Abstract
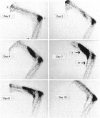
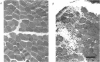
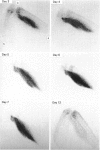
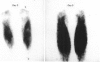
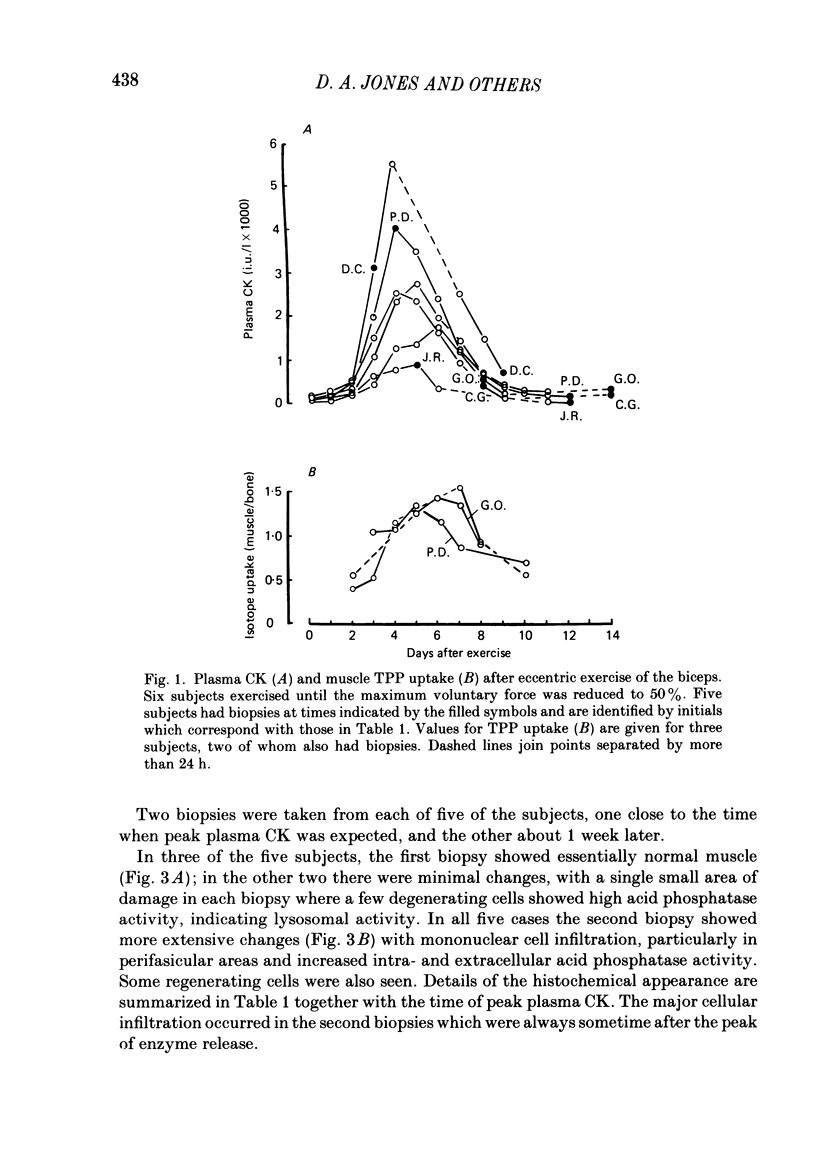
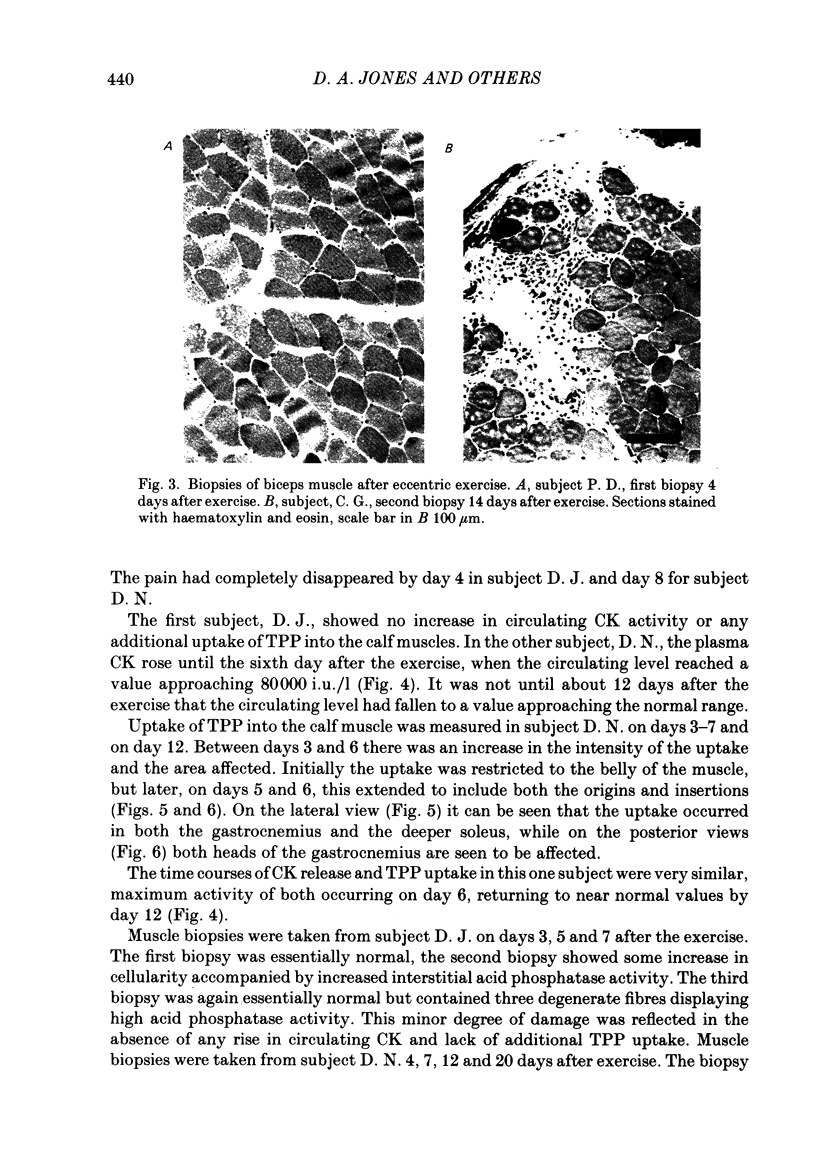
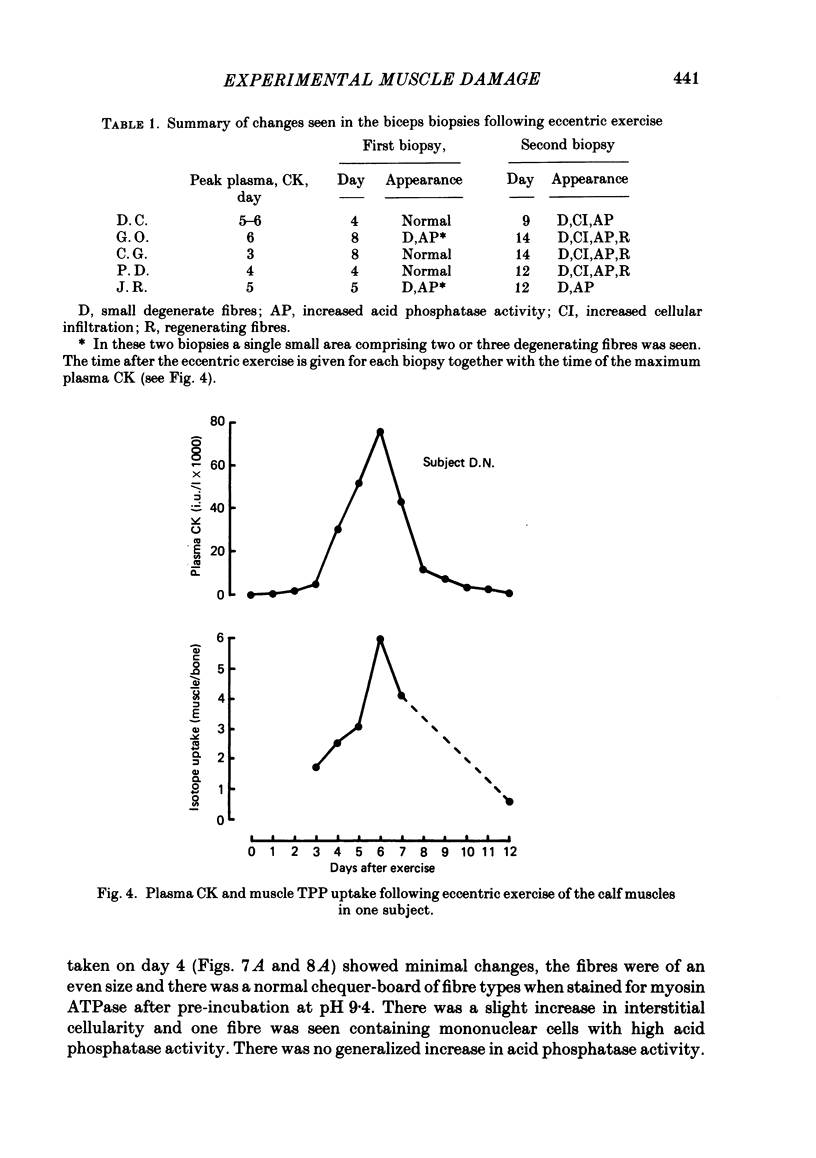
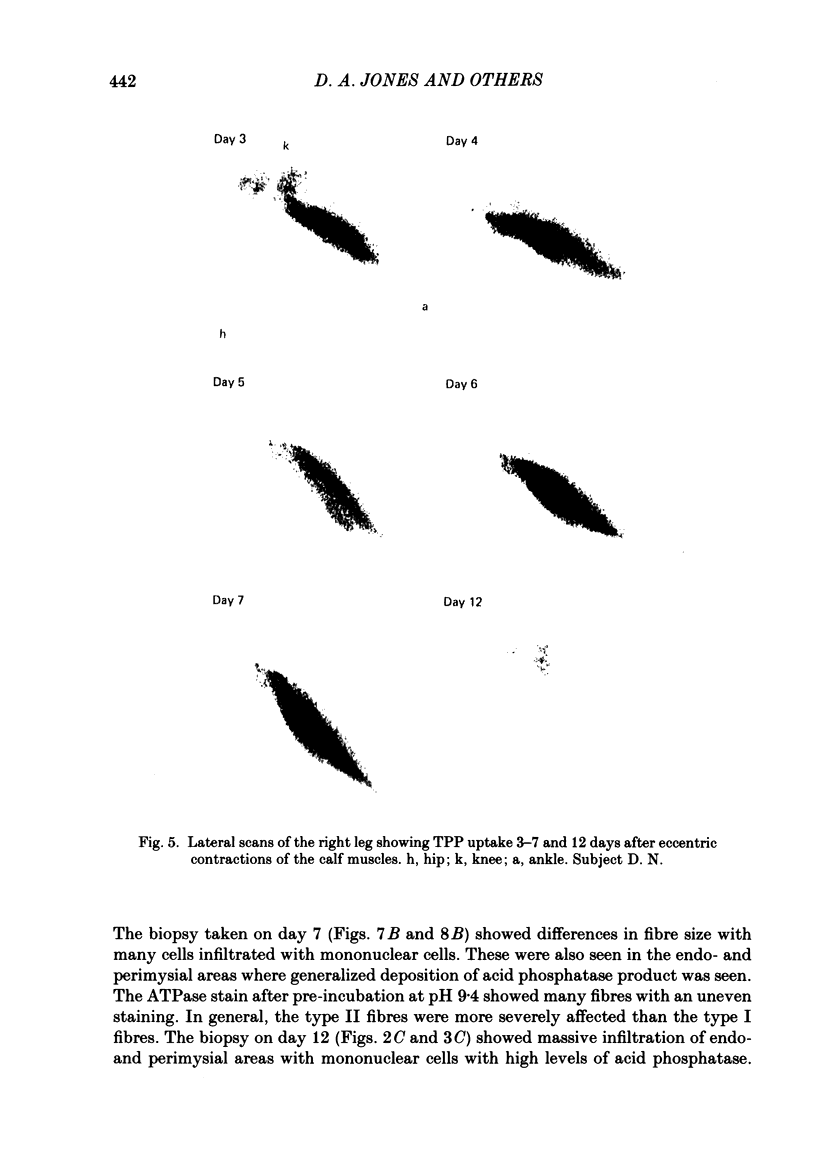
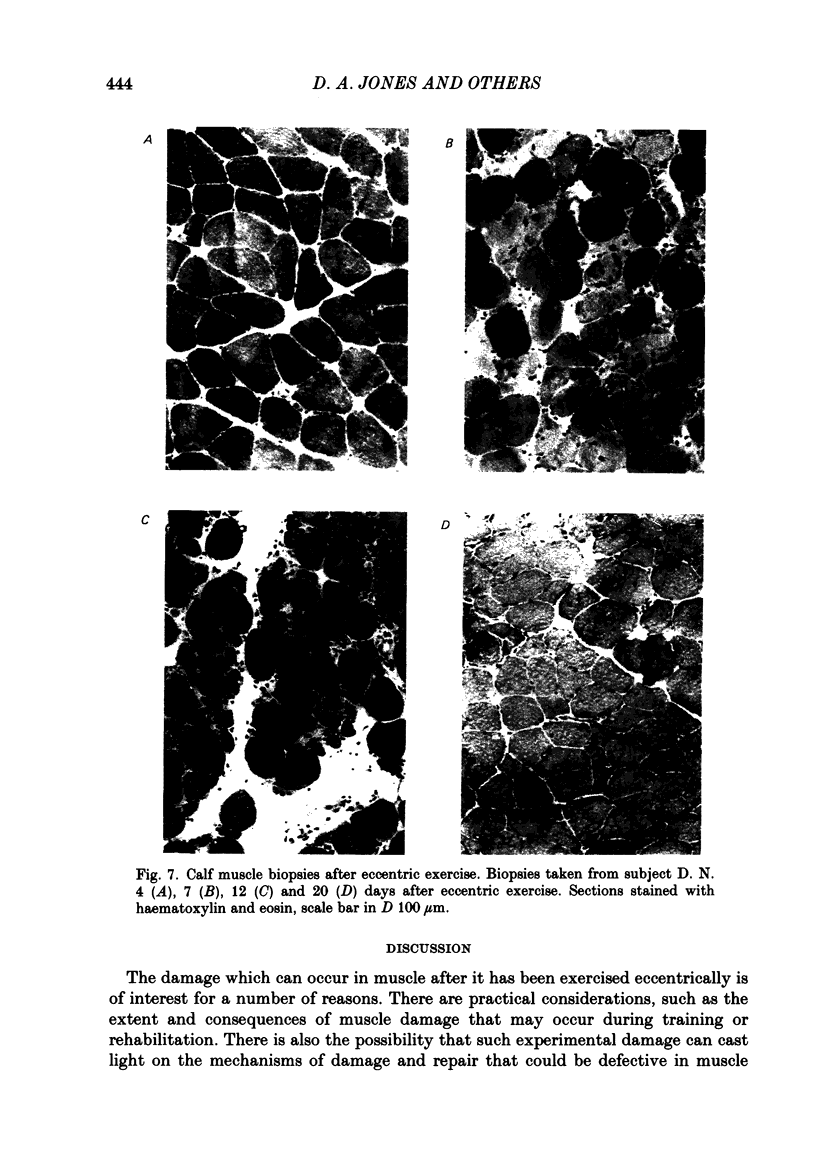
The effects of eccentric exercise have been examined in human calf and biceps muscles. Release of muscle creatine kinase and uptake of technetium pyrophosphate have been followed for up to 20 days after the exercise and the results are related to the morphological changes seen in needle biopsy samples. The response to exercise was variable, all subjects developing pain and tenderness in the exercised muscles after 1-2 days and this was followed, in most subjects, by a large increase in plasma creatine kinase 4-6 days after the exercise. This was paralleled by an increased uptake of technetium pyrophosphate into the exercised muscle. Biopsies of the affected muscles showed little or no change in the first 7 days after the exercise but later degenerating fibres were seen, as well as infiltration by mononuclear cells and eventually, by 