Abstract
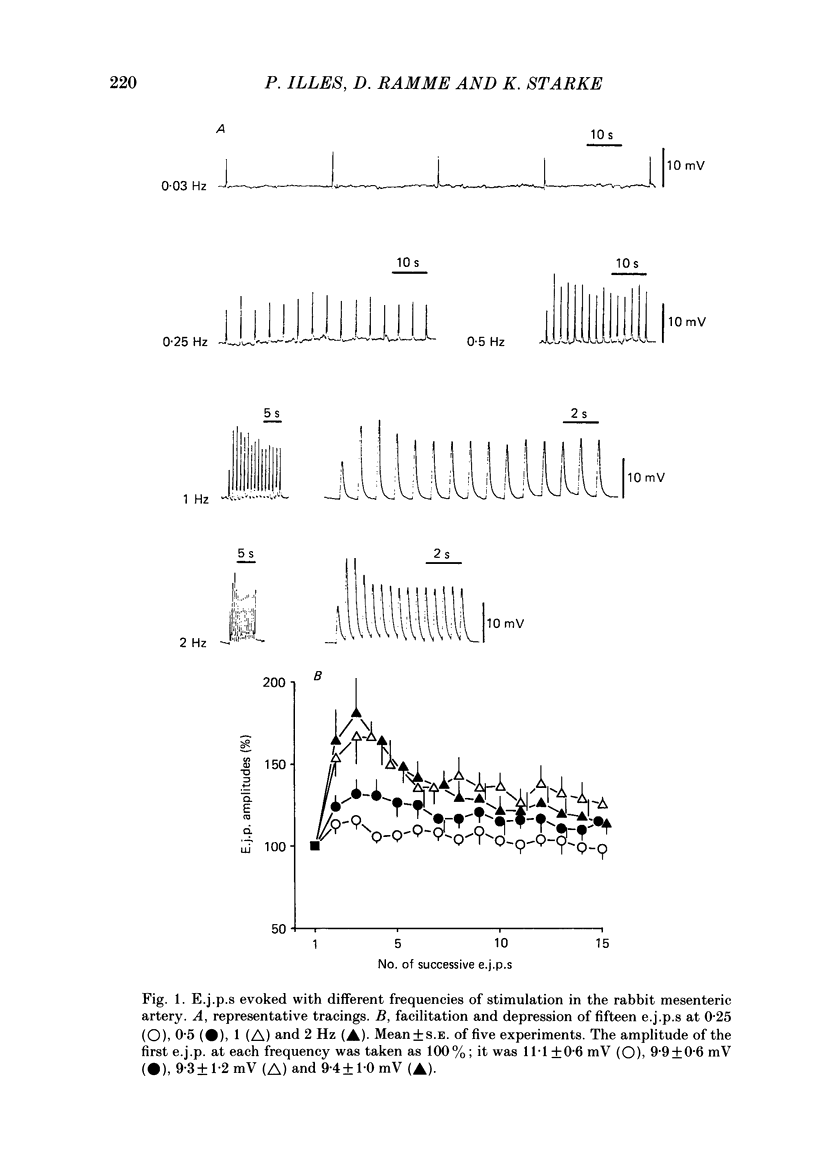
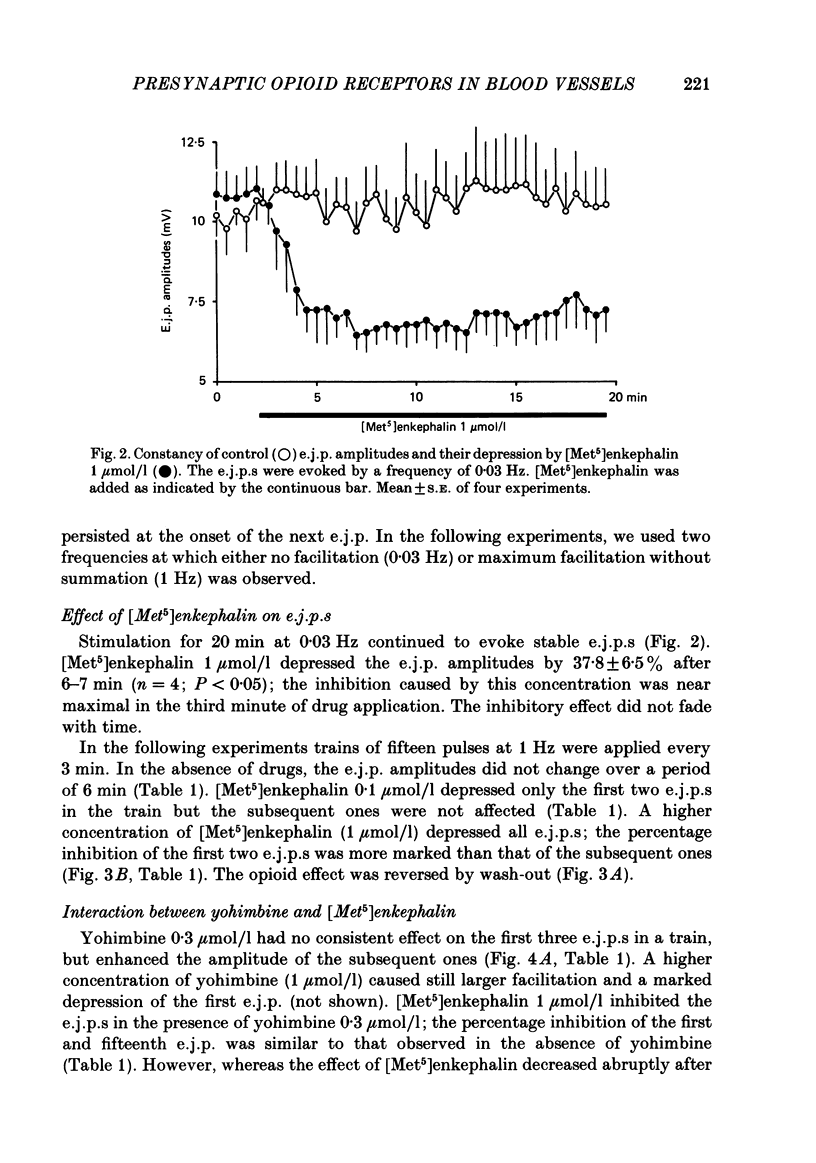
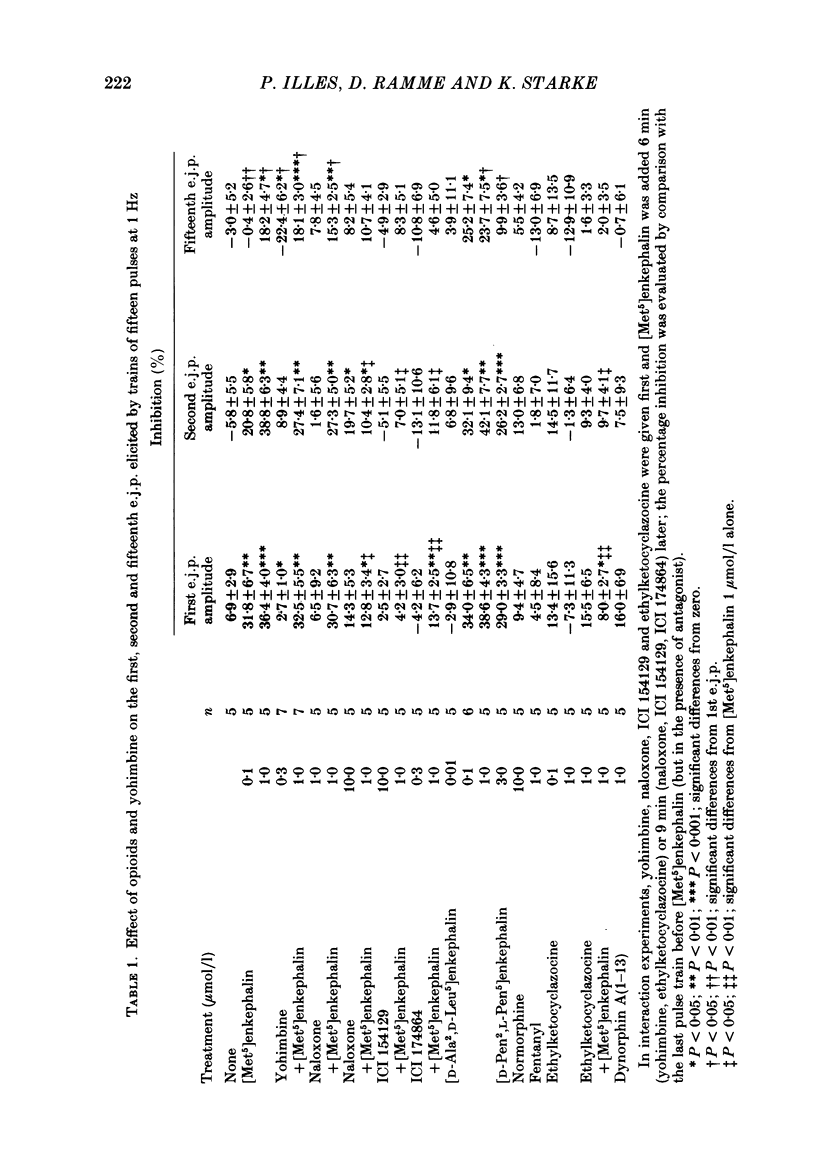
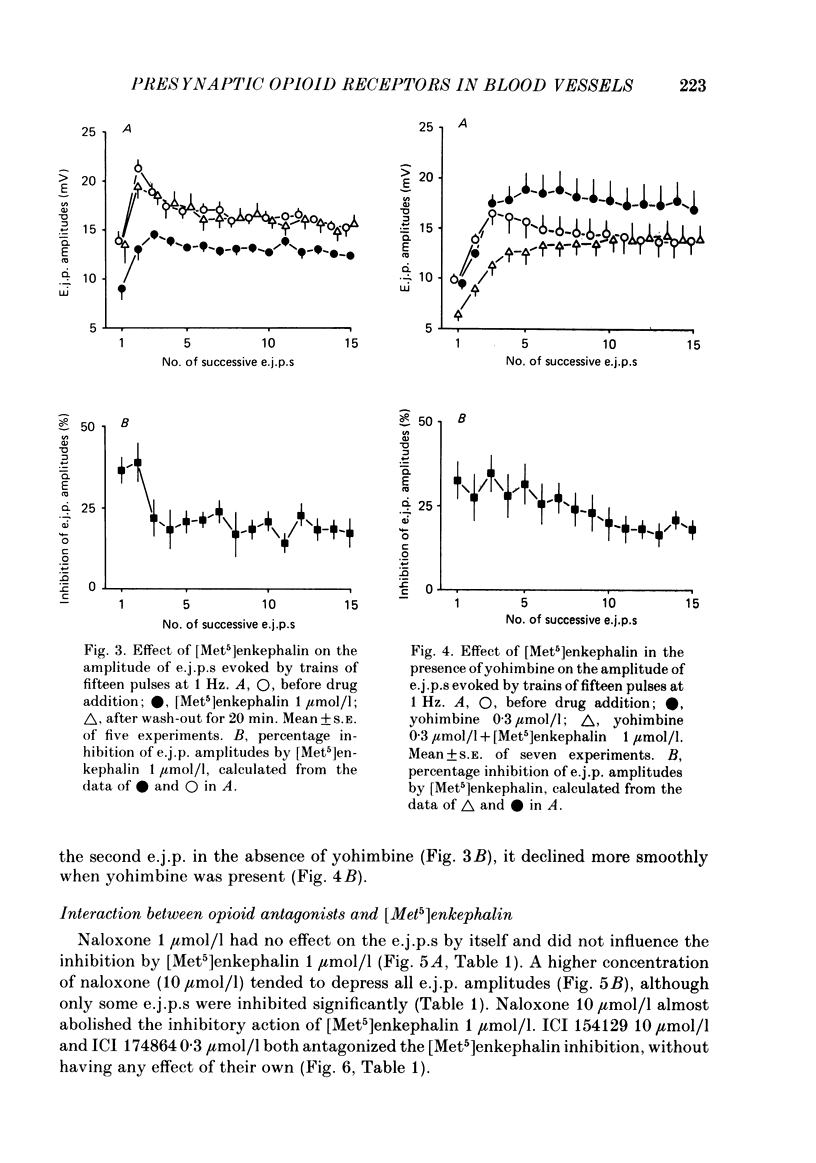
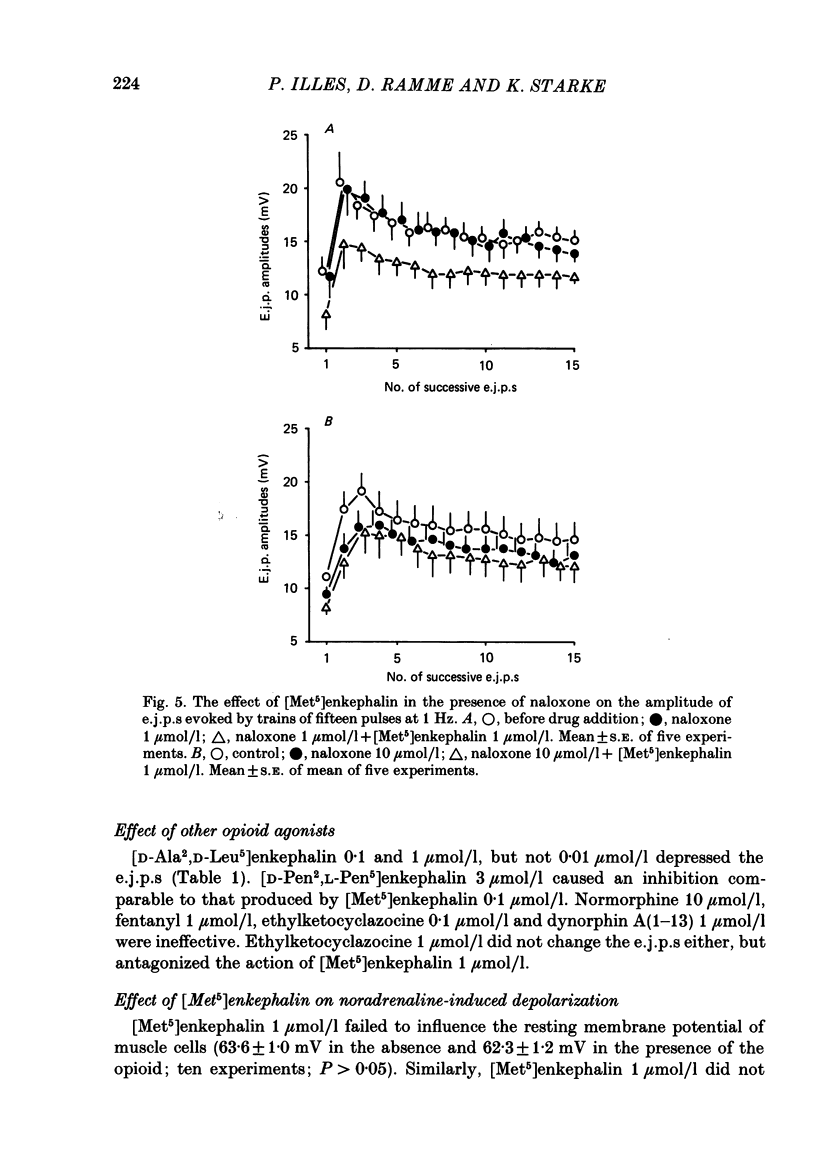
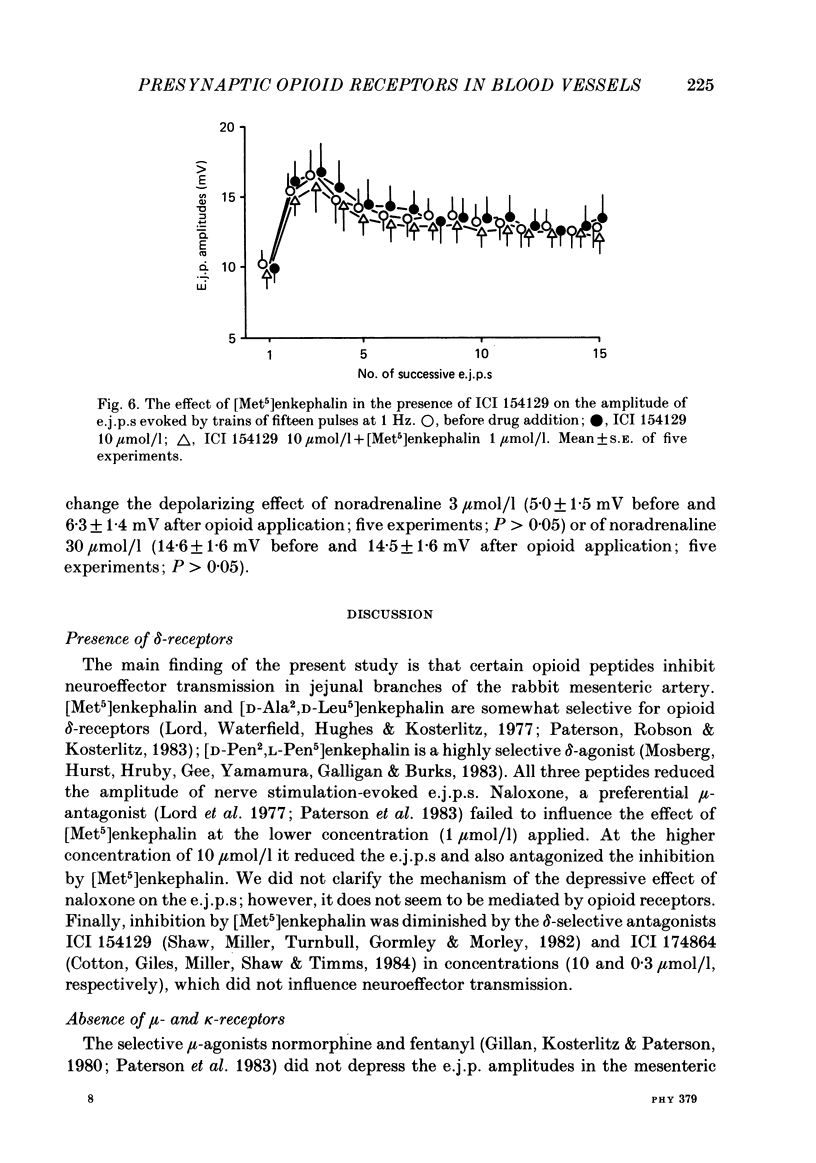
Excitatory junction potentials (e.j.p.s) evoked by nerve stimulation were recorded from muscle cells of the rabbit isolated mesenteric artery. At 0.03 Hz the e.j.p. amplitudes were stable. When a train of fifteen pulses was applied at 0.25 Hz or at higher frequencies (0.5, 1 and 2 Hz), e.j.p.s showed an initial facilitation followed by depression. [Met5]enkephalin 0.1 and 1 mumol/l, [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin 0.1 and 1, but not 0.01 mumol/l, and [D-Pen2, L-Pen5]enkephalin 3 mumol/l all depressed the e.j.p.s evoked by trains of fifteen pulses at 1 Hz. When more than one concentration was used ([Met5]enkephalin, [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin), the inhibition was concentration dependent. It was always greater for the first few e.j.p.s than for the later ones in a train. [Met5]enkephalin 1 mumol/l reduced the first e.j.p. at 1 Hz and the e.j.p.s evoked by 0.03 Hz to a similar extent. The inhibitory effect of [Met5]enkephalin 1 mumol/l on e.j.p.s persisted in the presence of yohimbine 0.3 mumol/l. Naloxone 1 mumol/l did not interfere with the effect of [Met5]enkephalin 1 mumol/l. Naloxone 10 mumol/l depressed some e.j.p.s and prevented the inhibition by [Met5]enkephalin 1 mumol/l. Neither ICI 154129 10 mumol/l nor ICI 174864 0.3 mumol/l had any effect of their own and both compounds antagonized the action of [Met5]enkephalin 1 mumol/l. Normorphine 10 mumol/l, fentanyl 1 mumol/l, ethylketocyclazocine 0.1 mumol/l, and