Abstract
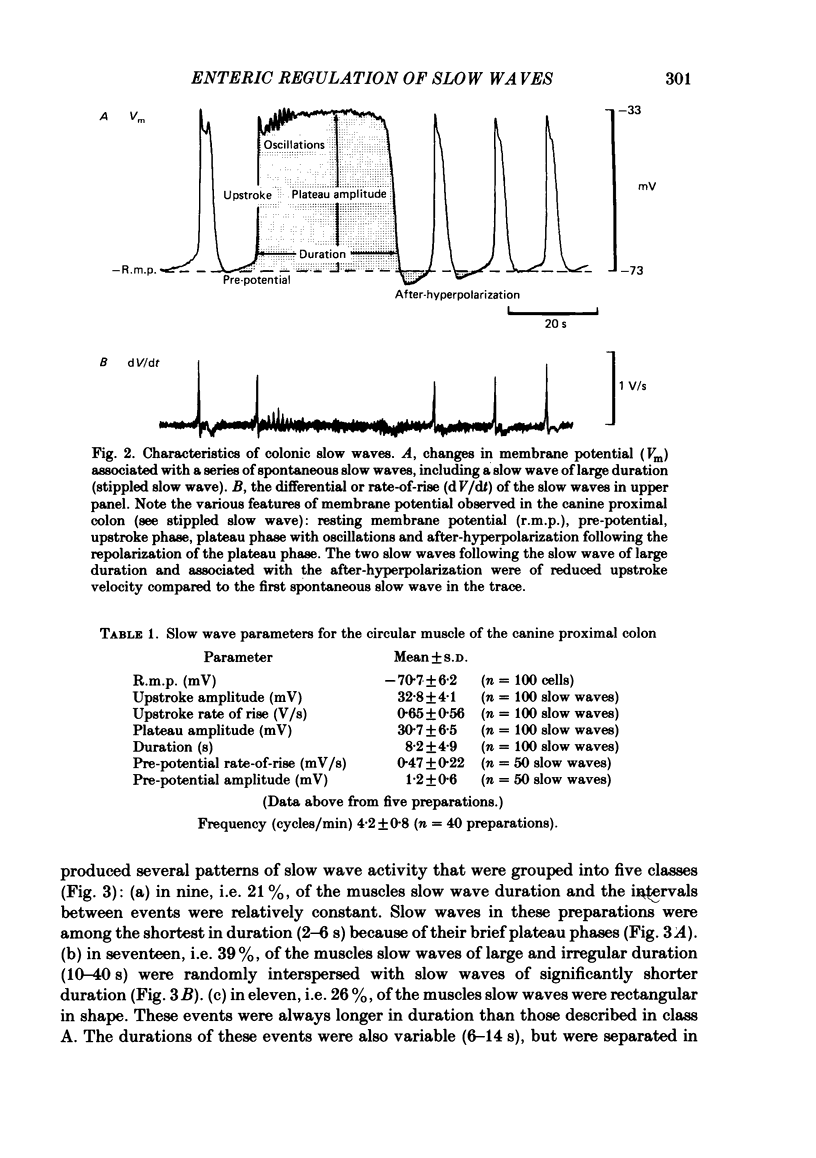
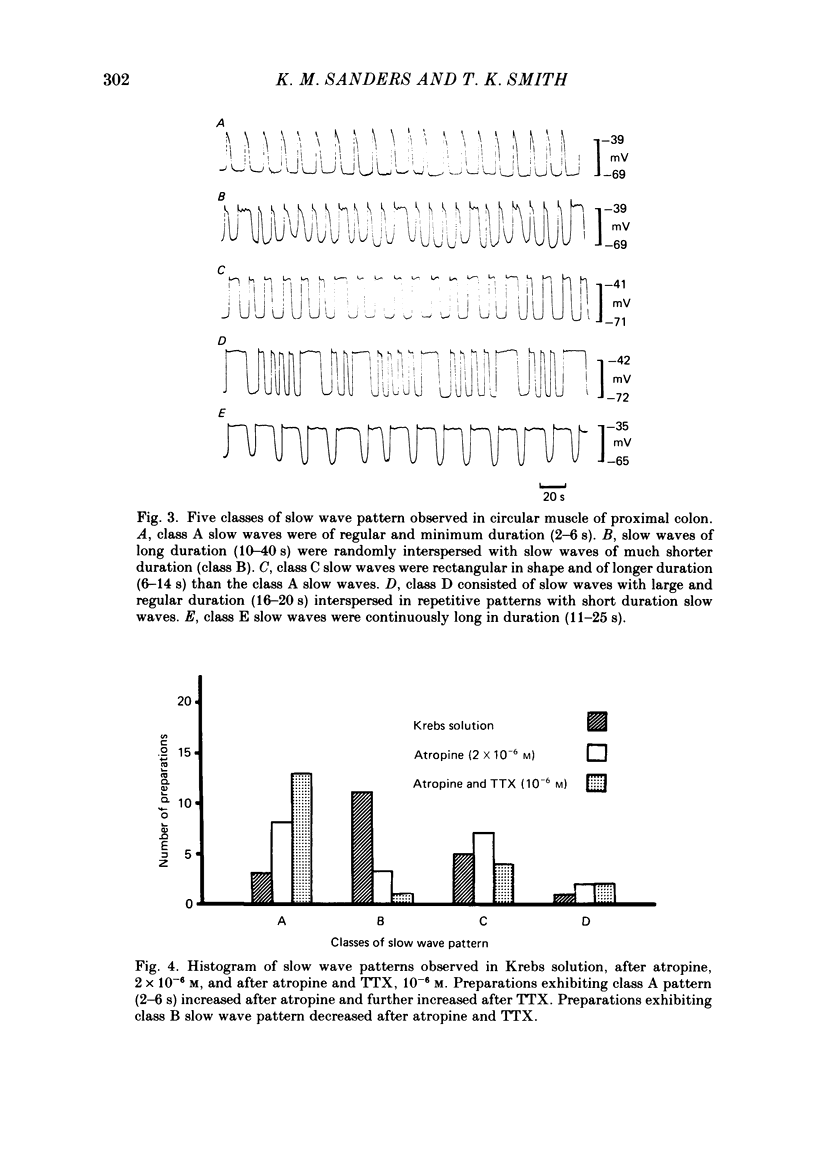
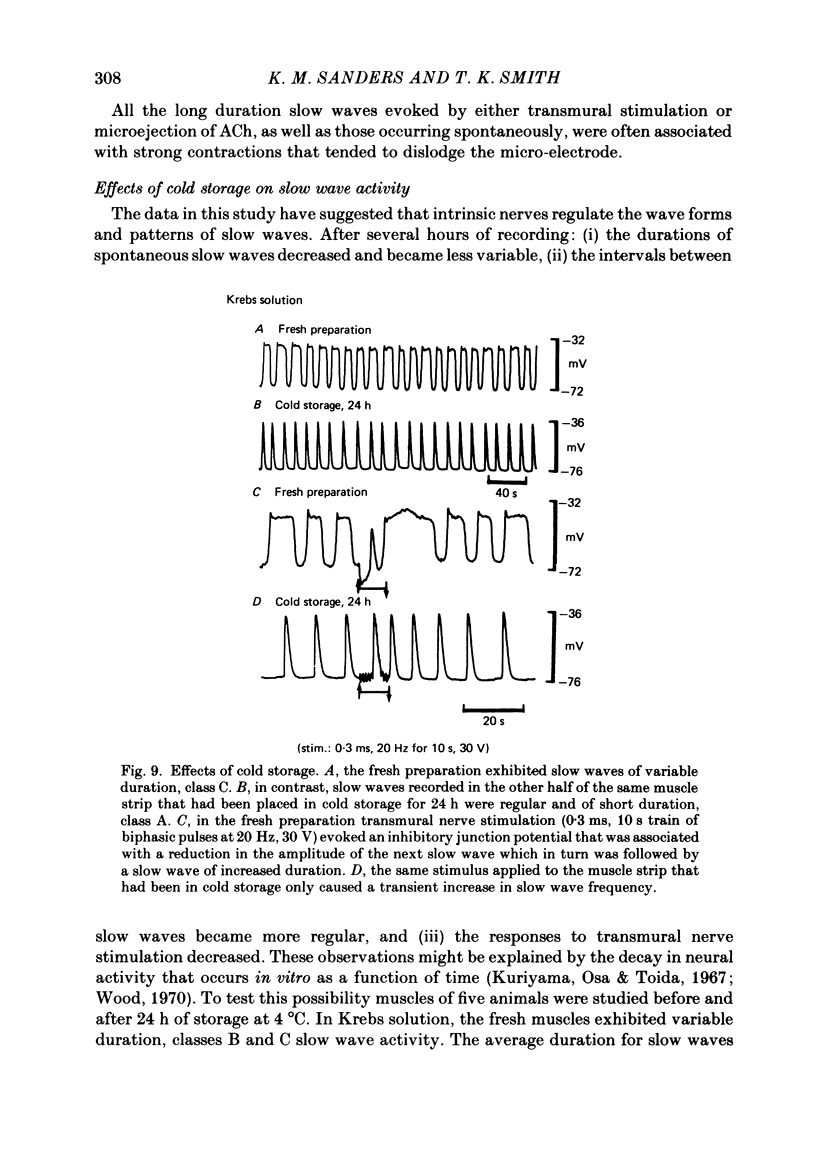
The spontaneous electrical activities of circular muscle cells of the canine proximal colon were studied with intracellular micro-electrodes. All circular muscle cells exhibited slow waves at frequencies ranging between 2.8 and 7.0 cycles/min. The slow waves consisted of an upstroke phase followed by a plateau phase of variable duration (2-40 s). Many cells displayed a slow diastolic depolarization, or 'pre-potential' between slow waves. Slow waves spontaneously varied in duration and frequency in most preparations, creating distinctive slow wave patterns. Atropine, 2 X 10(-6) M, decreased the durations of slow waves in many preparations and often changed the pattern to a series of relatively uniform slow waves. A further reduction in mean slow wave duration was produced by additional treatment with tetrodotoxin, 10(-6) M. These results suggested that slow wave duration and pattern were affected by spontaneous discharge from both cholinergic and non-cholinergic excitatory nerves. Transmural nerve stimulation caused a short latency increase in slow wave duration (up to 38 s) that was abolished by atropine. In the presence of atropine, transmural stimulation evoked inhibitory junction potentials that reduced the amplitude and duration of the subsequent slow wave. The slow wave of reduced amplitude was followed by a slow wave of increased duration. The increase in duration of the slow wave did not appear to be related to the size of the preceding hyperpolarization, suggesting it was mediated by the release from non-cholinergic excitatory nerves. All responses to transmural stimulation were blocked by tetrodotoxin. Microejection of acetylcholine on to the muscle adjacent to the micro-electrode also produced an atropine-sensitive increase in slow wave duration. Tissues that had been stored in the cold overnight to reduce intrinsic neural activity exhibited regular slow waves of short duration. It is proposed that the basic myogenic pattern of spontaneous slow wave activity consists of regularly occurring slow waves of short duration (2-5 s). Intrinsic cholinergic and non-cholinergic excitatory nerves appear to modulate slow wave activity in vitro, producing distinctive slow wave patterns of variable instantaneous frequency and duration.