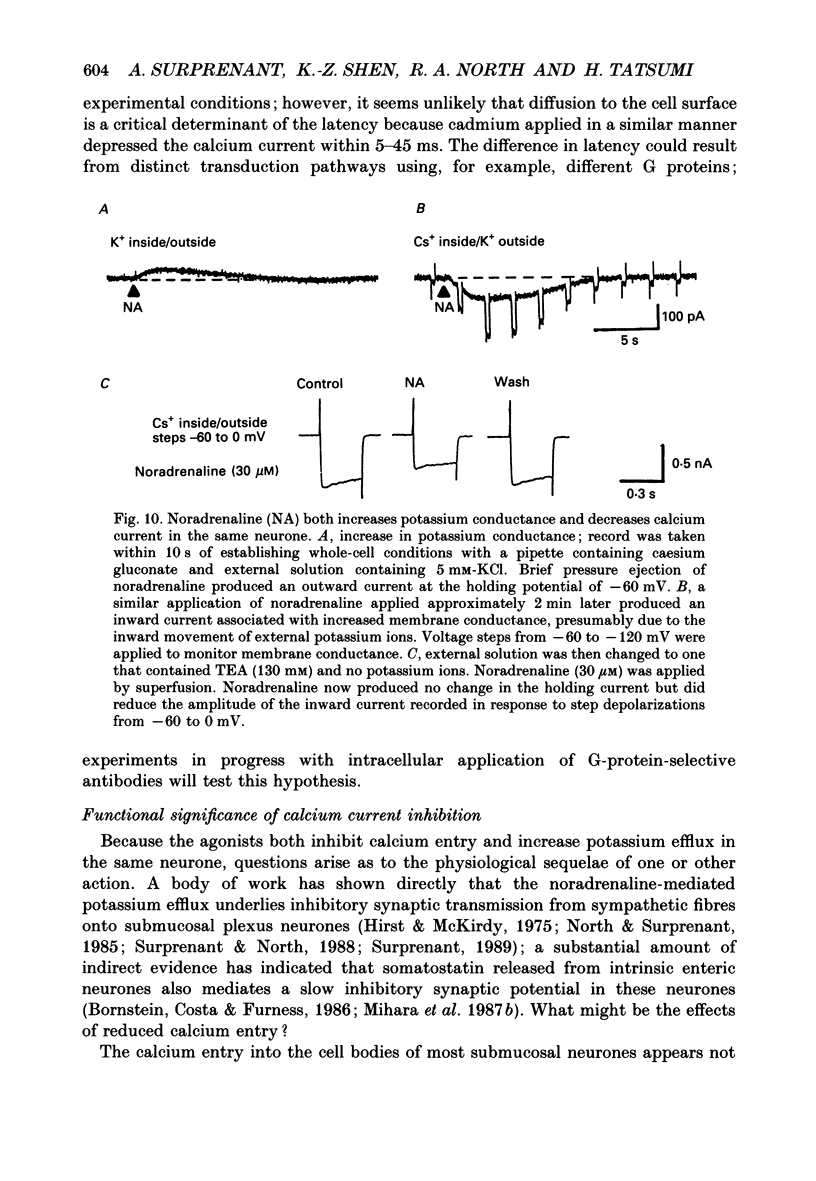
1. Whole-cell recordings were made from submucosal neurones acutely dissociated from guinea-pigs. The actions of noradrenaline, somatostatin and [Met5]enkephalin on currents carried by calcium ions were studied. 2. On depolarization from a holding potential of -70 mV, an inward current activated at -40 mV, reached its peak amplitude at 10 mV and reversed to outward at 72 mV (with external calcium of 5 mM and internal caesium of 160 mM). 3. Cadmium, nickel and cobalt reversibly blocked the calcium current; concentrations causing 50% block were 2.5, 500 and 2000 microM respectively. The calcium current (holding at -70 or -30 mV) was reversibly blocked by omega-conotoxin (100 nM), and unaffected by Bay K 8644 (0.1-10 microM) and nifedipine (1 microM). Cadmium caused an outward shift in holding current at -30 mV, implying that there was a persistent inward calcium current at this potential. 4. Noradrenaline, somatostatin and [Met5]enkephalin decreased the calcium current. The maximal inhibition observed with any one agonist, or with a combination of two agonists, did not exceed 50%; concentrations giving half-maximal inhibition were 5.5 microM for noradrenaline, 4 nM for somatostatin and 1 microM for [Met5]enkephalin. The inhibition was independent of membrane potential. All three agonists also reduced the persistent calcium current at -30 mV. 5. Inhibition of the calcium current by noradrenaline occurred with a latency of not less than 175 ms; cadmium applied by the same method depressed the current within 5-45 ms. 6. Experiments with selective agonists and antagonists indicated that the receptor types involved in calcium current inhibition were alpha 2-adrenoceptors and delta-opioid receptors. Somatostatin acted at a distinct receptor. 7. Calcium currents were also inhibited by intracellular dialysis with guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) (GTP-gamma-S). Agonists were ineffective in cells pre-treated with pertussis toxin, but their action was restored when purified GTP-binding proteins (Go or Gi) were included in the intracellular recording solution. 8. It is concluded that noradrenaline, somatostatin and [Met5]enkephalin act at their respective receptors on guinea-pig submucosal neurones to inhibit a voltage-dependent calcium current. Activation of the same receptors also increases a potassium conductance in these cells: in both cases a pertussis-sensitive G protein is involved.
