Abstract
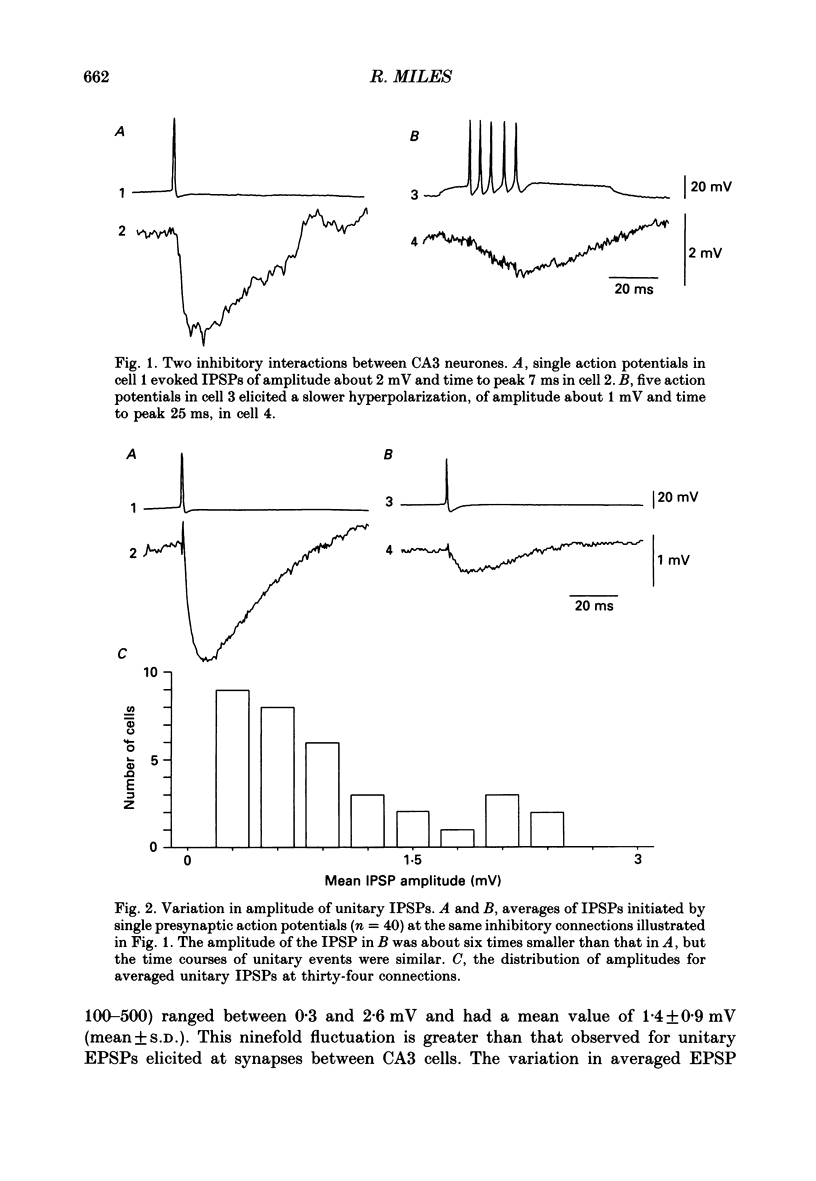
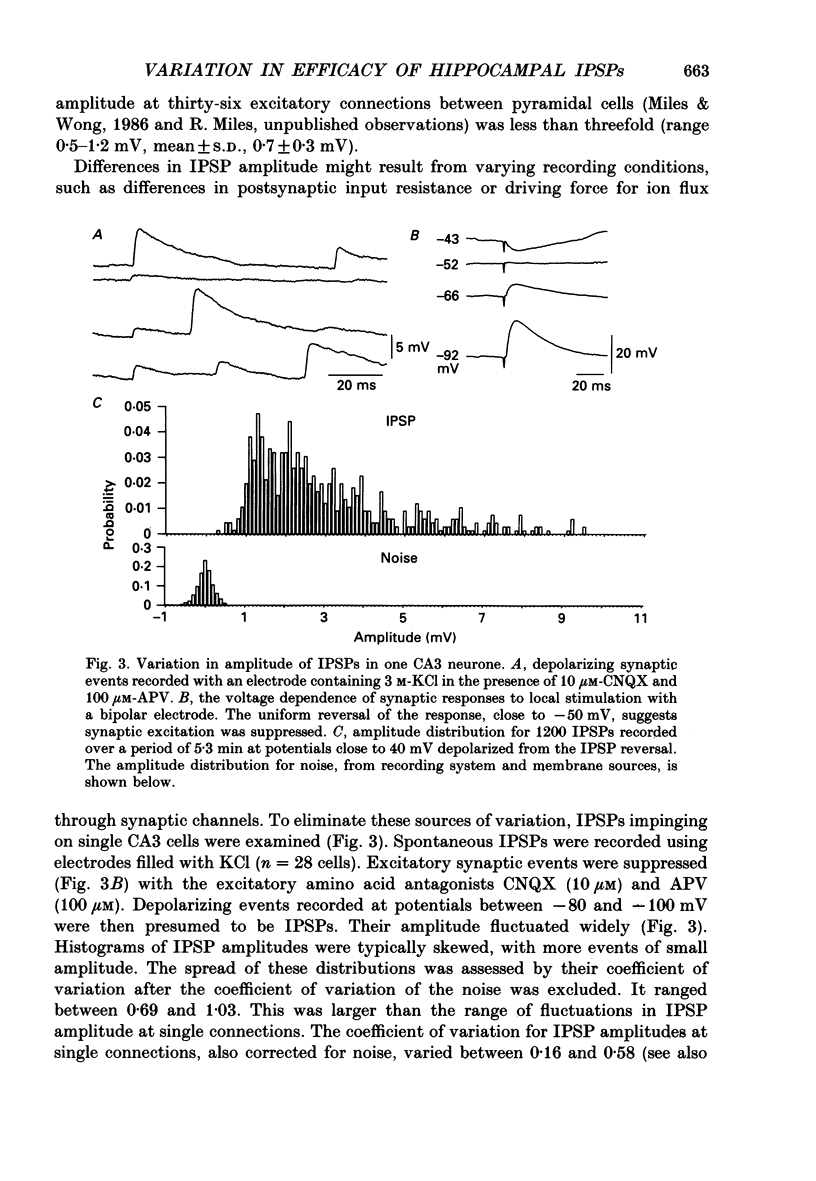
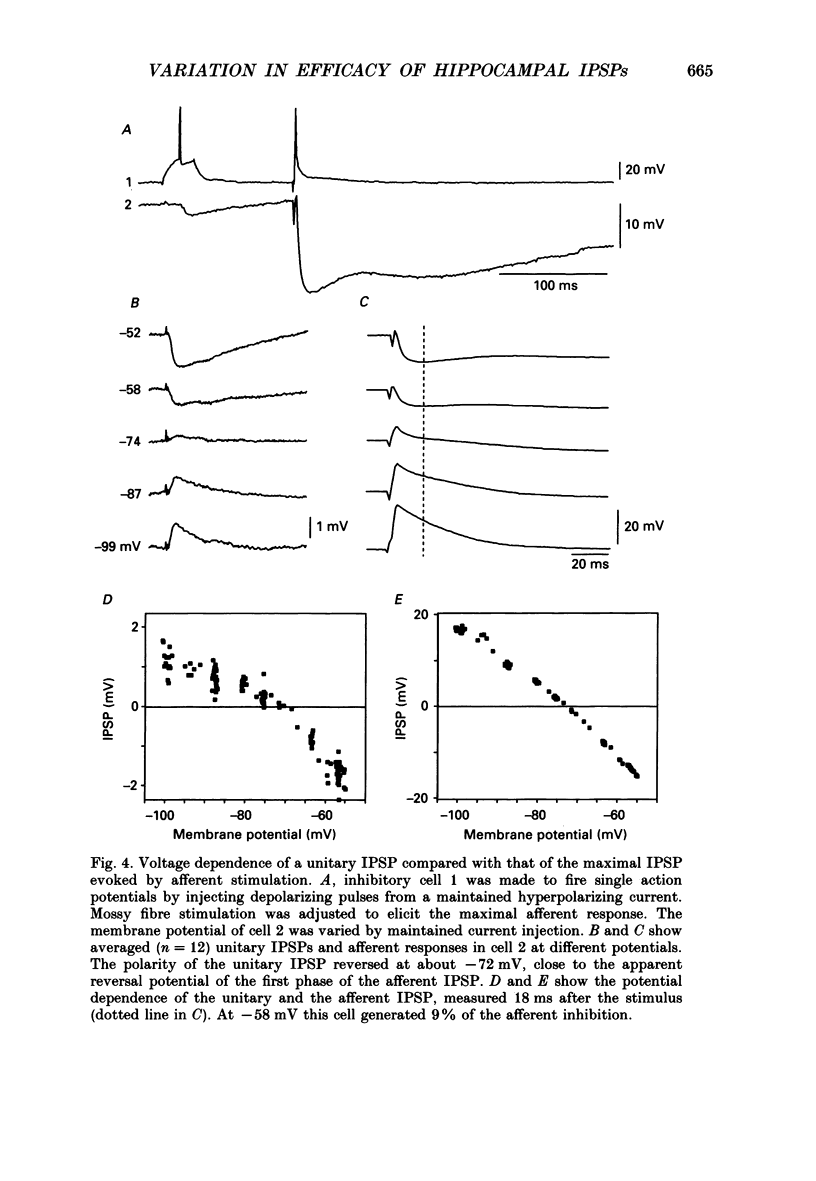
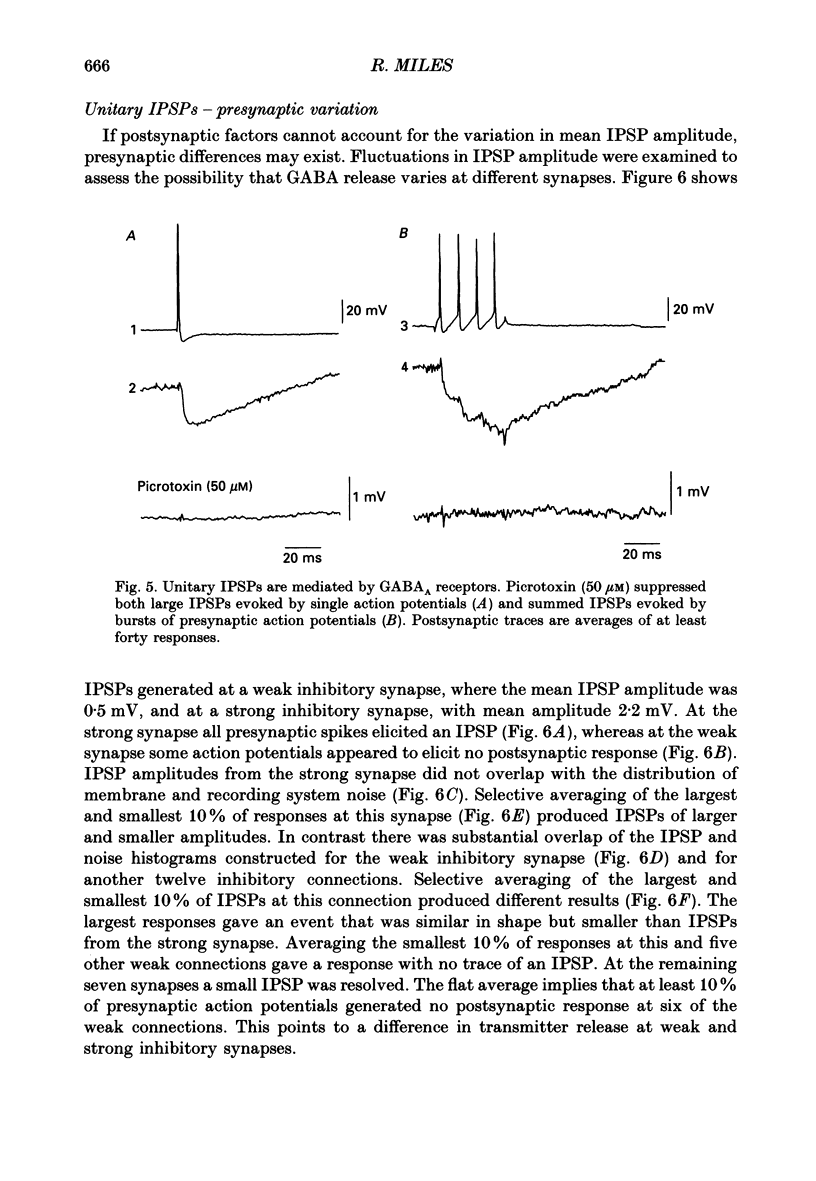
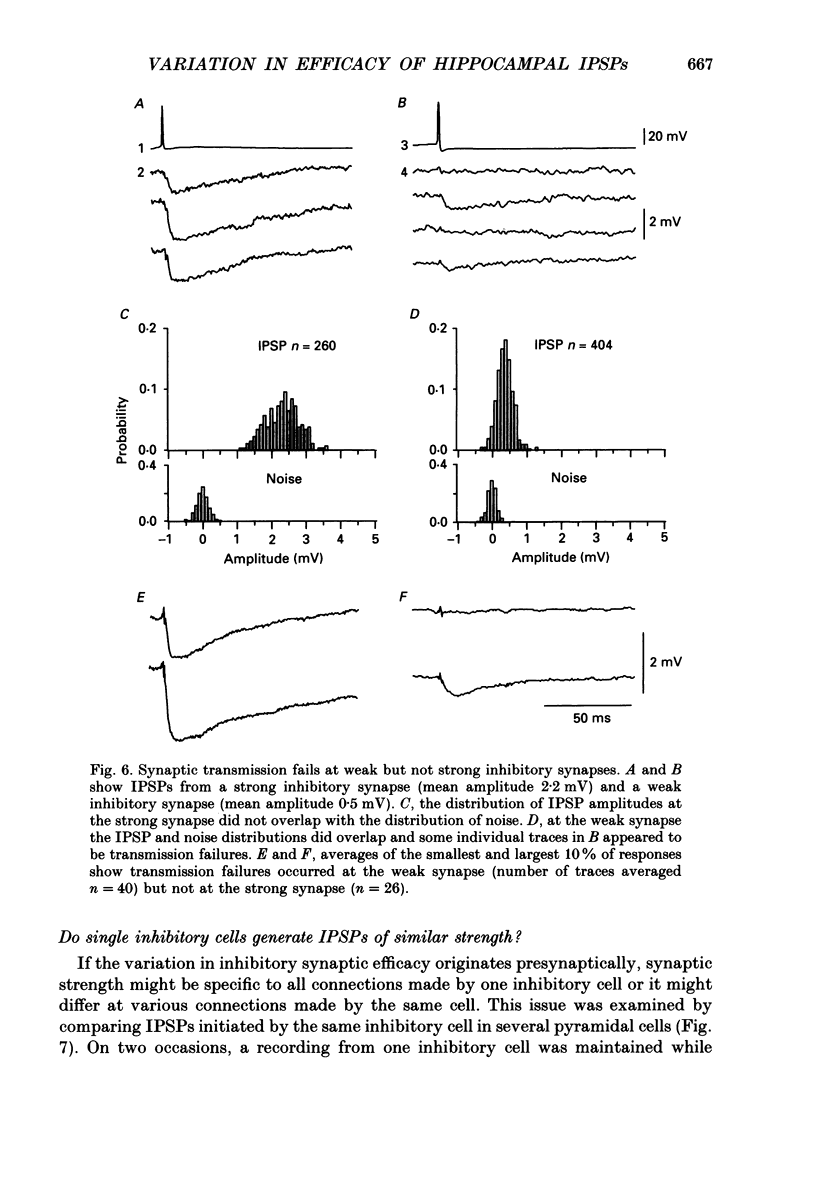
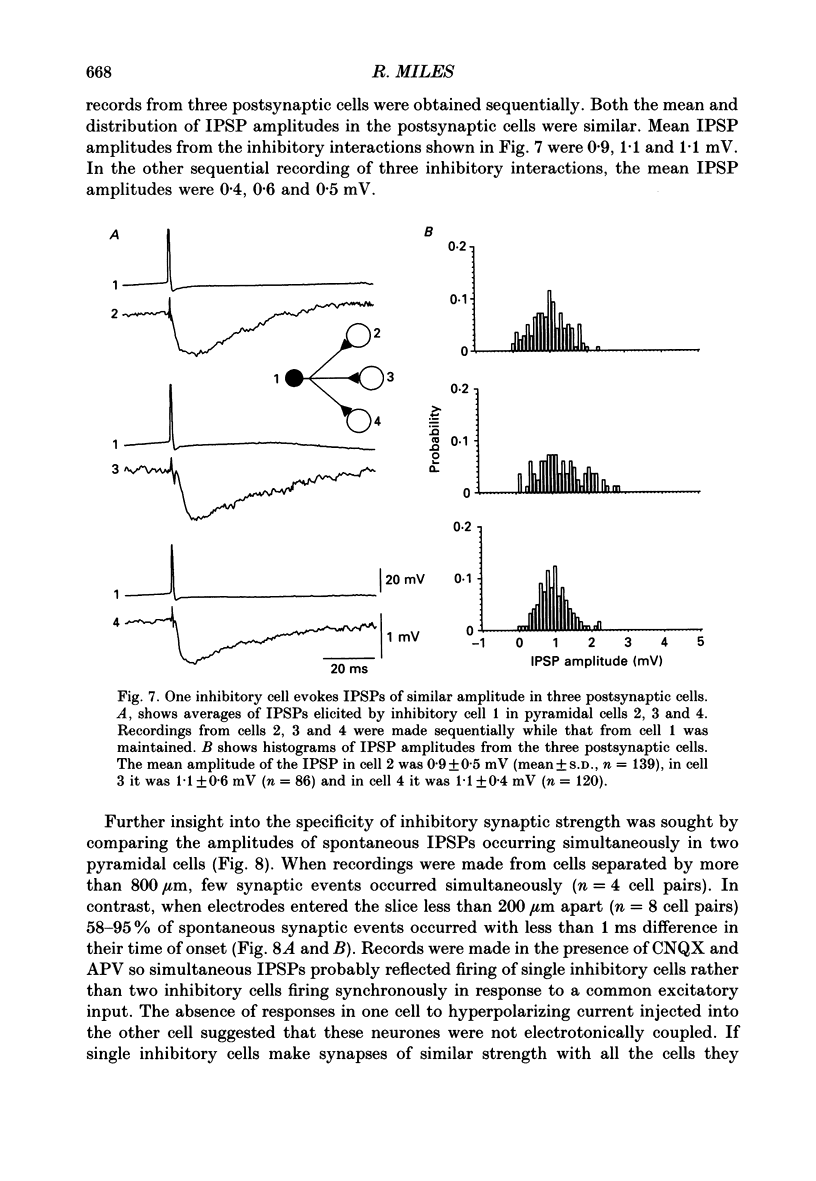
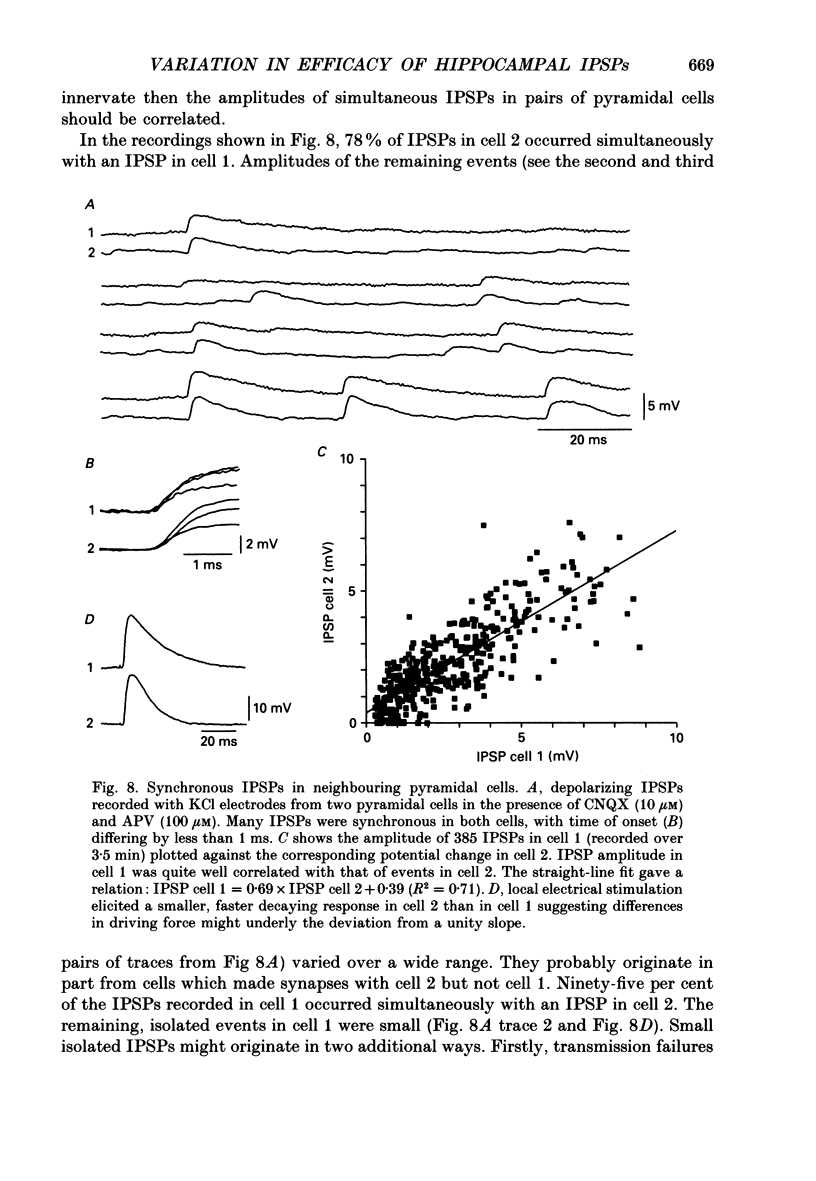
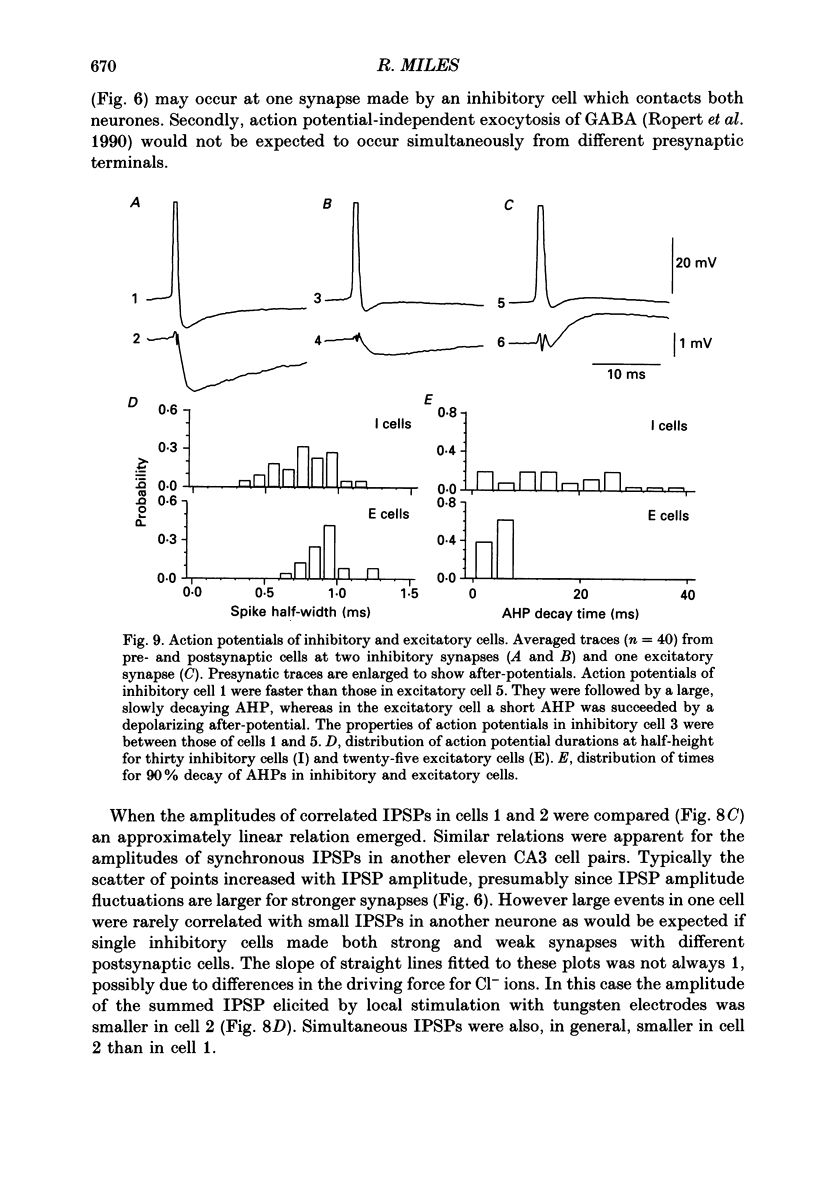
1. Simultaneous recordings were made from inhibitory cells located close to the stratum pyramidale and from pyramidal cells in the CA3 region of guinea-pig hippocampal slices, to examine inhibitory synaptic interactions. 2. The average amplitude of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) initiated by single action potentials at different synapses varied between 0.3 and 2.6 mV. Experiments were performed to investigate the source of this variation. 3. Unitary IPSPs reversed at similar potentials to the first phase of the synaptic inhibition elicited by afferent fibre stimulation. IPSPs evoked by single action potentials or repetitive inhibitory cell firing were suppressed by picrotoxin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptor antagonists. 4. The time to peak and amplitude of averaged IPSPs were not related as predicted if amplitude variations resulted simply from different electrotonic locations of inhibitory terminals. 5. Transmission failures could be resolved at connections which generated small averaged IPSPs, but were not apparent at connections where averaged IPSPs were large. 