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BULBRING E., LIN R. C., SCHOFIELD G. An investigation of the peristaltic reflex in relation to anatomical observations. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1958 Jan;43(1):26–37. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1958.sp001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. J., Publicover N. G., Sanders K. M. Origin and spread of slow waves in canine gastric antral circular muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985 Dec;249(6 Pt 1):G800–G806. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.6.G800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortoff A. Electrical transmission of slow waves from longitudinal to circular intestinal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1965 Dec;209(6):1254–1260. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.6.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprilli R., Onori L. Origin, transmission and ionic dependence of colonic electrical slow waves. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1972;7(1):65–74. doi: 10.3109/00365527209180740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers M. M., Kingma Y. J., Bowes K. L. Intracellular electrical activity in circular muscle of canine colon. Gut. 1984 Nov;25(11):1268–1270. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.11.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Anuras S., Arthur C. Influence of intrinsic nerves on electromyogram of cat colon in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jun;234(6):E641–E647. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.6.E641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Caprilli R., Lund G. F. Electric slow waves in circular muscle of cat colon. Am J Physiol. 1969 Sep;217(3):771–776. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.3.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Kreulen D., Prosser C. L., Weigel R. Interaction between longitudinal and circular muscle in intestine of cat. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):665–689. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Prosser C. L., Weems W. A. A study of pace-maker activity in intestinal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;240(3):671–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groat W. C., Krier J. The central control of the lumbar sympathetic pathway to the large intestine of the cat. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:449–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durdle N. G., Kingma Y. J., Bowes K. L., Chambers M. M. Origin of slow waves in the canine colon. Gastroenterology. 1983 Feb;84(2):375–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Sharkawy T. Y., Daniel E. E. Electrical activity of small intestinal smooth muscle and its temperature dependence. Am J Physiol. 1975 Nov;229(5):1268–1276. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.5.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Sharkawy T. Y. Electrical activities of the muscle layers of the canine colon. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:67–83. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry R. C. The nervous control of the caudal region of the large bowel in the cat. J Physiol. 1933 Mar 15;77(4):422–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp002977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga J. D., Chang G., Diamant N. E., El-Sharkawy T. Y. Electrophysiological basis of excitation of canine colonic circular muscle by cholinergic agents and substance P. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Dec;231(3):692–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga J. D., Chang G., Diamant N. E., el-Sharkawy T. Y. The effects of cholecystokinin-octapeptide and pentagastrin on electrical and motor activities of canine colonic circular muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;62(12):1440–1447. doi: 10.1139/y84-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga J. D., Diamant N. E., El-Sharkawy T. Y. Electrical basis of contractions in the muscle layers of the pig colon. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):G482–G491. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.4.G482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Nagai T., Prosser C. L. Electrical interaction between muscle layers of cat intestine. Am J Physiol. 1966 Dec;211(6):1281–1291. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.6.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Osa T., Toida N. Nervous factors influencing the membrane activity of intestinal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(2):257–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K. G., Szurszewski J. H. Mechanisms of phasic and tonic actions of pentagastrin on canine gastric smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:229–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa H., Prosser C. L. Functions of neurons in enteric plexuses of cat intestine. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jun;222(6):1420–1426. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.6.1420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Vizi E. S., Zar M. A. The mechanism of acetylcholine release from parasympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):819–848. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M. Excitation-contraction coupling without Ca2+ action potentials in small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):C356–C361. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.5.C356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snape W. J., Jr, Shiff S. Neurohumoral control of colonic motility in the rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):G582–G588. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.4.G582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. Two types of neurones lacking synaptic input in the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:363–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuneberg L. Interstitial cells of Cajal: intestinal pacemaker cells? Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1982;71:1–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienbeck M., Christensen J. Effects of some drugs on electrical activity of the isolated colon of the cat. Gastroenterology. 1971 Oct;61(4):470–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D. Electrical activity from single neurons in Auerbach's plexus. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jul;219(1):159–169. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Intracellular study of electrical activity of Auerbach's plexus in guinea-pig small intestine. Pflugers Arch. 1978 May 31;374(3):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00585604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


