Abstract
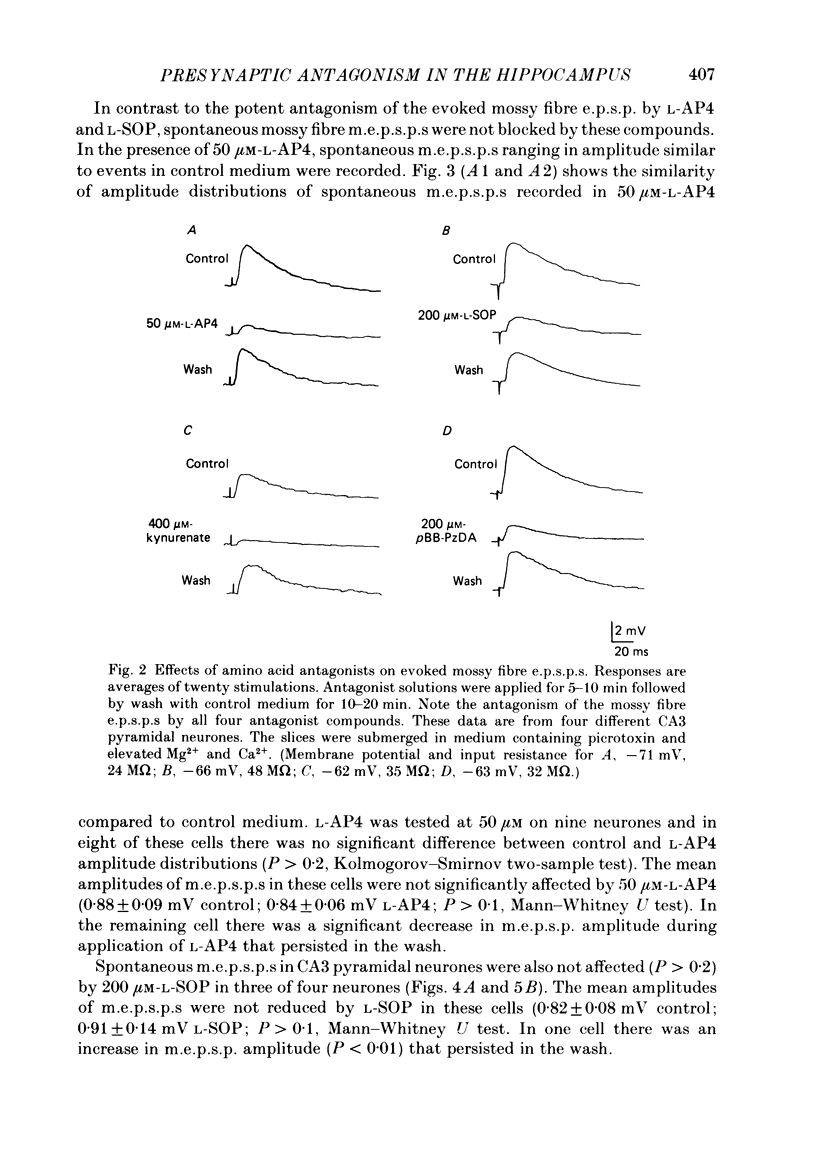
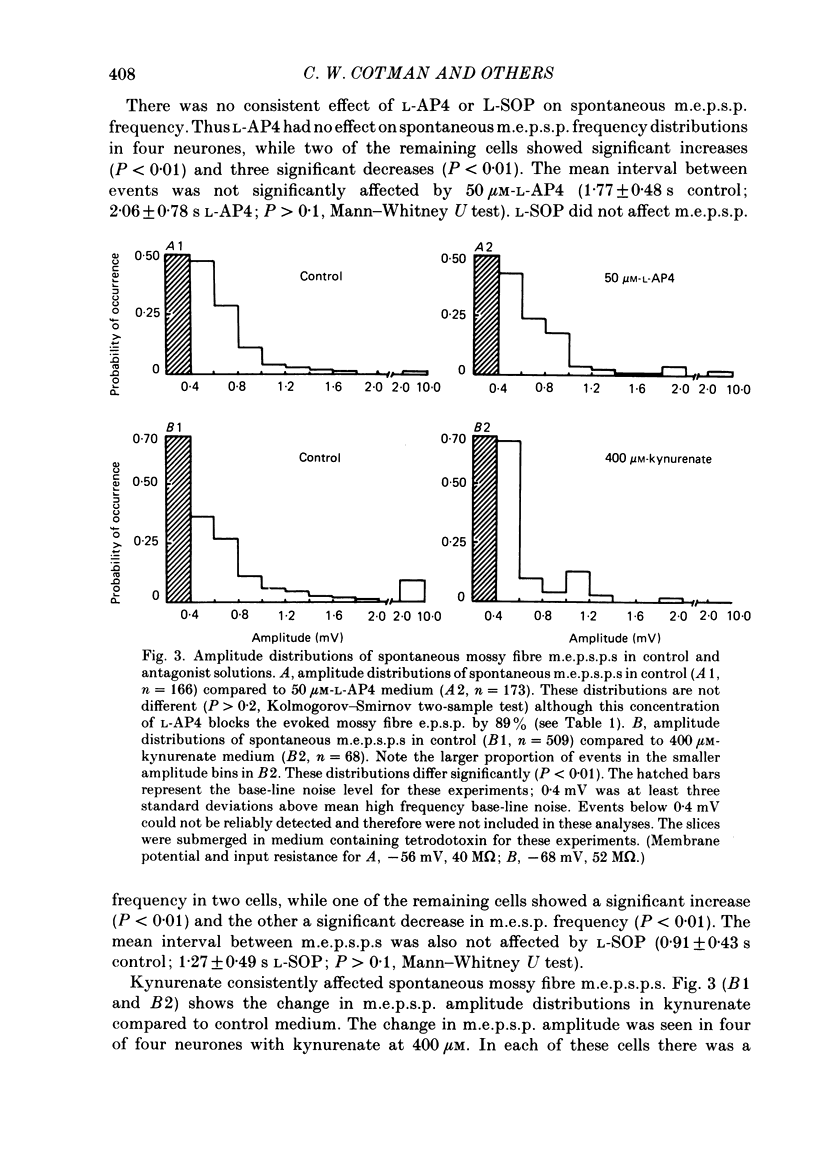
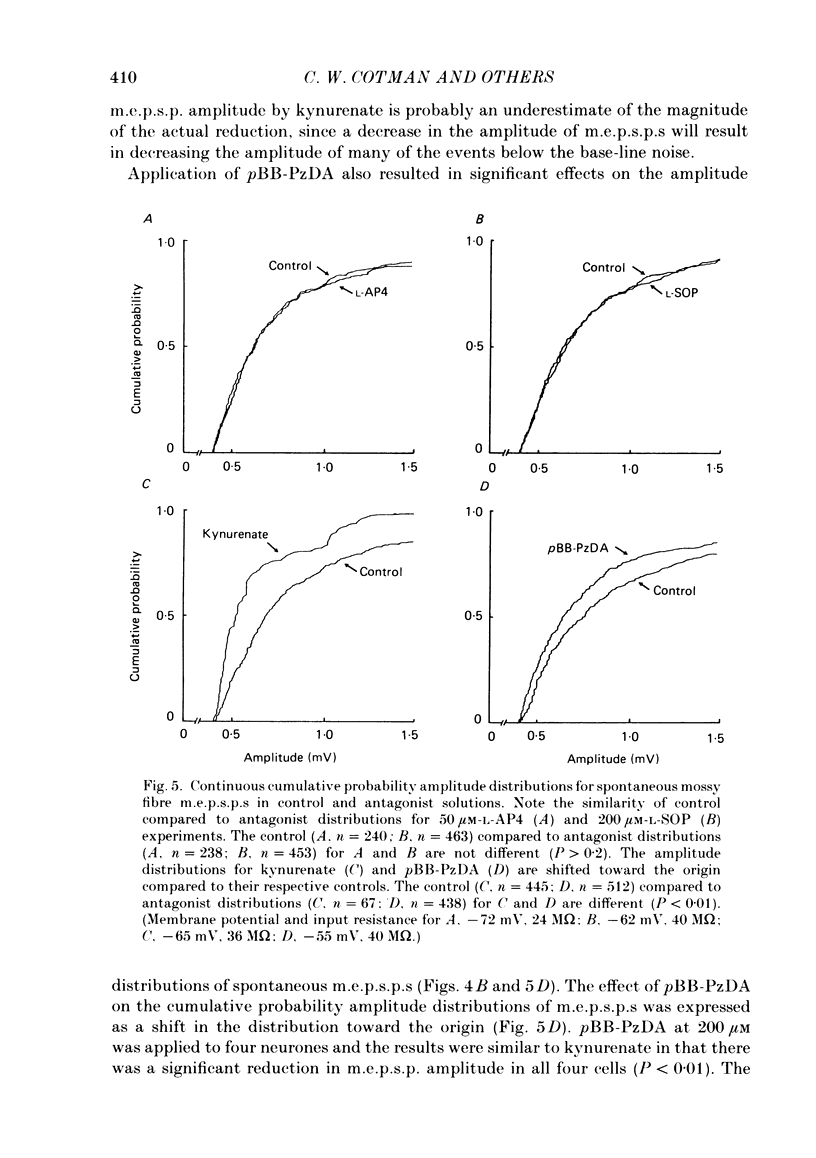
Evoked and spontaneous excitatory post-synaptic potentials (e.p.s.p.s) at the mossy fibre input to CA3 pyramidal neurones were recorded intracellularly in slices from the guinea-pig hippocampus. The effects of several amino acid antagonists on these responses were examined. L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate (L-AP4), L-serine-O-phosphate (L-SOP), kynurenate, and N-(p-bromobenzoyl)piperazine-2,3-dicarboxylate (pBB-PzDA) reduced the amplitude of evoked mossy fibre e.p.s.p.s without affecting membrane potential or input resistance. Antagonism of mossy fibre spontaneous miniature e.p.s.p.s (m.e.p.s.p.s) by these compounds fell into two groups. L-AP4 and L-SOP applied at concentrations that blocked evoked e.p.s.p.s did not affect amplitude distributions of spontaneous m.e.p.s.p.s. Kynurenate and pBB-PzDA significantly affected the amplitude distributions and reduced the mean amplitude of spontaneous m.e.p.s.p.s. These results are consistent with a presynaptic site of action for L-AP4 and L-SOP and a post-synaptic site of action for kynurenate and pBB-PzDA as antagonists of e.p.s.p.s at the guinea-pig mossy fibre-CA3 pyramidal neurone synapse.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annoni J. M., Cochran S. L., Precht W. Pharmacology of the vestibular hair cell-afferent fiber synapse in the frog. J Neurosci. 1984 Aug;4(8):2106–2116. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-08-02106.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Johnston D. Voltage-clamp analysis of mossy fiber synaptic input to hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Aug;50(2):487–507. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.2.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Spontaneous miniature synaptic potentials in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1979 Nov 9;177(1):194–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90931-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. Excitatory amino acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. The action of some analogues of the excitatory amino acids in the dentate gyrus of the rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Apr;62(4):424–429. doi: 