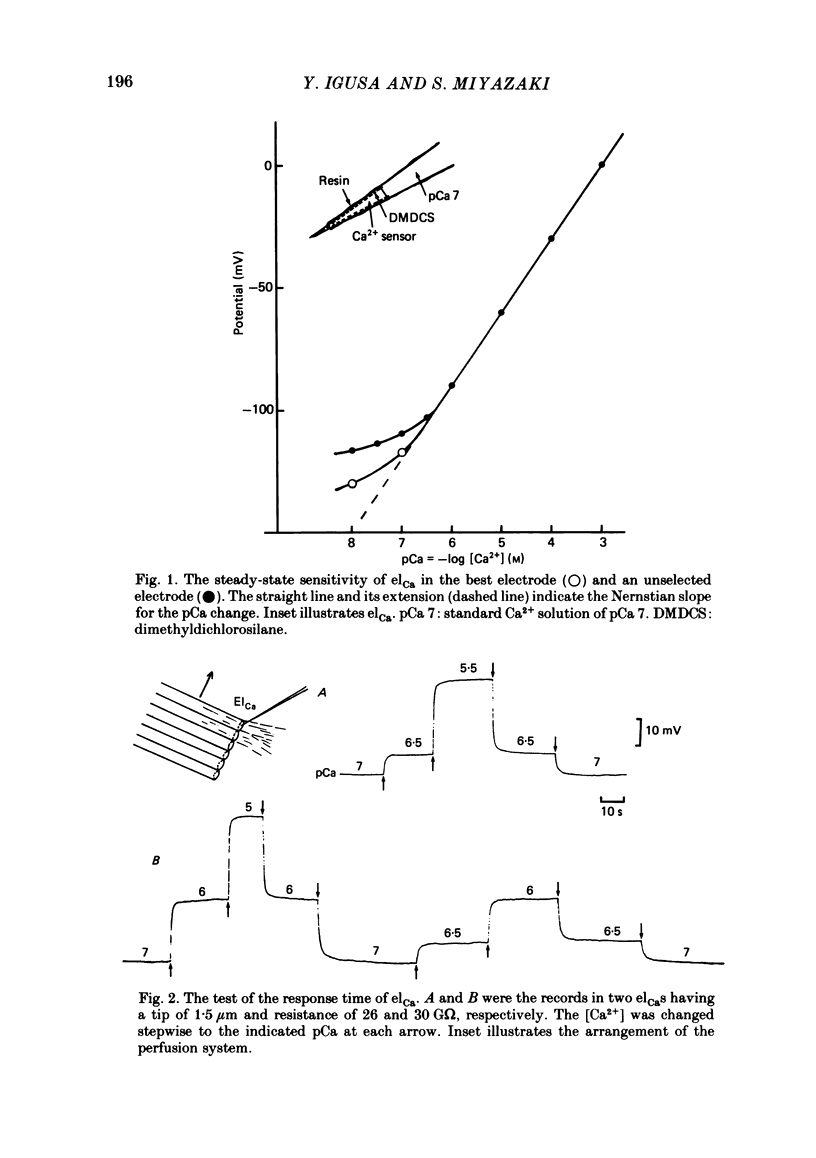
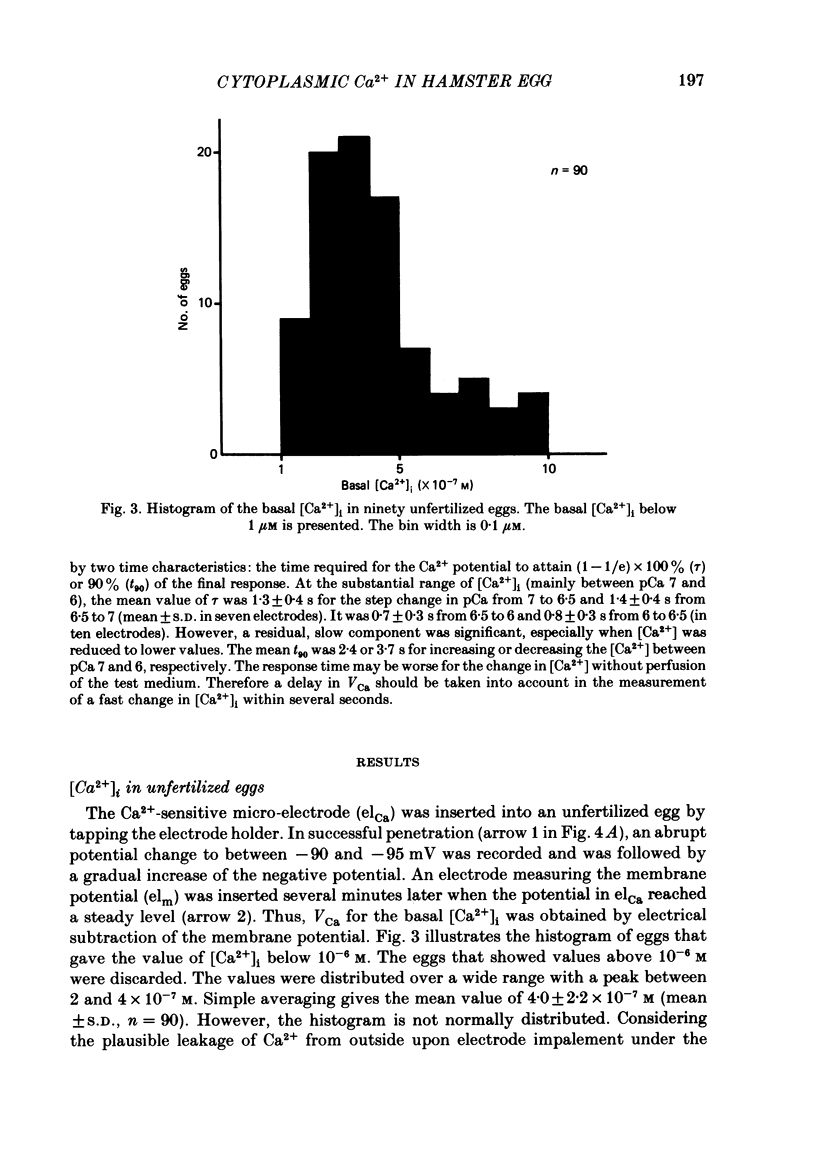
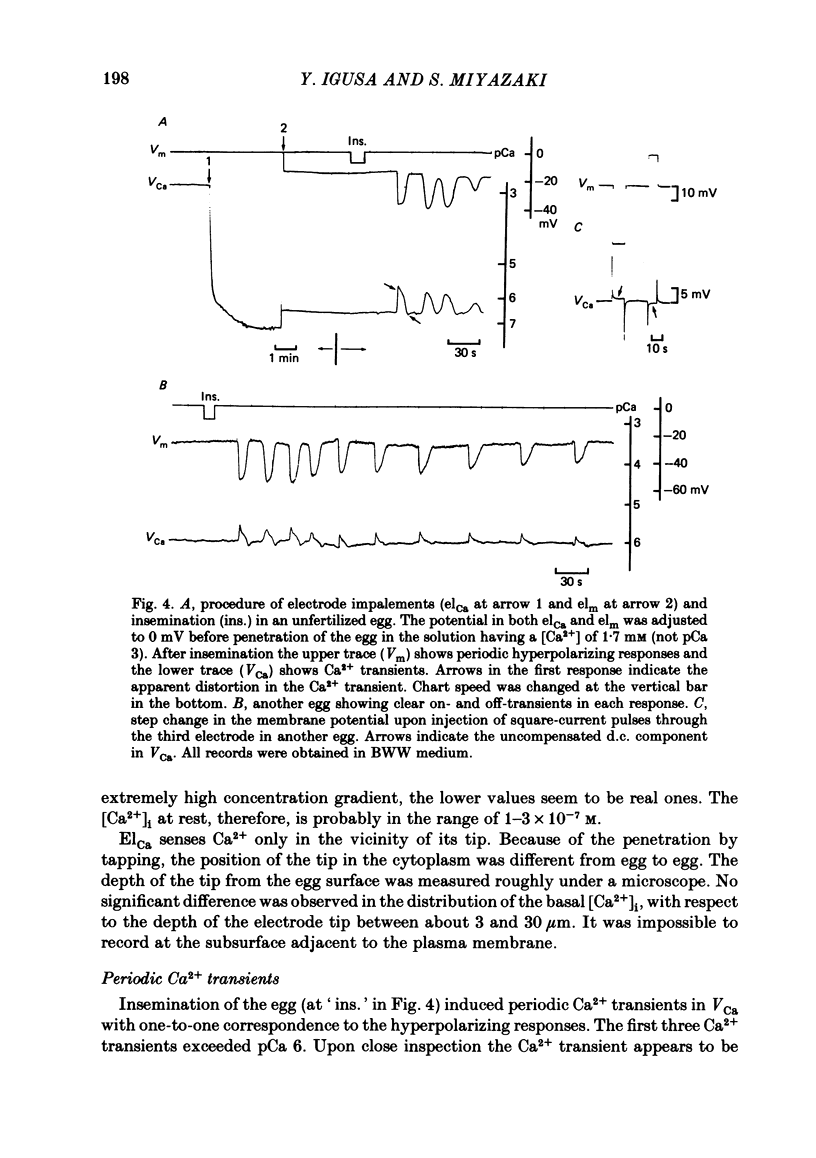
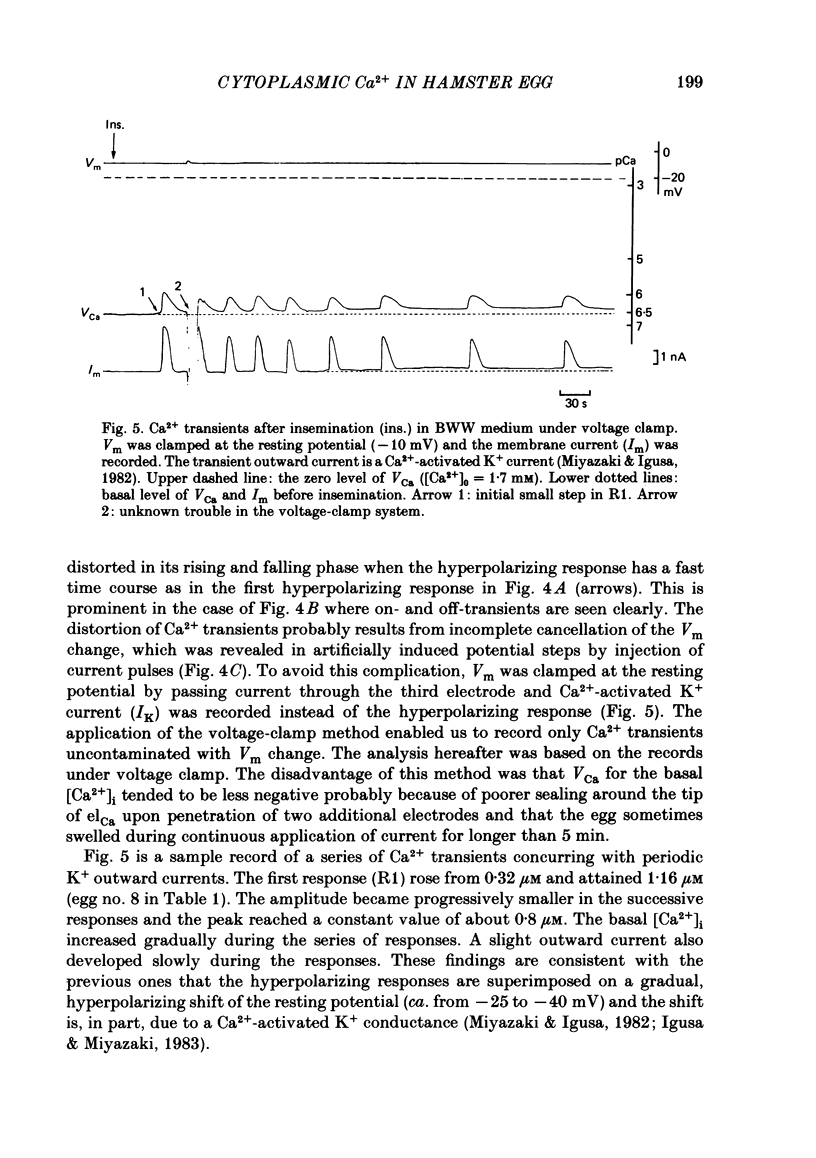
Abstract
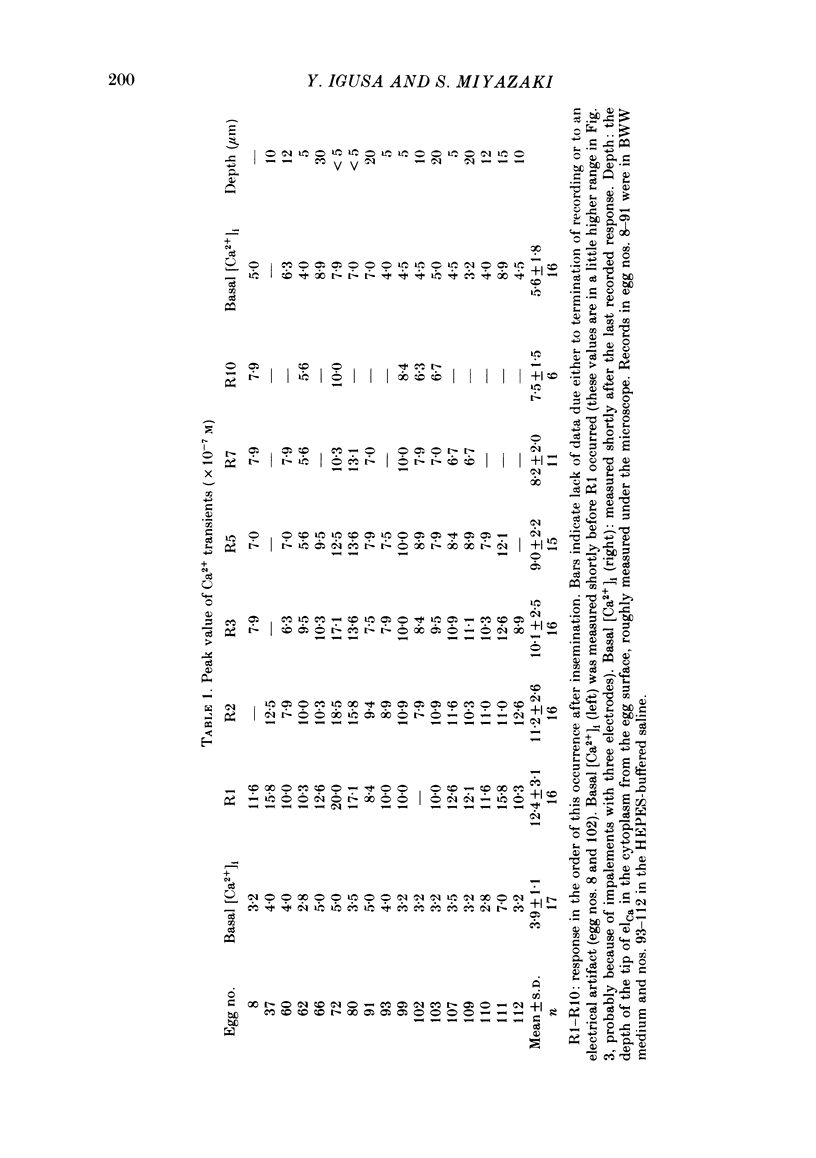
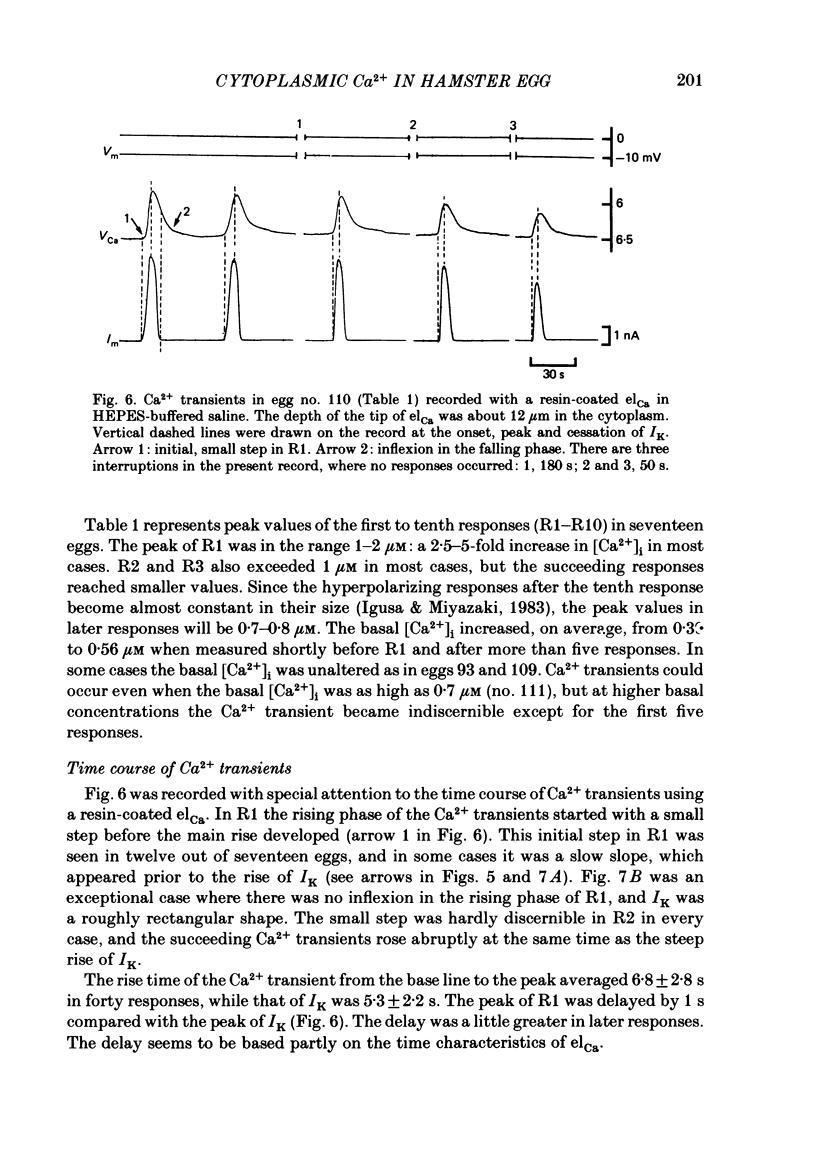
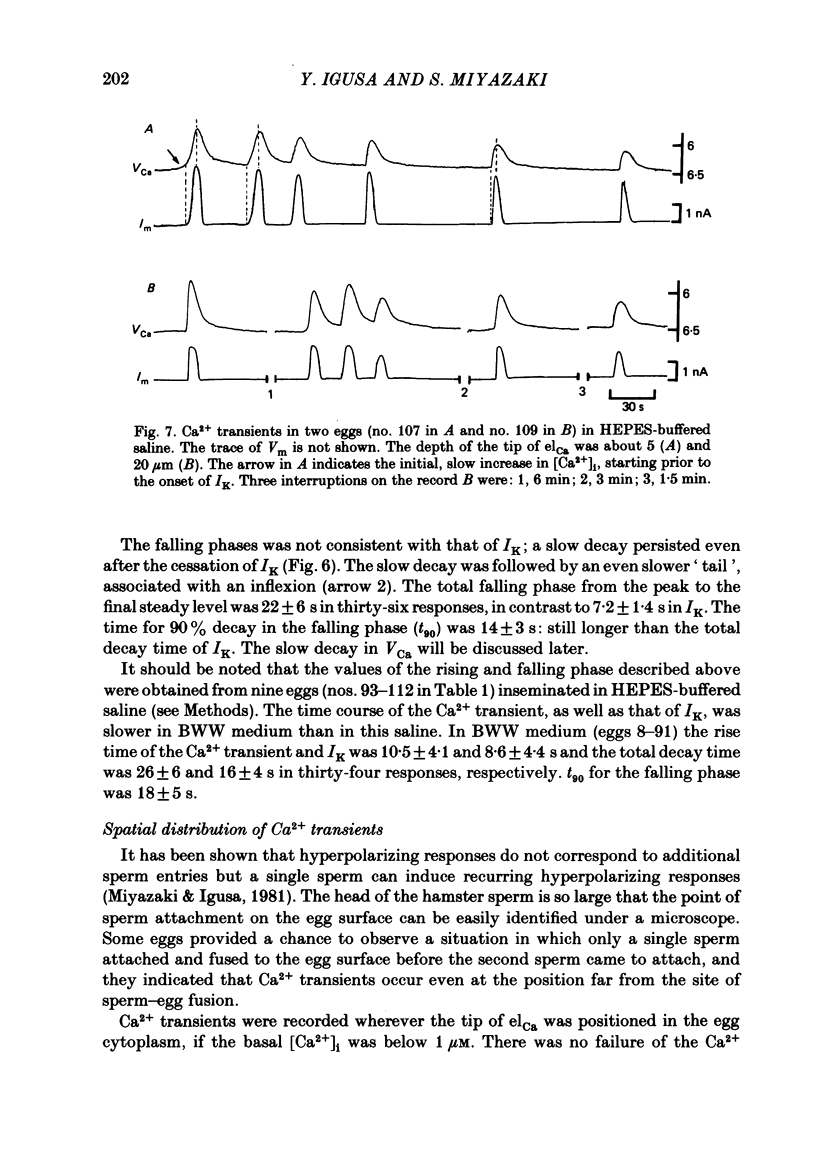
The hamster egg at fertilization shows transient, periodic hyperpolarizing responses due to a Ca2+-activated K+ conductance. The suggested increase of the intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) was measured with Ca2+-sensitive microelectrodes in combination with the voltage-clamp technique. Calculated values of the basal [Ca2+]i before fertilization averaged in the range 0.2-0.4 microM. Insemination of eggs induced periodic Ca2+ transients with exact one-to-one correspondence to periodic, Ca2+-activated K+ currents. They were recorded anywhere in the cytoplasm, even far from the site of sperm-egg fusion, indicating that [Ca2+]i increases in the whole egg upon each response. During a series of responses after insemination the increase in [Ca2+]i reached 1-2 microM in the first three responses and the peak value decreased to 0.7-0.8 microM in the later responses. The rise and decay times of each Ca2+ transient were 6.8 +/- 2.8 and 22 +/- 6 s (mean +/- S.D., n = 36), respectively. No significant difference in the amplitude and time course of the Ca2+ transient was detected in relation to the depth of the cytoplasm about 3-30 micron from the surface. The basal [Ca2+]i increased gradually from 0.39 to 0.56 microM (average in fourteen eggs) during the series of Ca2+ transients. The biological significance and mechanism of the periodic increase in [Ca2+]i and the response time of the Ca2+ electrode are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eisen A., Kiehart D. P., Wieland S. J., Reynolds G. T. Temporal sequence and spatial distribution of early events of fertilization in single sea urchin eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1647–1654. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epel D. Mechanisms of activation of sperm and egg during fertilization of sea urchin gametes. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1978;12:185–246. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60597-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkey J. C., Jaffe L. F., Ridgway E. B., Reynolds G. T. A free calcium wave traverses the activating egg of the medaka, Oryzias latipes. J Cell Biol. 1978 Feb;76(2):448–466. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Jaffe L. A. Electrical properties of egg cell membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:385–416. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igusa Y., Miyazaki S. Effects of altered extracellular and intracellular calcium concentration on hyperpolarizing responses of the hamster egg. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:611–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igusa Y., Miyazaki S., Yamashita N. Periodic hyperpolarizing responses in hamster and mouse eggs fertilized with mouse sperm. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:633–647. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marban E., Rink T. J., Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Free calcium in heart muscle at rest and during contraction measured with Ca2+ -sensitive microelectrodes. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):845–850. doi: 10.1038/286845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Igusa Y. Ca-mediated activation of a K current at fertilization of golden hamster eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):931–935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Igusa Y. Fertilization potential in golden hamster eggs consists of recurring hyperpolarizations. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):702–704. doi: 10.1038/290702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Tsien R. Y., Steinhardt R. A. Changes of free calcium levels with stages of the cell division cycle. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):147–149. doi: 10.1038/315147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R., Zucker R., Schatten G. Intracellular calcium release at fertilization in the sea urchin egg. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 1;58(1):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90084-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker M. J., Baker P. F. Calcium-dependent exocytosis in an in vitro secretory granule plasma membrane preparation from sea urchin eggs and the effects of some inhibitors of cytoskeletal function. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Jul 22;218(1213):397–413. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagimachi R. Sperm-egg association in animals. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1978;12:83–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