Full text
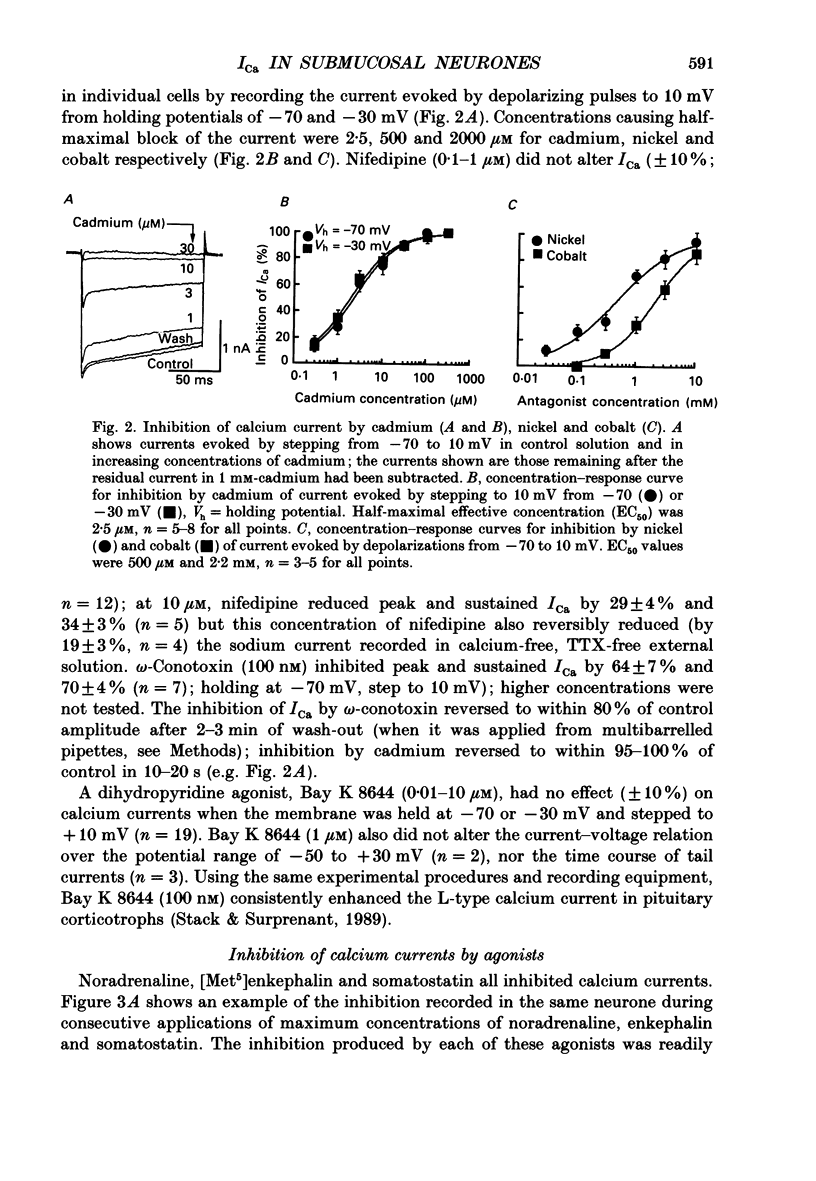
PDF




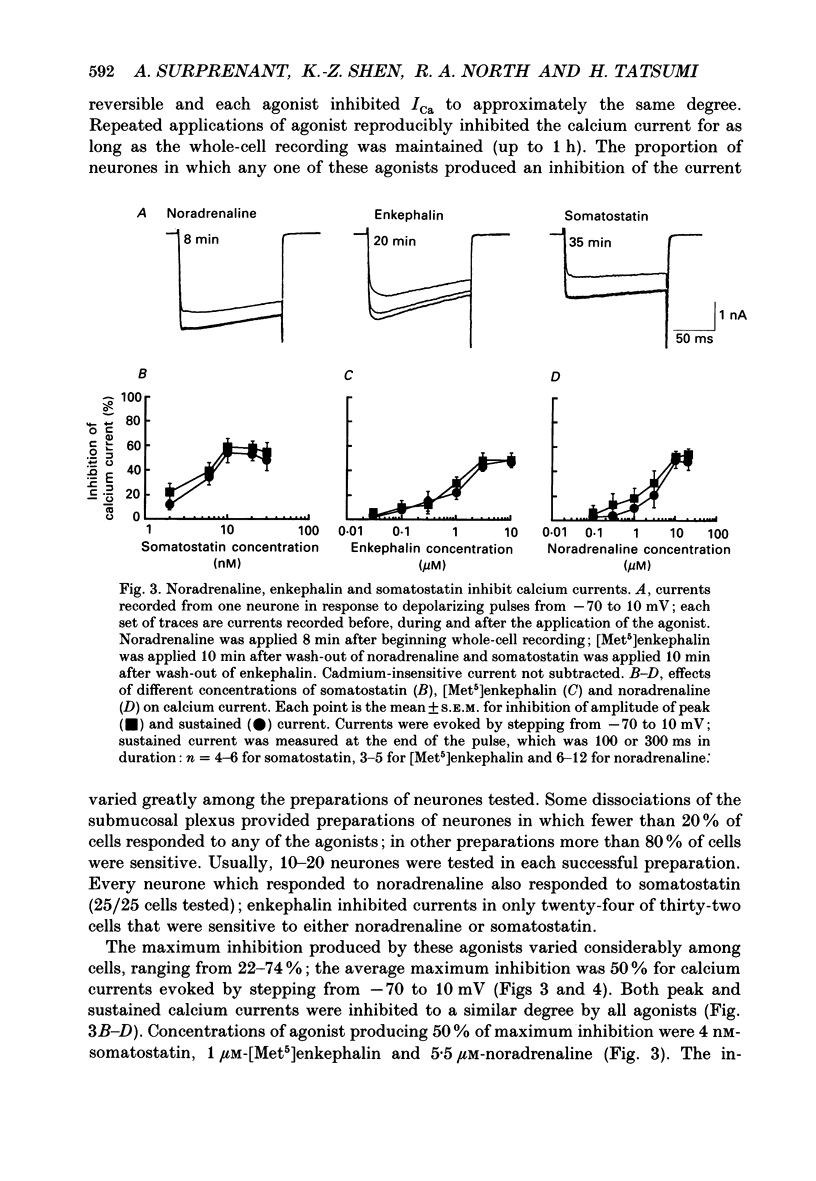
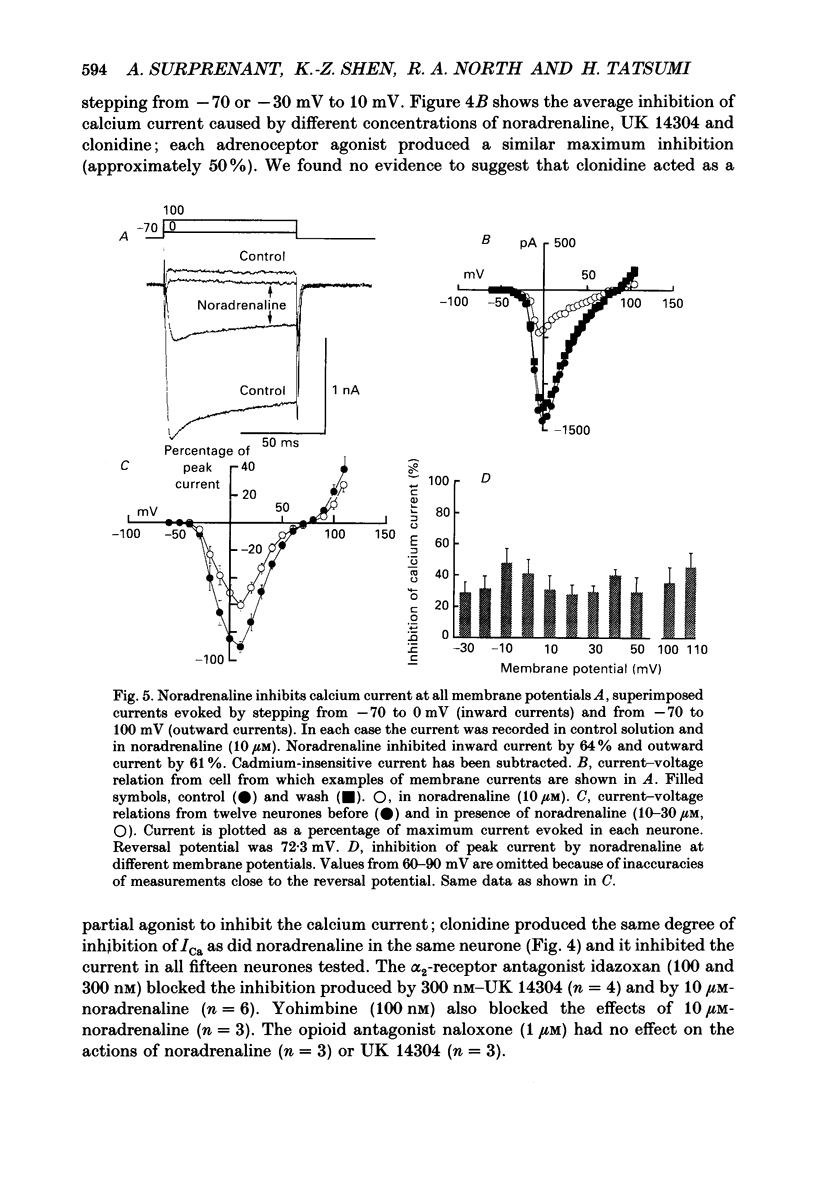

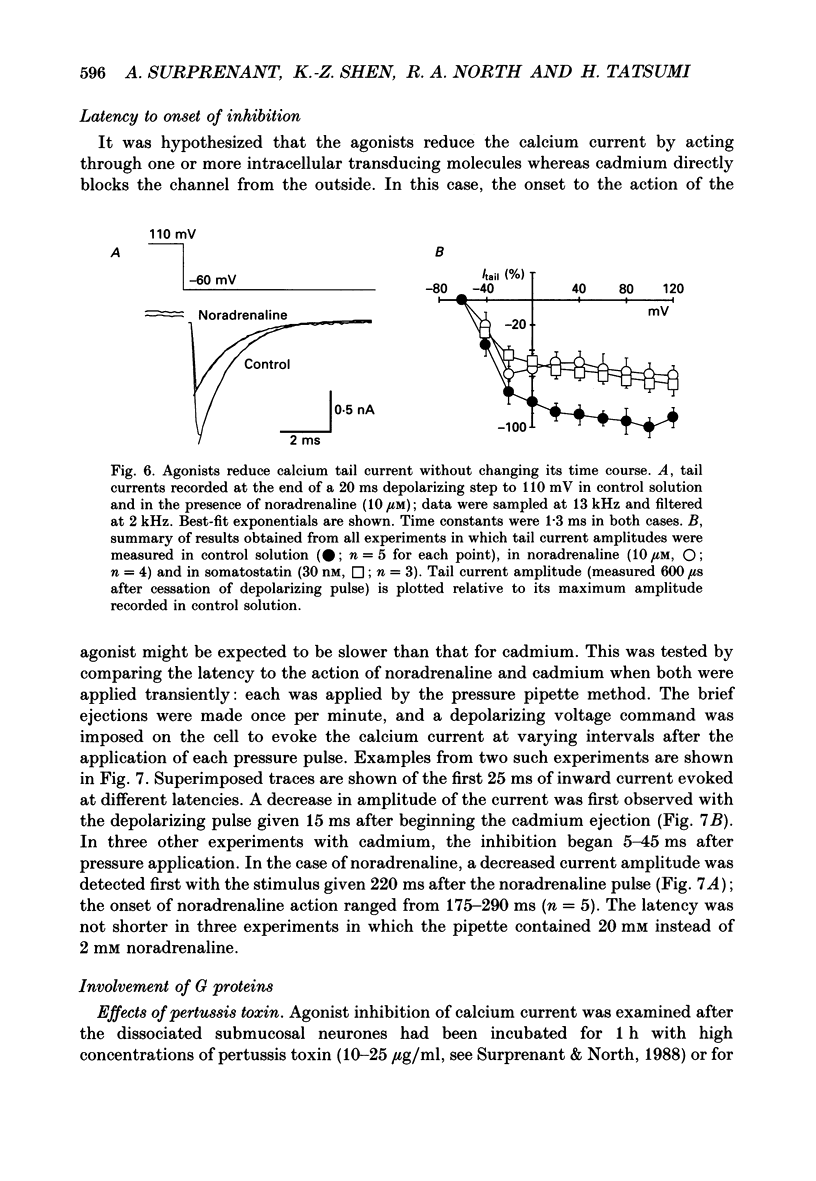
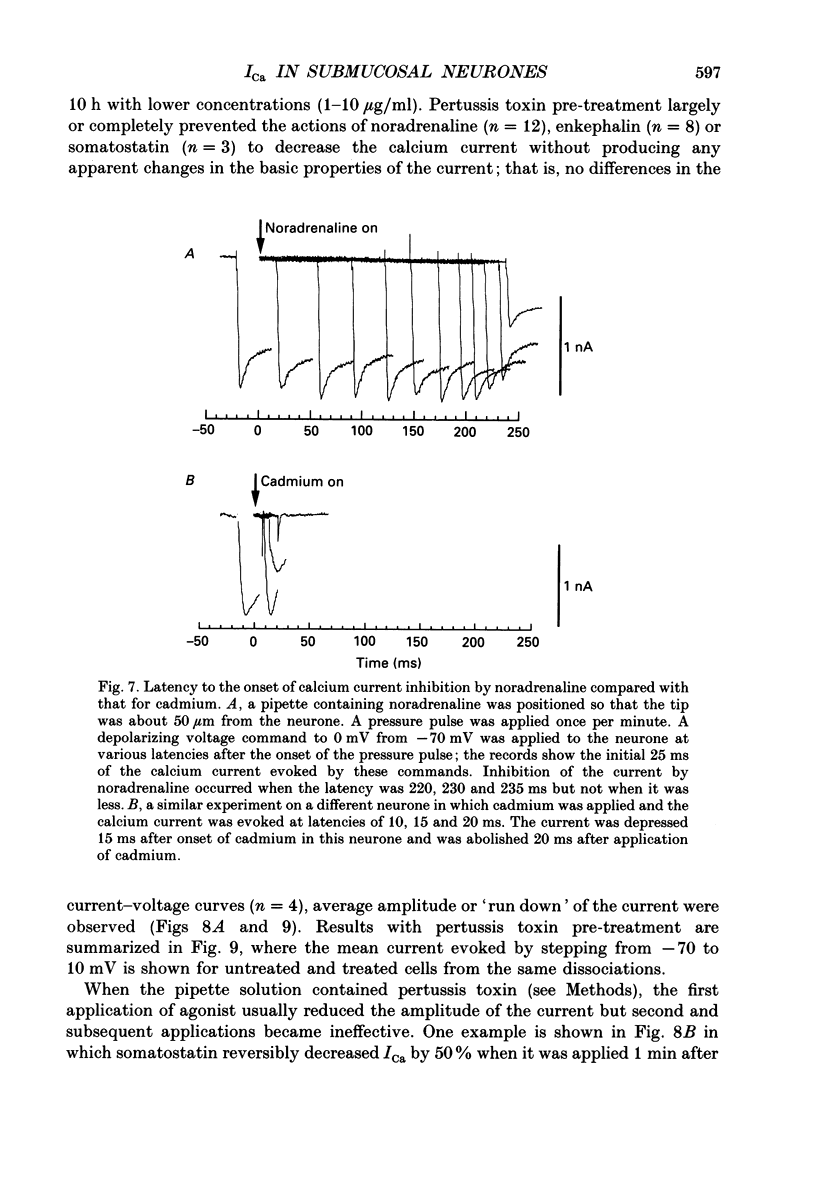
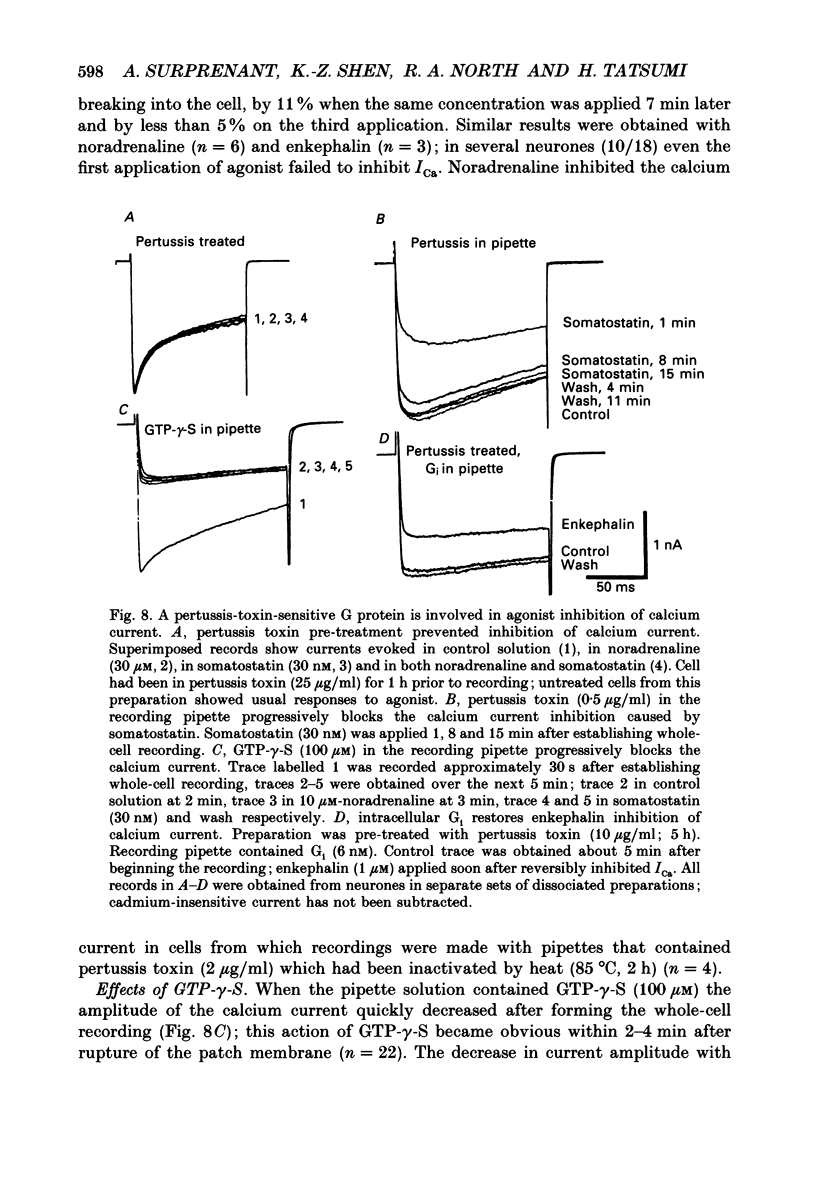








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
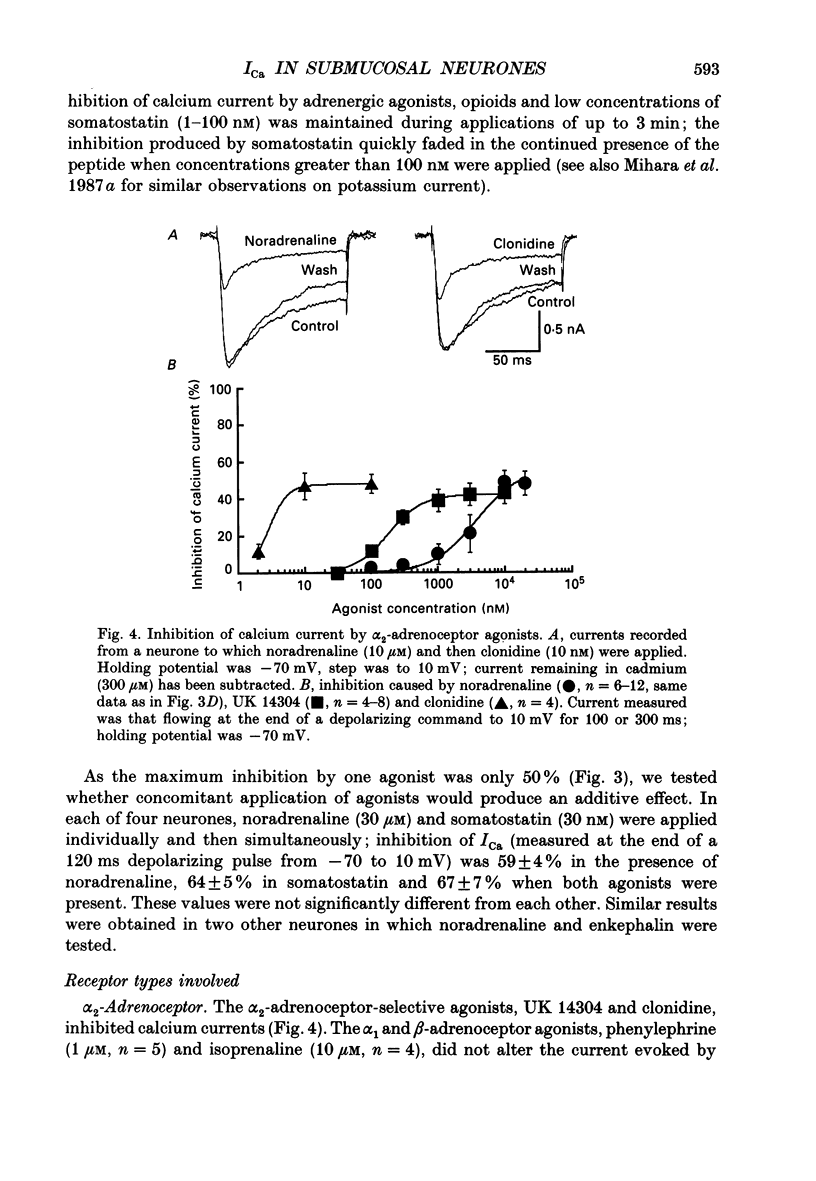
- Akasu T., Tokimasa T. Potassium currents in submucous neurones of guinea-pig caecum and their synaptic modification. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:571–588. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):153–156. doi: 10.1038/340153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belluzzi O., Sacchi O. Calcium currents in the normal adult rat sympathetic neurone. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:493–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein J. C., Costa M., Furness J. B. Synaptic inputs to immunohistochemically identified neurones in the submucous plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:465–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Docherty R. J., McFadzean I. Calcium channels in vertebrate neurons. Experiments on a neuroblastoma hybrid model. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;560:358–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptors: pharmacological and molecular biological evidence converge. