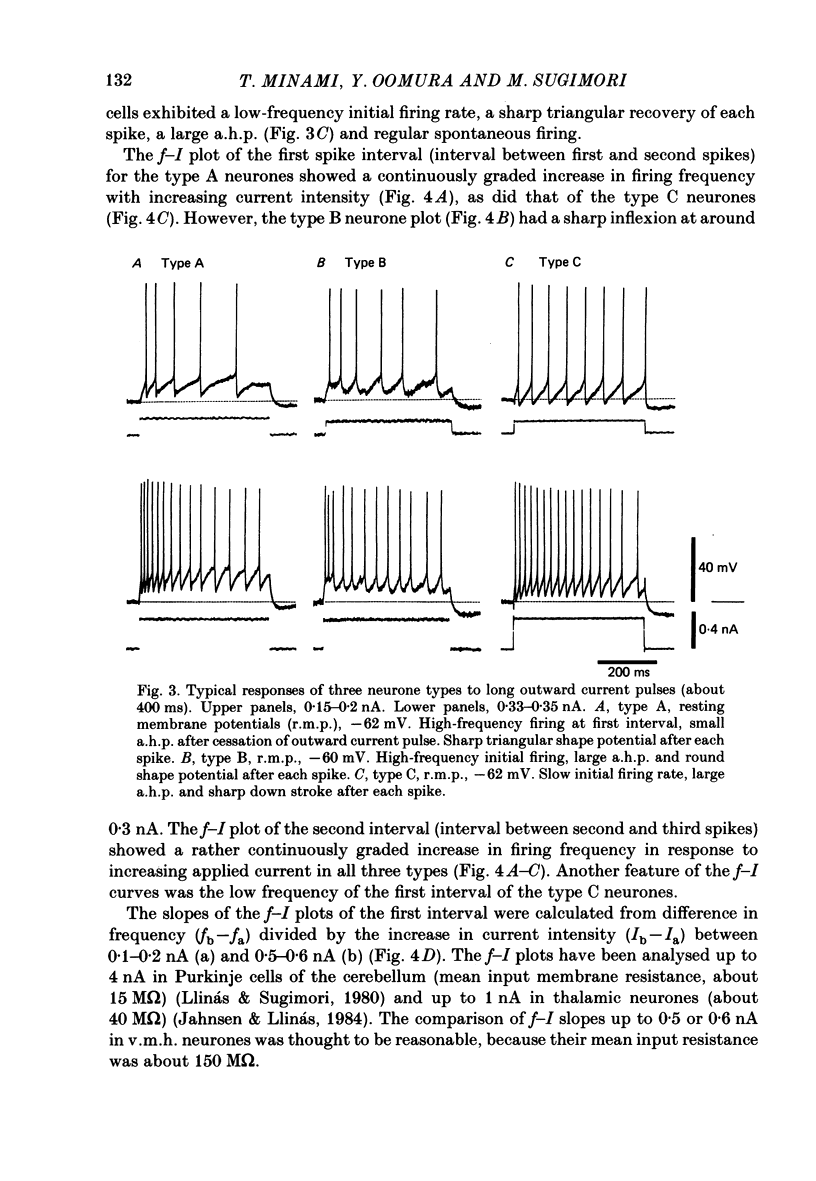
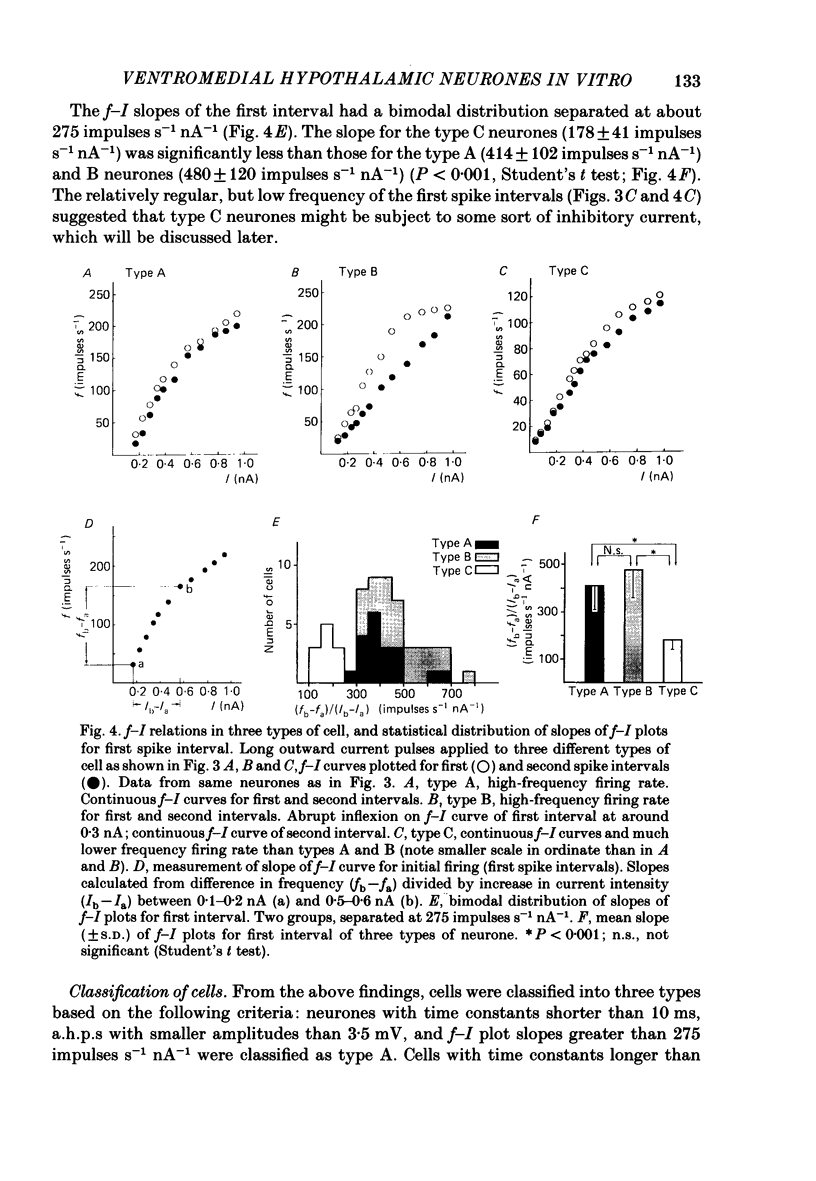
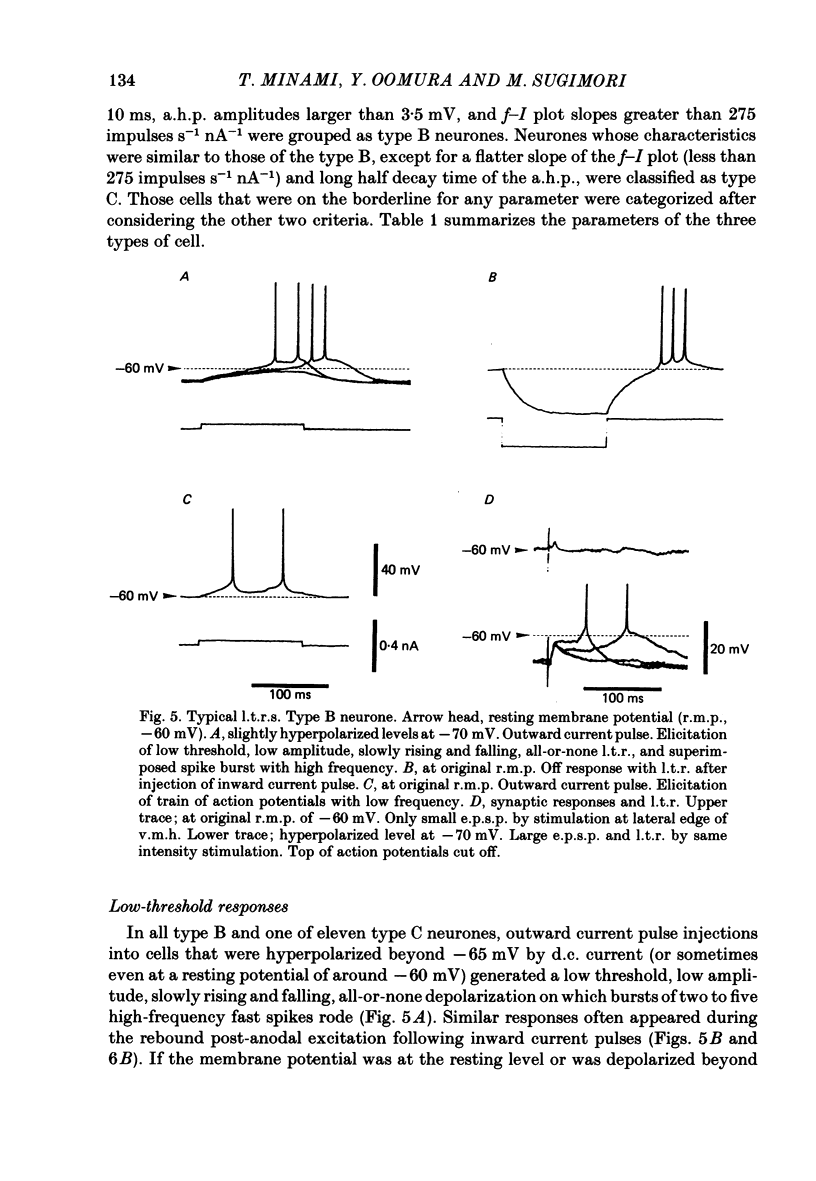
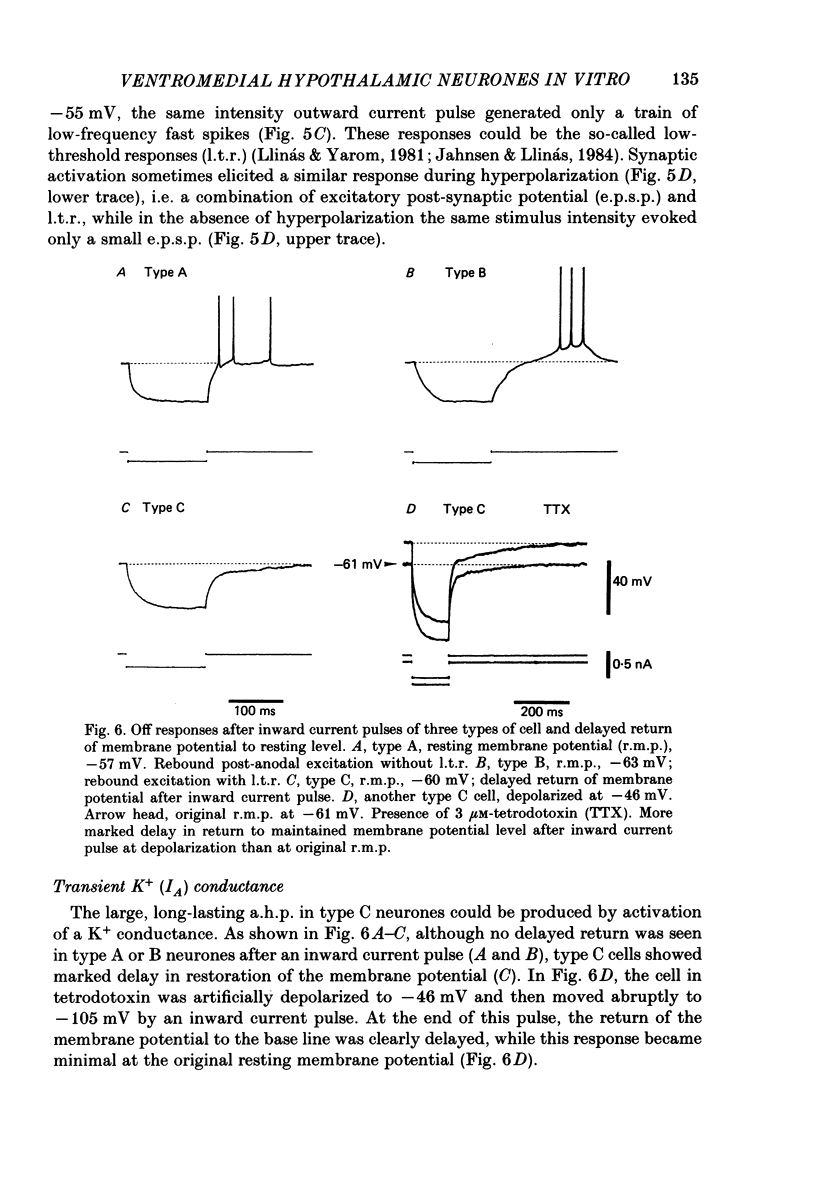
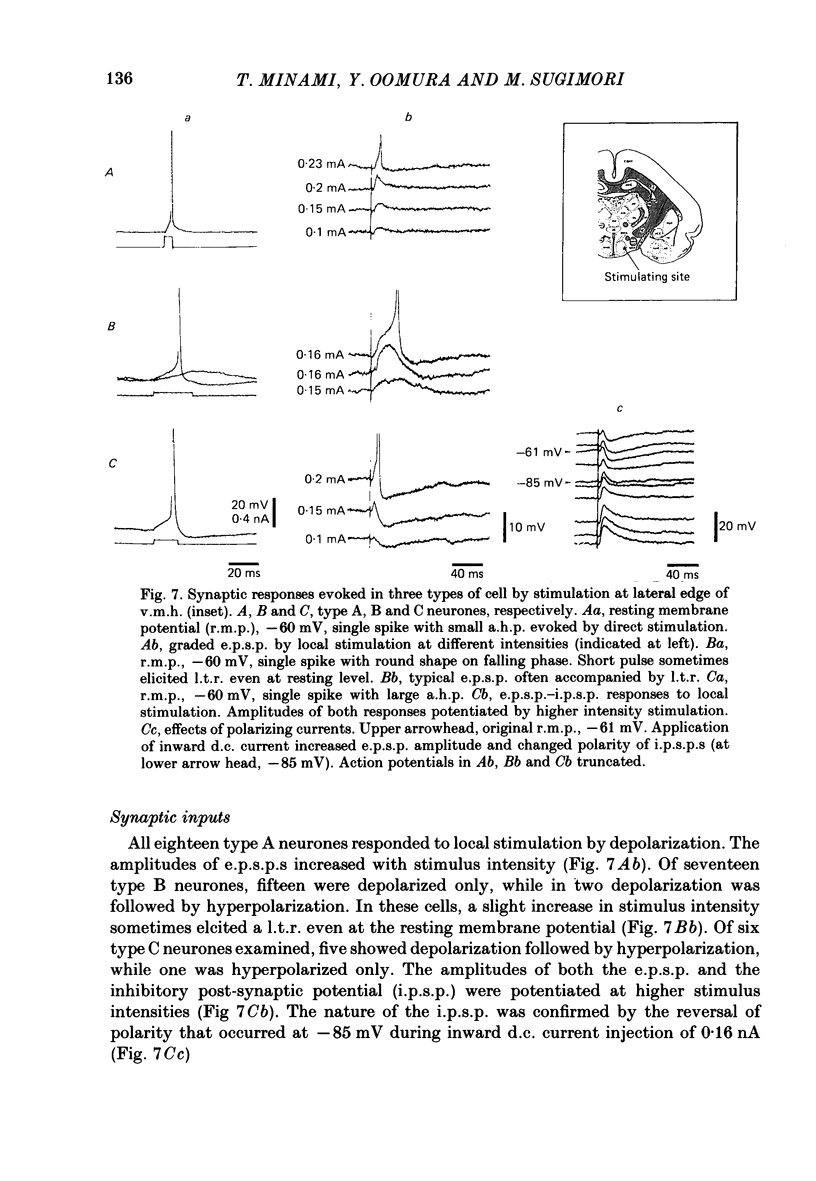
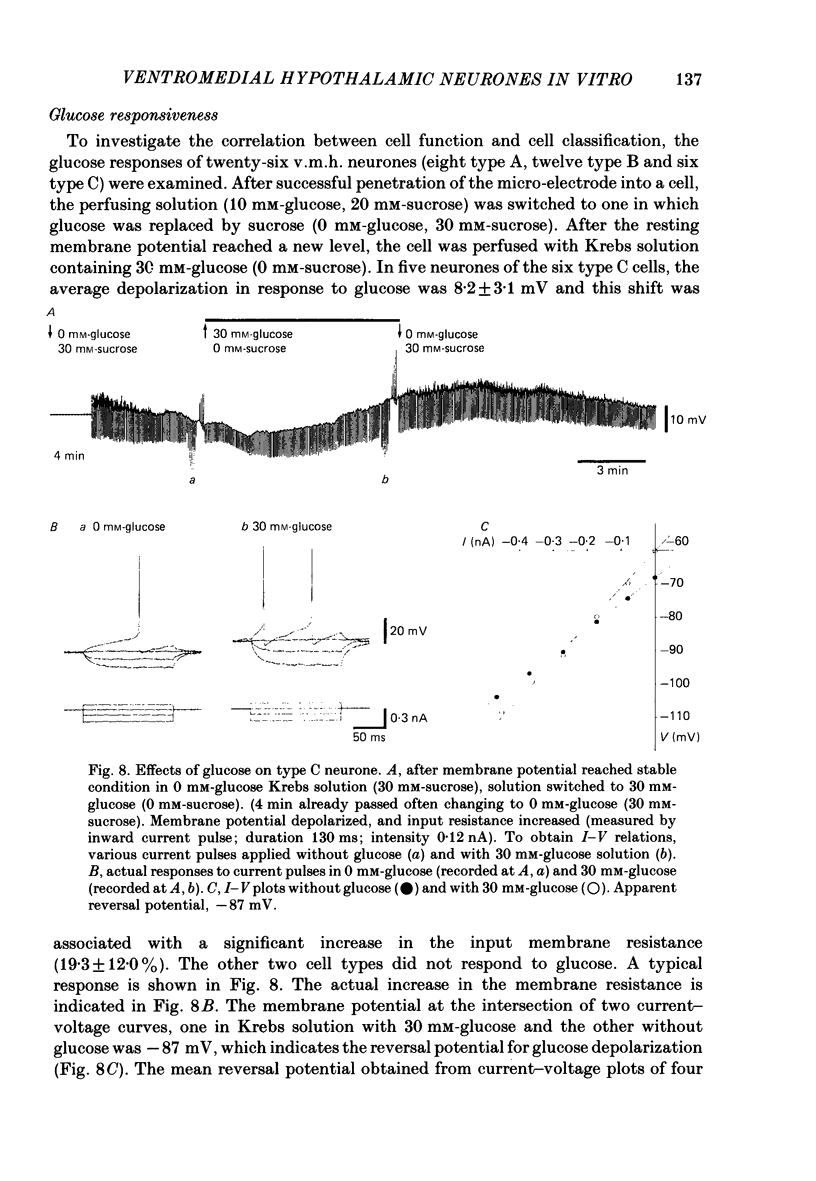
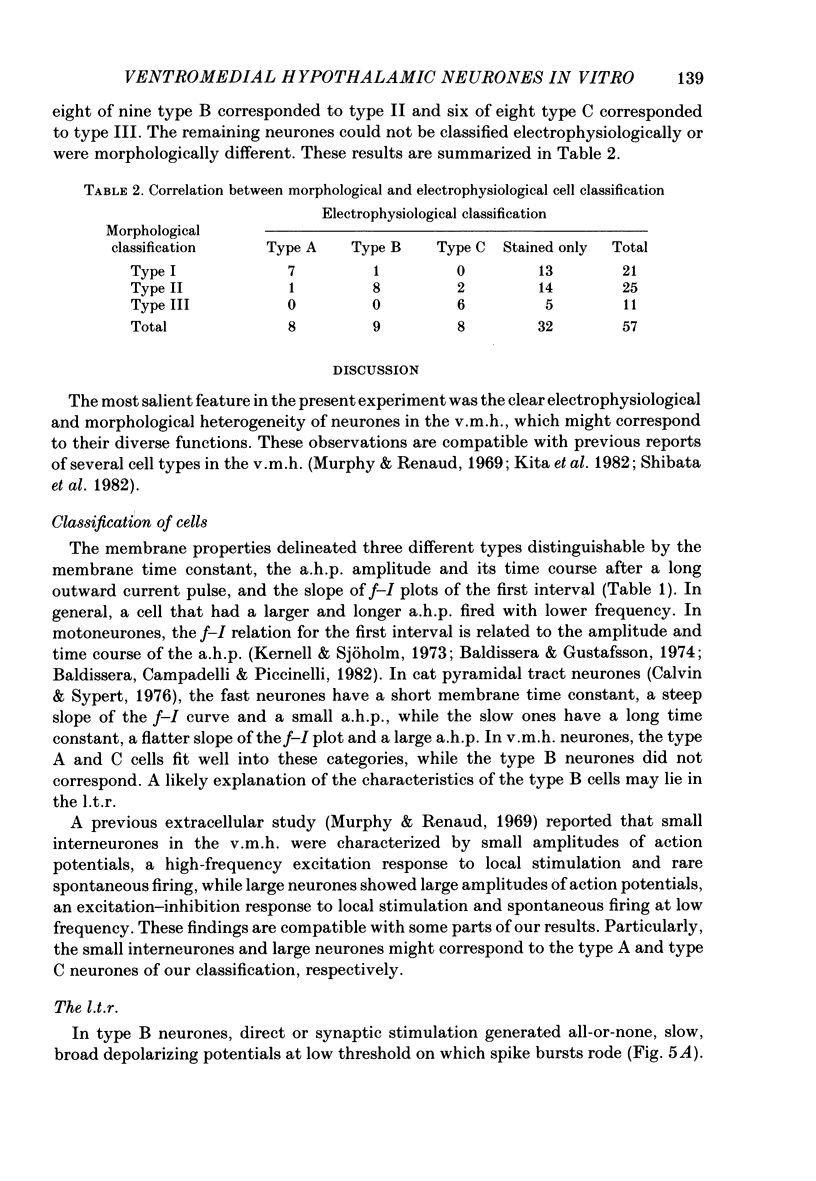
Abstract
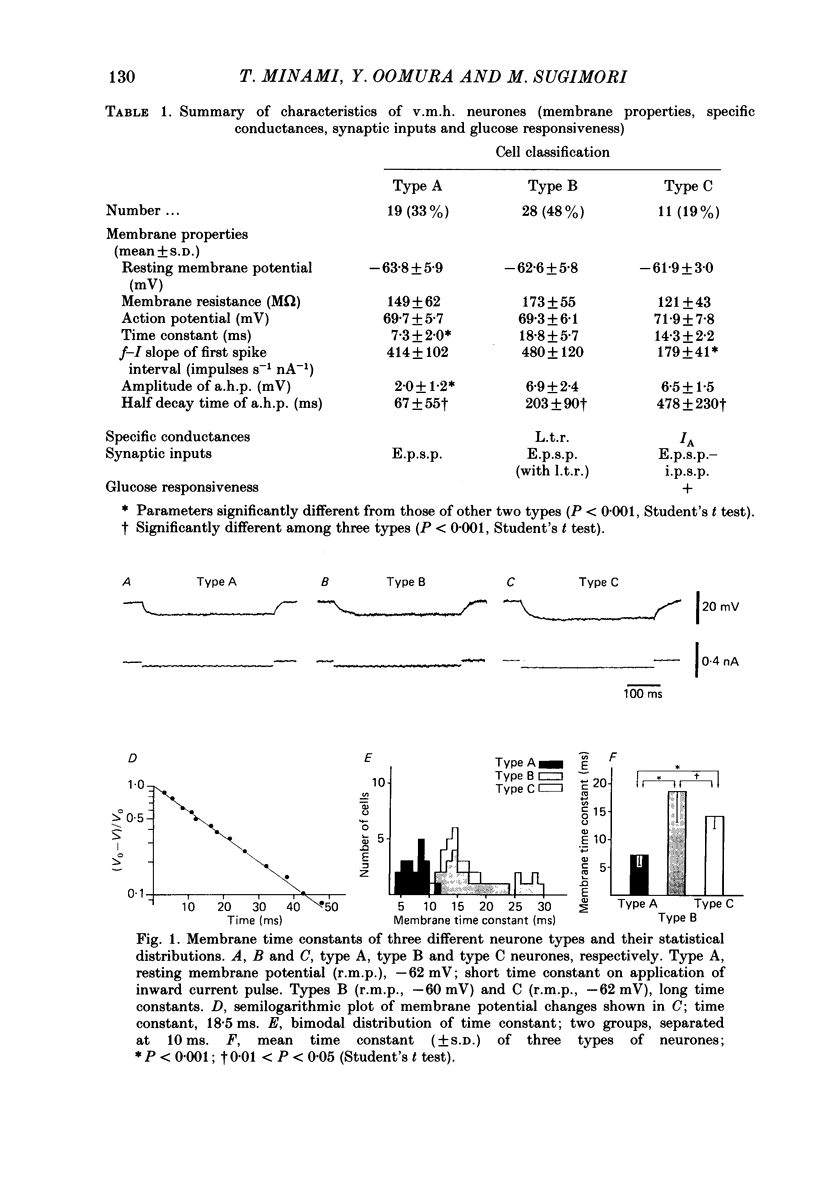
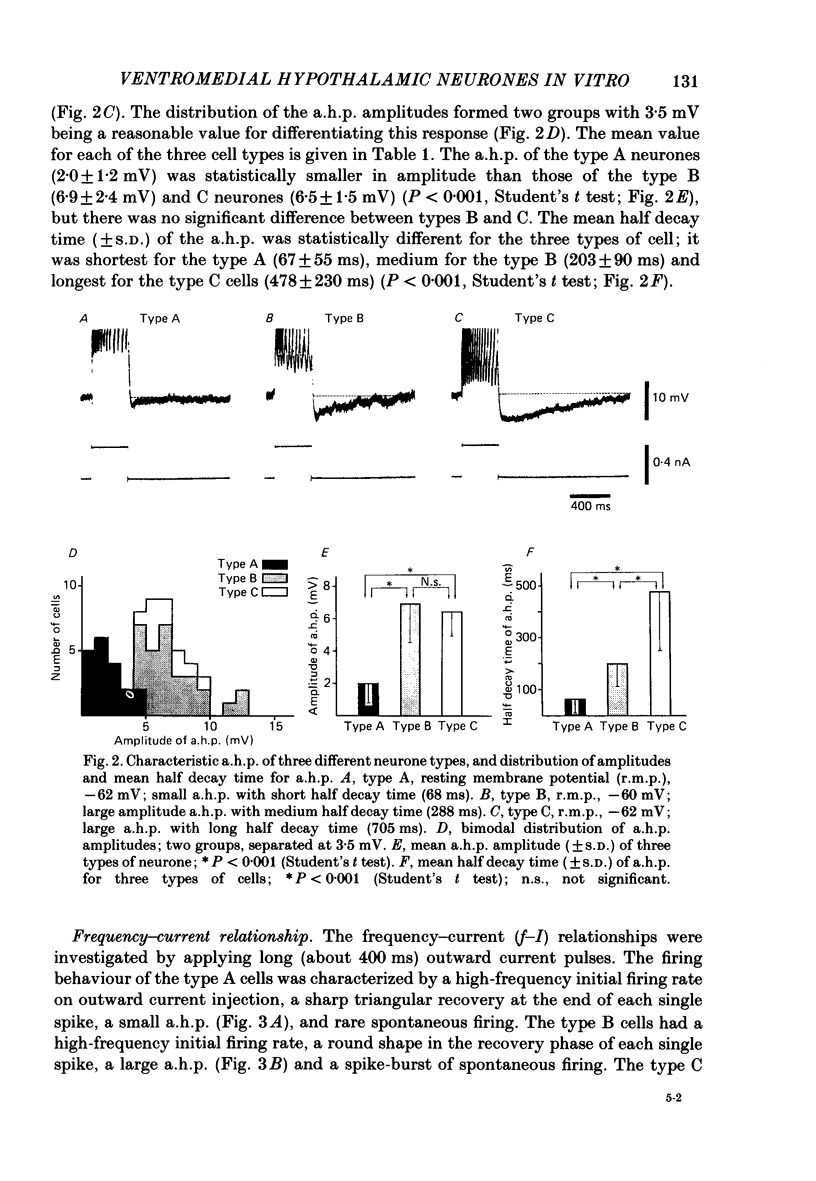
The membrane properties of neurones in the guinea-pig ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus (v.m.h.) were studied in in vitro brain slice preparations. The average resting potential was -62.9 +/- 5.4 mV (mean +/- S.D.), input resistance was 155 +/- 58 M omega, and action potential amplitude was 69.9 +/- 6.3 mV. Three types of neurone were identified. The type A neurones were characterized by a short membrane time constant (7.3 +/- 2.0 ms) and a small after-hyperpolarization (a.h.p.) (2.0 +/- 1.2 mV) with a short half decay time of 67 +/- 55 ms after stimulation with a long outward current pulse. Type B had a long time constant (18.8 +/- 5.7 ms) and a large a.h.p. (6.9 +/- 2.4 mV) with a medium half decay time of 203 +/- 90 ms. Type C was characterized by a long time constant (14.3 +/- 2.3 ms) and a large a.h.p. (6.5 +/- 1.5 mV) with a long half decay time of 478 +/- 230 ms. The slopes of the frequency-current (f-I) plots of the three types were different, particularly for the first spike interval. The slopes for the type A (414 +/- 102 impulses s-1 nA-1) and type B neurones (480 +/- 120 impulses s-1 nA-1) were steeper than that for the type C