Abstract
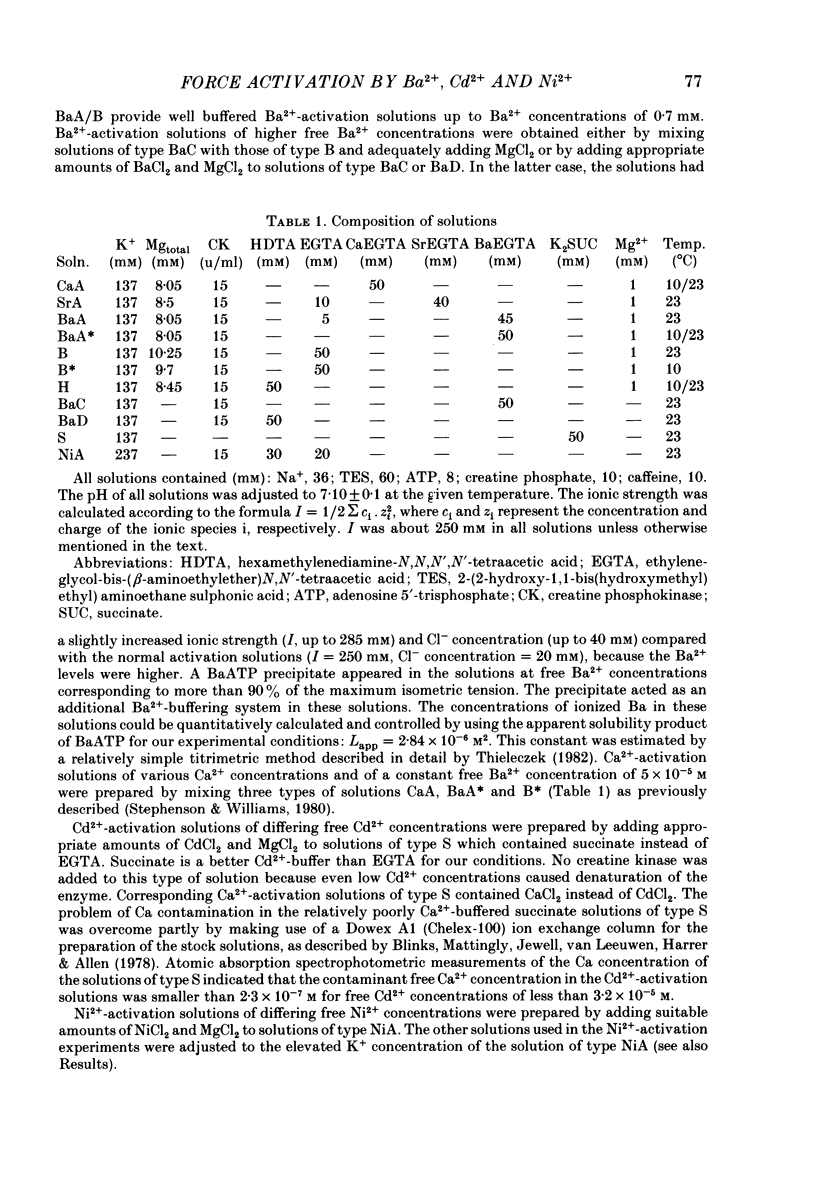
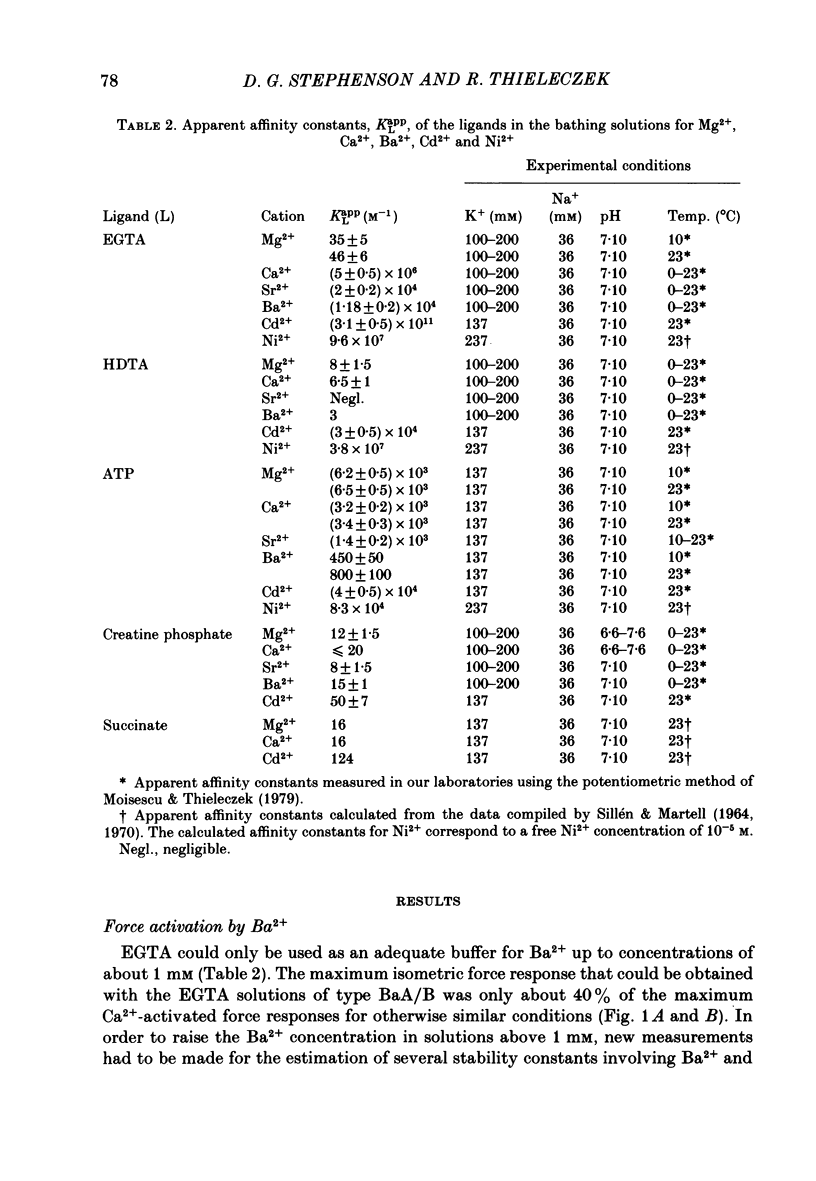
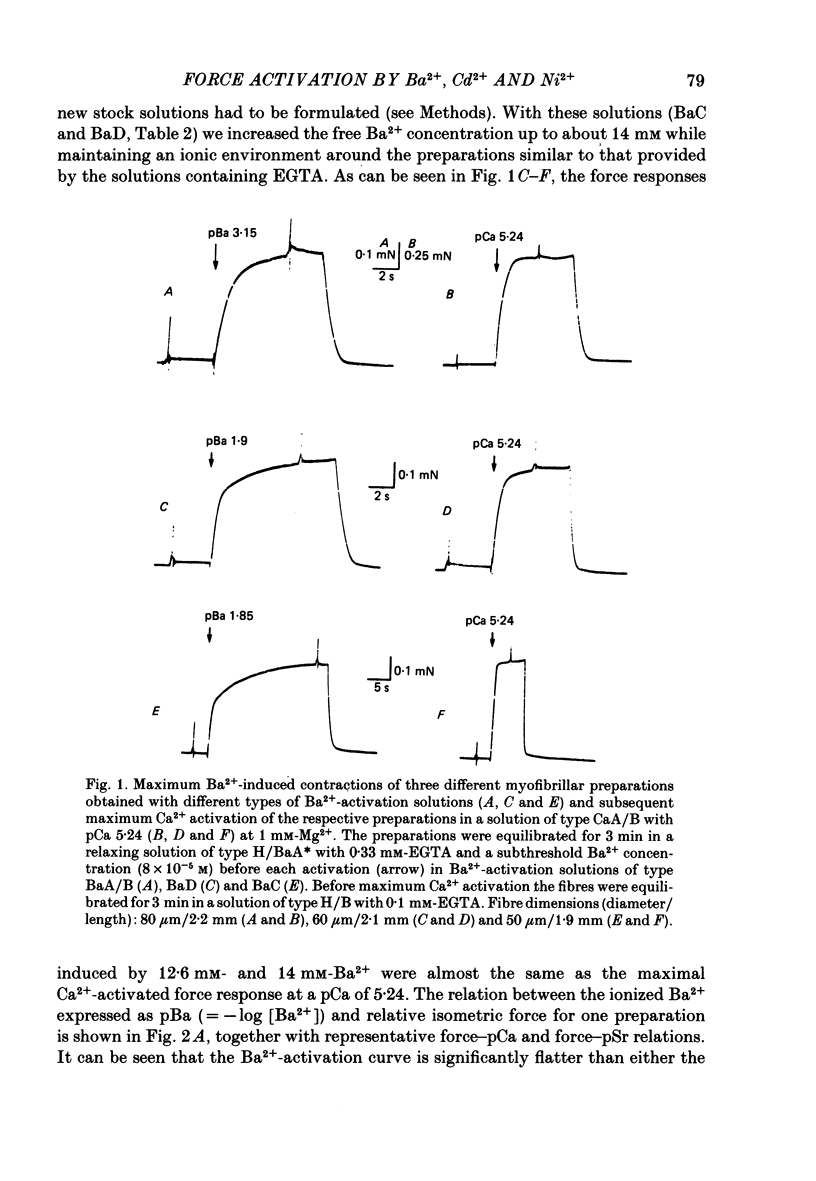
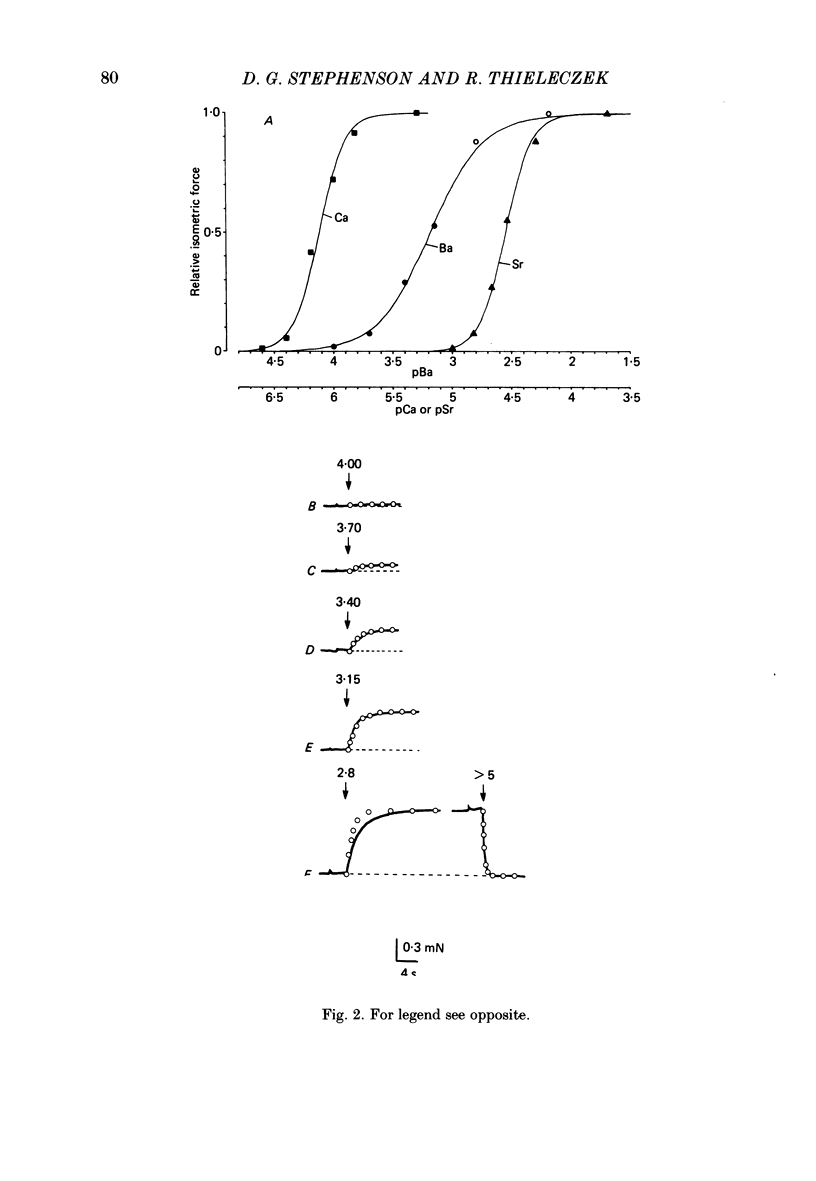
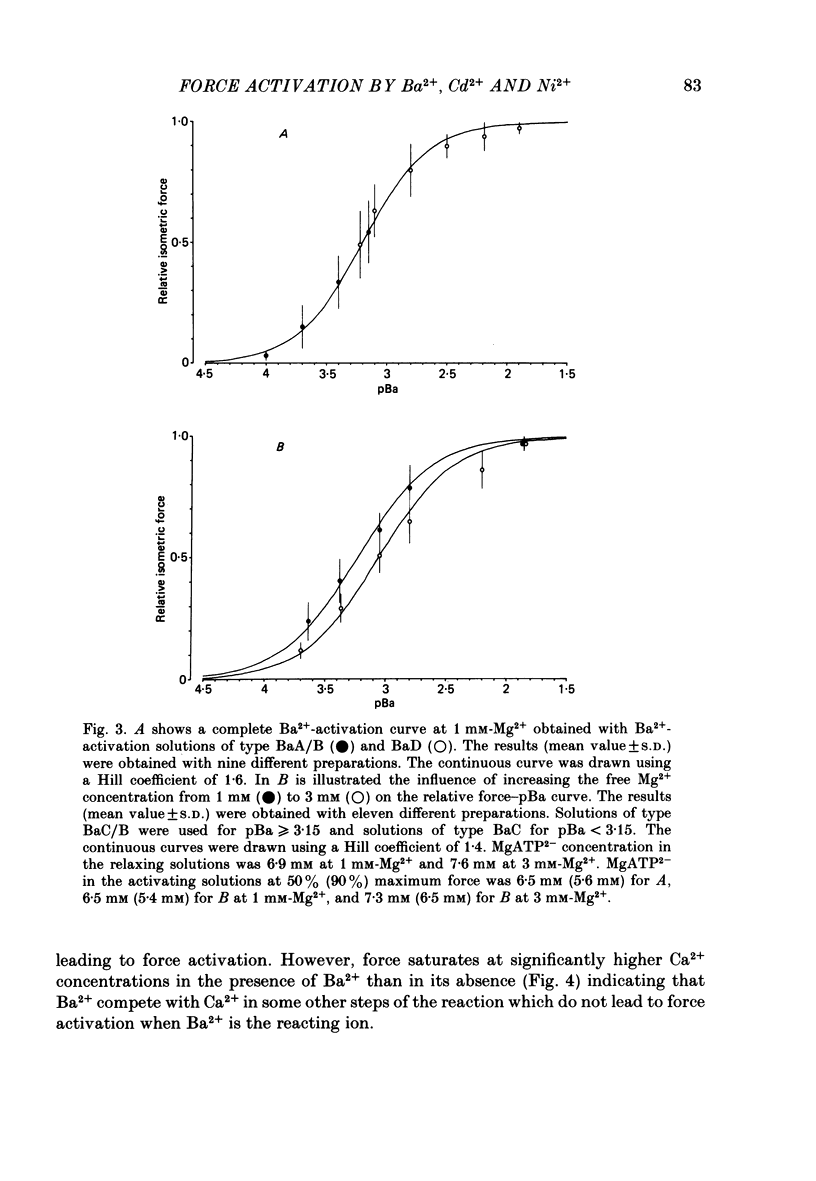
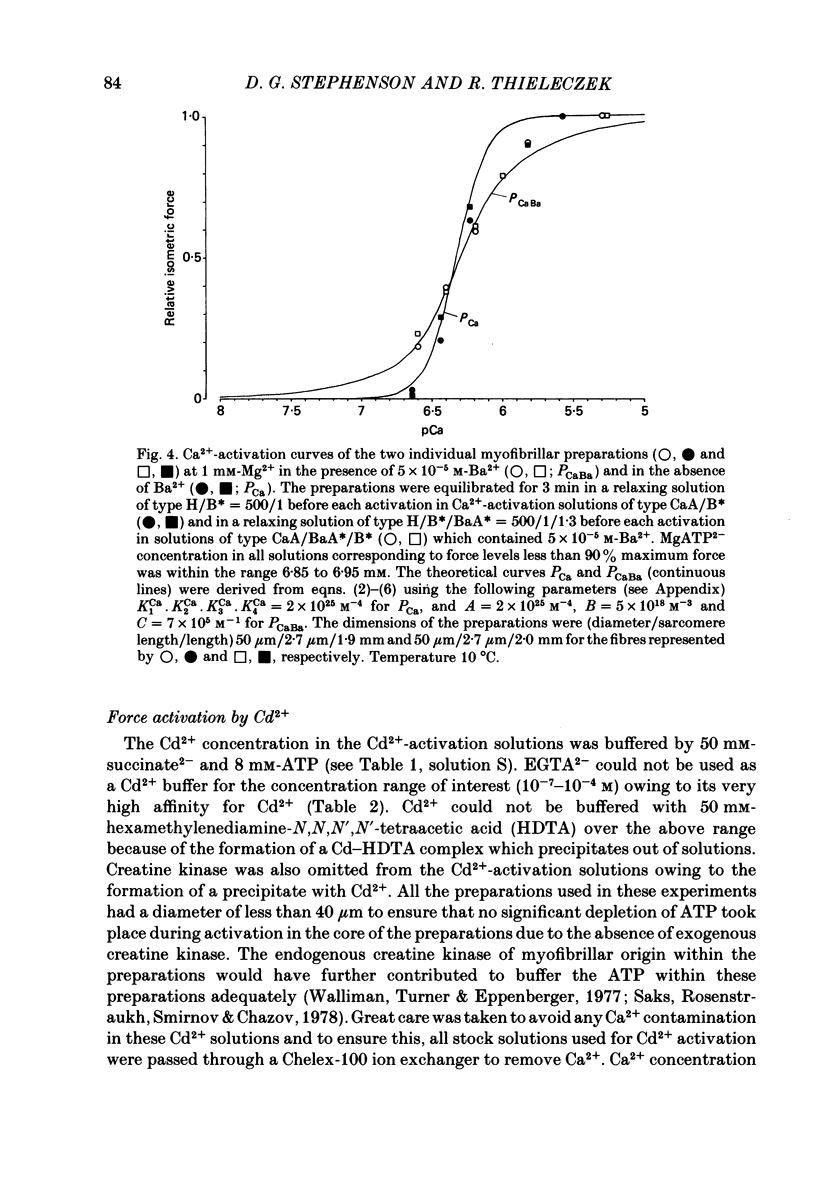
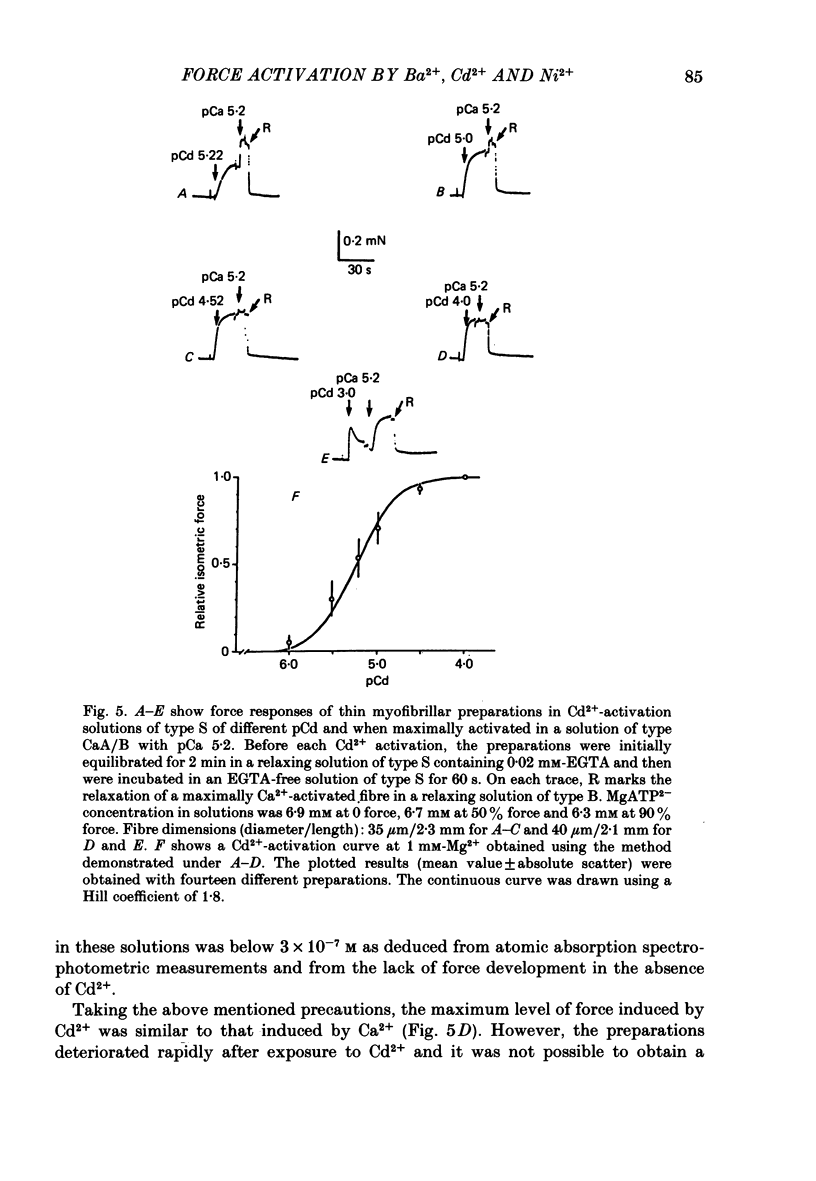
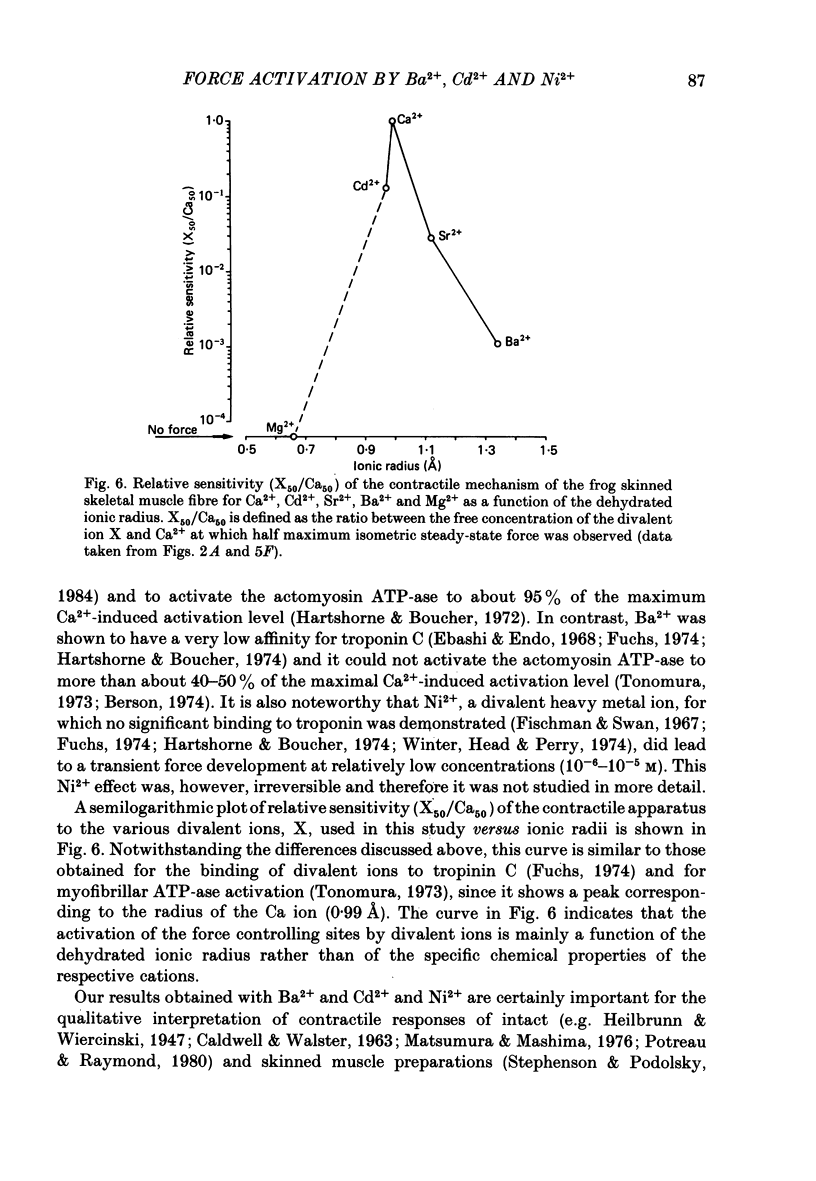
The contractile apparatus of mechanically skinned muscle fibres of frog can be reversibly activated by Ba2+ and Cd2+. The maximum force induced by both Ba2+ and Cd2+ is the same as that induced by Ca2+ and Sr2+. The ionic concentrations of the divalent cations required to induce 50% of the maximum activated force at 1 mM-Mg2+, pH 7.10, 22 degrees C and 250 mM ionic strength are about 8 X 10(-7) M for Ca2+, 5 X 10(-6) M for Cd2+, 2.6 X 10(-5) M for Sr2+ and 7 X 10(-4) M for Ba2+. Exposure of the skinned fibre to relatively low Ni2+ concentrations (between 10(-6) and 10(-5) M) resulted in a transient force