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Oct;9(10):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield D. R., Dunlap K. Pharmacological characterization of amine receptors on embryonic chick sensory neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;82(3):557–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10794.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Regan J. W., Nakata H., Codina J., Benovic J. L., Gierschik P., Somers R. L., Spiegel A. M., Birnbaumer L., Lefkowitz R. J. Functional reconstitution of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3901–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkach V., Surprenant A., North R. A. 5-HT3 receptors are membrane ion channels. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):706–709. doi: 10.1038/339706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty R. J., McFadzean I. Noradrenaline-Induced Inhibition of Voltage-Sensitive Calcium Currents in NG108-15 Hybrid Cells. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 Mar;1(2):132–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K., Fischbach G. D. Neurotransmitters decrease the calcium conductance activated by depolarization of embryonic chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:519–535. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewald D. A., Pang I. H., Sternweis P. C., Miller R. J. Differential G protein-mediated coupling of neurotransmitter receptors to Ca2+ channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons in vitro. Neuron. 1989 Feb;2(2):1185–1193. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvan M., Adams P. R. Control of calcium current in rat sympathetic neurons by norepinephrine. Brain Res. 1982 Jul 22;244(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90911-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafe P., Mayer C. J., Wood J. D. Synaptic modulation of calcium-dependent potassium conductance in myenteric neurones in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:235–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., Macdonald R. L. Dynorphin A selectively reduces a large transient (N-type) calcium current of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R. Somatostatin inhibits the release of acetylcholine induced electrically in the myenteric plexus. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1653–1654. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirning L. D., Fox A. P., McCleskey E. W., Olivera B. M., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J., Tsien R. W. Dominant role of N-type Ca2+ channels in evoked release of norepinephrine from sympathetic neurons. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):57–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2447647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Johnson S. M., van Helden D. F. The calcium current in a myenteric neurone of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:297–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Johnson S. M., van Helden D. F. The slow calcium-dependent potassium current in a myenteric neurone of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:315–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McKirdy