Abstract
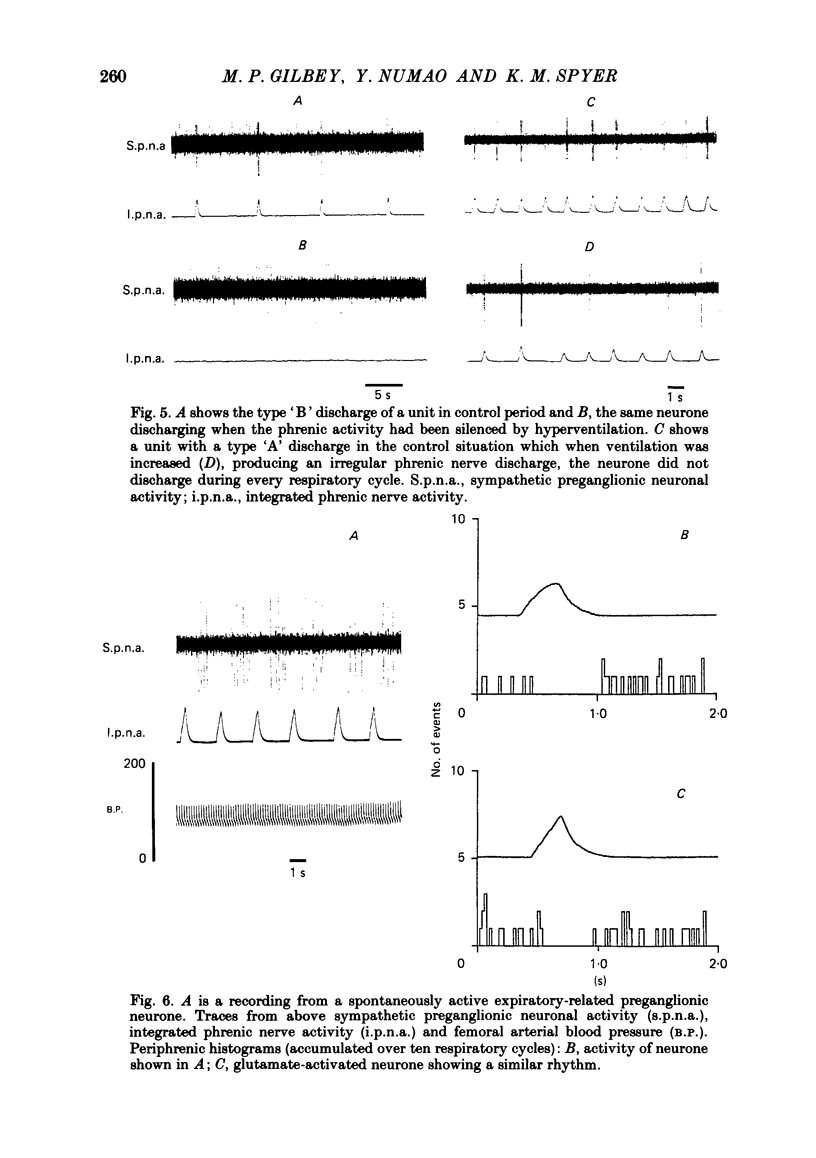
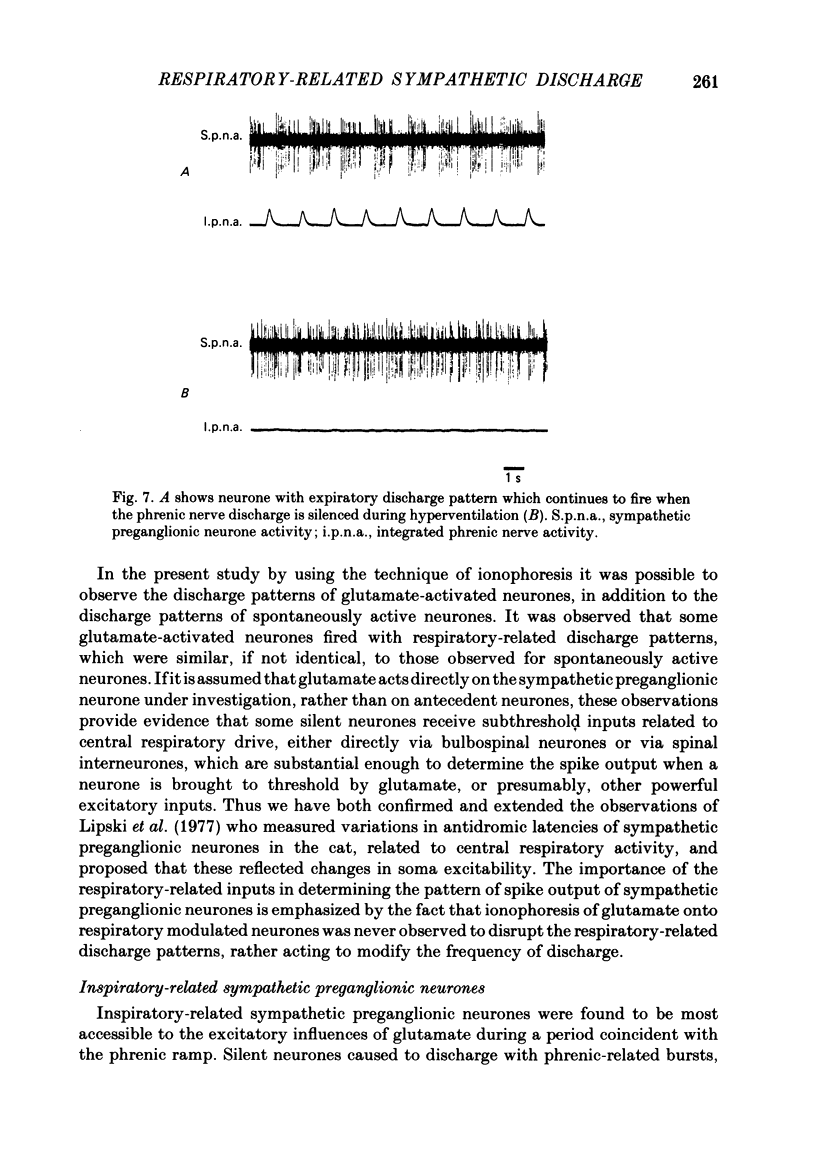
The central respiratory-drive-related inputs to antidromically identified cervical sympathetic preganglionic neurones have been investigated, in the rat, using extracellular recording techniques, the ionophoretic application of an excitatory amino acid (glutamate) to increase their excitability, and phrenic nerve discharge as an indicator of central respiratory drive. Three distinct firing patterns of sympathetic preganglionic neurones are described: maximal discharge during phrenic nerve activity, maximal discharge during phrenic silence, and a firing pattern unrelated to phrenic nerve discharge. Both spontaneously active and glutamate-activated silent cervical sympathetic preganglionic neurones had similar, if not identical, firing patterns. The application of glutamate, using ionophoretic currents of up to 100 nA, did not disrupt central respiratory-drive-related discharge patterns indicating that these inputs are an important contribution in the regulation of the firing pattern of a proportion of sympathetic preganglionic neurones. On the basis of these observations it is proposed that some sympathetic preganglionic neurones may receive central respiratory drive potentials similar to those received by respiratory motoneurones.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Takeda K., Umbach J. A. Inhibitors of calcium buffering depress evoked transmitter release at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:145–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian E. D., Bronk D. W., Phillips G. Discharges in mammalian sympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1932 Feb 8;74(2):115–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1932.sp002832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachoo M., Polosa C. Properties of a sympatho-inhibitory and vasodilator reflex evoked by superior laryngeal nerve afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:183–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton C. R., Kirkwood P. A. The effect of carbon dioxide on the tonic and the rhythmic discharges of expiratory bulbospinal neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:291–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton C. R., Richter D. W., Seller H., Ballantyne D., Klein J. P. Respiratory modulation of sympathetic activity. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1985 Jan;12(1):77–90. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(85)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne D., Richter D. W. Post-synaptic inhibition of bulbar inspiratory neurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:67–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne D., Richter D. W. The non-uniform character of expiratory synaptic activity in expiratory bulbospinal neurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:433–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barman S. M., Gebber G. L. Basis for synchronization of sympathetic and phrenic nerve discharges. Am J Physiol. 