Abstract
The Vaseline-gap technique was used to record asymmetric charge movement in small segments of muscle fibres from the white sternomastoid or the soleus muscle of the rabbit. At 22 degrees C, non-linear ionic currents (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca2+) were virtually eliminated for potential steps to 0 mV or below by specific blocking agents or ion substitution. A Boltzmann fit of charge movement (Q) vs. potential (V) produced the mean values Qmax = 15.2 nC/microF, V = -26.8 mV and k = 15.3 mV for twenty-three sternomastoid fibres, and 4.8 nC/microF, -32 mV and 13.7 mV for seven soleus fibres. Qmax for the sternomastoid fibres was similar to that for other fast-twitch fibres when normalized by surface area rather than capacitance. Using a 55 ms step, the mean threshold potential (Vth) for contraction in twenty-eight fibres was -25.9 (+/- 2.9) mV (+/- S.E. of mean), and the mean amount of charge moved (qth) at the threshold potential was 8.5 (+/- 0.4) nC/microF. In some contracting fibres, a component of charge movement was observed which was analogous to q gamma in amphibian muscle in its time course and potential dependence. Addition of 80 mM-sucrose to the external solution increased the speed of both the asymmetric charge movement and the charging of the linear capacitance of each fibre. The effect was reversible. A clear relation between the time course of these two parameters was established, and this strongly indicated that the majority of the asymmetric charge was located in the transverse tubular system or beyond. Moreover, it was shown that at 22 degrees C nearly all asymmetric charge moved in less than 0.5 ms after depolarization of the T-system. Sucrose in the external solution affected the Q vs. V relation, steepening the curve and shifting it to more negative potentials, as well as slightly increasing Qmax. The actions of sucrose strongly suggest that it effectively dilates and/or shortens the transverse tubular system, probably by osmotic effects.
Full text
PDF



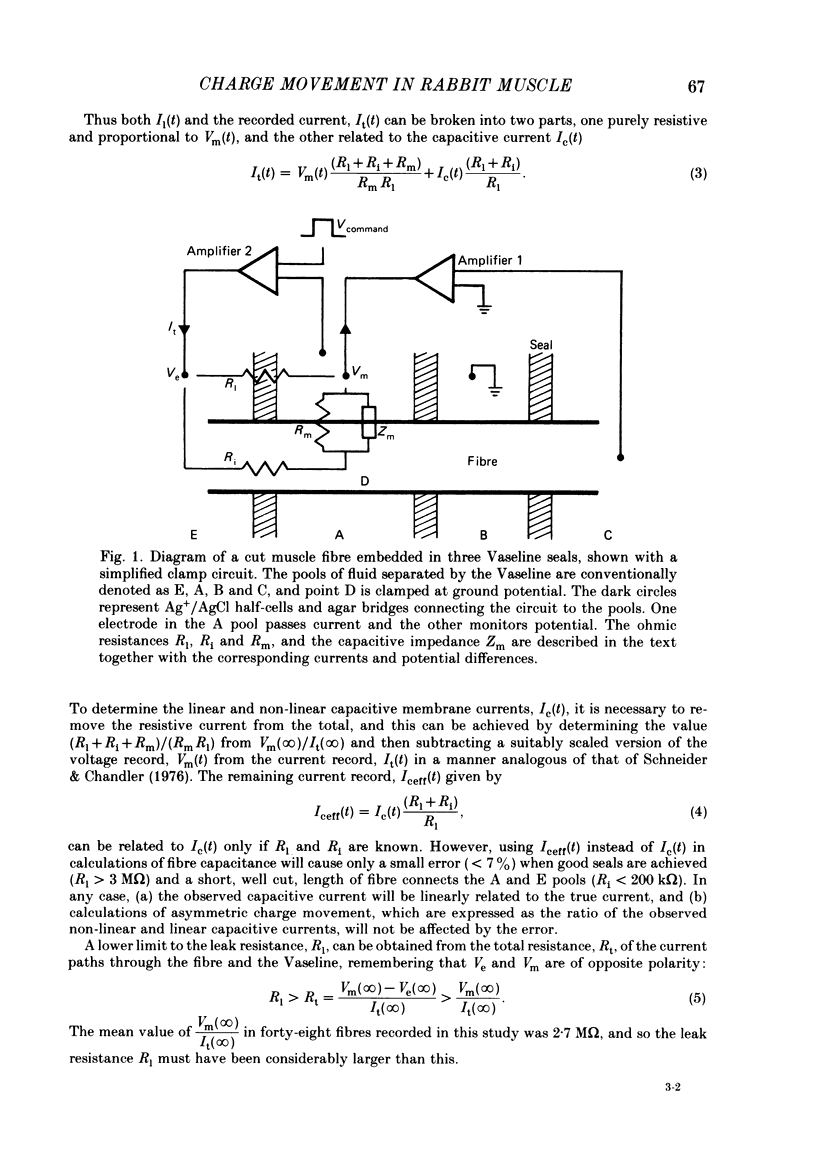

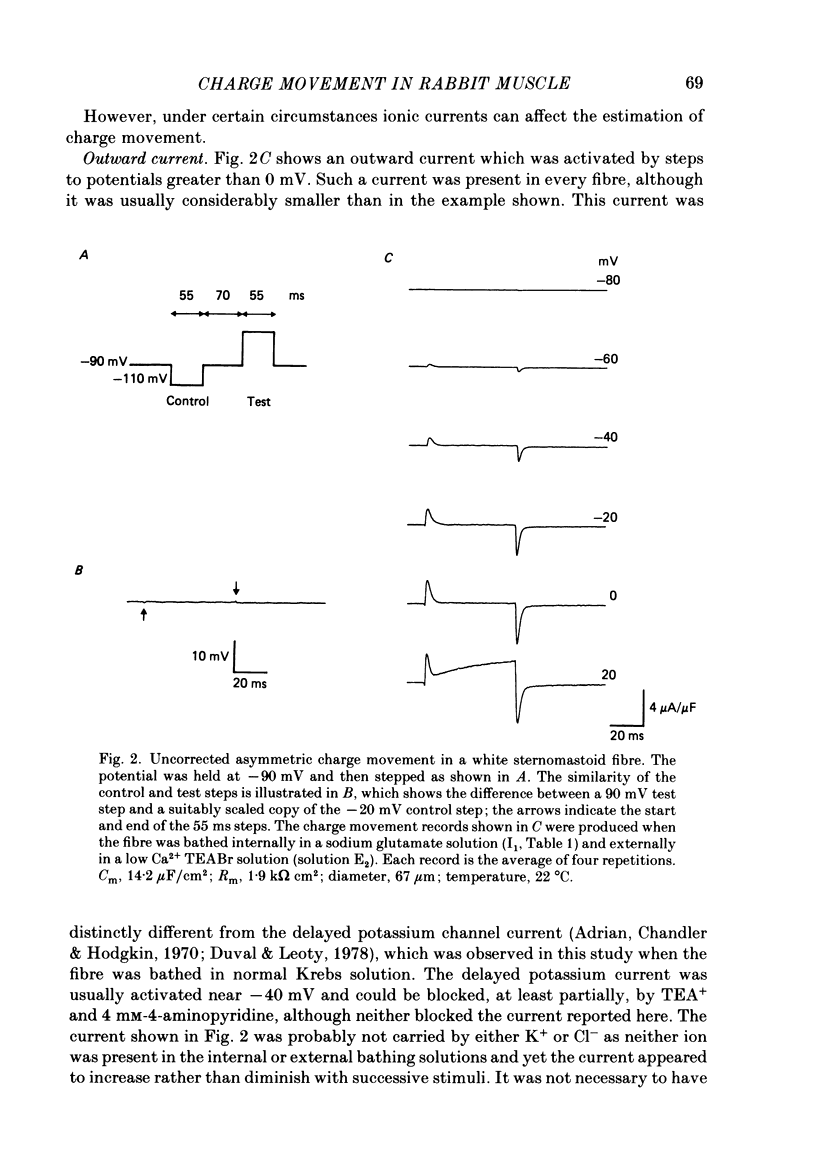


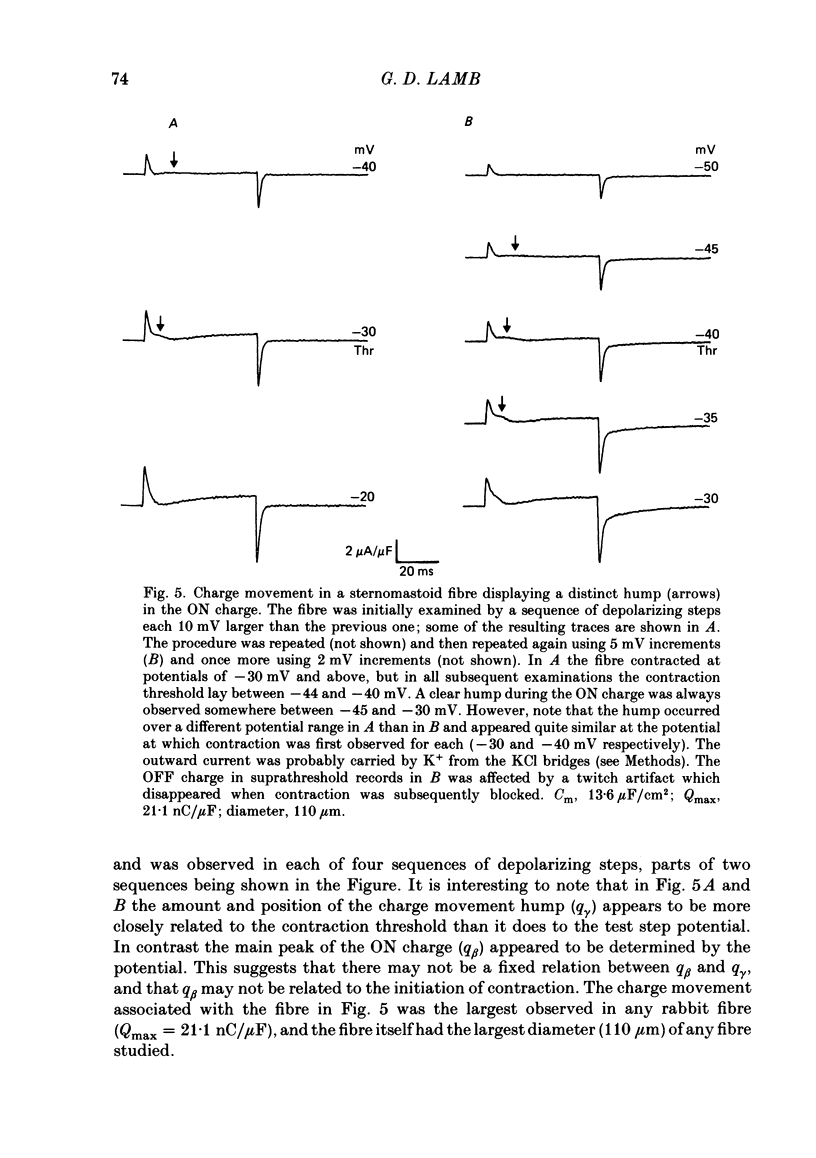
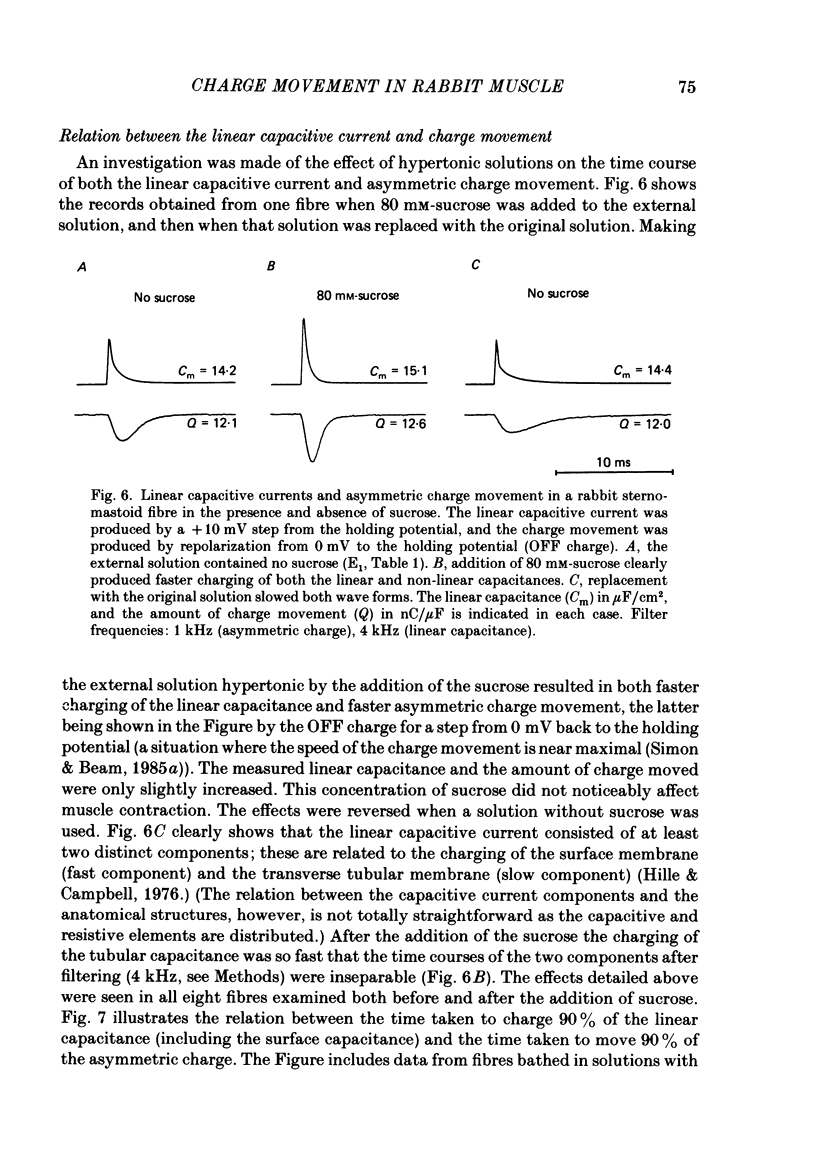
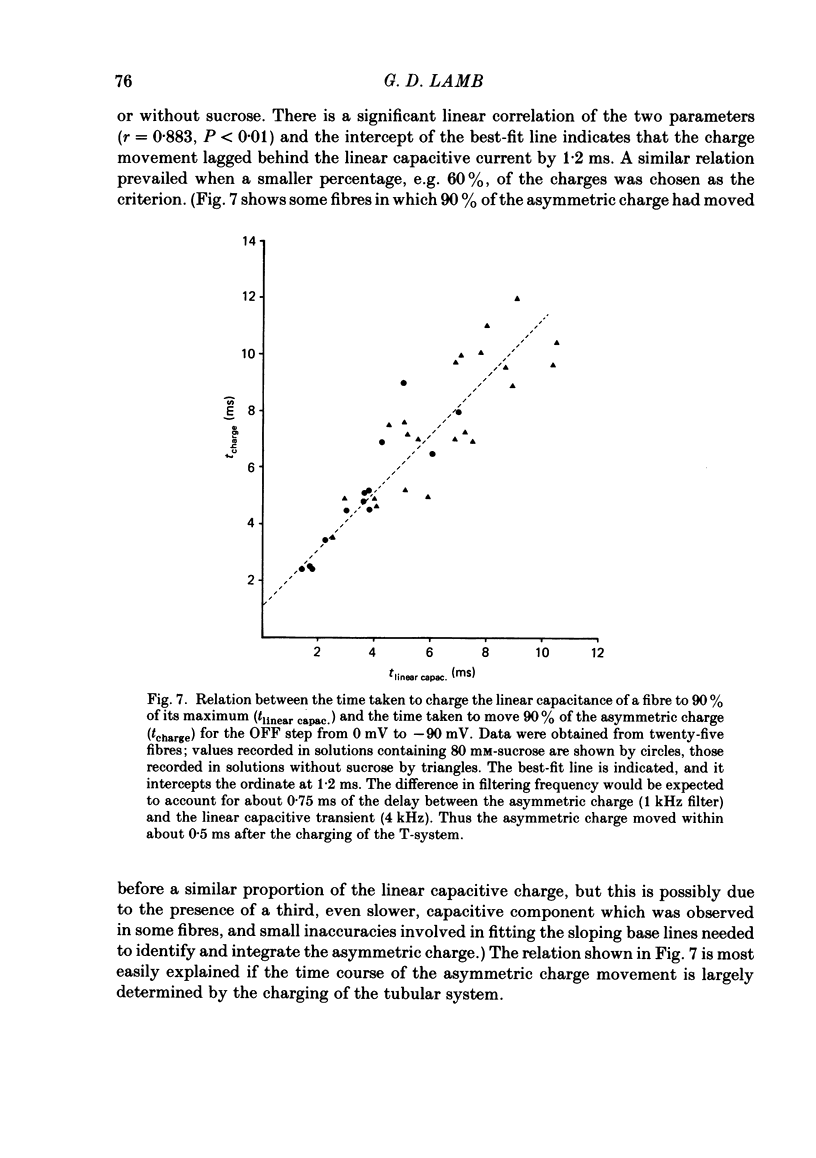
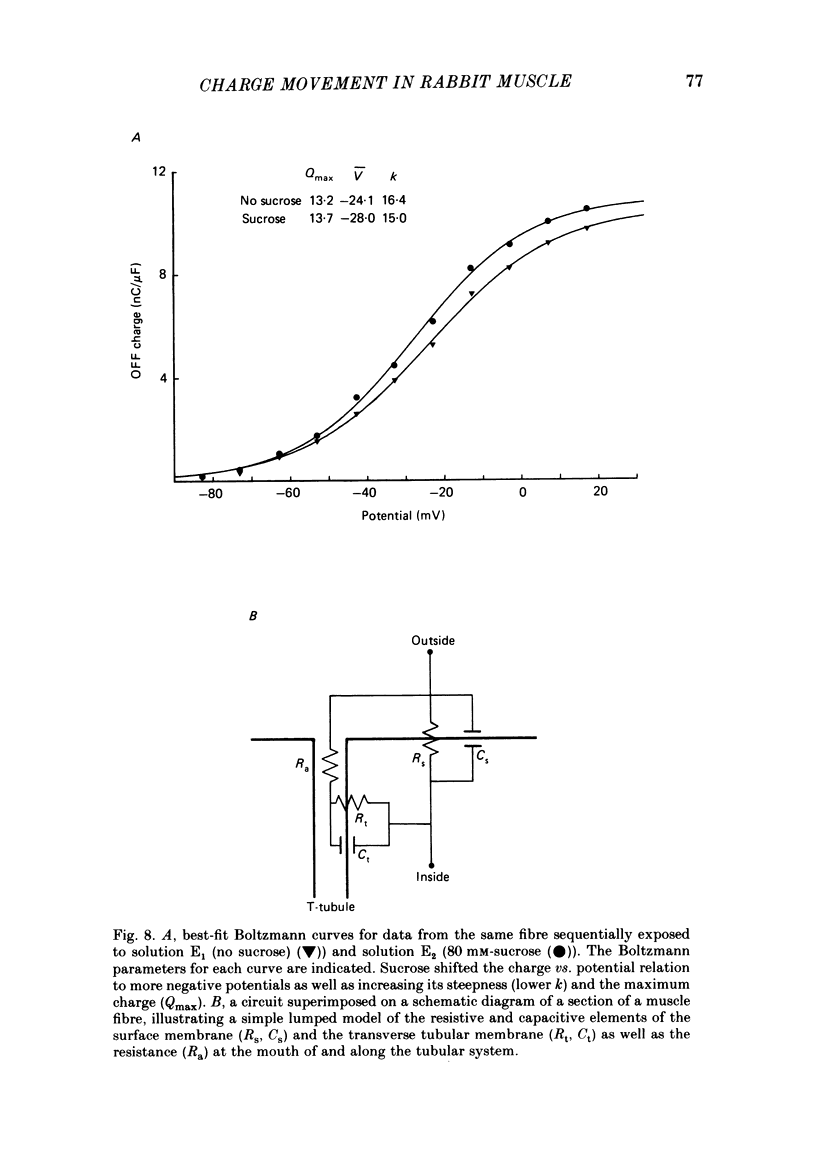






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
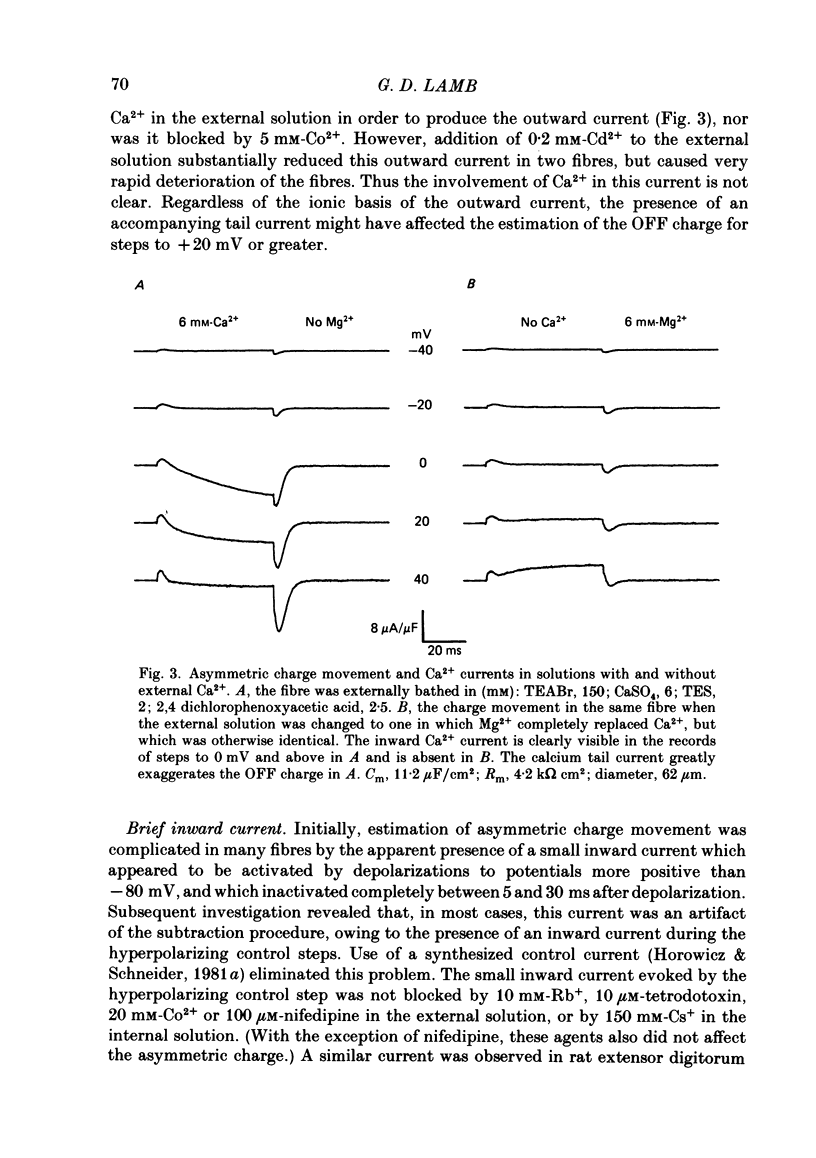