H. C. Synaptic potentials recorded from neurones of the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):369–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Marks T. N. Calcium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. I. Activation kinetics and pharmacology. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):151–167. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Marks T. N. Calcium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. II. Inactivation. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):169–182. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. Reversal of current through calcium channels in dialysed single heart cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):498–501. doi: 10.1038/297498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie F. M. Methods used for the study of opioid receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Sep;39(3):197–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Kongsamut S., Tsien R. W. Alpha-adrenergic inhibition of sympathetic neurotransmitter release mediated by modulation of N-type calcium-channel gating. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):639–642. doi: 10.1038/340639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Werz M. A. Dynorphin A decreases voltage-dependent calcium conductance of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:237–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti C., Carbone E., Lux H. D. Effects of dopamine and noradrenaline on Ca channels of cultured sensory and sympathetic neurons of chick. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Feb;406(2):104–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00586670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadzean I., Mullaney I., Brown D. A., Milligan G. Antibodies to the GTP binding protein, Go, antagonize noradrenaline-induced calcium current inhibition in NG108-15 hybrid cells. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., Nishi S., North R. A., Surprenant A. A non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic slow inhibitory post-synaptic potential in neurones of the guinea-pig submucous plexus. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:357–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., North R. A. Opioids increase potassium conductance in submucous neurones of guinea-pig caecum by activating delta-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;88(2):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., North R. A., Surprenant A. Somatostatin increases an inwardly rectifying potassium conductance in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:335–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Simonds W. F., Streaty R. A., Tocque B., Klee W. A. Functional control of the delta-opiate receptor by the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Biochem Soc Trans. 