Abstract
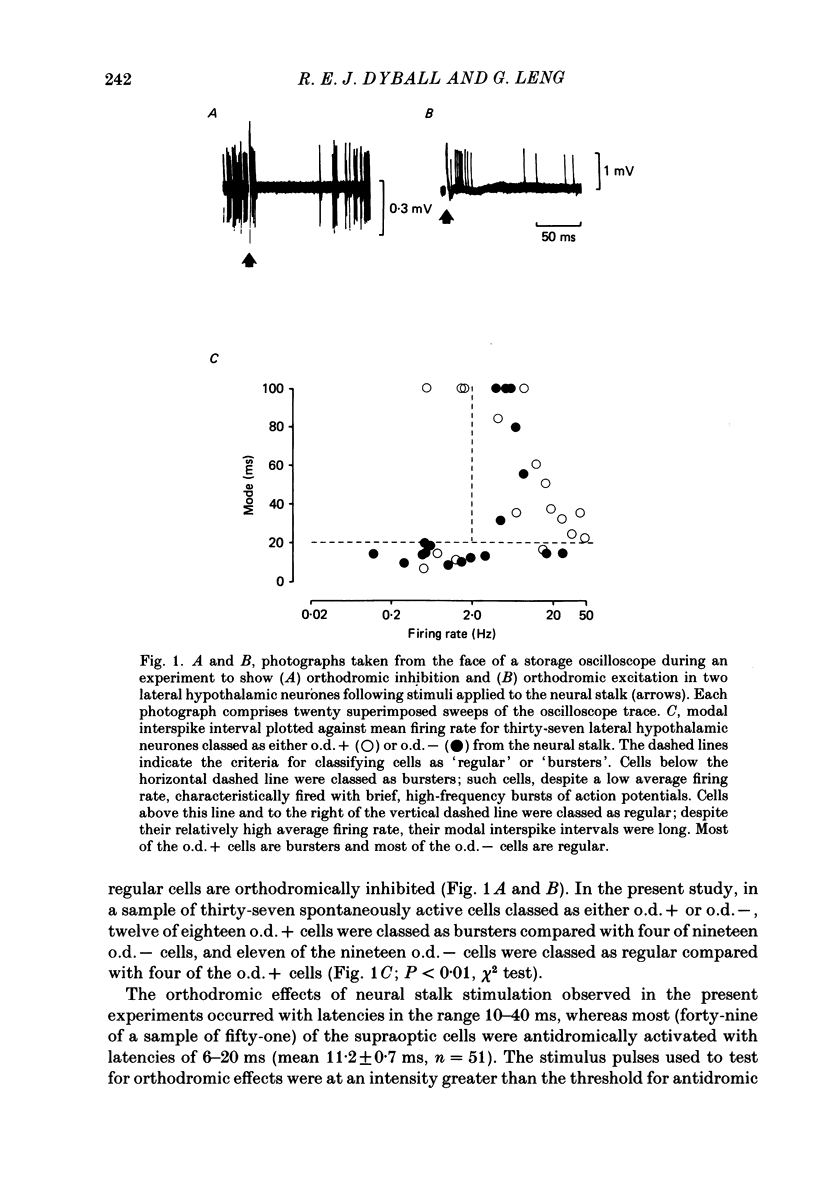
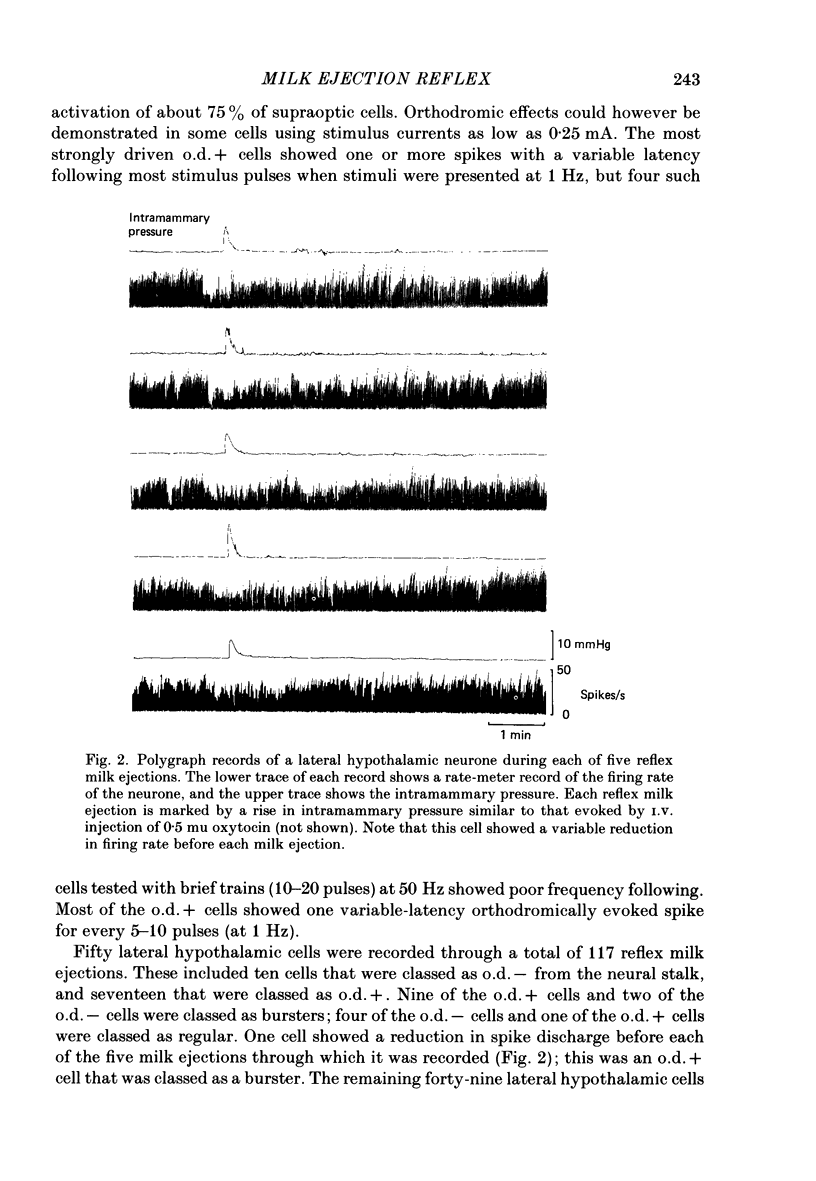
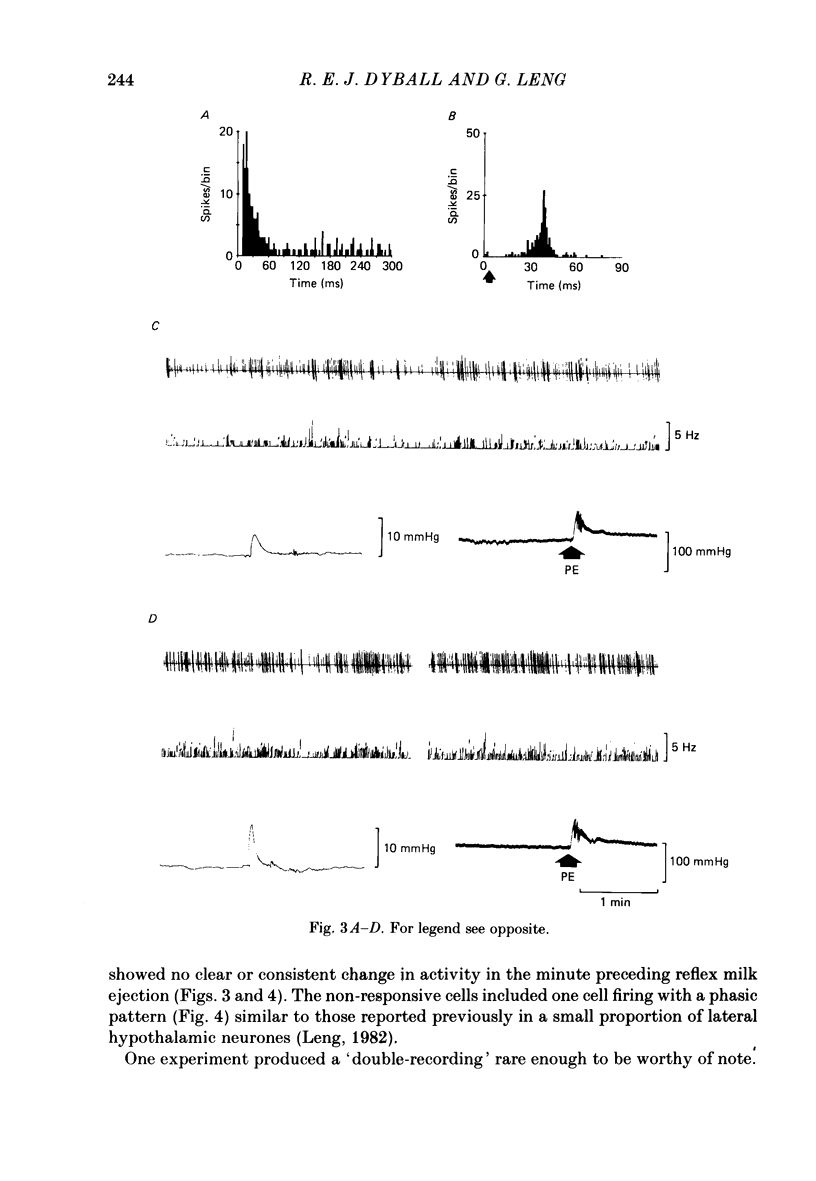
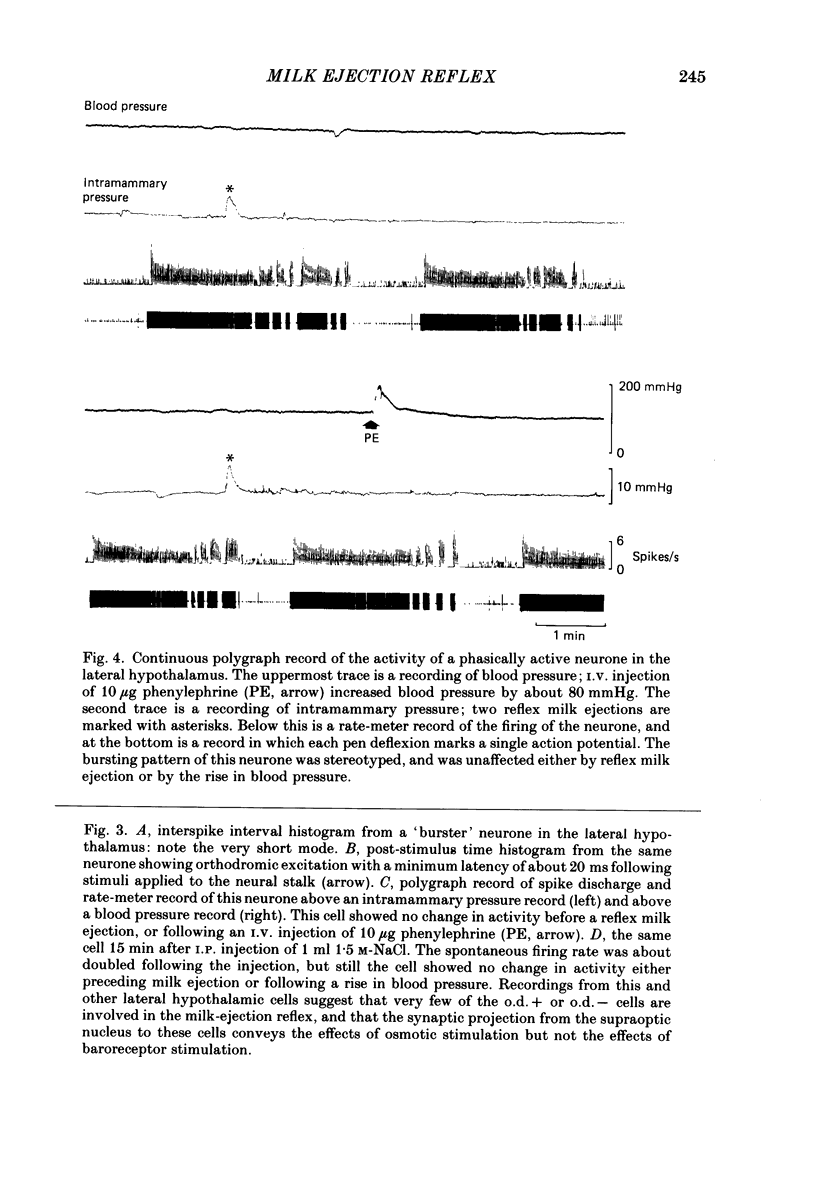
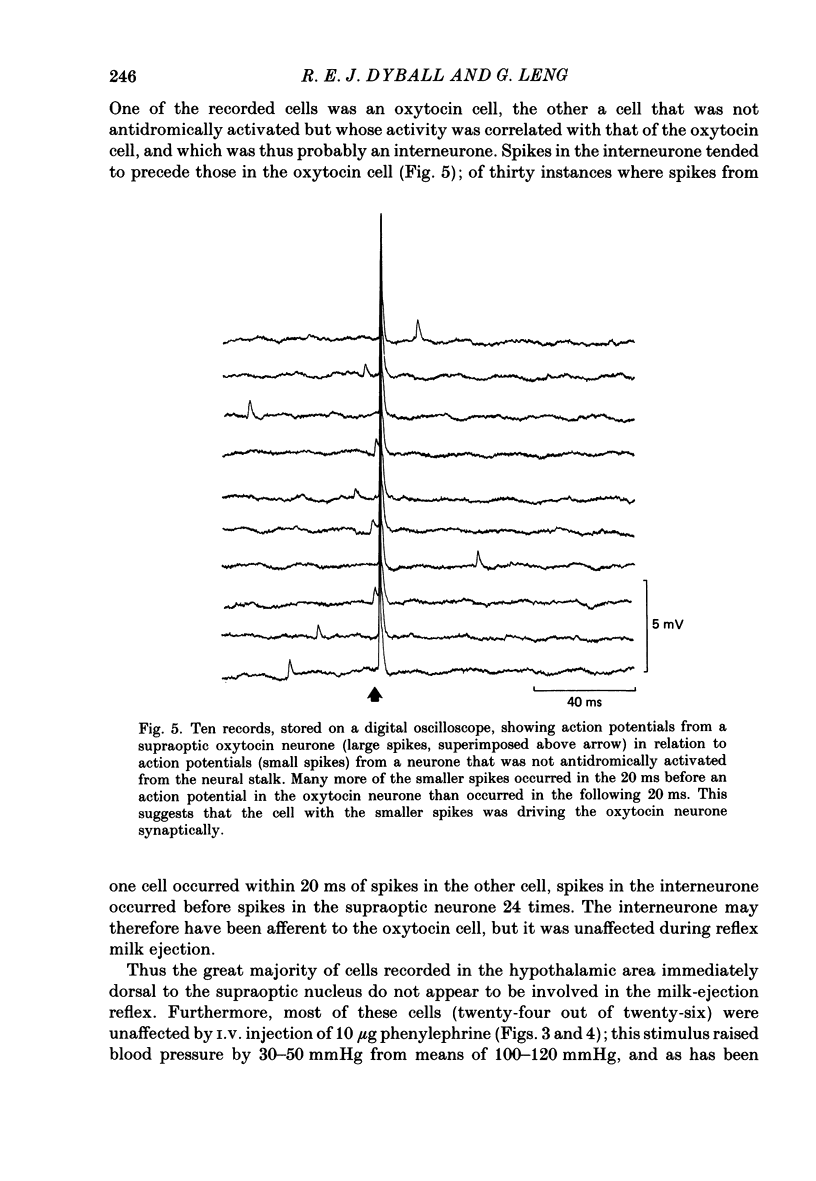
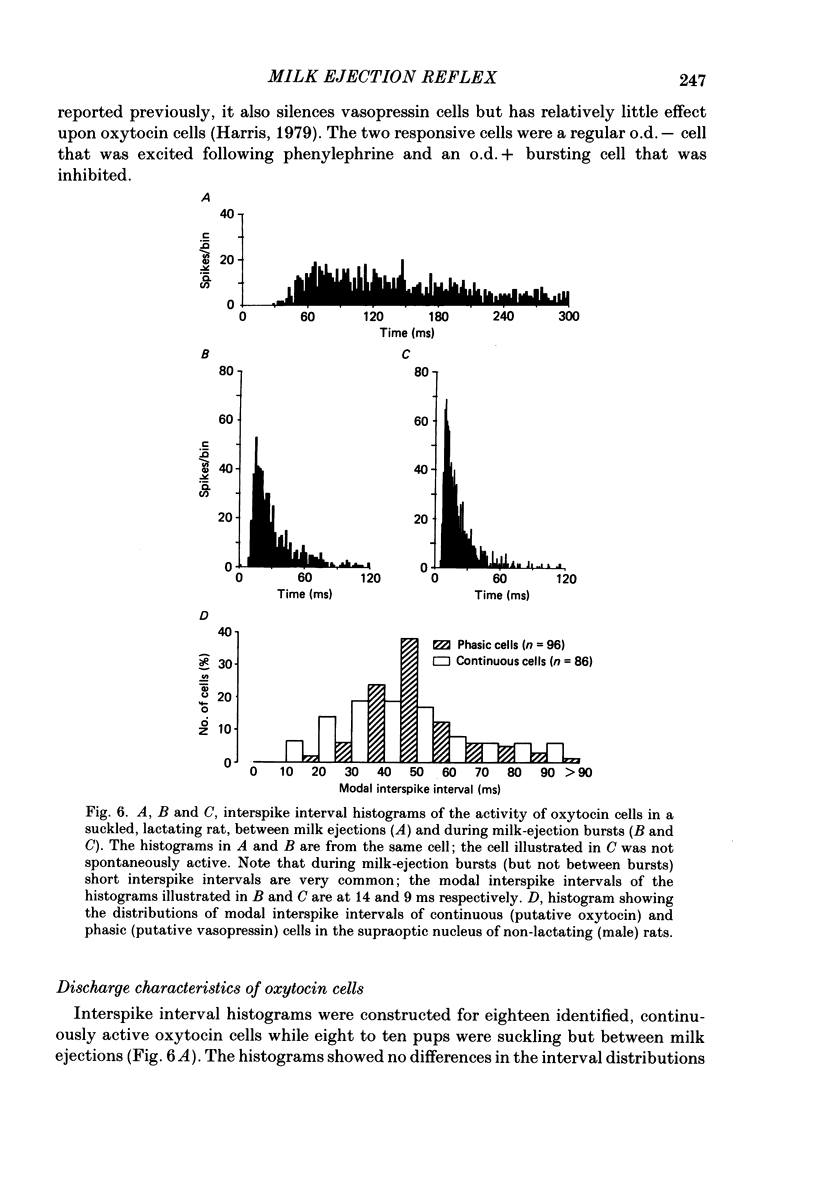
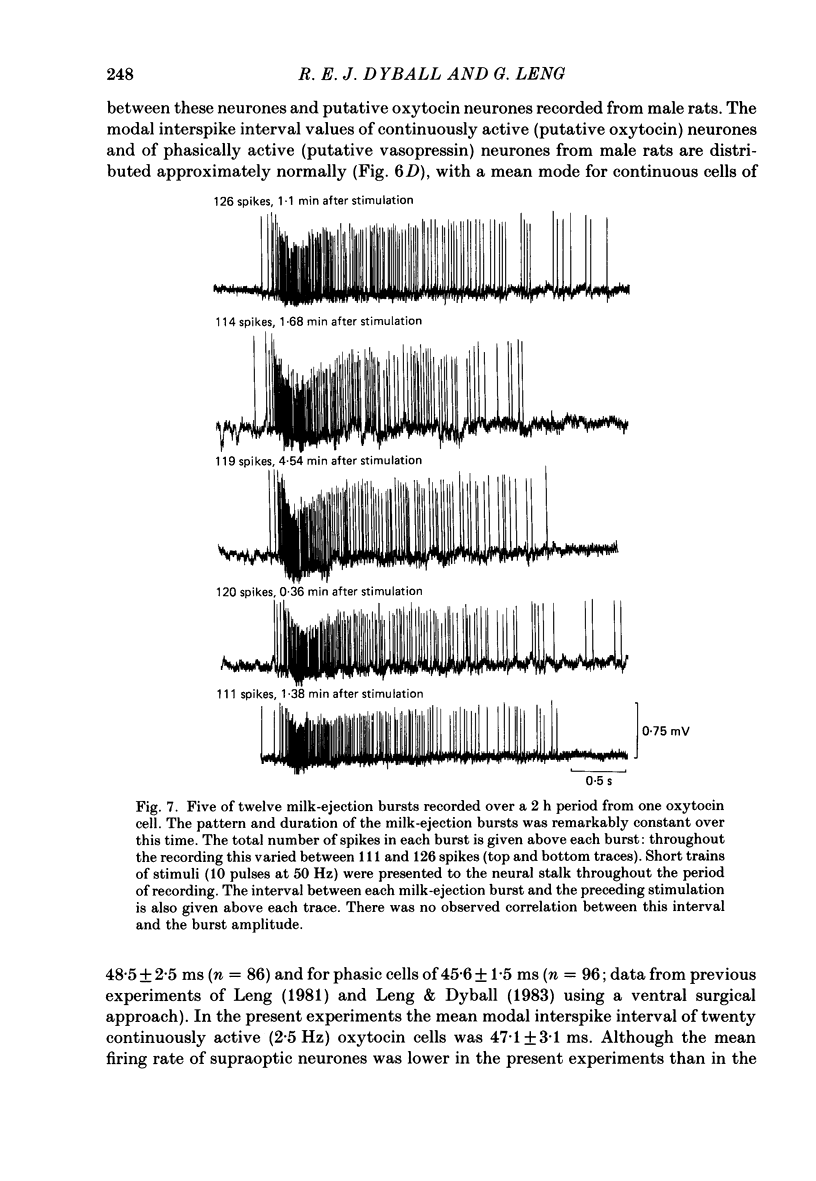
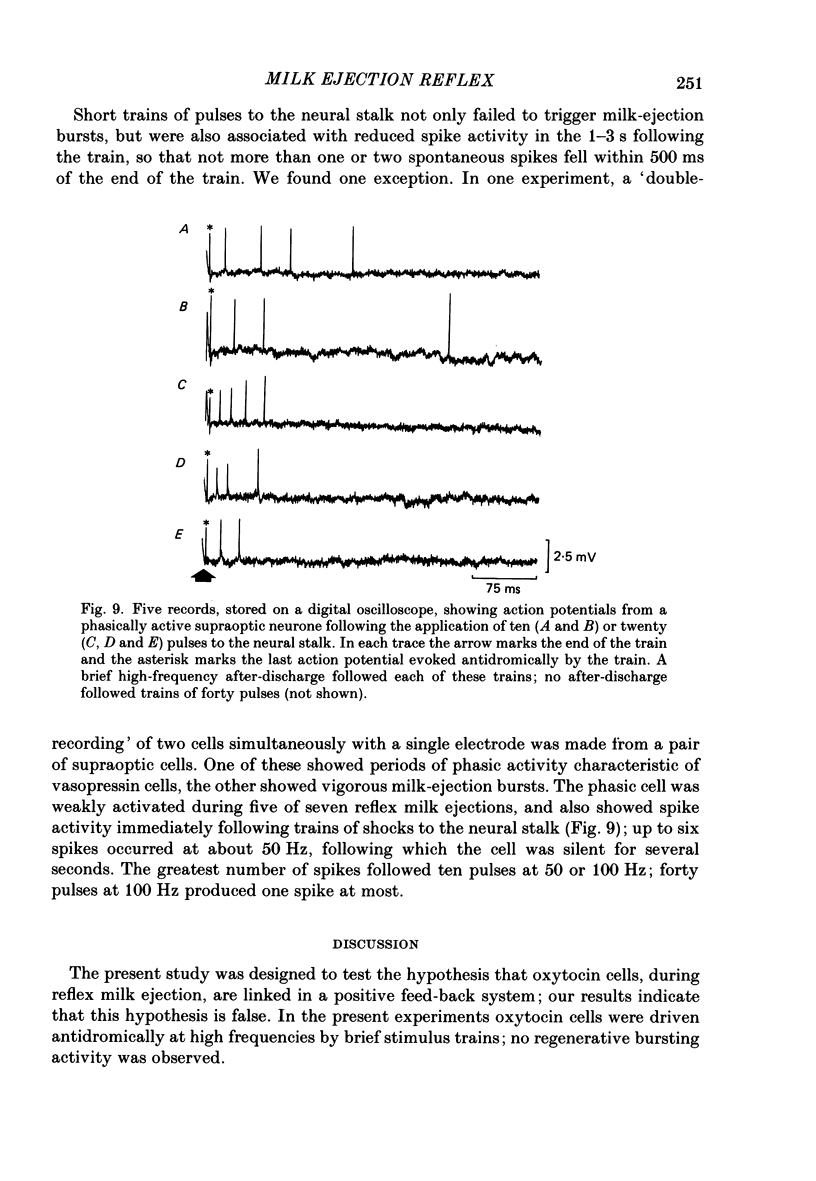
Extracellular recordings were made from neurones in or near the supraoptic nucleus in suckled lactating rats under urethane anaesthesia to investigate the mechanism by which the firing of oxytocin cells is synchronized during reflex milk ejection. Cells synaptically driven but not antidromically activated by neural stalk stimulation, which thus probably receive an afferent input from supraoptic neurones, were classified as 'regular' or 'bursters' on the basis of their spontaneous electrical activity. The majority (twelve out of eighteen) of synaptically excited cells (o.d.+) were bursters and the majority of inhibited (o.d.-) cells (eleven out of nineteen) were regular, but only one o.d.