neurones (178 +/- 41 impulses s-1 nA-1). This difference is probably related to the relatively long first interval observed in the type C neurones. In all type B and a few type C neurones, when the membrane potential was hyperpolarized beyond--65 mV the application of orthodromic or direct stimulation generated a burst of spikes, consisting of a low-threshold response (l.t.r.) of low amplitude and superimposed high-frequency spikes. At the original resting potential, outward current pulses produced a train of low-frequency spikes. In type C neurones maintained in a depolarized state (about -50 mV), inward current pulses produced a specific delay of the return to the original membrane potential. This delayed return was thought to be generated by activation of a transient K+ (IA) conductance. Stimulation at the lateral edge of the v.m.h. produced excitatory post-synaptic potentials (e.p.s.p.s) in type A neurones, e.p.s.p.s with l.t.r. in type B neurones and e.p.s.p.-inhibitory post-synaptic potential sequences in type C neurones. About 20% of v.m.h. neurones, particularly the type C cells, were depolarized by glucose application with an associated increase in the input membrane resistance.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANAND B. K., CHHINA G. S., SHARMA K. N., DUA S., SINGH B. ACTIVITY OF SINGLE NEURONS IN THE HYPOTHALAMIC FEEDING CENTERS: EFFECT OF GLUCOSE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Nov;207:1146–1154. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.5.