1985 Dec;13(6):1110–1113. doi: 10.1042/bst0131110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A. Clonidine activates membrane potassium conductance in myenteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct;74(2):419–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Surprenant A. Inhibitory synaptic potentials resulting from alpha 2-adrenoceptor activation in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:17–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Persistent calcium-sensitive potassium current and the resting properties of guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:333–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Twelfth Gaddum memorial lecture. Drug receptors and the inhibition of nerve cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;98(1):13–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb16855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Vizi E. S. The inhibitory action of noradrenaline and adrenaline on acetylcholine output by guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle strip. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):10–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAUMANN W. Zusammenhänge zwischen der Wirkung der Analgetica und Sympathicomimetica auf den Meerschweinchen-Dunndarm. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1958;233(1):112–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sah D. W. Neurotransmitter modulation of calcium current in rat spinal cord neurons. J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;10(1):136–141. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-01-00136.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield G. G., Ikeda S. R. Sodium and calcium currents of acutely isolated adult rat superior cervical ganglion neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1988 May;411(5):481–490. doi: 10.1007/BF00582368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., Surprenant A. Mechanisms underlying presynaptic inhibition through alpha 2-adrenoceptors in guinea-pig submucosal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:609–628. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., North R. A. Mechanism of synaptic inhibition by noradrenaline acting at alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jun 22;234(1274):85–114. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. Two types of neurones lacking synaptic input in the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:363–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi H., Costa M., Schimerlik M., North R. A. Potassium conductance increased by noradrenaline, opioids, somatostatin, and G-proteins: whole-cell recording from guinea pig submucous neurons. J Neurosci. 1990 May;10(5):1675–1682. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-05-01675.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tota M. R., Kahler K. R., Schimerlik M. I. Reconstitution of the purified porcine atrial muscarinic acetylcholine receptor with purified porcine atrial inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8175–8182. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Bley K. R., Fox A. P. Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