1976 Nov;231(5 Pt 1):1601–1607. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.5.1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger A. J. Phrenic motoneurons in the cat: subpopulations and nature of respiratory drive potentials. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Jan;42(1 Pt 1):76–90. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. I. Discharge patterns of brain-stem respiratory neurons in relation to carbon dioxide tension. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Mar;31(2):142–165. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.2.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. I., Gootman P. M. Periodicities in efferent discharge of splanchnic nerve of the cat. Am J Physiol. 1970 Apr;218(4):1092–1101. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.4.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Westbury D. R. Intracellular recordings from sympathetic preganglionic neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Dec;15(2-3):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)96108-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembowsky K., Czachurski J., Seller H. An intracellular study of the synaptic input to sympathetic preganglionic neurones of the third thoracic segment of the cat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1985 Jul;13(3):201–244. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(85)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez de Molina A., Kuno M., Perl E. R. Antidromically evoked responses from sympathetic preganglionic neurones. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(2):321–335. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber U., Polosa C. Effects of pulmonary stretch receptor afferent stimulation on sympathetic preganglionic neuron firing. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Apr;56(2):191–198. doi: 10.1139/y78-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber U., Polosa C. Some effects of superior laryngeal nerve stimulation on sympathetic preganglionic neuron firing. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;57(10):1073–1081. doi: 10.1139/y79-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey M. P., Coote J. H., Fleetwood-Walker S., Peterson D. F. The influence of the paraventriculo-spinal pathway, and oxytocin and vasopressin on sympathetic preganglionic neurones. Brain Res. 1982 Nov 18;251(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90745-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey M. P., Jordan D., Richter D. W., Spyer K. M. Synaptic mechanisms involved in the inspiratory modulation of vagal cardio-inhibitory neurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:65–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey M. P., Peterson D. F., Coote J. H. Some characteristics of sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the rat. Brain Res. 1982 Jun 3;241(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor M., Jänig W., Wiprich L. Cardiac and respiratory rhythmicities in cutaneous and muscle vasoconstrictor neurones to the cat's hindlimb. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Sep 16;370(3):299–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00585543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D., Spyer K. M. Effects of acetylcholine on respiratory neurones in the nucleus ambiguus-retroambigualis complex of the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:103–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänig W., Szulczyk P. Functional properties of lumbar preganglionic neurones. Brain Res. 1980 Mar 17;186(1):115–131. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubin L., Trzebski A., Lipski J. Split medulla preparation in the cat: arterial chemoreceptor reflex and respiratory modulation of the renal sympathetic nerve activity. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1985 Feb-Mar;12(2-3):211–225. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(85)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J., Coote J. H., Trzebski A. Temporal patterns of antidromic invasion latencies of sympathetic preganglionic neurons related to central inspiratory activity and pulmonary stretch receptor reflex. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 21;135(1):162–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannard A., Rajchgot P., Polosa C. Effect of post-impulse depression on background firing of sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Brain Res. 1977 May 6;126(2):243–261. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90724-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan E. M., Hirst G. D. Some properties of preganglionic neurons in upper thoracic spinal cord of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1980 May;43(5):1251–1265. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.5.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss G., Kirchner F., Polosa C. Patterning of sympathetic preganglionic neuron firing by the central respiratory drive. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 11;87(2-3):363–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss G., Polosa C. The relation between end-tidal CO2 and discharge patterns of sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 18;122(2):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90293-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. THE SLOW POTENTIALS OF THORACIC RESPIRATORY MOTONEURONES AND THEIR RELATION TO BREATHING. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:404–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saum W. R., Brown A. M., Tuley F. H. An electrogenic sodium pump and baroreceptor function in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circ Res. 1976 Oct;39(4):497–505. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.4.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