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Cyclic changes in potential and resistance of the beta-cell membrane induced by glucose in islets of Langerhans from mouse. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:117–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldissera F., Campadelli P., Piccinelli L. Neural encoding of input transients investigated by intracellular injection of ramp currents in cat alpha-motoneurones. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:73–86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldissera F., Gustafsson B. Firing behaviour of a neurone model based on the afterhyperpolarization conductance time course. First interval firing. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Aug;91(4):528–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin W. H., Sypert G. W. Fast and slow pyramidal tract neurons: an intracellular analysis of their contrasting repetitive firing properties in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Mar;39(2):420–434. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.2.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clattenburg R. E. Ultrastructure of hypothalamic neurons and of the median eminence. Can J Neurol Sci. 1974 Feb;1(1):40–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Prediction of repetitive firing behaviour from voltage clamp data on an isolated neurone soma. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):31–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Harris M. C., Tribollet E. Excitation of phasically firing hypothalamic supraoptic neurones by carotid occlusion in rats. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(2):337–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Galvan M., Grafe P., Wigström H. A transient outward current in a mammalian central neurone blocked by 4-aminopyridine. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):252–254. doi: 10.1038/299252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., KUSANO K., SAITO N. Membrane changes of Onchidium nerve cell in potassium-rich media. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:470–489. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto P. H., Hama K. An electron microscopic study of protein uptake into brain regions devoid of the blood-brain barrier. Med J Osaka Univ. 1968 Mar;18(4):331–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H., Llinás R. Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:205–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. J., Kuhnt U., Wuttke W. Morphological features of physiologically identified hypothalamic neurons as revealed by intracellular marking. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Jan 2;34(1):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00238344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. J., Ronnekleiv O. K., Eskay R. L. Identification of estrogen-responsive LHRH neurons in the guinea pig hypothalamus. Brain Res Bull. 1984 Apr;12(4):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(84)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Sjöholm H. Repetitive