Abstract
1. Experiments were performed to assess the extent to which knee joint blood flow in cats and rabbits is affected by electrical stimulation of the nerve supply to the knee. 2. Absolute changes in blood flow were measured using the radiolabelled microsphere (approximately 15 microns) technique whilst relative changes in blood flow were assessed using laser Doppler flowmetry. 3. Despite deep general anaesthesia, sympathetic nerve fibres innervating cat knee joint blood vessels showed marked 'tone'. 4. Blood flow to the joint capsule (synovium and overlying fibrous and areolar tissues) was substantially reduced (by approximately 90% in the cat and approximately 45% in the rabbit) during electrical stimulation of the articular nerve supply. 5. The percentage change in the laser Doppler flowmeter signal did not differ significantly from the percentage change in blood flow measured by microsphere technique. 6. Blood vessels in the cancellous bone of the distal femur (condyles) and proximal tibia (plateau) appear to be innervated by vasoconstrictor fibres which reach their effectors via the articular nerves. However, the cortical bone and red marrow of the diaphysis of the femur do not receive such innervation. 7. The potency of the vasoconstrictor influences acting on joint blood vessels could be of relevance in the pathogenesis of inflammatory joint diseases.
Full text
PDF



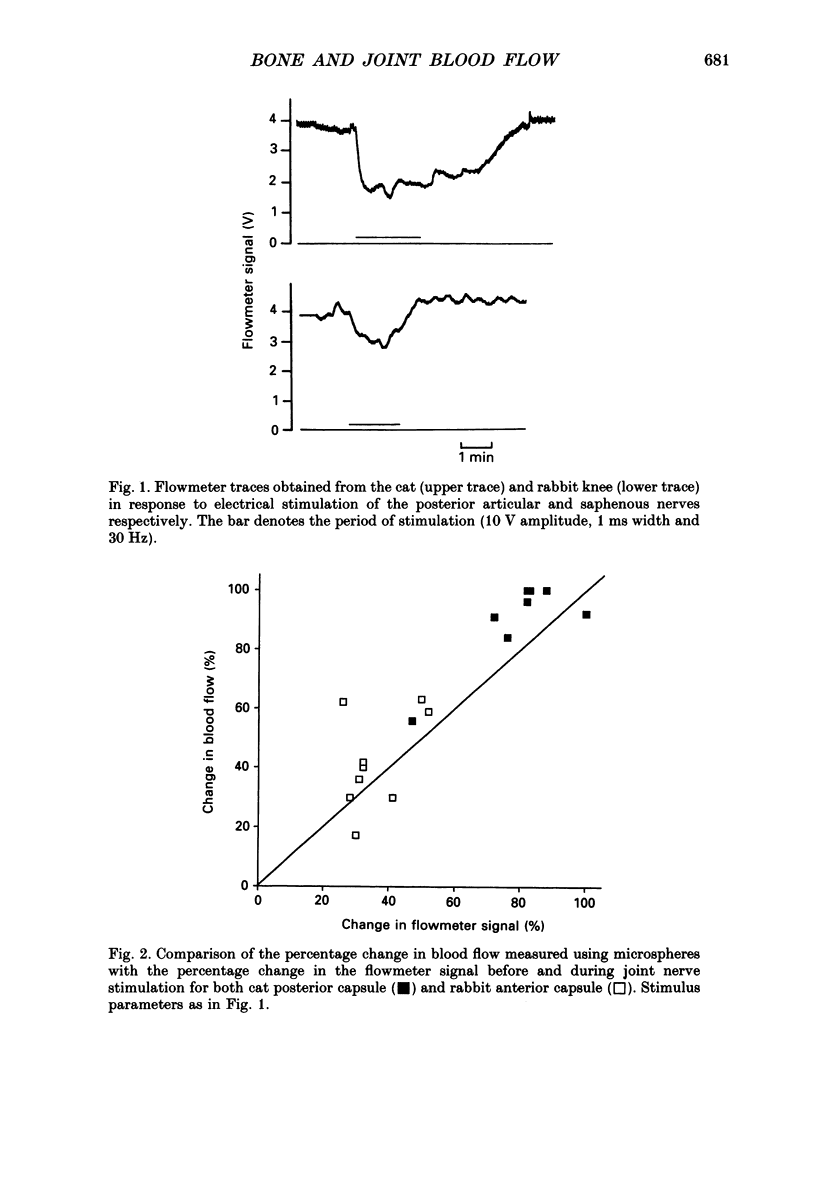
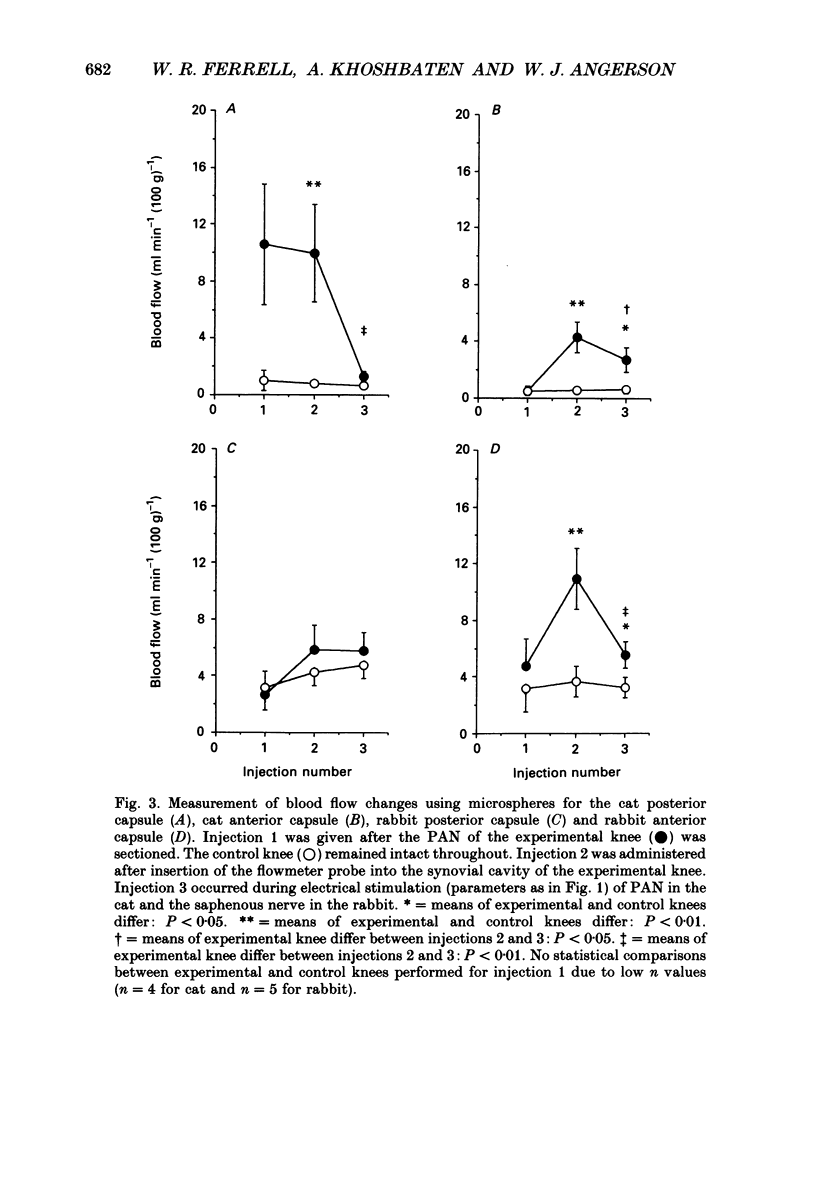
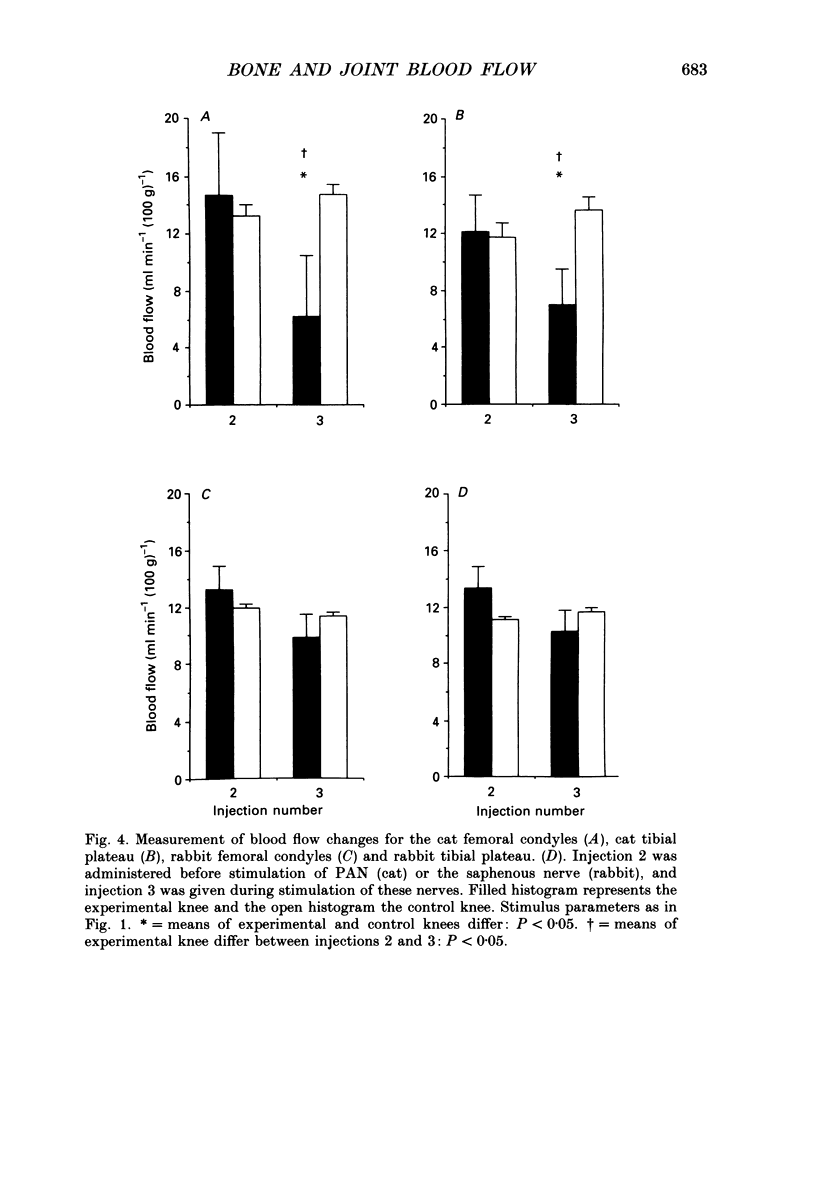




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn H., Lindhagen J., Nilsson G. E., Salerud E. G., Jodal M., Lundgren O. Evaluation of laser Doppler flowmetry in the assessment of intestinal blood flow in cat. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):951–957. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., Clark F. J. Characteristics of knee joint receptors in the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):317–335. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busija D. W., Heistad D. D., Marcus M. L. Continuous measurement of cerebral blood flow in anesthetized cats and dogs. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):H228–H234. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.241.2.H228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bünger C., Hjermind J., Bülow J. Hemodynamics of the juvenile knee in relation to increasing intra-articular pressure. An experimental study in dogs. Acta Orthop Scand. 1983 Feb;54(1):80–87. doi: 10.3109/17453678308992873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COBBOLD A. F., LEWIS O. J. The nervous control of joint blood vessels. J Physiol. 1956 Aug 28;133(2):467–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick W. C., Onge R. A., Gillepsie F. C., Downie W. W., Nuki G., Gordon I., Whaley K., Boyle J. A., Buchanan W. W. Derivation of knee joint synovial perfusion. Using the Xenon (133Xe) clearance technique. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Mar;29(2):131–134. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell W. R. The adequacy of stretch receptors in the cat knee joint for signalling joint angle throughout a full range of movement. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:85–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. A., Wyke B. The innervation of the knee joint. An anatomical and histological study in the cat. J Anat. 1967 Jun;101(Pt 3):505–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geborek P., Forslind K., Wollheim F. A. Direct assessment of synovial blood flow and its relation to induced hydrostatic pressure changes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Apr;48(4):281–286. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.4.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigg P., Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Mechanical sensitivity of group III and IV afferents from posterior articular nerve in normal and inflamed cat knee. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Apr;55(4):635–643. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.4.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberl R. L., Heizer M. L., Ellis E. F. Laser-Doppler assessment of brain microcirculation: effect of local alterations. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):H1255–H1260. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.4.H1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberl R. L., Heizer M. L., Marmarou A., Ellis E. F. Laser-Doppler assessment of brain microcirculation: effect of systemic alterations. