Abstract
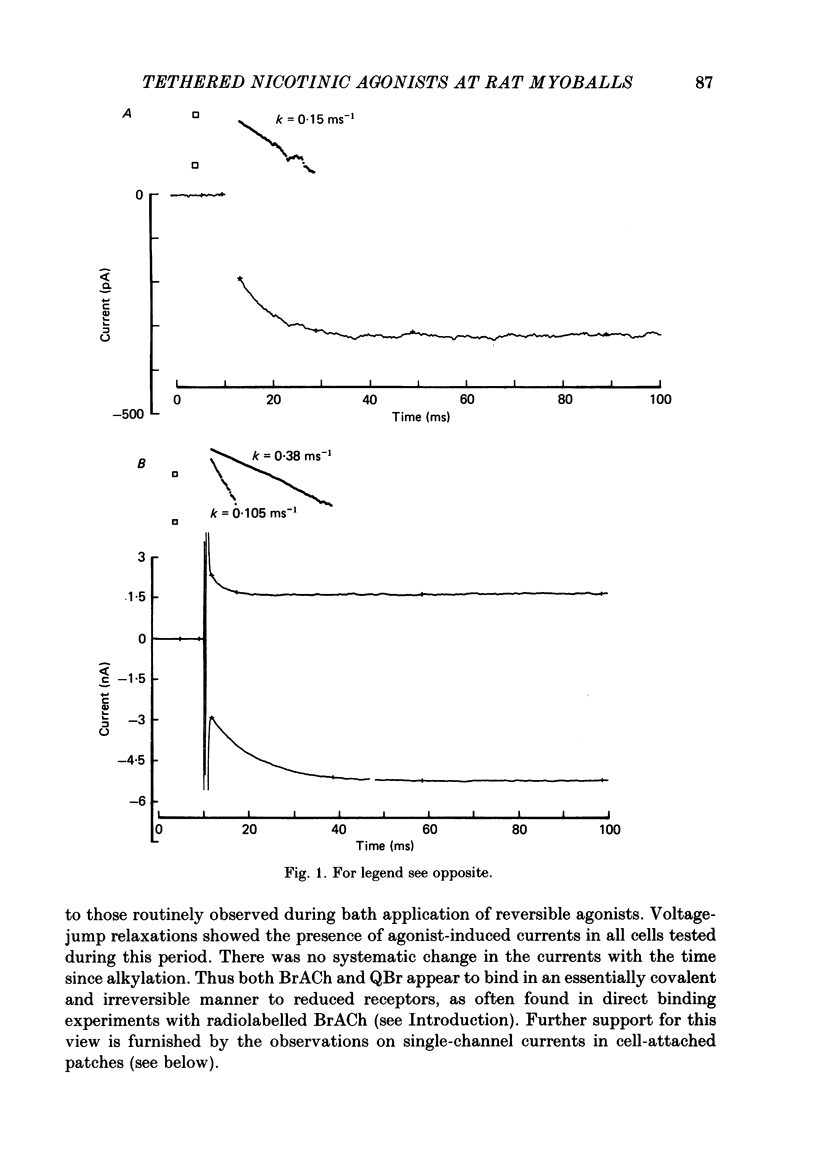
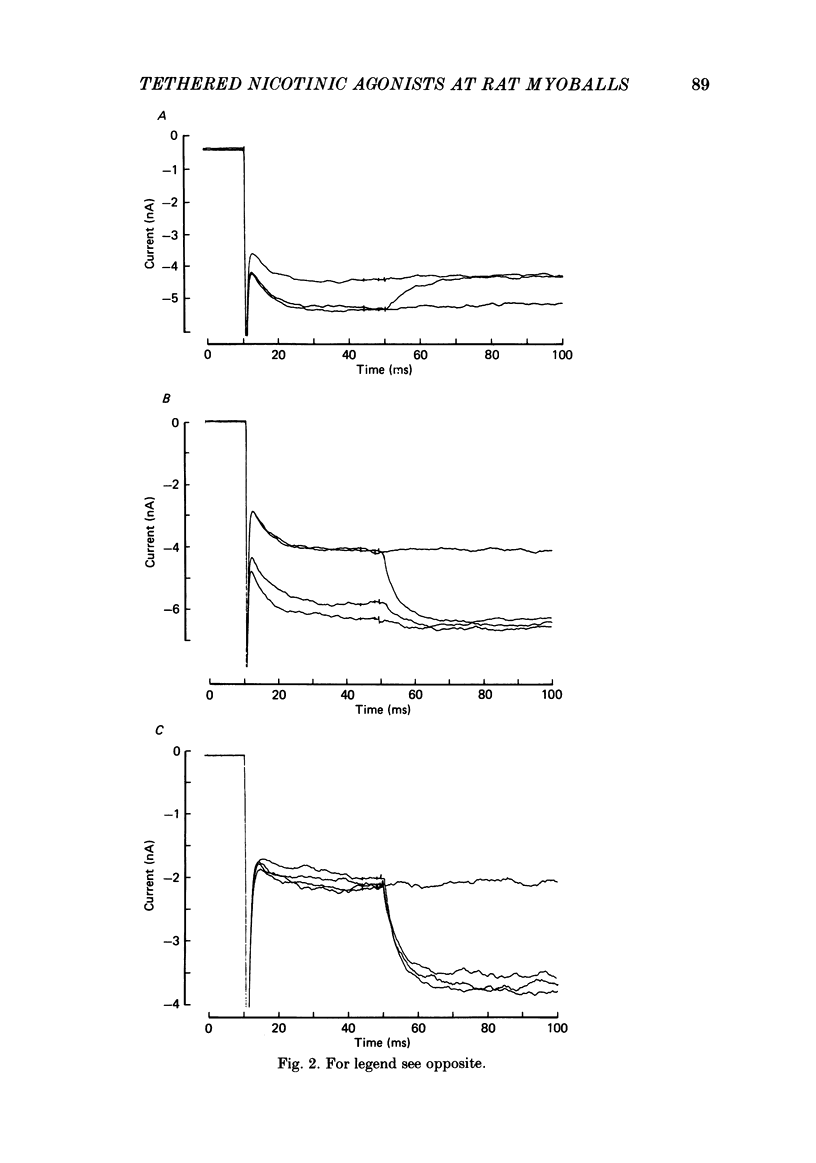
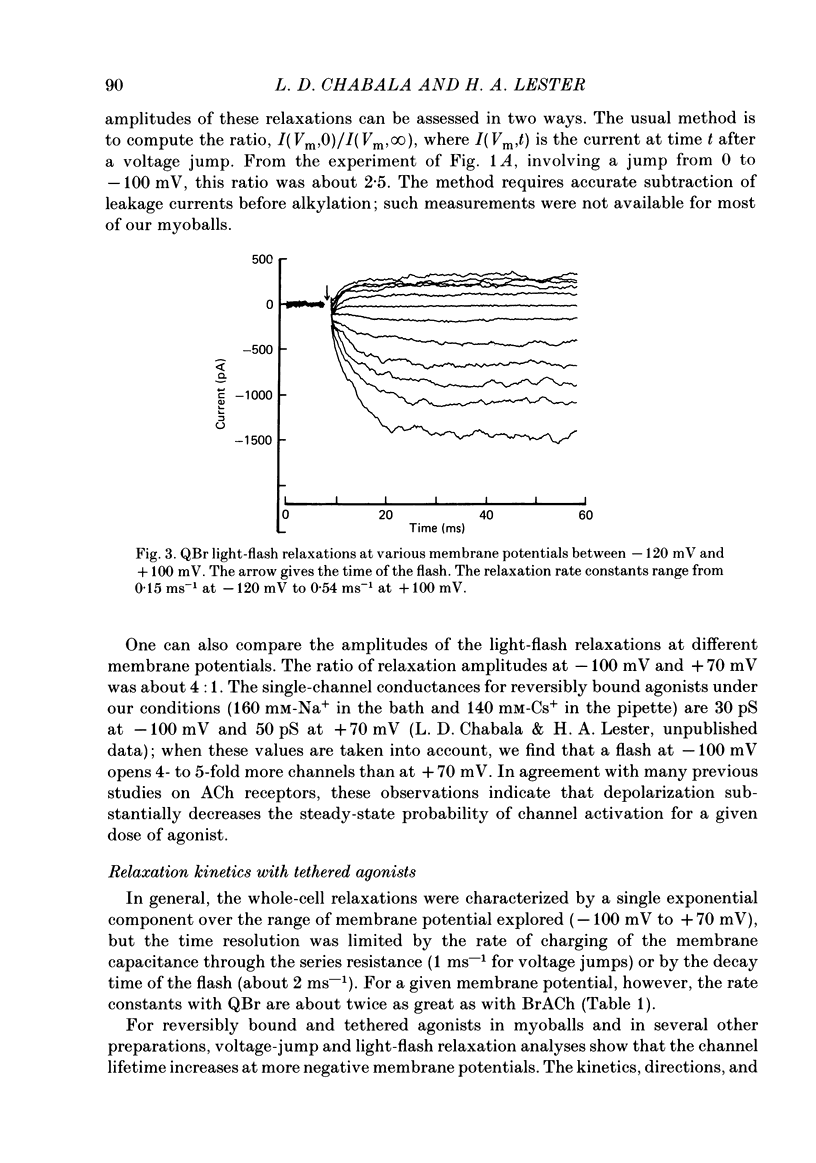
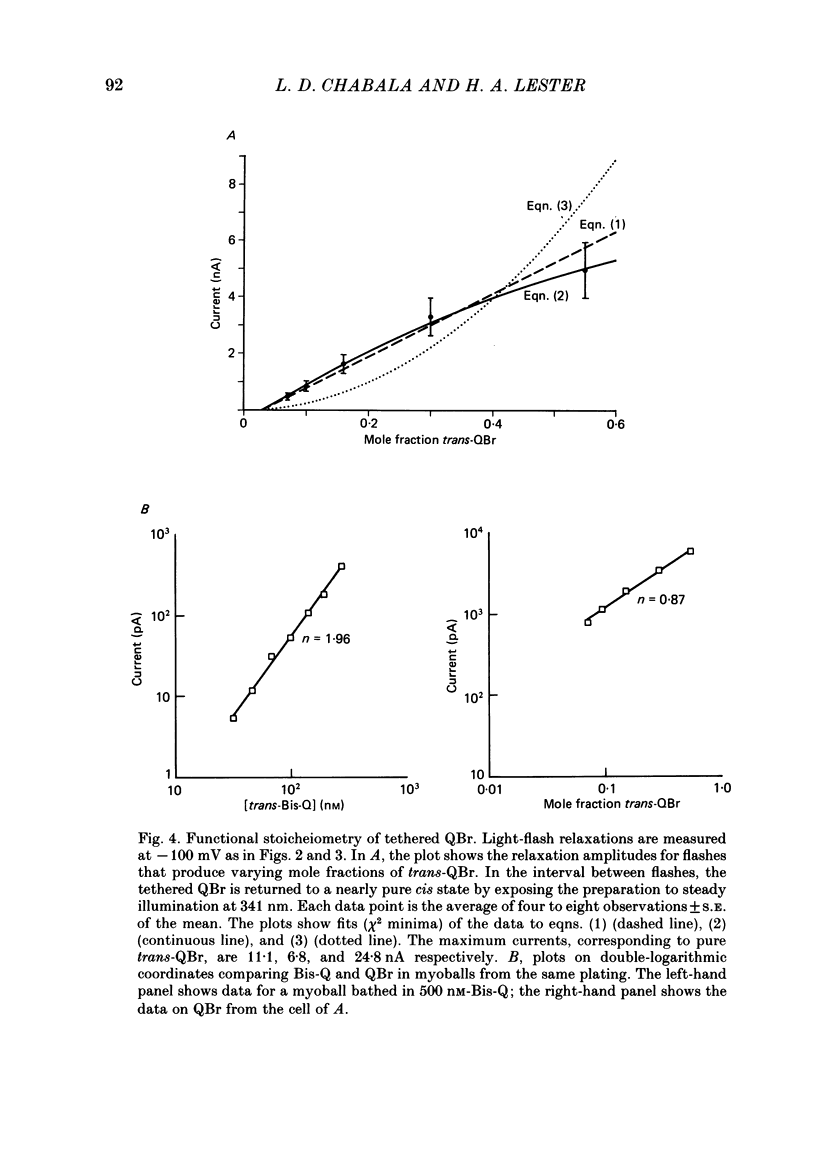
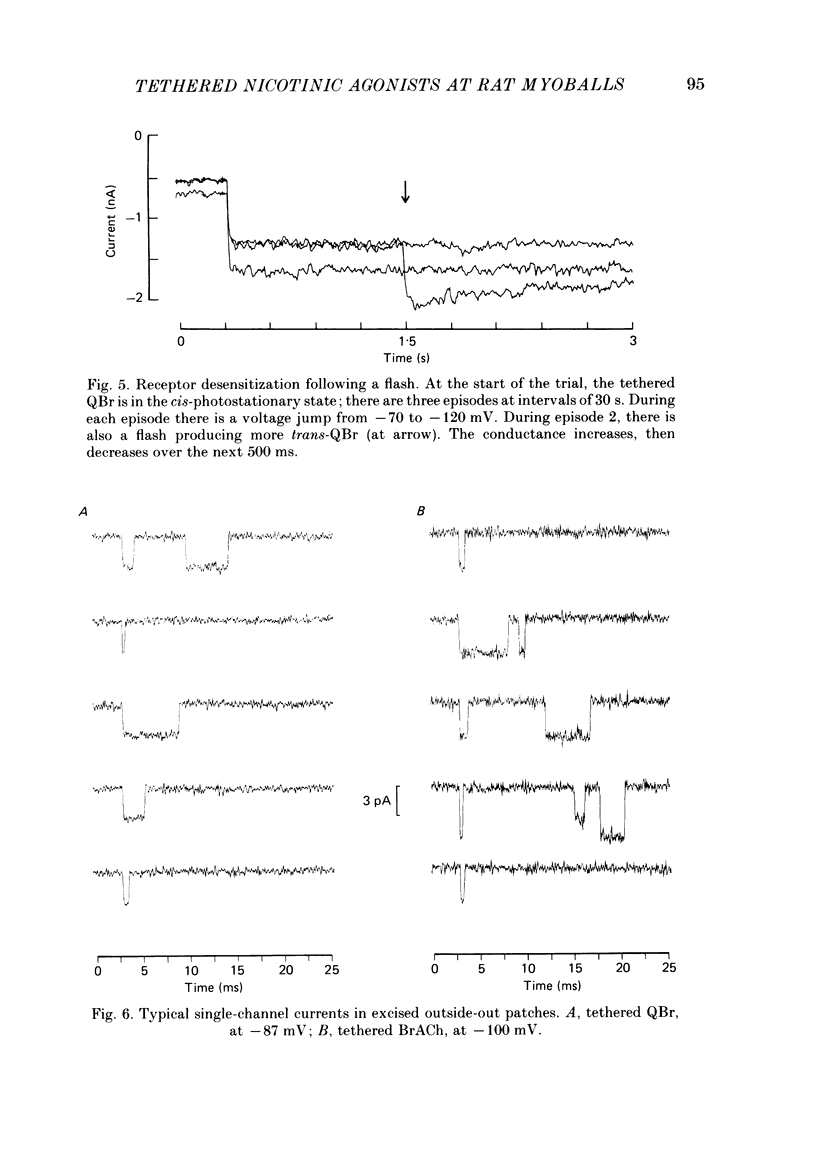
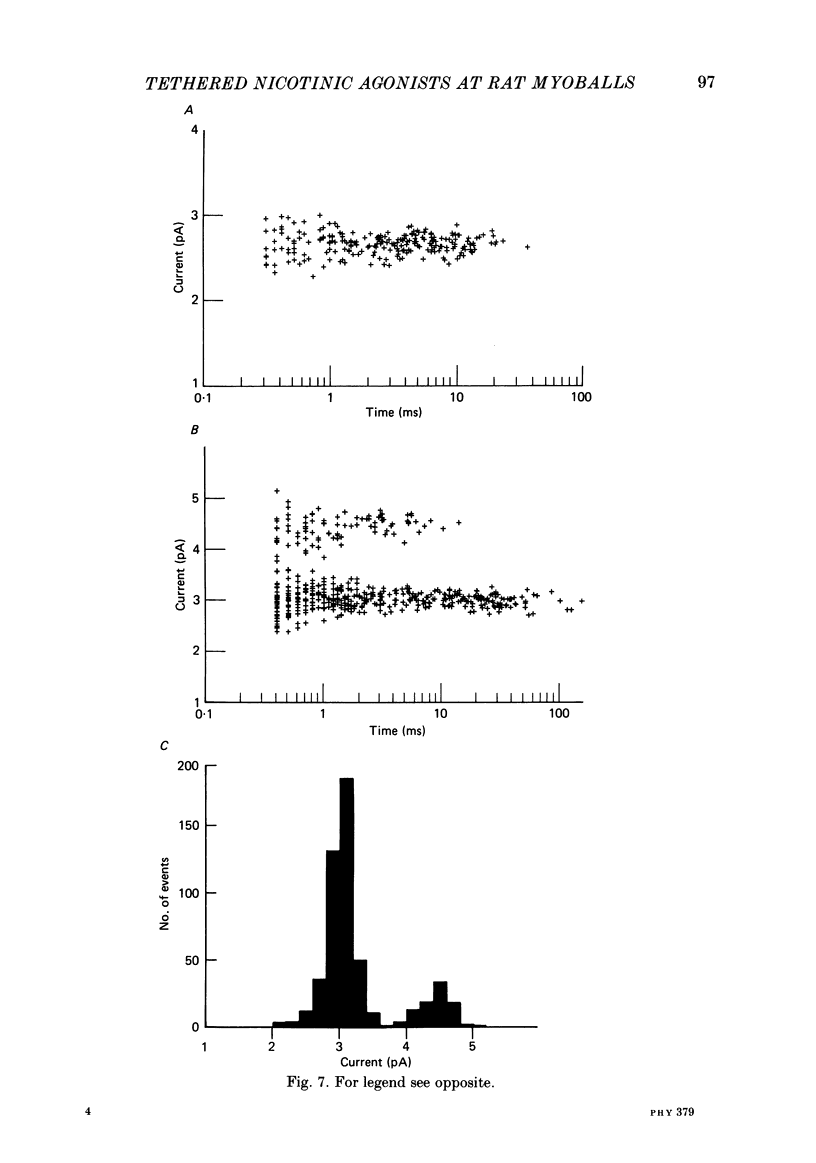
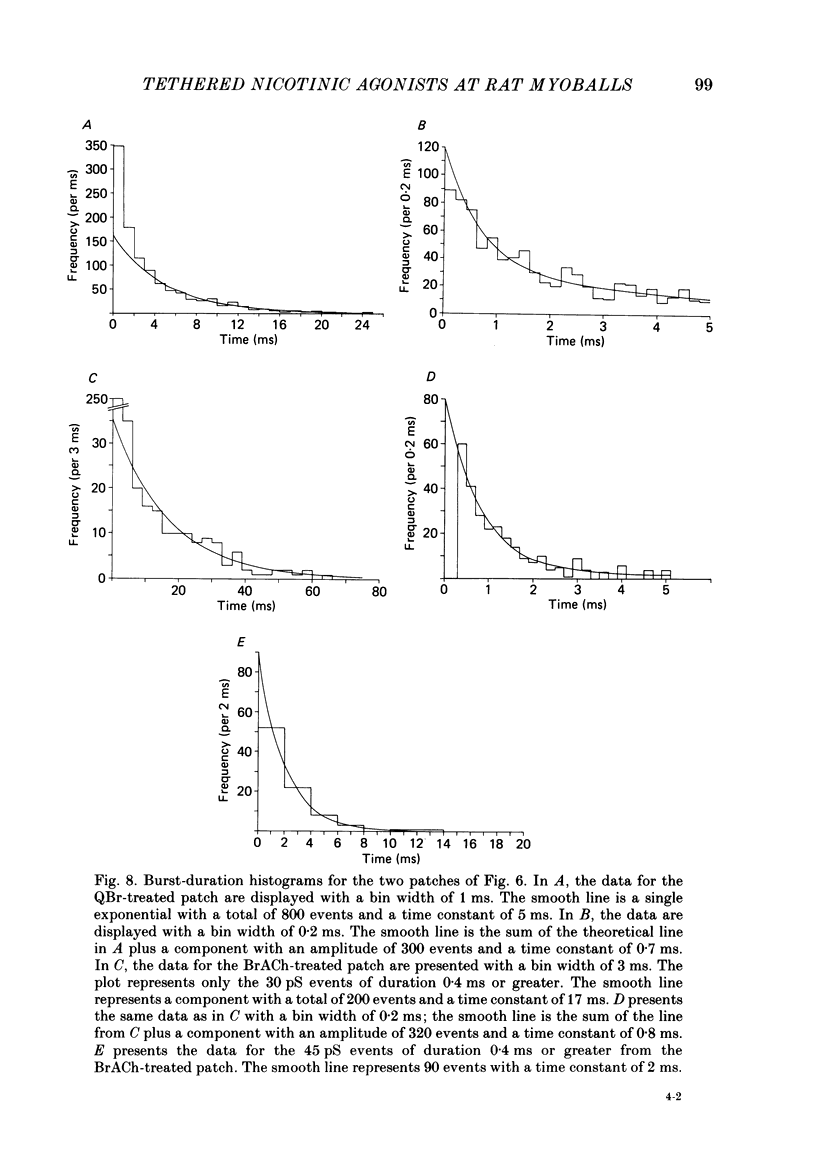
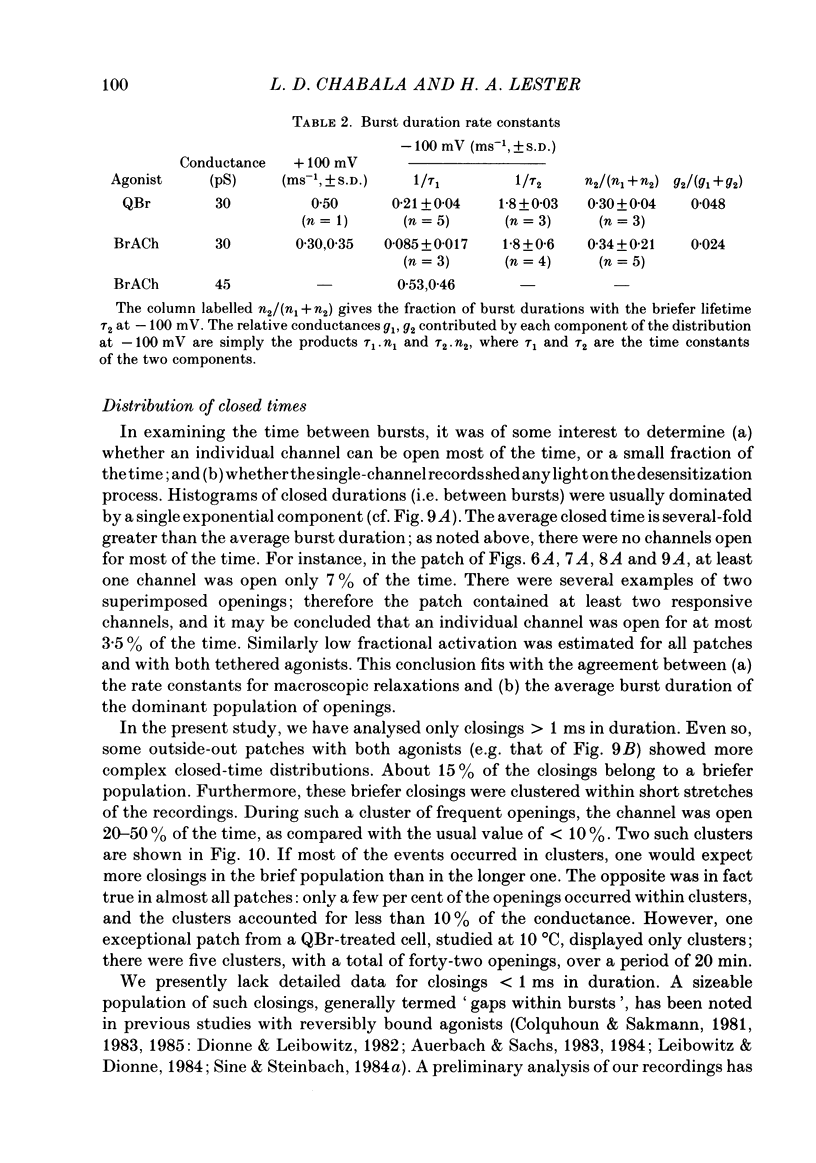
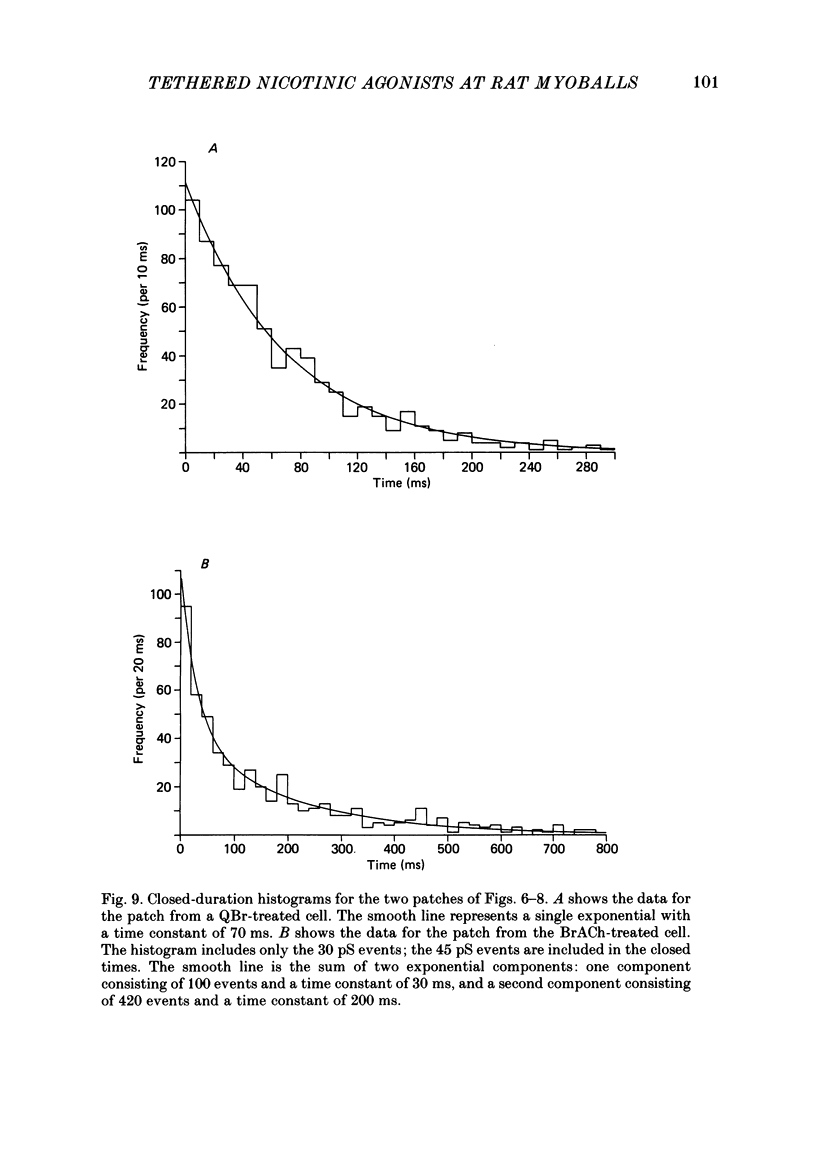
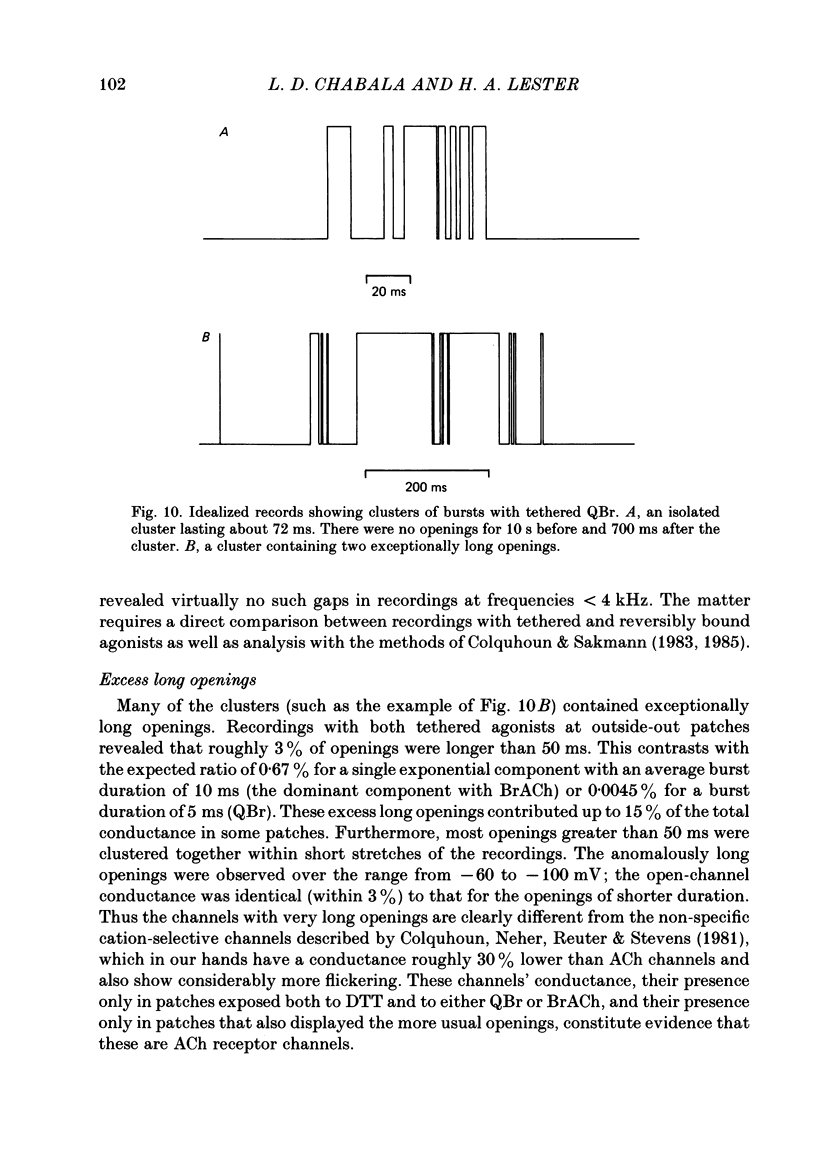
Kinetic and equilibrium aspects of receptor activation by two irreversibly bound ('tethered') agonists, QBr and bromoacetylcholine (BrACh), were examined in cultured embryonic rat muscle. Myoballs were treated with dithiothretitol (2 mM), washed, exposed to BrACh or QBr, and then washed again. Voltage-clamp recordings were made both in the whole-cell mode and with excised outside-out patches at 15 degrees C. Whole-cell voltage-jump relaxations resembled those observed with reversibly bound agonists. The relaxation time constants were 5 ms for tethered QBr and 10 ms for tethered BrACh (-100 mV, 15 degrees C). At more positive membrane potentials, the relaxation rate constants increased and the conductance decreased. Whole-cell light-flash relaxations with tethered QBr were also studied. The conductance was increased and decreased, respectively, by cis----trans and trans----cis photoisomerizations. The relaxation time constants equalled those for voltage jumps. The functional stoicheiometry of tethered QBr was investigated by studying the relaxations in response to light flashes that produced known changes in the mole fractions of the two isomers. It is concluded that the open