10.1139/y84-067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. The antagonism of amino acid-induced excitations of rat hippocampal CA1 neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:19–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G., Anson J., Surtees L. Presynaptic kainate and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors regulate excitatory amino acid release in the olfactory cortex. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 11;265(1):157–159. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G. Some effects of excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists on synaptic transmission in the rat olfactory cortex slice. Brain Res. 1982 Jul 29;244(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crunelli V., Forda S., Kelly J. S. Blockade of amino acid-induced depolarizations and inhibition of excitatory post-synaptic potentials in rat dentate gyrus. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:627–640. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Jones A. W., Sheardown M. J., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. Phosphono dipeptides and piperazine derivatives as antagonists of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation in mammalian and amphibian spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Nov 23;52(1-2):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Actions of D and L forms of 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate and 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 11;235(2):378–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Foster A. C. Amino acid neurotransmitters and their pathways in the mammalian central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1983 Aug;9(4):701–719. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Foster A. C., Harris E. W., Lanthorn T. H., Cotman C. W. Structure--activity relationships of L-glutamate receptor ligands: role of the omega-acidic terminal. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Jul 20;31(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferkany J. W., Zaczek R., Coyle J. T. Kainic acid stimulates excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter release at presynaptic receptors. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):757–759. doi: 10.1038/298757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong A. H., Cotman C. W. Acidic amino acid antagonists of lateral perforant path synaptic transmission: agonist-antagonist interactions in the dentate gyrus. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Dec 30;34(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong A. H., Cotman C. W. Kynurenic acid and quinolinic acid act at N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the rat hippocampus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jan;236(1):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong A. H., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C., Cotman C. W. Parallel antagonism of synaptic transmission and kainate/quisqualate responses in the hippocampus by piperazine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid analogs. J Neurosci. 1986 Apr;6(4):930–937. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-04-00930.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong A. H., Lanthorn T. H., Cotman C. W. Kynurenic acid inhibits synaptic and acidic amino acid-induced responses in the rat hippocampus and spinal cord. Brain Res. 1983 Aug 22;273(1):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. W., Cotman C. W. Effects of acidic amino acid antagonists on paired-pulse potentiation at the lateral perforant path. Exp Brain Res. 1983;52(3):455–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00238039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. W., Cotman C. W. Effects of synaptic antagonists on perforant path paired-pulse plasticity: differentiation of pre- and postsynaptic antagonism. Brain Res. 1985 May 20;334(2):348–353. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrling P. L. Pharmacology of the corticocaudate excitatory postsynaptic potential in the cat: evidence for its mediation by quisqualate- or kainate-receptors. Neuroscience. 1985 Feb;14(2):417–426. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori N., Auker C. R., Braitman D. J., Carpenter D. O. Pharmacologic sensitivity of amino acid responses and synaptic activation of in vitro prepyriform neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Dec;48(6):1289–1301. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.6.1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner J. F., Cotman C. W. Micromolar L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid selectively inhibits perforant path synapses from lateral entorhinal cortex. Brain Res. 1981 Jul 6;216(1):192–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner J. F., Johnson R. L., Freund R. K., Robinson M. B., Crooks S. L. Structure - function relationships for gamma-substituted glutamate analogues on dentate granule cells. Brain Res. 1983 Aug 8;272(2):299–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90577-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanthorn T. H., Ganong A. H., Cotman C. W. 2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyrate selectively blocks mossy fiber-CA3 responses in guinea pig but not rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1984 Jan 2;290(1):174–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90750-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBean G. J., Roberts P. J. Glutamate-preferring receptors regulate the release of D-[3H]aspartate from rat hippocampal slices. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):593–594. doi: 10.1038/291593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H. Receptors for the excitatory amino acids in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1983;20(3-4):251–271. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(83)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. N., Stone T. W. An iontophoretic investigation of the actions of convulsant kynurenines and their interaction with the endogenous excitant quinolinic acid. Brain Res. 1982 Sep 9;247(1):184–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. Characterization of an extended glutamate receptor of the on bipolar neuron in the vertebrate retina. J Neurosci. 1985 Jan;5(1):224–233. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-01-00224.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay J. P., Laurie R. E., Colonnier M. Is the MEPP due to the release of one vesicle or to the simultaneous release of several vesicles at one active zone? Brain Res. 1983 Dec;287(3):299–314. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(83)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto C., Sawada S., Takada S. Suppressing action of 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid on mossy fiber-induced excitation in the guinea pig hippocampus. Exp Brain Res. 1983;51(1):128–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00236810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