impulse firing: comparisons between neurone models based on 'voltage clamp equations' and spinal motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Jan;87(1):40–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita H., Shibata S., Oomura Y., Ohki K. Excitatory effects of the suprachiasmatic nucleus on the ventromedial nucleus in the rat hypothalamic slice. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 4;235(1):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:171–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Yarom Y. Electrophysiology of mammalian inferior olivary neurones in vitro. Different types of voltage-dependent ionic conductances. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:549–567. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millhouse O. E. Cytological observations on the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Aug 16;191(3):473–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00219810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami T., Oomura Y., Sugimori M. Ionic basis for the electroresponsiveness of guinea-pig ventromedial hypothalamic neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:145–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno Y., Oomura Y. Glucose responding neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the rat: in vitro study. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 30;307(1-2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90466-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. T., Renaud L. P. Mechanisms of inhibition in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Jan;32(1):85–102. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAO H. Emotional behavior produced by hypothalamic stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1958 Aug;194(2):411–418. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.194.2.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OOMURA Y., KIMURA K., OOYAMA H., MAENO T., IKI M., KUNIYOSHI M. RECIPROCAL ACTIVITIES OF THE VENTROMEDIAL AND LATERAL HYPOTHALAMIC AREAS OF CATS. Science. 1964 Jan 31;143(3605):484–485. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3605.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Nishino H., Fukuda M., Sasaki K., Muramoto K., Oomura Y. Glucoresponsive neurons in rat ventromedial hypothalamic tissue slices in vitro. Brain Res. 1982 Jan 28;232(2):494–499. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oomura Y., Ono T., Ooyama H., Wayner M. J. Glucose and osmosensitive neurones of the rat hypothalamus. Nature. 1969 Apr 19;222(5190):282–284. doi: 10.1038/222282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oomura Y., Ono T., Sugimori M. Immunological study of the rat hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus. Brain Res Bull. 1985 Feb;14(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(85)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oomura Y., Ooyama H., Naka F., Yamamoto T., Ono T., Kobayashi N. Some stochastical patterns of single unit discharges in the cat hypothalamus under chronic