state of each receptor channel is controlled by the isomeric state of a single tethered QBr molecule. In single-channel recordings, tethered agonists opened channels with the same conductance as reversibly bound agonists (30 pS at 15 degrees C and -100 mV). More than 80% of the conductance was contributed by a population of openings with an average burst duration (lifetime) of 5 ms for QBr and 10 ms for BrACh. Thus the single-channel and macroscopic currents seem to be dominated by the same type of channel; these are presumably monoliganded receptors. About 30% of the openings belonged to a population with an average lifetime of about 0.5 ms. This population contributed less than 5% of the conductance. There were also more long openings (greater than 50 ms) than expected from a simple exponential distribution. A few patches from BrACh-treated cells showed openings with a conductance of 45 pS (-100 mV) and an average duration of approximately 2 ms. These data allow one to assess whether the agonist-receptor binding step plays a role in generating the brief openings. The main population of openings (burst durations 5 ms with QBr and 10 ms with BrACh) seem to be contributed by monoliganded receptors. One can therefore rule out the hypothesis that the brief channels arise exclusively from mono- and biliganded receptors, respectively.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. An analysis of the dose-response curve at voltage-clamped frog-endplates. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Oct 28;360(2):145–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00580537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A., Sachs F. Flickering of a nicotinic ion channel to a subconductance state. Biophys J. 1983 Apr;42(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84362-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A., Sachs F. Single-channel currents from acetylcholine receptors in embryonic chick muscle. Kinetic and conductance properties of gaps within bursts. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):187–198. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84147-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartels E., Wassermann N. H., Erlanger B. F. Photochromic activators of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1820–1823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgen A. S. The drug-receptor complex. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1966 Mar;18(3):137–149. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1966.tb07840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabala L. D., Gurney A. M., Lester H. A. Dose-response of acetylcholine receptor channels opened by a flash-activated agonist in voltage-clamped rat myoballs. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:407–433. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabala L. D., Gurney A. M., Lester H. A. Photoactivation and dissociation of agonist molecules at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in voltage-clamped rat myoballs. Biophys J. 1985 Aug;48(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83777-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fluctuations in the microsecond time range of the current through single acetylcholine receptor ion channels. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):464–466. doi: 10.1038/294464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Raftery M. A. Molecular weight and structural nonequivalence of the mature alpha subunits of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2631–2634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. N., Kawai M., Karlin A., Brandt P. W. Voltage fluctuations at the frog sartorius motor endplate produced by a covalently attached activator. J Membr Biol. 1979 Dec 14;51(2):145–159. doi: 10.1007/BF01869166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle V. N., McLaughlin M., Karlin A. Bromoacetylcholine as an affinity label of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 30;84(4):845–851. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91661-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Leibowitz M. D. Acetylcholine receptor kinetics. A description from single-channel currents at snake neuromuscular junctions. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):253–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84515-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchek J. R., Huebner J. S. Voltage transients from photo-isomerizing azo dye in bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1979 Aug;27(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85220-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. M., Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. Separate sites of low and high affinity for agonists on Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2512–2518. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Schuetze S. M. A post-natal decrease in acetylcholine channel open time at rat end-plates. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:125–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Roisin M. P., Gu Y., Gorin P. D. A developmental change in the immunological properties of acetylcholine receptors at the rat neuromuscular junction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):101–108. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Multiple conductance states of single acetylcholine receptor channels in embryonic muscle cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):462–464. doi: 10.1038/294462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Brodwick M. S. Acetylcholine-induced current in perfused rat myoballs. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Mar;75(3):297–321. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.3.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B. Spontaneous openings of the acetylcholine receptor channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3901–3904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Wong B. S., Morris C. E., Lecar H., Christian C. N. Successive openings of the same acetylcholine receptor channel are correlated in open time. Biophys J. 1983 Apr;42(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84375-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. N., Dwork A. J., Kaldany R. R., Silver M. L., Wideman J., Stein S., Karlin A. Identification