response accompanied by an irreversible change in the ability of the preparation to develop force. The Ba2+- and Cd2+-activation curves are considerably flatter than the corresponding curves for Ca2+ and Sr2+. An increase in Mg2+ concentration from 1 to 3 mM decreased the sensitivity of the contractile apparatus to Ba2+ by a factor of about 1.5 without affecting the maximum force response. The Ca2+-activation curve was modified in the presence of subthreshold concentrations of Ba2+ and the results indicate that Ba2+ could have both an activating and an inhibitory action on the Ca2+-activated force. A kinetic model which can quantitatively explain the results for activation of contraction by Ba2+ and Ca2+, is described.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., Palade P. T. Slow calcium and potassium currents across frog muscle membrane: measurements with a vaseline-gap technique. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:159–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley C. C., Moisescu D. G. Effect of changing the composition of the bathing solutions upon the isometric tension-pCa relationship in bundles of crustacean myofibrils. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):627–652. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALDWELL P. C., WALSTER G. STUDIES ON THE MICRO-INJECTION OF VARIOUS SUBSTANCES INTO CRAB MUSCLE FIBRES. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:353–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C. Nickel substitution for calcium and the time course of potassium contractures of single muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1981 Jun;2(2):167–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00711867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson S. K., Kerrick W. G. Characterization of the effects of Mg2+ on Ca2+- and Sr2+-activated tension generation of skinned skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Oct;66(4):427–444. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.4.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis P. D., Strang P., Potter J. D. Cadmium-substituted skeletal troponin C. Cadmium-113 NMR spectroscopy and metal binding investigations. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10348–10356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischman D. A., Swan R. C. Nickel substitution for calcium in excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6):1709–1728. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsén S., Thulin E., Lilja H. 113Cd NMR in the study of calcium binding proteins: troponin C. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. B., Rohani F. Ba2+ ions block K+-induced contractures by antagonizing K+-induced membrane depolarization in frog skeletal muscle fibres. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;60(1):47–51. doi: 10.1139/y82-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J. The effect of calcium on the force-velocity relation of briefly glycerinated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):117–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura M., Mashima H. Contraction produced by intracellular injection of calcium, strontium, and barium in the single crayfish muscle fibers. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(2):145–157. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G. Kinetics of reaction in calcium-activated skinned muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):610–613. doi: 10.1038/262610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G., Thieleczek R. Calcium and strontium concentration changes within skinned muscle preparations following a change in the external bathing solution. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:241–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G., Thieleczek R. Sarcomere length effects on the Sr2+- and Ca2+-activation curves in skinned frog muscle fibres. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 11;546(1):64–76. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potreau D., Raymond G. Slow inward barium current and contraction on frog single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:91–109. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saks V. A., Rosenshtraukh L. V., Smirnov V. N., Chazov E. I. Role of creatine phosphokinase in cellular function and metabolism. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;56(5):691–706. doi: 10.1139/y78-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Williams D. A. Calcium-activated force responses in fast- and slow-twitch skinned muscle fibres of the rat at different temperatures. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:281–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Williams D. A. Effects of sarcomere length on the force-pCa relation in fast- and slow-twitch skinned muscle fibres from the rat. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:637–653. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. W., Podolsky R. J. Influence of magnesium on chloride-induced calcium release in skinned muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jan;69(1):17–35. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. W., Podolsky R. J. Regulation by magnesium of intracellular calcium movement in skinned muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jan;69(1):1–16. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallimann T., Turner D. C., Eppenberger H. M. Localization of creatine kinase isoenzymes in myofibrils. I. Chicken skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):297–317. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