+ burster showed any change of activity (inhibition) before milk ejection. Putative oxytocin cells in suckled lactating rats showed a firing pattern between milk-ejection bursts which could not be distinguished from that of putative oxytocin cells in male animals. The mode interspike interval between milk ejections was 47.1 +/- 3.1 ms (mean +/- S.E. of mean) compared with 47.3 +/- 3.3 ms in male rats, and fewer than 1.4% of interspike intervals were less than 20 ms in duration. By contrast, within milk-ejection bursts 40% of interspike intervals were in the range 8-20 ms. Short trains (10 or 20) of pulses applied to the neural stalk at regular (5 min) intervals, in an attempt to simulate the initial part of the milk ejection burst, failed to trigger bursts. In only 2 of 150 tests was the interval between train and milk-ejection burst less than 10 s, and after the pulse train all but one cell showed reduced activity for 1-3 s. The trains of pulses were however not without effect: they significantly (P less than 0.01) enhanced the chance of a milk-ejection burst occurring within the next 2.5 min. Our observation that pulse trains do not trigger bursts suggests that local positive feed-back mechanisms are not responsible for orchestrating the activation of oxytocin cells during the milk-ejection reflex. Moreover, because spontaneous tiring pattern is the same in lactating and non-lactating rats, we found no evidence that the anatomical changes in the synaptic organization within the supraoptic nuclei in lactation have any influence on the firing of oxytocin cells. It is likely, however, since pulse trains alter the timing of milk ejections, that oxytocin released locally in the region of the supraoptic nucleus can influence reflex milk ejection.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew R. D., Dudek F. E. Intrinsic inhibition in magnocellular neuroendocrine cells of rat hypothalamus. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:171–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew R. D., MacVicar B. A., Dudek F. E., Hatton G. I. Dye transfer through gap junctions between neuroendocrine cells of rat hypothalamus. Science. 