Abstract
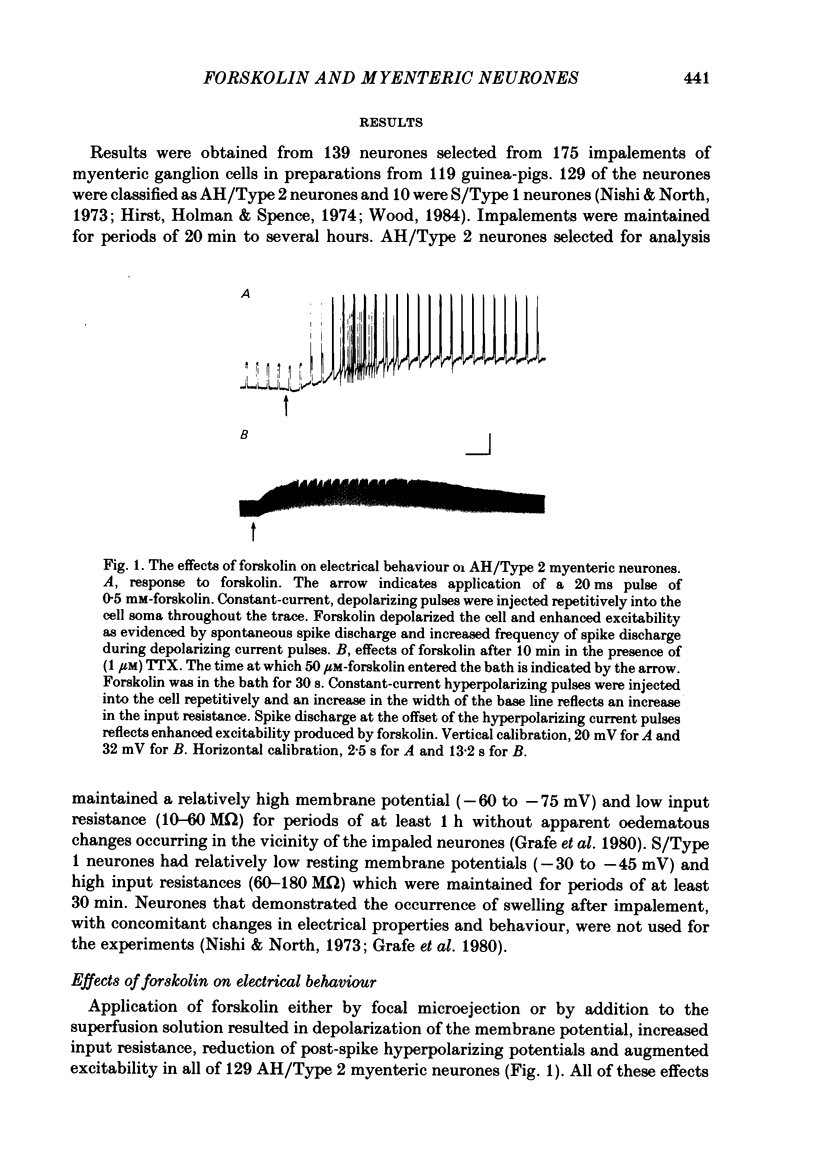
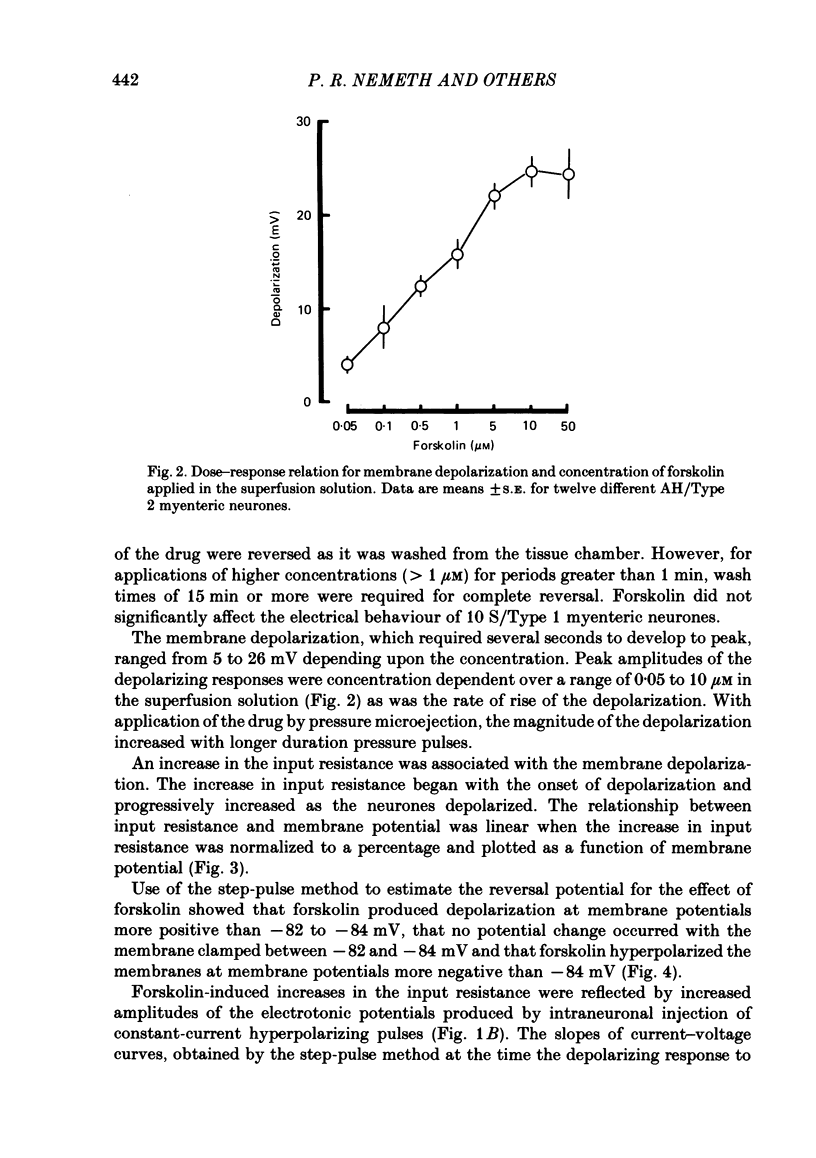
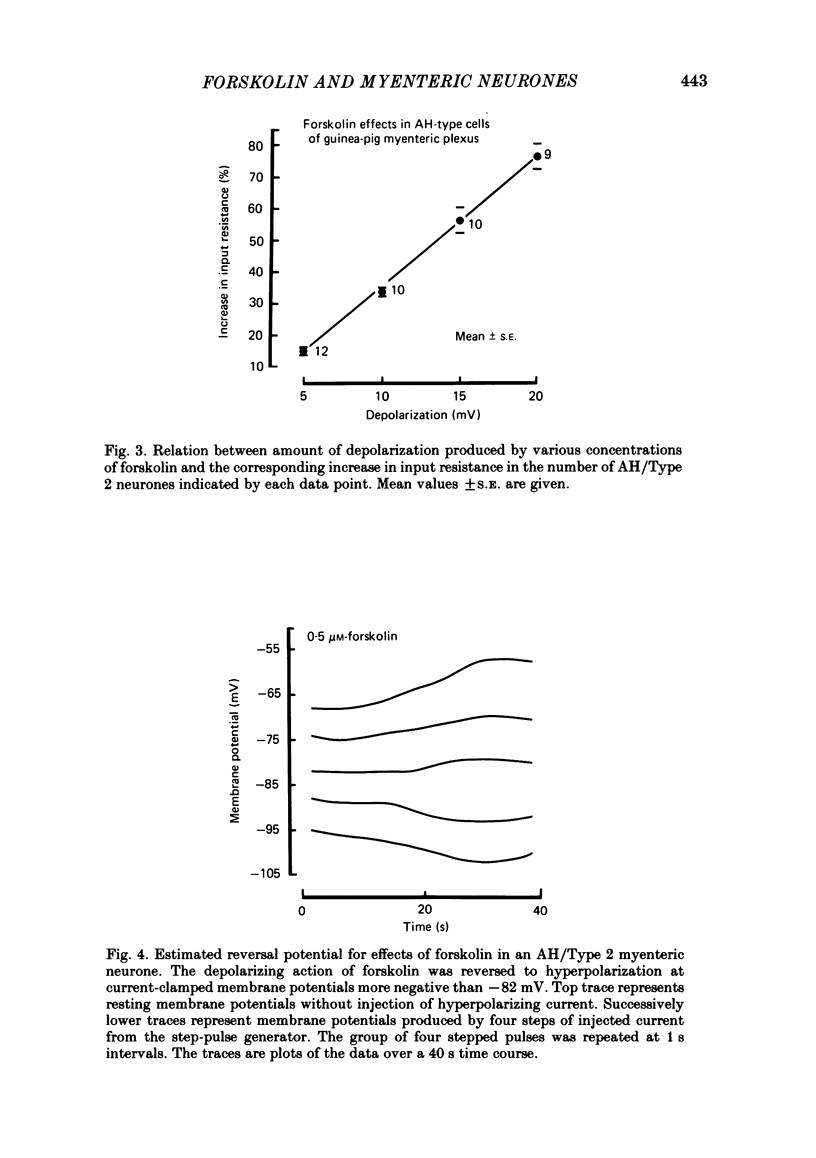
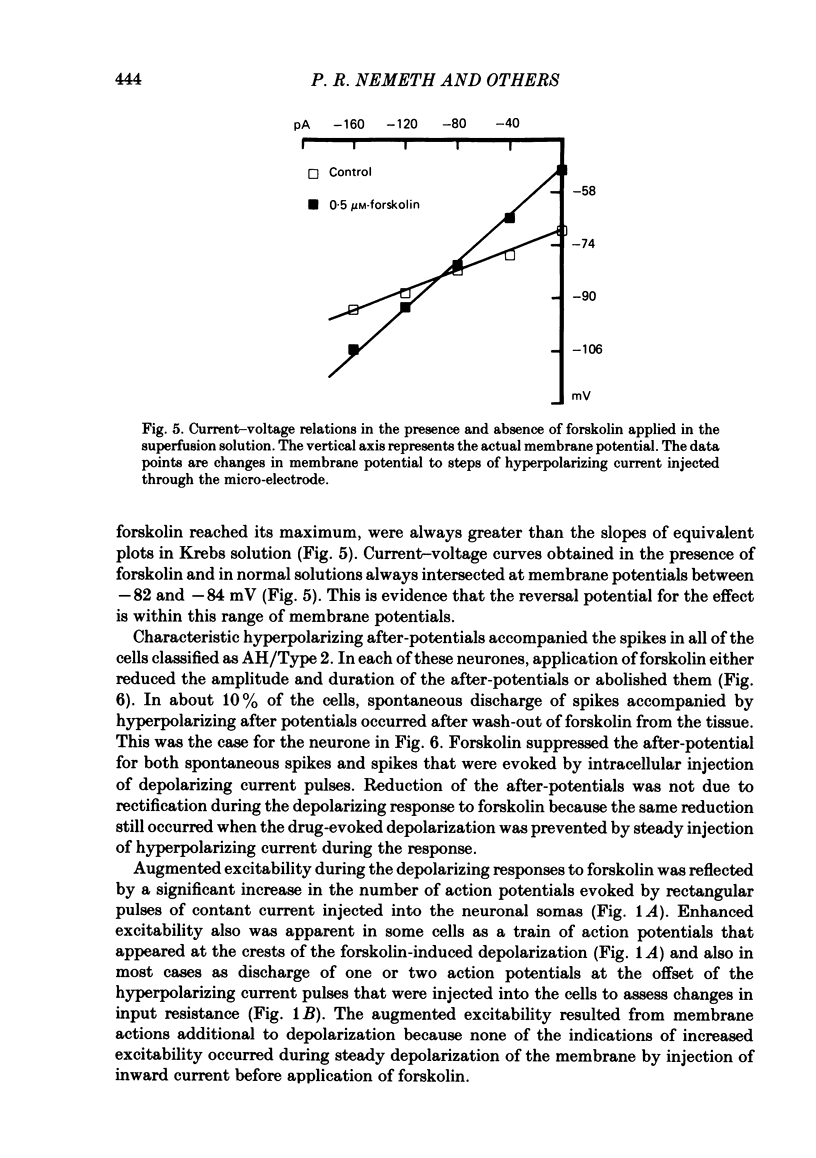
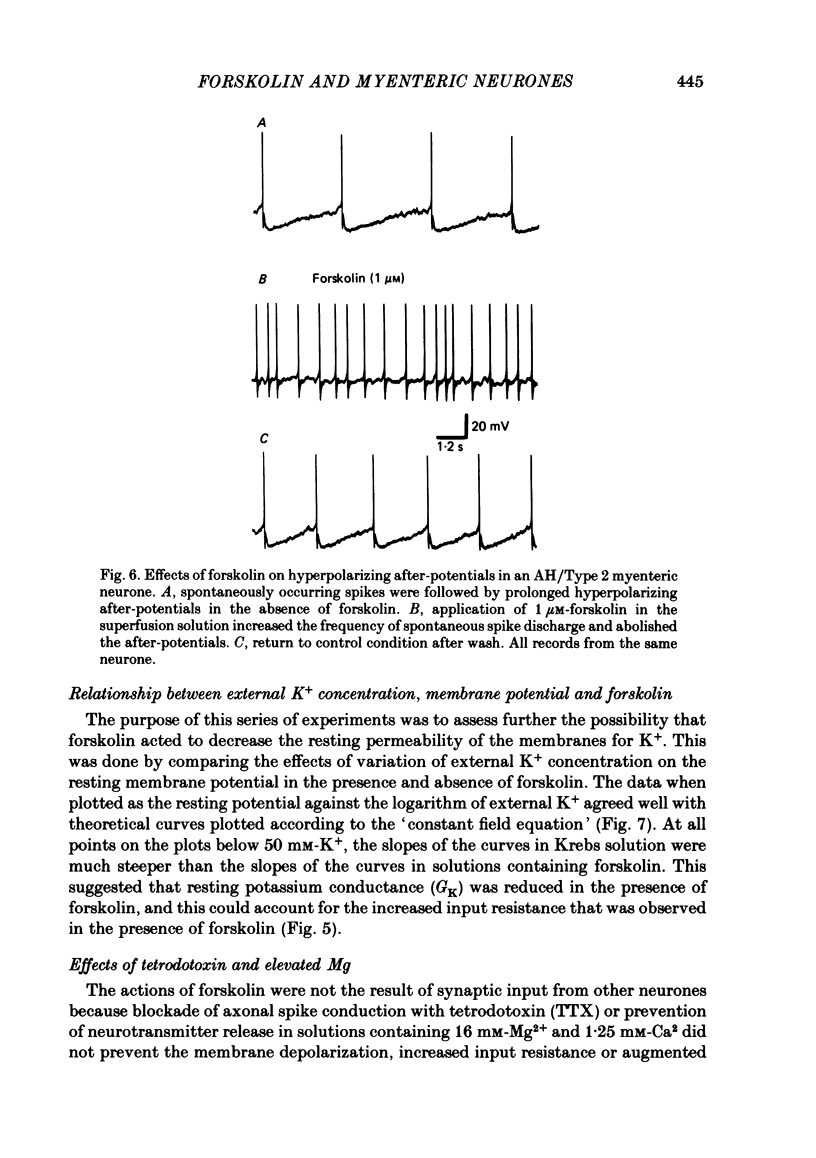
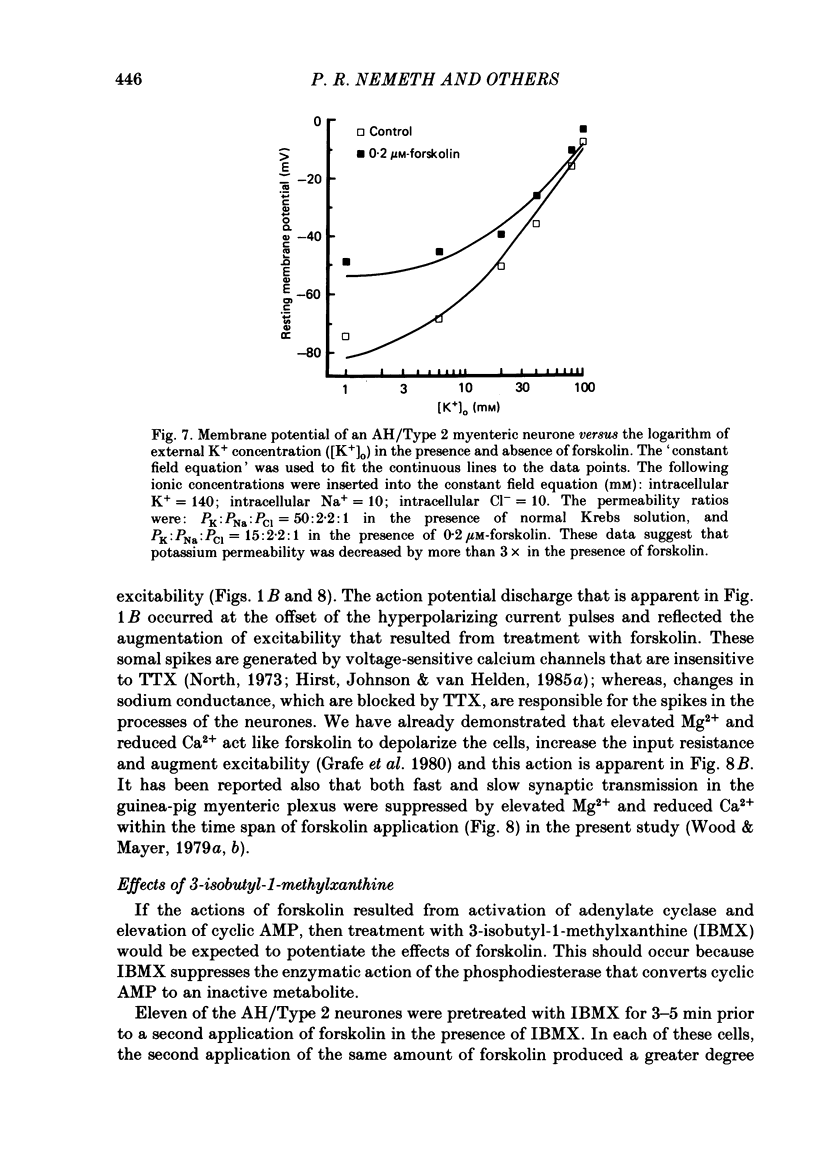
The actions of forskolin on electrical behaviour of myenteric neurones were investigated with intracellular recording methods in guinea-pig small intestine. The actions of forskolin were: membrane depolarization, increased input resistance, suppression of post-spike hyperpolarizing potentials and repetitive spike discharge. These effects occurred always in AH/Type 2 myenteric neurones and never in the cells classified as S/Type 1. Reversal potentials for the depolarizing effects were near the estimated potassium equilibrium potential. Analyses based on the 'constant field equation' indicated that the permeability ratios of K+ to other permeant ionic species were reduced by forskolin. Pretreatment of the neurones with a phosphodiesterase inhibitor potentiated the effects of forskolin. The results suggest that activation of adenylate cyclase by forskolin and subsequent elevation of