conditions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 May 15;157(2):666–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb12913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff D. W. Impact of estrogens on hypothalamic nerve cells: ultrastructural, chemical, and electrical effects. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1983;39:127–179. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571139-5.50007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff D. W., Sakuma Y. Facilitation of the lordosis reflex of female rats from the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:189–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud L. P. Influence of medial preoptic-anterior hypothalamic area stimulation of the excitability of mediobasal hypothalamic neurones in the rat. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(2):541–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma Y., Tada K. Evidence that two sizes of ventromedial hypothalamic neurones project to the mesencephalic central grey matter in rats. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:287–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saphier D. J., Dyer R. G. Bursting activity in tuberoinfundibular neurones during electrical stimulation of the rostral hypothalamus. Exp Brain Res. 1980;39(1):113–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00237074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata S., Oomura Y., Hori N. Neuronal control of the ventromedial nucleus from the periventricular nucleus in the hypothalamic slice of the rat. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jun;8(6):613–616. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimono M. [Cellular architecture of the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus of the rat; a quantitative morphological study]. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi. 1983 Jul;74(7):432–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TINDAL J. S. THE FOREBRAIN OF THE GUINEA PIG IN STEREOTAXIC COORDINATES. J Comp Neurol. 1965 Apr;124:259–266. doi: 10.1002/cne.901240210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M., Noda Y. Light and electron microscope studies on the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus of the cat, with special reference to the fine structures of neurons and synapses. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1974 Jan;28(1):45–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1974.tb02285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten M., Brawer J. R. Cytology of neurons of the hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus in the adult male rat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Mar 1;178(1):89–116. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita H., Inenaga K., Kawata M., Sano Y. Phasically firing neurons in the supraoptic nucleus of the rat hypothalamus: immunocytochemical and electrophysiological studies. Neurosci Lett. 1983 May 27;37(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90509-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]