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):H1247–H1254. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.4.H1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway G. A., Jr, Watkins D. W. Laser Doppler measurement of cutaneous blood flow. J Invest Dermatol. 1977 Sep;69(3):306–309. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12507665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight A. D., Levick J. R. The density and distribution of capillaries around a synovial cavity. Q J Exp Physiol. 1983 Oct;68(4):629–644. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1983.sp002753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford L. A., Schmidt R. F. Afferent and efferent axons in the medial and posterior articular nerves of the cat. Anat Rec. 1983 May;206(1):71–78. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092060109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre A. K., Proske U., Tracey D. J. Afferent fibres from muscle receptors in the posterior nerve of the cat's knee joint. Exp Brain Res. 1978 Nov 15;33(3-4):415–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00235563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G. E., Tenland T., Obert P. A. A new instrument for continuous measurement of tissue blood flow by light beating spectroscopy. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1980 Jan;27(1):12–19. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1980.326686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nötzli H. P., Swiontkowski M. F., Thaxter S. T., Carpenter G. K., 3rd, Wyatt R. Laser Doppler flowmetry for bone blood flow measurements: helium-neon laser light attenuation and depth of perfusion assessment. J Orthop Res. 1989;7(3):413–424. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100070314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D., Bowen P. D., Parma R., Osgood R. W., Bowman R. L., Stein J. H. Measurement of renal cortical and medullary blood flow by laser-Doppler spectroscopy in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jan;236(1):F80–F87. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.1.F80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