dynorphin A(1-13) 1 mumol/l were all ineffective. Ethylketocyclazocine 1 mumol/l did not change the e.j.p.s either, but antagonized [Met5]enkephalin 1 mumol/l. [Met5]enkephalin 1 mumol/l failed to influence both the resting membrane potential of the muscle cells and the depolarizing effect of noradrenaline 3 and 30 mumol/l. We suggest that the axon terminals of post-ganglionic sympathetic neurones in the rabbit mesenteric artery possess opioid delta-, but not mu- or kappa-receptors. The activation of presynaptic delta-receptors inhibits the release of the neuroeffector transmitter. There is no evidence for any effect of co-released endogenous opioid peptides under our experimental conditions.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altura B. T., Altura B. M., Quirion R. Identification of benzomorphan-kappa opiate receptors in cerebral arteries which subserve relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;82(2):459–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. D., Paterson S. J., McKnight A. T., Magnan J., Kosterlitz H. W. Dynorphin and dynorphin are ligands for the kappa-subtype of opiate receptor. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):79–81. doi: 10.1038/299079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R., Giles M. G., Miller L., Shaw J. S., Timms D. ICI 174864: a highly selective antagonist for the opioid delta-receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan 27;97(3-4):331–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinger H., Hedler L., Schurr C., Starke K. Ethylketocyclazocine decreases noradrenaline release and blood pressure in the rabbit at a peripheral opioid receptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;328(1):20–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00496099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J. Comparison of the binding characteristics of tritiated opiates and opioid peptides. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;70(3):481–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb08727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanko J. H., Hardebo J. E. Enkephalin-induced dilatation of pial arteries in vitro probably mediated by opiate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct 1;51(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder D. R., Madden J. A. Cellular mechanisms of opiate receptor stimulation in cat middle cerebral artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 20;102(3-4):411–416. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90560-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. A new example of a morphine-sensitive neuro-effector junction: adrenergic transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Dec;46(4):764–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06901.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., North R. A. Depression by morphine of excitatory junction potentials in the vas deferens of the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;57(3):341–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holaday J. W. Cardiovascular effects of endogenous opiate systems. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:541–594. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W., Leslie F. M. Effect of morphine on adrenergic transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Assessment of agonist and antogonist potencies of narcotic analgesics. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Mar;53(3):371–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illes P., Pfeiffer N., von Kügelgen I., Starke K. Presynaptic opioid receptor subtypes in the rabbit ear artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Feb;232(2):526–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illes P., Ramme D., Starke K. Inhibition of neuroeffector transmission in the rabbit mesenteric artery by [Met5]enkephalin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 8;107(3):397–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illes P., Starke K. An electrophysiological study of presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors in the vas deferens of the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Feb;78(2):365–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illes P., Zieglgänsberger W., Herz A. Calcium reverses the inhibitory action of morphine on neuroeffector transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Brain Res. 1980 Jun 9;191(2):511–522. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91299-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. Neuronal peptide (enkephalin) receptors in the ear artery of the rabbit. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;39(2):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. E., Hermann K., Dietz R., Gaida W., Ganten D., Kraft K., Unger T. Evidence for the presence of enkephalins in the heart. Life Sci. 1983 Jan 24;32(4):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Anggård A., Uvnäs-Wallensten K., Brimijoin S., Brodin E., Fahrenkrug J. Peripheral peptide neurons: distribution, axonal transport, and some aspects on possible function. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1980;22:25–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnan J., Paterson S. J., Tavani A., Kosterlitz H. W. The binding spectrum of narcotic analgesic drugs with different agonist and antagonist properties. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;319(3):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00495865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. T., Corbett A. D., Marcoli M., Kosterlitz H. W. Hamster vas deferens contains delta-opioid receptors. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen D. S. Opioid peptide interactions with respiratory and circulatory systems. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):77–82. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima S., Miyahara H., Suzuki H. Transmitter release modulated by alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists in the rabbit mesenteric artery: a comparison between noradrenaline outflow and electrical activity. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):537–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Gee K., Yamamura H. I., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F. Bis-penicillamine enkephalins possess highly improved specificity toward delta opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5871–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson S. J., Robson L. E., Kosterlitz H. W. Classification of opioid receptors. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):31–36. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruth J. A., Doerr A. L., Eiden L. E. [Leu5]enkephalin inhibits norepinephrine-induced contraction of rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 1;105(1-2):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90667-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rónai A. Z., Hársing L. G., Berzétei I. P., Bajusz S., Vizi E. S. [Met5]enkephalin-Arg-Phe ACTS on vascular opiate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 23;79(3-4):337–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90645-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. S., Miller L., Turnbull M. J., Gormley J. J., Morley J. S. Selective antagonists at the opiate delta-receptor. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1259–1262. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Schöffel E., Illes P. The sympathetic axons innervating the sinus node of the rabbit possess presynaptic opioid kappa- but not mu- or delta-receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;329(2):206–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00501214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Kügelgen I., Illes P., Wolf D., Starke K. Presynaptic inhibitory opioid delta- and kappa-receptors in a branch of the rabbit ileocolic artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 26;118(1-2):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90667-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P., Klein R. L., Chang K. J., Gasparis M. S., Viveros O. H., Yang W. H. Are opioid peptides co-transmitters in noradrenergic vesicles of sympathetic nerves? Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):707–709. doi: 10.1038/288707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüster M., Schulz R., Herz A. Multiple opiate receptors in peripheral tissue preparations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 15;30(14):1883–1887. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