6. IPSPs elicited by the same inhibitory cell in several pyramidal cells were of similar amplitude. The amplitudes of simultaneous IPSPs impinging on pairs of neighboring pyramidal cells were positively correlated. 7. Thus, the variation in efficacy of inhibitory synapses may result from differences in transmitter release from different inhibitory cells and not from postsynaptic factors.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bittner G. D. Differentiation of nerve terminals in the crayfish opener muscle and its functional significance. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Jun;51(6):731–758. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.6.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamann H. P., Henneman E., Lüscher H. R., Mathis J. Structural and topographical influences on functional connectivity in spinal monosynaptic reflex arcs in the cat. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:483–507. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Gage P. W., Robertson B. Inhibitory post-synaptic currents in rat hippocampal CA1 neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:551–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A. GABA, bicuculline and central inhibition. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1222–1224. doi: 10.1038/2261222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Roberts A. Dual-component amino-acid-mediated synaptic potentials: excitatory drive for swimming in Xenopus embryos. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:35–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Nicoll R. A. A physiological role for GABAB receptors in the central nervous system. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):156–158. doi: 10.1038/332156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Konnerth A., Sakmann B., Takahashi T. A thin slice preparation for patch clamp recordings from neurones of the mammalian central nervous system. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Sep;414(5):600–612. doi: 10.1007/BF00580998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. Variations in amplitude and time course of inhibitory postsynaptic currents. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Nov;56(5):1424–1438. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.56.5.1424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getting P. A. Mechanisms of pattern generation underlying swimming in Tritonia. I. Neuronal network formed by monosynaptic connections. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jul;46(1):65–79. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell A. D., Herrera A. A. Physiological regulation of synaptic effectiveness at frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:301–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Bormann J., Sakmann B. Activation of multiple-conductance state chloride channels in spinal neurones by glycine and GABA. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):805–808. doi: 10.1038/305805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Roberts W. J. Synaptic actions of single interneurones mediating reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):623–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsumaru H., Kosaka T., Heizmann C. W., Hama K. Immunocytochemical study of GABAergic neurons containing the calcium-binding protein parvalbumin in the rat hippocampus. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72(2):347–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00250256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi Y., Hama K. Physiological heterogeneity of nonpyramidal cells in rat hippocampal CA1 region. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72(3):494–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00250594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe J. The physiological role of three acetylcholine receptors in synaptic transmission in Aplysia. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;225(1):147–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisvarday Z. F., Martin K. A., Friedlander M. J., Somogyi P. Evidence for interlaminar inhibitory circuits in the striate cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jun 1;260(1):1–19. doi: 10.1002/cne.902600102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisvárday Z. F., Martin K. A., Whitteridge D., Somogyi P. Synaptic connections of intracellularly filled clutch cells: a type of small basket cell in the visual cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Nov 8;241(2):111–137. doi: 10.1002/cne.902410202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles W. D., Schwartzkroin P. A. Local circuit synaptic interactions in hippocampal brain slices. J Neurosci. 1981 Mar;1(3):318–322. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-03-00318.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Faber D. S. Transmission at a central inhibitory synapse. IV. Quantal structure of synaptic noise. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jan;63(1):198–222. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.1.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Faber D. S., Triller A. Probabilistic determination of synaptic strength. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Feb;55(2):402–421. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.2.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T., Kosaka K., Tateishi K., Hamaoka Y., Yanaihara N., Wu J. Y., Hama K. GABAergic neurons containing CCK-8-like and/or VIP-like immunoreactivities in the rat hippocampus and dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Sep 22;239(4):420–430. doi: 10.1002/cne.902390408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C., Chan-Palay V. Somatostatin-like immunoreactive neurons in the hippocampus: an immunocytochemical study in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Dec 