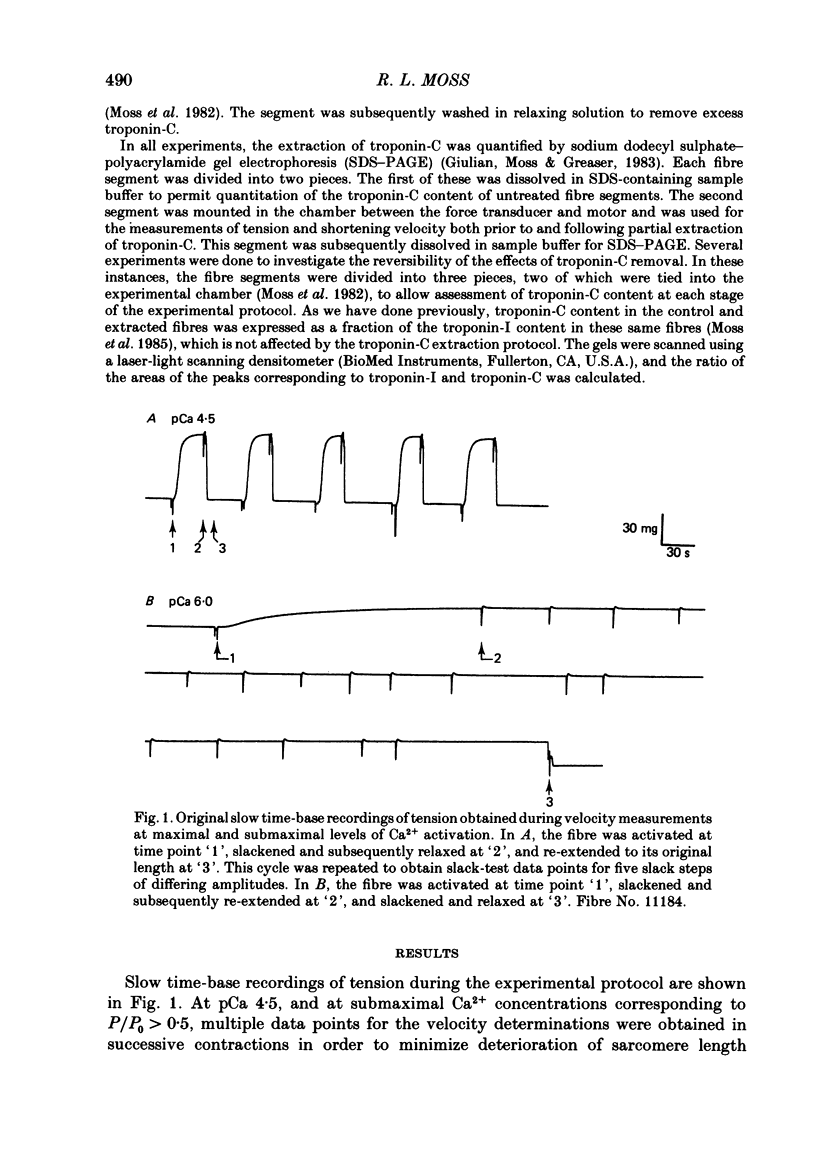
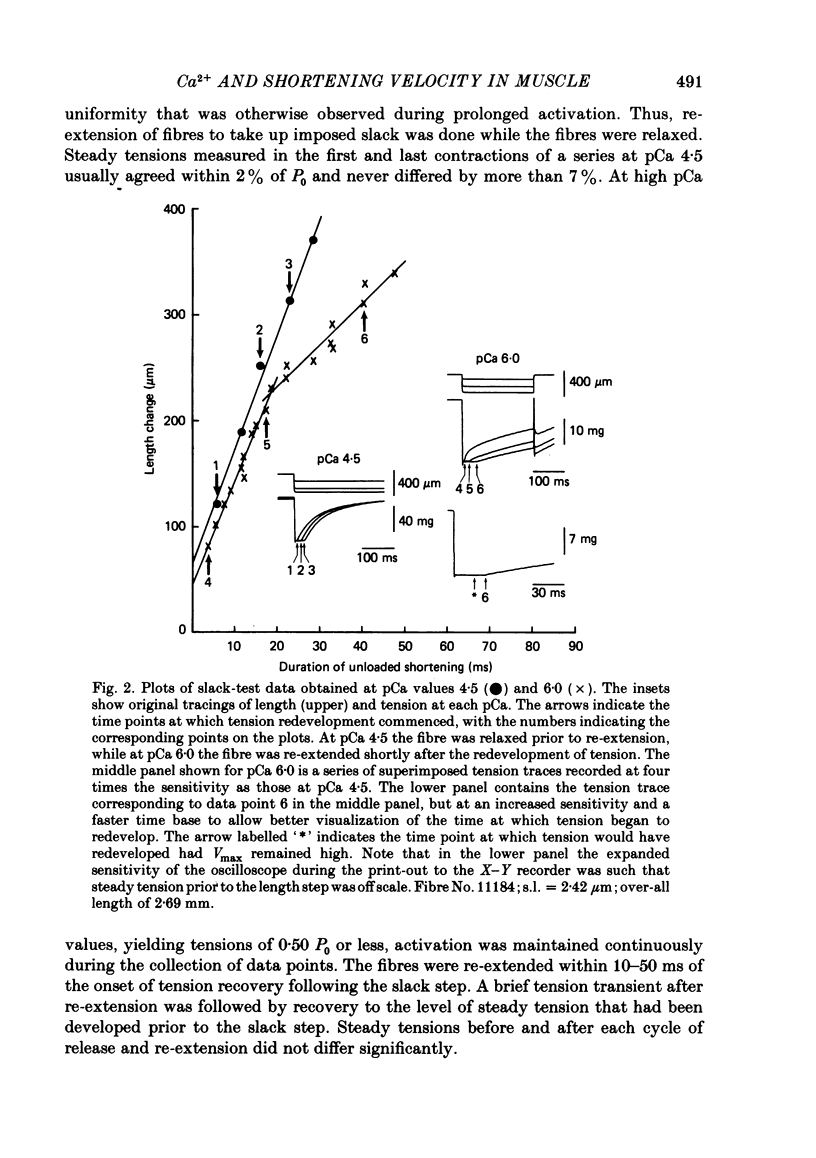
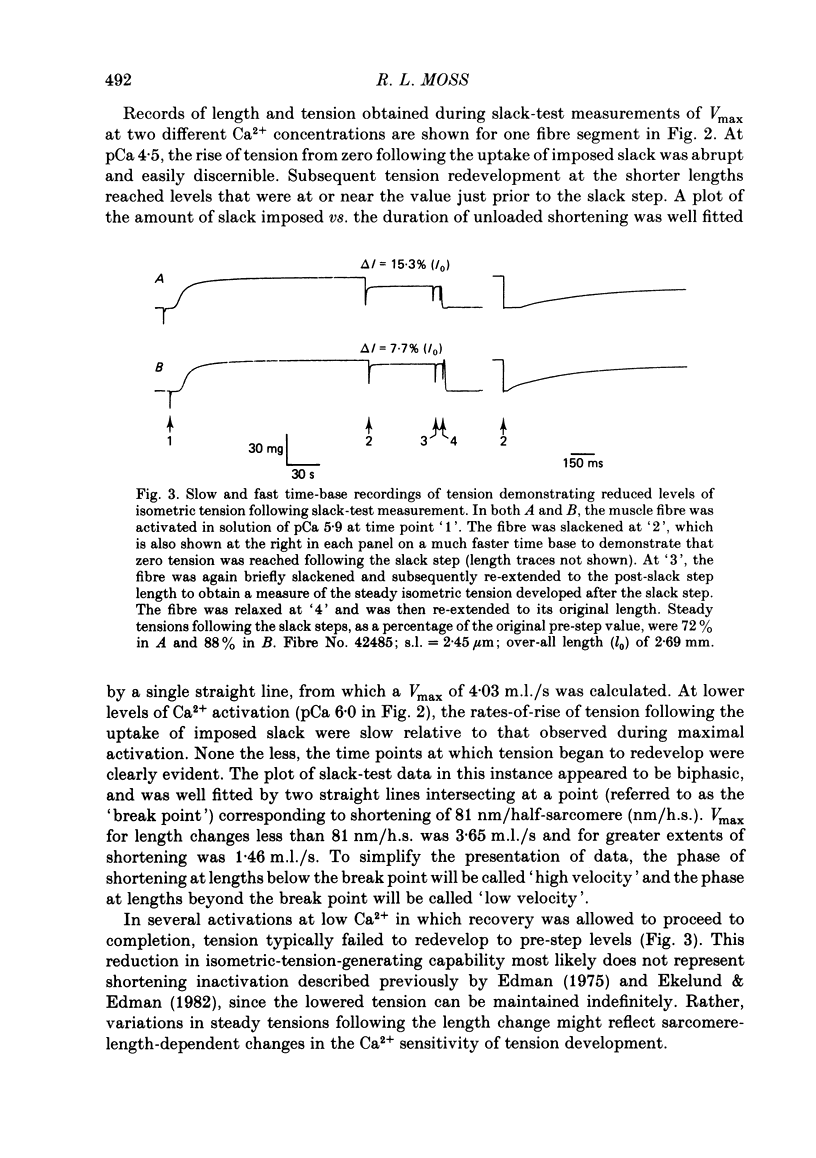
Abstract
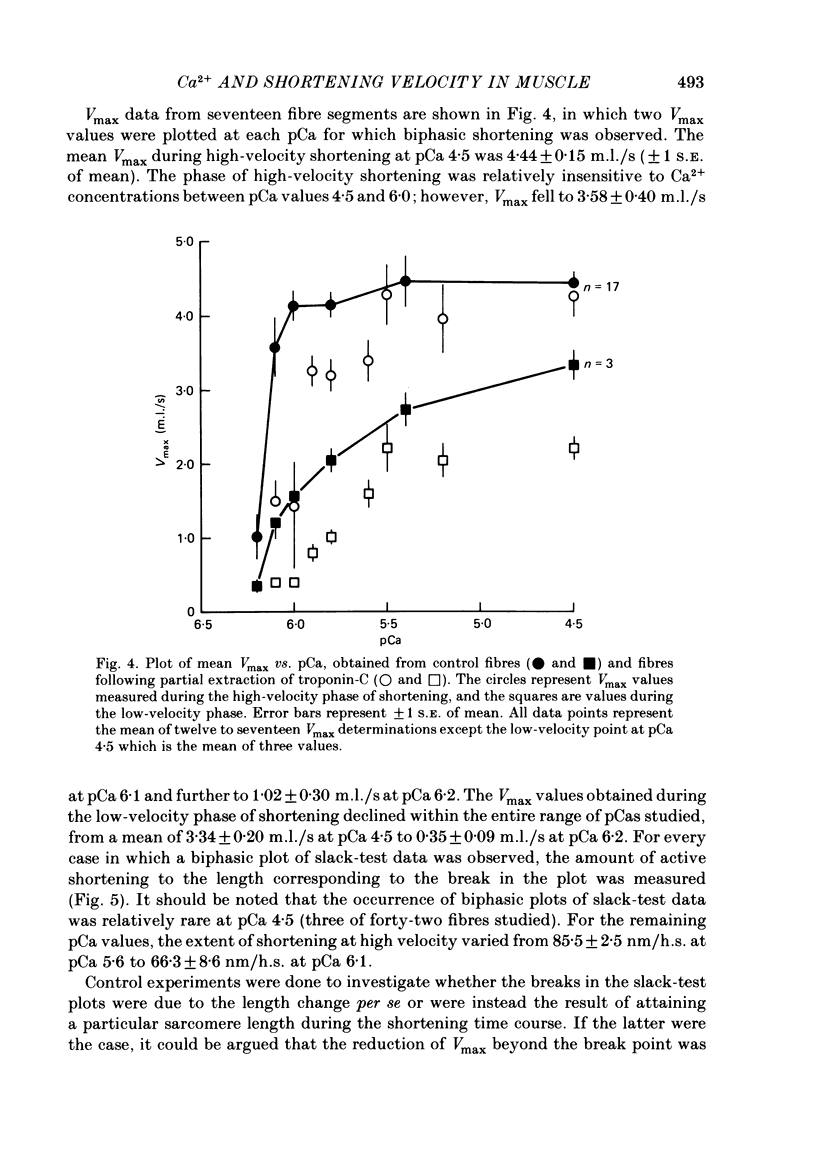
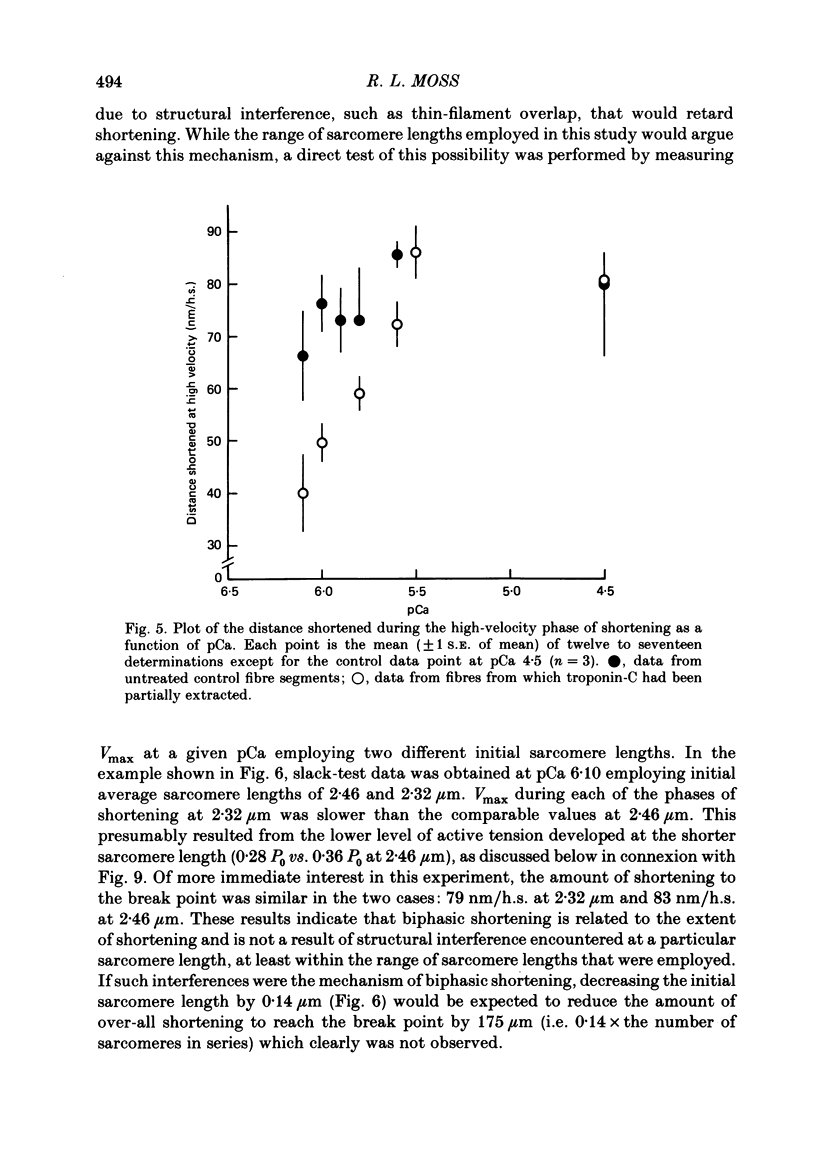
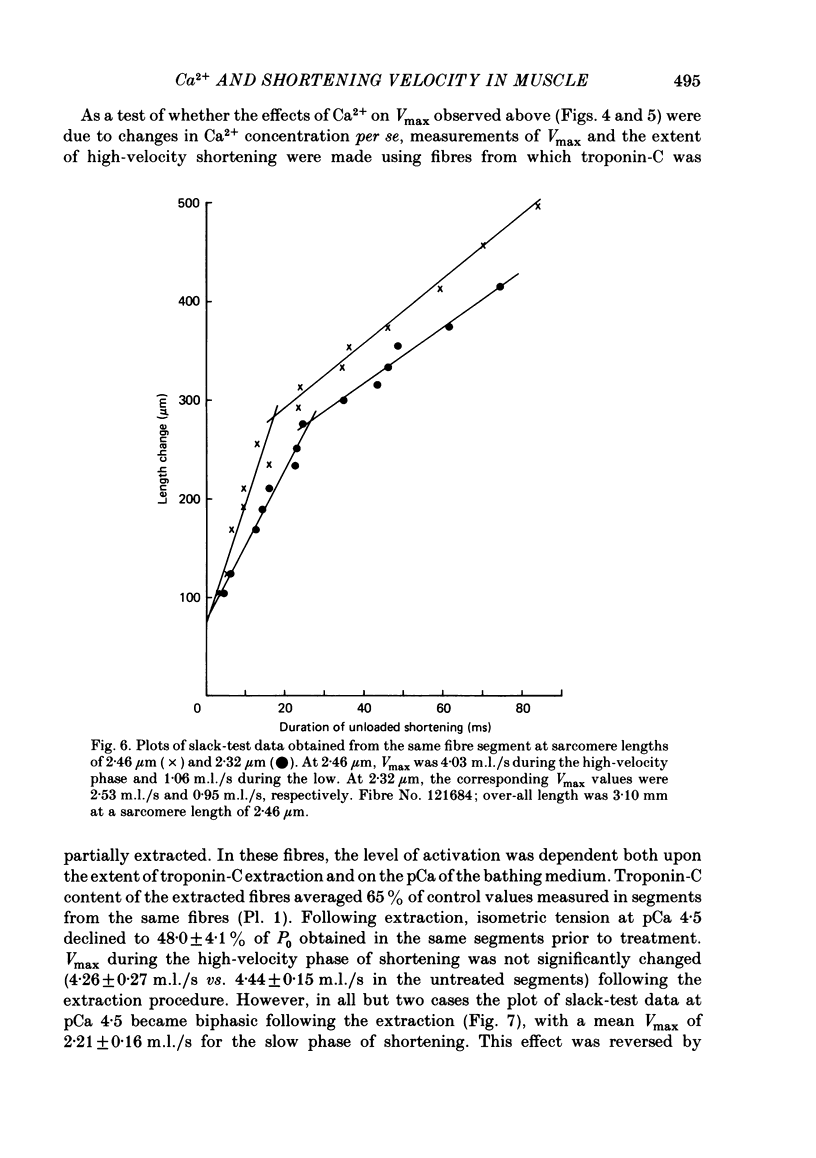
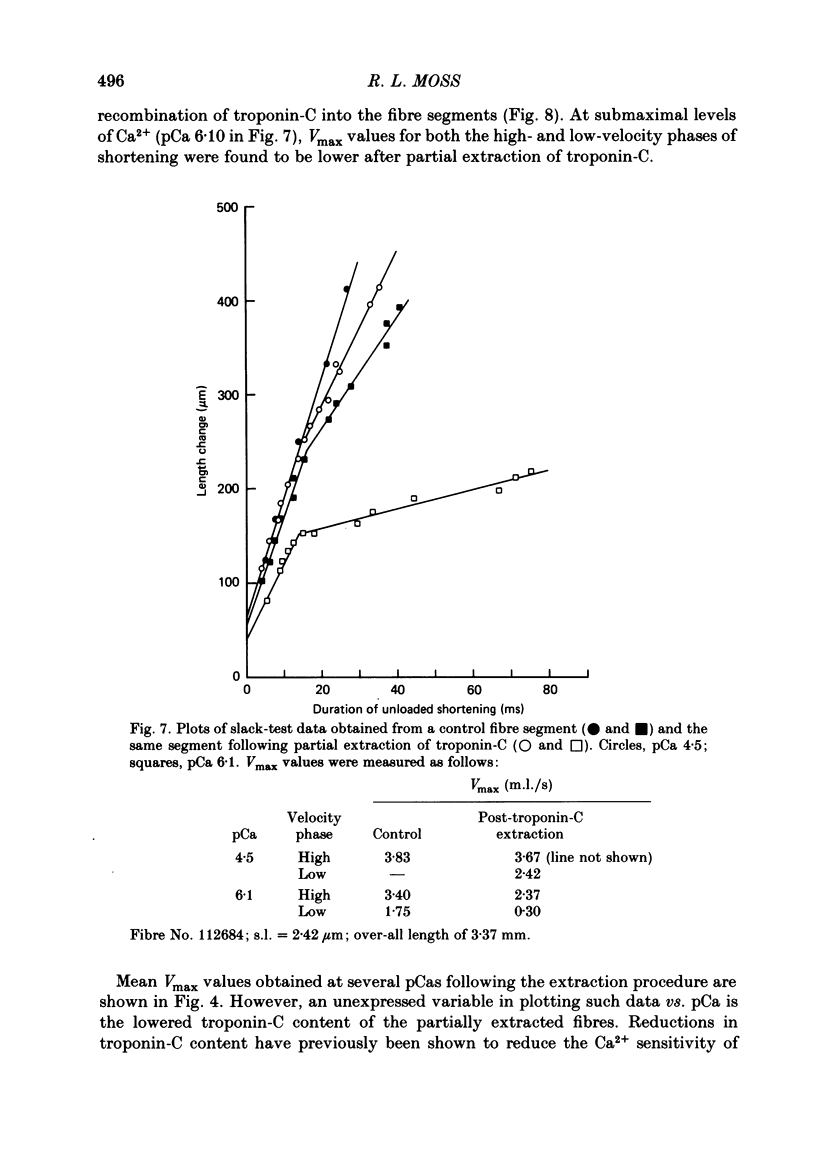
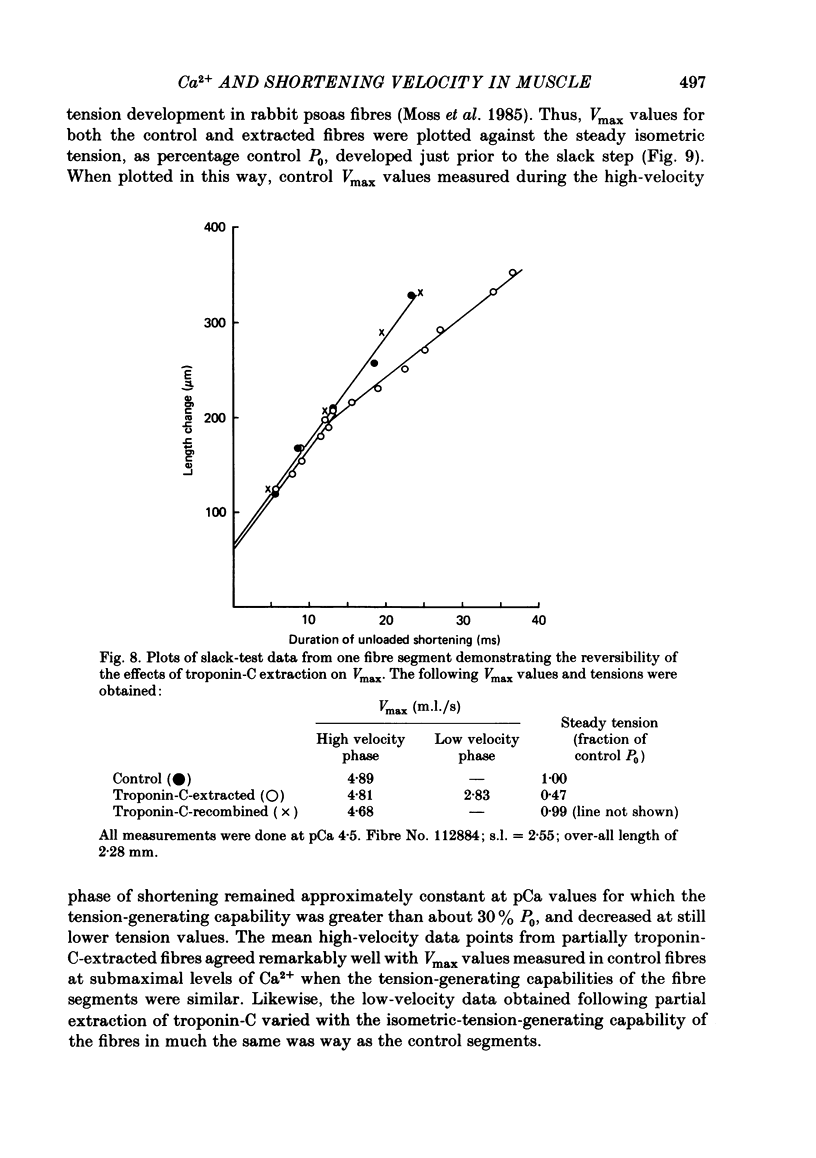
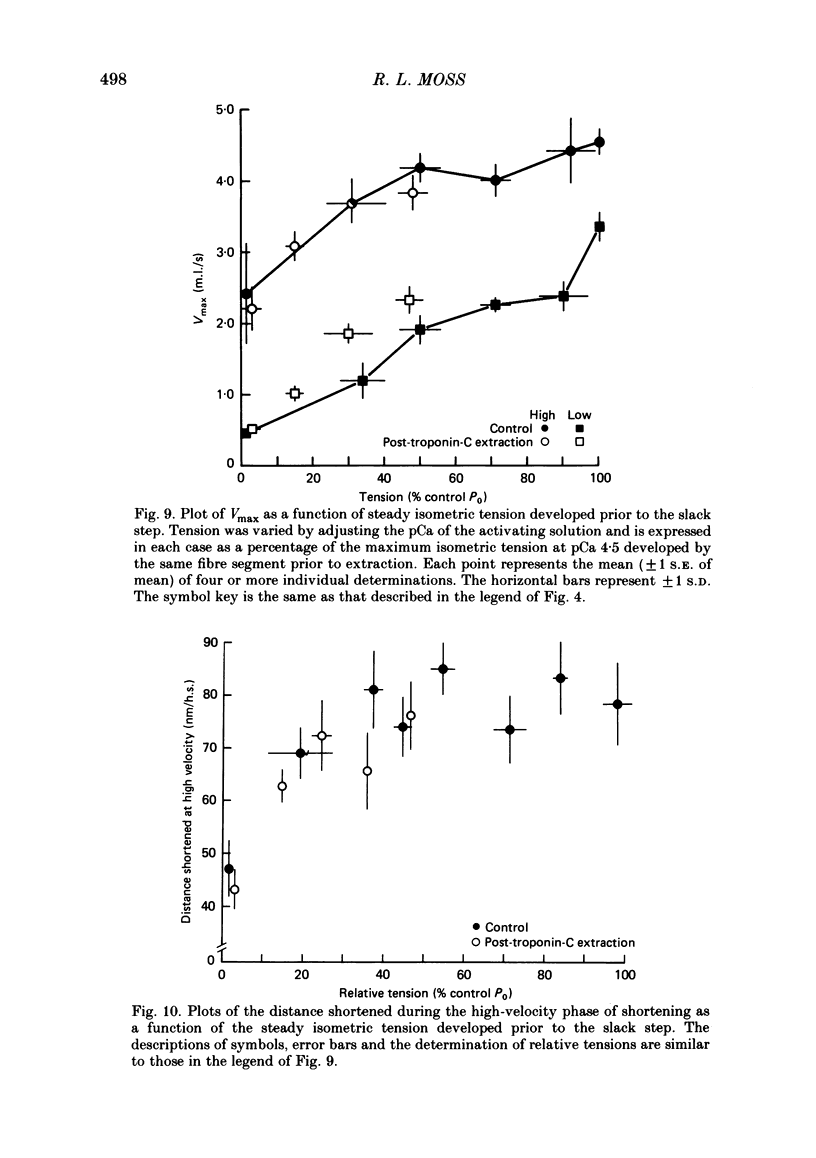
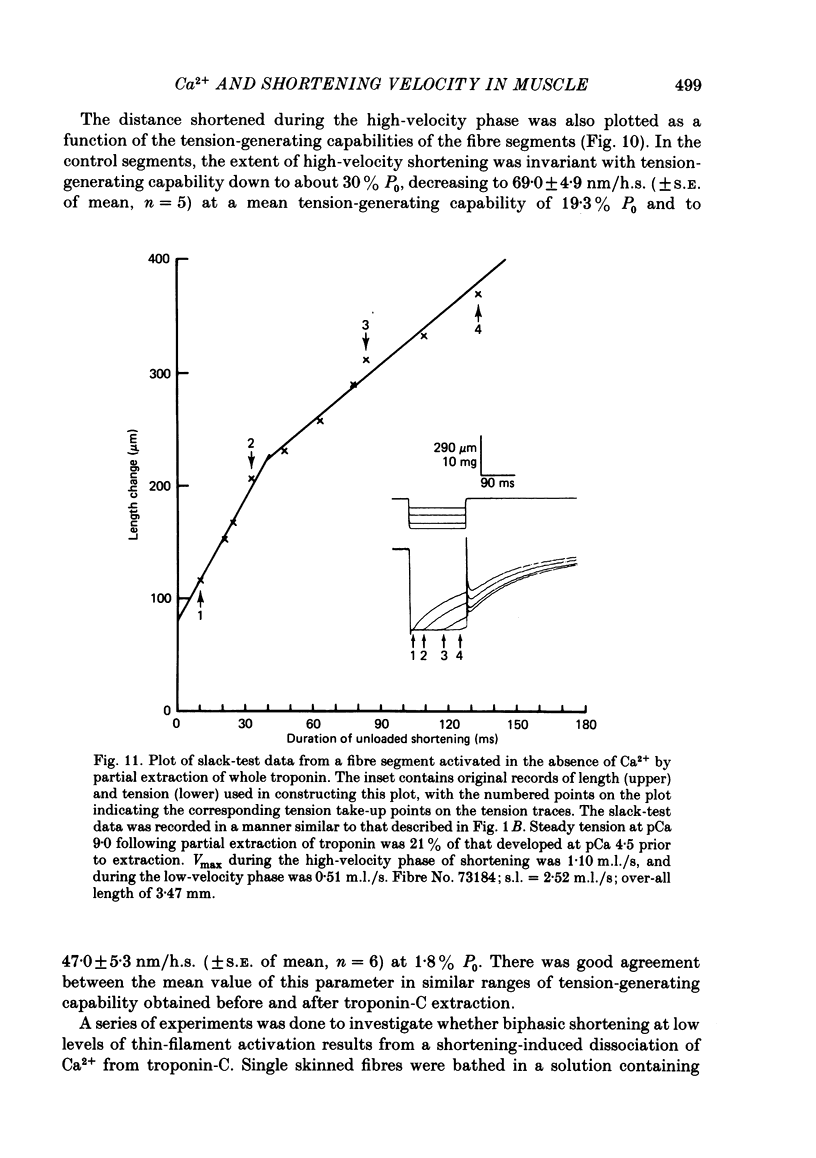
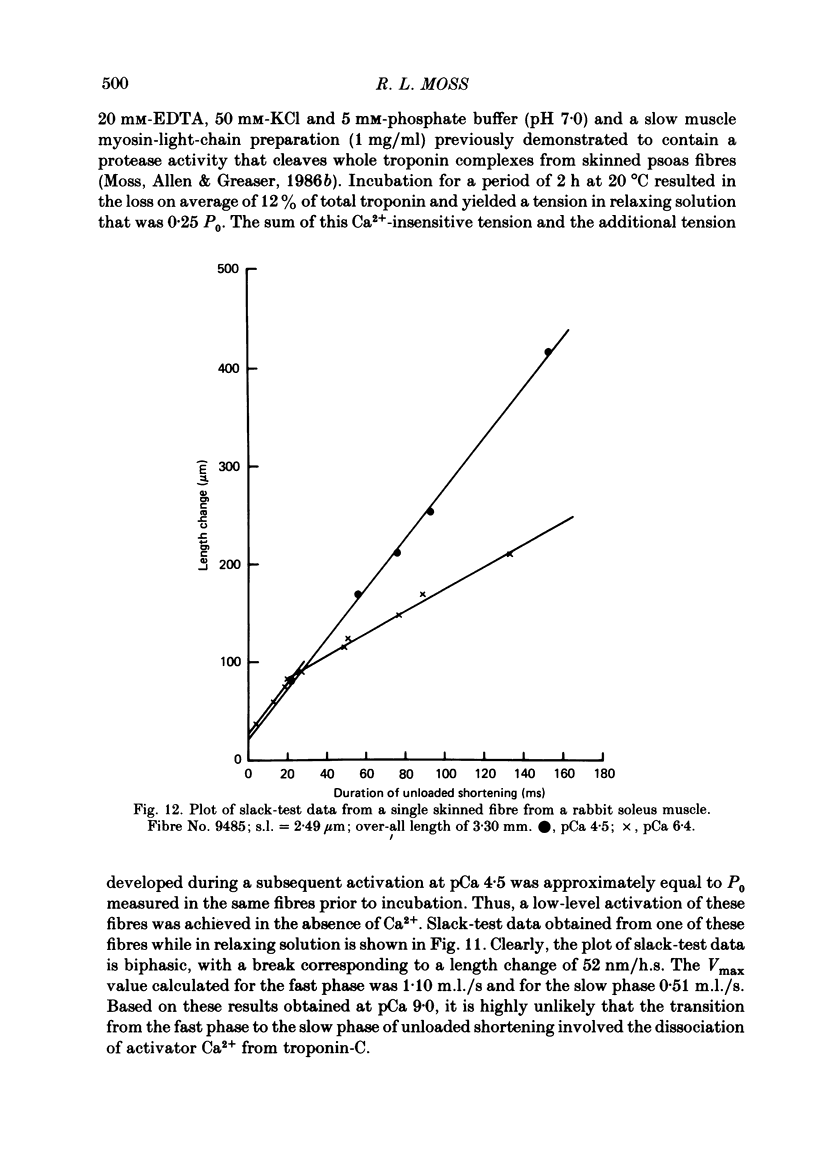
The effect of Ca2+ upon maximum shortening velocity (Vmax) has been investigated in skinned single fibres from rabbit psoas muscles. Vmax was obtained at 15 degrees C by measuring the amounts of time (delta t) required to take up various amounts of slack (delta l) imposed at one end of the fibre. During maximal activation with Ca2+, plots of delta l vs. delta t were well fitted by a single straight line. Calculation of Vmax from the slopes of the fitted lines yielded a Vmax of 4.44 +/- 0.15 (S.E. of mean) muscle lengths per second (m.l./s). However, at lower levels of Ca2+ activation, plots of delta l vs. delta t were biphasic, containing an initial phase