intraneuronal adenosine 3',5'-phosphate (cyclic AMP) mimic slow synaptic excitation in AH/Type 2 myenteric neurones. They support the possibility that cyclic AMP functions as a second messenger in signal transduction which appears to involve closure of calcium-dependent K+ channels and other membrane changes that lead to depolarization and a dramatic increase in the excitability of the neurones.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Grafe P., Mayer C. J., Wood J. D. Synaptic modulation of calcium-dependent potassium conductance in myenteric neurones in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:235–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Johnson S. M., van Helden D. F. The calcium current in a myenteric neurone of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:297–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Johnson S. M., van Helden D. F. The slow calcium-dependent potassium current in a myenteric neurone of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:315–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Spence I. Calcium action potentials in mammalian peripheral neurones. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 9;243(123):54–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Katayama Y., North R. A. Multiple actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine on myenteric neurones of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:459–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., North R. A. Does substance P mediate slow synaptic excitation within the myenteric plexus? Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):387–388. doi: 10.1038/274387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., North R. A., Williams J. T. The action of substance P on neurons of the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Nov 30;206(1163):191–208. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmer S. L., Carlsen R. C. Forskolin activation of adenylate cyclase in vivo stimulates nerve regeneration. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):455–457. doi: 10.1038/307455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth P. R., Ort C. A., Wood J. D. Intracellular study of effects of histamine on electrical behaviour of myenteric neurones in guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1984 Oct;355:411–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth P. R., Zafirov D. H., Wood J. D. Effects of cholecystokinin, caerulein and pentagastrin on electrical behavior of myenteric neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 22;116(3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth P. R., Zafirov D., Wood J. D. Forskolin mimics slow synaptic excitation in myenteric neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun 1;101(3-4):303–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. The calcium-dependent slow after-hyperpolarization in myenteric plexus neurones with tetrodotoxin-resistant action potentials. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;49(4):709–711. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. M., Wood J. D., Zafirov D. H. Elevation of adenosine 3',5'-phosphate mimics slow synaptic excitation in myenteric neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:451–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Daly J. W. Forskolin: a unique diterpene activator of cyclic AMP-generating systems. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(4):201–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D. Enteric neurophysiology. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 1):G585–G598. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.6.G585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Adrenergic inhibition of serotonin release from neurons in guinea pig Auerback's plexus. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Mar;42(2):594–603. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.2.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Serotonergic activation of tonic-type enteric neurons in guinea pig small bowel. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Mar;42(2):582–593. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.2.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafirov D. H., Palmer J. M., Nemeth P. R., Wood J. D. Bombesin, gastrin releasing peptide and vasoactive intestinal peptide excite myenteric neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 10;115(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90590-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