31;34(3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacaille J. C., Schwartzkroin P. A. Stratum lacunosum-moleculare interneurons of hippocampal CA1 region. II. Intrasomatic and intradendritic recordings of local circuit synaptic interactions. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1411–1424. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01411.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: location, density, and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):171–187. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R. Synaptic excitation of inhibitory cells by single CA3 hippocampal pyramidal cells of the guinea-pig in vitro. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:61–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Wong R. K. Excitatory synaptic interactions between CA3 neurones in the guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:397–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Wong R. K. Unitary inhibitory synaptic potentials in the guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:97–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misgeld U., Frotscher M. Postsynaptic-GABAergic inhibition of non-pyramidal neurons in the guinea-pig hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):193–206. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. Comparison of the action of baclofen with gamma-aminobutyric acid on rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:161–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Distinguishing theoretical synaptic potentials computed for different soma-dendritic distributions of synaptic input. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1138–1168. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribak C. E., Vaughn J. E., Saito K. Immunocytochemical localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase in neuronal somata following colchicine inhibition of axonal transport. Brain Res. 1978 Jan 27;140(2):315–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90463-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropert N., Miles R., Korn H. Characteristics of miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents in CA1 pyramidal neurones of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:707–722. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloviter R. S. Calcium-binding protein (calbindin-D28k) and parvalbumin immunocytochemistry: localization in the rat hippocampus with specific reference to the selective vulnerability of hippocampal neurons to seizure activity. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Feb 8;280(2):183–196. doi: 10.1002/cne.902800203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Hodgson A. J., Smith A. D., Nunzi M. G., Gorio A., Wu J. Y. Different populations of GABAergic neurons in the visual cortex and hippocampus of cat contain somatostatin- or cholecystokinin-immunoreactive material. J Neurosci. 1984 Oct;4(10):2590–2603. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-10-02590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Nunzi M. G., Gorio A., Smith A. D. A new type of specific interneuron in the monkey hippocampus forming synapses exclusively with the axon initial segments of pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1983 Jan 17;259(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalmann R. H. Blockade of a late inhibitory postsynaptic potential in hippocampal CA3 neurons in vitro reveals a late depolarizing potential that is augmented by pentobarbital. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Dec 19;95(1-3):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90649-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R. D., Miles R., Wong R. K. Model of the origin of rhythmic population oscillations in the hippocampal slice. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1319–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.2646715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tömböl T., Somogyi G., Hajdu F. Golgi study on cat hippocampal formation. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1978 Jun 12;153(3):331–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00315935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Afterpotential generation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):86–97. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