20 days, signs of regeneration. Very extensive changes were seen in the calf muscle of one subject; changes in the biceps were qualitatively similar but not so severe. In the severely affected calf muscle type II fibres were preferentially damaged. Mononuclear cell infiltration both between and within degenerating fibres was maximal well after the time of peak plasma creatine kinase and it is likely that in eccentrically exercised muscle infiltrating mononuclear cells act to scavenge cellular debris rather than to cause damage to the muscle.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASMUSSEN E. Observations on experimental muscular soreness. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1956;2(2):109–116. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1956.2.issue-1-4.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASMUSSEN E. Positive and negative muscular work. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953;28(4):364–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. B., Ogilvie R. W., Schwane J. A. Eccentric exercise-induced injury to rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Jan;54(1):80–93. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRENDSTRUP P. Late edema after muscular exercise. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1962 Aug;43:401–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Carroll J. E., Davis J. E., Hagberg J. M. The prolonged exercise test. Neurology. 1979 May;29(5):636–643. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.5.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. T., Barnes C. Negative (eccentric) work. I. Effects of repeated exercise. Ergonomics. 1972 Jan;15(1):3–14. doi: 10.1080/00140137208924402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Round J. M., Jones D. A. Needle biopsy of skeletal muscle: a review of 10 years experience. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Nov-Dec;6(9):676–683. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridén J., Sjöström M., Ekblom B. A morphological study of delayed muscle soreness. Experientia. 1981 May 15;37(5):506–507. doi: 10.1007/BF01986165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridén J., Sjöström M., Ekblom B. Myofibrillar damage following intense eccentric exercise in man. Int J Sports Med. 1983 Aug;4(3):170–176. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1026030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagen L. J. Myoglobinuric syndromes. Am J Med Sci. 1972 Aug;264(2):141–142. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197208000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komi P. V., Buskirk E. R. Effect of eccentric and concentric muscle conditioning on tension and electrical activity of human muscle. Ergonomics. 1972 Jul;15(4):417–434. doi: 10.1080/00140137208924444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., Jones D. A., Edwards R. H. Plasma creatine kinase changes after eccentric and concentric contractions. Muscle Nerve. 1986 Jan;9(1):59–63. doi: 10.1002/mus.880090109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., McPhail G., Mills K. R., Edwards R. H. Ultrastructural changes after concentric and eccentric contractions of human muscle. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Sep;61(1):109–122. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., Mills K. R., Quigley B. M., Edwards R. H. Pain and fatigue after concentric and eccentric muscle contractions. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Jan;64(1):55–62. doi: 10.1042/cs0640055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Round J. M., Matthews Y., Jones D. A. A quick, simple and reliable histochemical method for ATPase in human muscle preparations. Histochem J. 1980 Nov;12(6):707–710. doi: 10.1007/BF01012026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwane J. A., Johnson S. R., Vandenakker C. B., Armstrong R. B. Delayed-onset muscular soreness and plasma CPK and LDH activities after downhill running. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1983;15(1):51–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shumate J. B., Brooke M. H., Carroll J. E., Davis J. E. Increased serum creatine kinase after exercise: a sex-linked phenomenon. Neurology. 1979 Jun;29(6):902–904. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.6.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström M., Fridén J., Ekblom B. Fine structural details of human muscle fibres after fibre type specific glycogen depletion. Histochemistry. 1982;76(4):425–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00489899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson W. H., Sweetin J. C., Hamilton I. J. ATP and muscle enzyme efflux after physical exertion. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Mar 10;59(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]