of steady high-velocity shortening and a subsequent phase of steady low-velocity shortening. The transition between these two phases occurred following active shortening equivalent to 60-80 nm/half-sarcomere. Vmax during the high-velocity phase was relatively insensitive to Ca2+ concentration between pCas (i.e. -log [Ca2+]) of 4.5 and 6.0; however, Vmax fell to 3.58 +/- 0.40 m.l./s at pCa 6.1 and further to 1.02 +/- 0.30 m.l./s at pCa 6.2. Vmax during the low-velocity phase decreased as Ca2+ was lowered within the entire range of pCas studied to a minimum value of 0.35 +/- 0.09 m.l./s at pCa 6.2. The degree of thin-filament activation at a particular pCa was varied by partial extraction of troponin-C, which resulted in a permanent though reversible inactivation of parts of the thin filaments. Partial extraction of troponin-C altered the plots of delta l vs. delta t obtained at pCa 4.5 to a biphasic form. In addition, Vmax during the high- and low-velocity phases of shortening was reduced at each pCa greater than 4.5. Vmax values obtained in control fibres at low Ca2+ concentrations and extracted fibres were in good agreement when generated isometric tensions were equivalent. This was the case for both the high- and low-velocity phases of shortening. Fibres were also activated in the absence of Ca2+ by partial removal of total troponin complexes. These fibres developed steady tensions less than 30% of maximum and underwent biphasic shortening, indicating that this phenomenon cannot be the result of shortening-induced dissociation of Ca2+ from troponin-C.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bremel R. D., Weber A. Cooperation within actin filament in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):97–101. doi: 10.1038/newbio238097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Eisenberg E. Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity by troponin-tropomyosin without blocking the binding of myosin to actin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2432–2437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. A., Comte M., Stein E. A. Calmodulin-free skeletal-muscle troponin C prepared in the absence of urea. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):205–211. doi: 10.1042/bj1950205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman K. A. Mechanical deactivation induced by active shortening in isolated muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(1):255–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman K. A. The velocity of unloaded shortening and its relation to sarcomere length and isometric force in vertebrate muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:143–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund M. C., Edman K. A. Shortening induced deactivation of skinned fibres of frog and mouse striated muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Oct;116(2):189–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Tension responses to sudden length change in stimulated frog muscle fibres near slack length. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):441–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
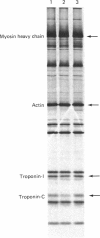
- Giulian G. G., Moss R. L., Greaser M. Improved methodology for analysis and quantitation of proteins on one-dimensional silver-stained slab gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Mar;129(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90551-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Lindley B. D. Influence of temperature upon contractile activation and isometric force production in mechanically skinned muscle fibers of the frog. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Aug;80(2):279–297. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Morgan D. L. The effect on tension of non-uniform distribution of length changes applied to frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:379–392. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Moss R. L. Effects of calcium and ionic strength on shortening velocity and tension development in frog skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:179–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Moss R. L., Waller G. S. Mechanical properties and myosin light chain composition of skinned muscle fibres from adult and new-born rabbits. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:201–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J. The effect of calcium on the force-velocity relation of briefly glycerinated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):117–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavis P. C., Gergely J. Thin filament proteins and thin filament-linked regulation of vertebrate muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(3):235–305. doi: 10.3109/10409238409108717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W. Thick-filament-linked calcium regulation in vertebrate striated muscle. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):80–81. doi: 10.1038/274080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Giulian G. G., Greaser M. L. Effects of EDTA treatment upon the protein subunit composition and mechanical properties of mammalian single skeletal muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):970–978. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Giulian G. G., Greaser M. L. Physiological effects accompanying the removal of myosin LC2 from skinned skeletal muscle fibers. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8588–8591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Giulian G. G., Greaser M. L. The effects of partial extraction of TnC upon the tension-pCa relationship in rabbit skinned skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Oct;86(4):585–600. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L. Sarcomere length-tension relations of frog skinned muscle fibres during calcium activation at short lengths. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:177–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L. The effect of calcium on the maximum velocity of shortening in skinned skeletal muscle fibres of the rabbit. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1982 Sep;3(3):295–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00713039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolin R. A., Ford L. E. The influence of calcium on shortening velocity of skinned frog muscle cells. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Jun;4(3):263–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00711996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky R. J., Teichholz L. E. The relation between calcium and contraction kinetics in skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;211(1):19–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway E. B., Gordon A. M., Martyn D. A. Hysteresis in the force-calcium relation in muscle. Science. 1983 Mar 4;219(4588):1075–1077. doi: 10.1126/science.6823567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thames M. D., Teichholz L. E., Podolsky R. J. Ionic strength and the contraction kinetics of skinned muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Apr;63(4):509–530. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.4.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. M., Rondinone J. F., Briggs F. N. Effect of calcium on force-velocity characteristics of glycerinated skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):973–979. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida T., Arata T., Oosawa F. Sliding distance of actin filament induced by a myosin crossbridge during one ATP hydrolysis cycle. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):366–369. doi: 10.1038/316366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]