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F. Charge movement and mechanical repriming in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):361–388. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Huang C. L. Charge movements near the mechanical threshold in skeletal muscle of Rana temporaria. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:483–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
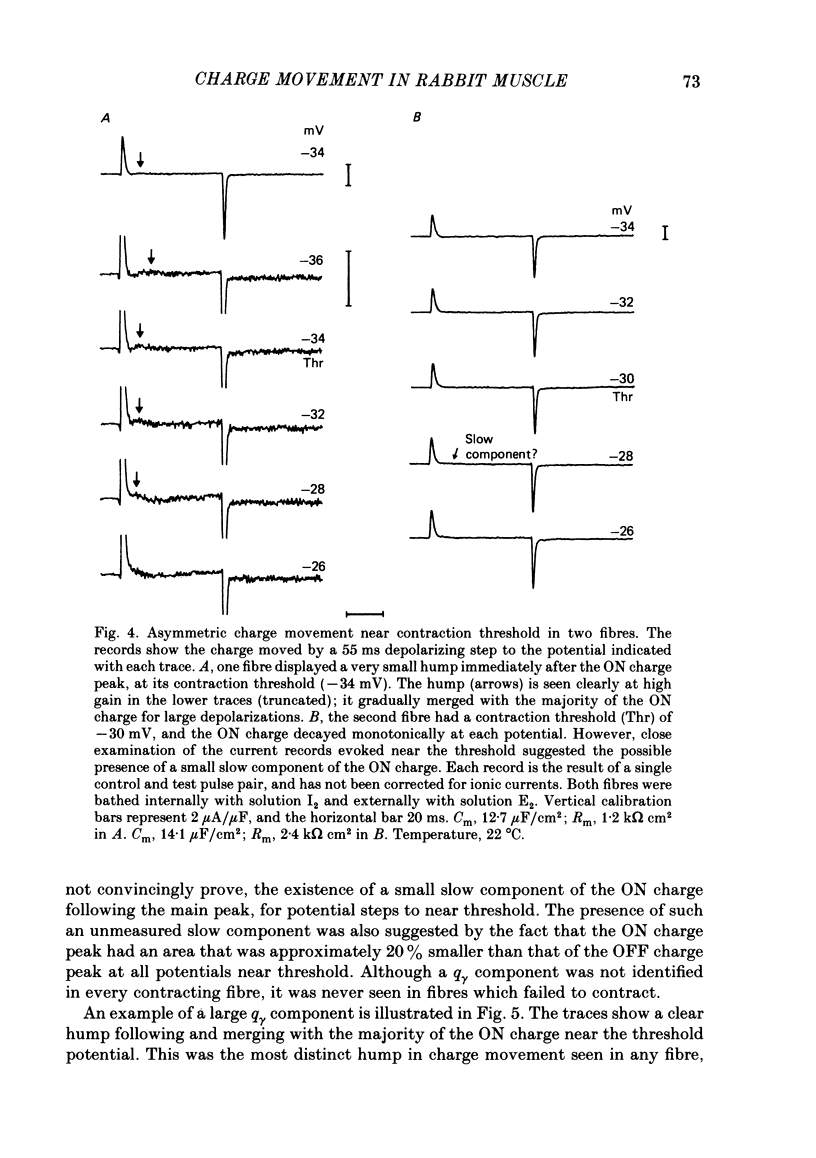
- Adrian R. H., Huang C. L. Experimental analysis of the relationship between charge movement components in skeletal muscle of Rana temporaria. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:419–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peres A. Charge movement and membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:83–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Best P. M. Effects of tetracaine on displacement currents and contraction of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(3):583–611. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W., Palade P. T. A non-selective cation conductance in frog muscle membrane blocked by micromolar external calcium ions. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:565–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Donaldson P. L. A quantitative study of potassium channel kinetics in rat skeletal muscle from 1 to 37 degrees C. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Apr;81(4):485–512. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.4.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. T. Sodium channel gating currents in frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Nov;82(5):679–701. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.5.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. A non-linear voltage dependent charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):245–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. Effects of glycerol treatment and maintained depolarization on charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):285–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey D. F., O'Brien G. M. The sarcoplasmic reticulum and T-system of rat extensor digitorum longus muscles exposed to hypertonic solutions. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1978 Aug;56(4):409–419. doi: 10.1038/icb.1978.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Gage P. W. Asymmetrical charge movement in slow- and fast-twitch mammalian muscle fibres in normal and paraplegic rats. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:213–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Gage P. W. Excitation-contraction coupling and charge movement in denervated rat extensor digitorum longus and soleus muscles. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:75–89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A., Carter G., Hinrichsen C. The membrane capacity of mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Jun;5(3):315–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00713110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval A., Léoty C. Comparison between the delayed outward current in slow and fast twitch skeletal muscle in the rat. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:43–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval A., Léoty C. Ionic currents in mammalian fast skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:403–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C., Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. T-tubule swelling in hypertonic solutions: a freeze substitution study. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:133–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Campbell D. T. An improved vaseline gap voltage clamp for skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):265–293. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth S., Marshall M. W. A comparative study of charge movement in rat and frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:583–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp014004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowicz P., Schneider M. F. Membrane charge moved at contraction thresholds in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:595–633. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowicz P., Schneider M. F. Membrane charge movement in contracting and non-contracting skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:565–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Effects of local anaesthetics on the relationship between charge movements and contractile thresholds in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:381–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Pharmacological separation of charge movement components in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:375–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S. Pharmacological studies of charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:509–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Ríos E., Schneider M. F. Calcium transients and intramembrane charge movement in skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):391–396. doi: 10.1038/279391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D. Components of charge movement in rabbit skeletal muscle: the effect of tetracaine and nifedipine. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:85–100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Effects of membrane potential on the capacitance of skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Feb;67(2):125–163. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. J., Beam K. G. Slow charge movement in mammalian skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jan;85(1):1–19. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. J., Beam K. G. The influence of transverse tubular delays on the kinetics of charge movement in mammalian skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jan;85(1):21–42. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