of the alpha subunit half-cystine specifically labeled by an affinity reagent for the acetylcholine receptor binding site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11662–11665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kegel D. R., Wolf B. D., Sheridan R. E., Lester H. A. Software for electrophysiological experiments with a personal computer. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Feb;12(4):317–330. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca P., Lindstrom J., Montal M. The acetylcholine receptor channel from Torpedo californica has two open states. J Neurosci. 1984 Feb;4(2):502–507. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-02-00502.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca P., Montal M. S., Lindstrom J. M., Montal M. The occurrence of long openings in the purified cholinergic receptor channel increases with acetylcholine concentration. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3409–3413. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03409.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz M. D., Dionne V. E. Single-channel acetylcholine receptor kinetics. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84144-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. J., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y., Takahashi T. Differential development of two classes of acetylcholine receptors in Xenopus muscle in culture. Science. 1984 Oct 5;226(4670):55–57. doi: 10.1126/science.6474189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A., Krouse M. E., Nass M. M., Wassermann N. H., Erlanger B. F. A covalently bound photoisomerizable agonist: comparison with reversibly bound agonists at Electrophorus electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Feb;75(2):207–232. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michler A., Sakmann B. Receptor stability and channel conversion in the subsynaptic membrane of the developing mammalian neuromuscular junction. Dev Biol. 1980 Nov;80(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90494-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Raftery M. A. Studies of reversible and irreversible interactions of an alkylating agonist with Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor in membrane-bound and purified states. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1862–1867. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. E., Wong B. S., Jackson M. B., Lecar H. Single-channel currents activated by curare in cultured embryonic rat muscle. J Neurosci. 1983 Dec;3(12):2525–2531. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-12-02525.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Voltage-dependence of drug-induced conductance in frog neuromuscular junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Patlak J., Neher E. Single acetylcholine-activated channels show burst-kinetics in presence of desensitizing concentrations of agonist. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):71–73. doi: 10.1038/286071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan R. E., Lester H. A. Functional stoichiometry at the nicotinic receptor. The photon cross section for phase 1 corresponds to two bis-Q molecules per channel. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Oct;80(4):499–515. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.4.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan R. E., Lester H. A. Relaxation measurements on the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3496–3500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Open channel noise. I. Noise in acetylcholine receptor currents suggests conformational fluctuations. Biophys J. 1985 May;47(5):709–720. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83968-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silman I., Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor: covalent attachment of depolarizing groups at the active site. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1420–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Activation of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84146-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Trautmann A. A patch-clamp study of the partial agonist actions of tubocurarine on rat myotubes. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:353–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosin J. M., Lyddiatt A., Dolly J. O., Barnard E. A. Stoichiometry of the ligand-binding sites in the acetylcholine-receptor oligomer from muscle and from electric organ. Measurement by affinity alkylation with bromoacetylcholine. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):495–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04821.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