1981 Mar 13;211(4487):1187–1189. doi: 10.1126/science.7466393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin V., Moos F., Richard P. Synchronization of oxytocin cells in the hypothalamic paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei in suckled rats: direct proof with paired extracellular recordings. Exp Brain Res. 1984;57(1):201–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00231147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimble M. J., Dyball R. E. Characterization of the responses of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones in the supraoptic nucleus to osmotic stimulation. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni J. E., Perumal P. M. Cytoarchitecture of the rat's supraoptic nucleus. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1984;170(2):129–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00318997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbett P., Smithson K. G., Hatton G. I. Dye-coupled magnocellular peptidergic neurons of the rat paraventricular nucleus show homotypic immunoreactivity. Neuroscience. 1985 Dec;16(4):885–895. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund-Mercier M. J., Richard P. Electrophysiological evidence for facilitatory control of oxytocin neurones by oxytocin during suckling in the rat. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:447–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. C. Effects of chemoreceptor and baroreceptor stimulation on the discharge of hypothalamic supraoptic neurones in rats. J Endocrinol. 1979 Jul;82(1):115–125. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0820115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton G. I., Ho Y. W., Mason W. T. Synaptic activation of phasic bursting in rat supraoptic nucleus neurones recorded in hypothalamic slices. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:297–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton G. I., Perlmutter L. S., Salm A. K., Tweedle C. D. Dynamic neuronal-glial interactions in hypothalamus and pituitary: implications for control of hormone synthesis and release. Peptides. 1984;5 (Suppl 1):121–138. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton G. I., Tweedle C. D. Magnocellular neuropeptidergic neurons in hypothalamus: increases in membrane apposition and number of specialized synapses from pregnancy to lactation. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Feb;8(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juss T. S., Wakerley J. B. Mesencephalic areas controlling pulsatile oxytocin release in the suckled rat. J Endocrinol. 1981 Nov;91(2):233–244. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0910233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G., Dyball R. E. Intercommunication in the rat supraoptic nucleus. Q J Exp Physiol. 1983 Jul;68(3):493–504. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1983.sp002742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G. Lateral hypothalamic neurones: osmosensitivity and the influence of activating magnocellular neurosecretory neurones. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:35–48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G. The effects of neural stalk stimulation upon firing patterns in rat supraoptic neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1981;41(2):135–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00236603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln D. W., Wakerley J. B. Electrophysiological evidence for the activation of supraoptic neurones during the release of oxytocin. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):533–554. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln D. W., Wakerley J. B. Factors governing the periodic activation of supraoptic and paraventricular neurosecretory cells during suckling in the rat. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(2):443–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. T., Ho Y. W., Hatton G. I. Axon collaterals of supraoptic neurones: anatomical and electrophysiological evidence for their existence in the lateral hypothalamus. Neuroscience. 1984 Jan;11(1):169–182. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos F., Freund-Mercier M. J., Guerné Y., Guerné J. M., Stoeckel M. E., Richard P. Release of oxytocin and vasopressin by magnocellular nuclei in vitro: specific facilitatory effect of oxytocin on its own release. J Endocrinol. 1984 Jul;102(1):63–72. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1020063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro H., Uchide K., Honda K., Higuchi T. Facilitatory effect of antidromic stimulation on milk ejection-related activation of oxytocin neurons during suckling in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Aug 16;59(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B., Dyball R. E. Electrophysiological differentiation of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Apr;196(1125):367–384. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodosis D. T. Oxytocin-immunoreactive terminals synapse on oxytocin neurones in the supraoptic nucleus. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):682–684. doi: 10.1038/313682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodosis D. T., Poulain D. A. Evidence for structural plasticity in the supraoptic nucleus of the rat hypothalamus in relation to gestation and lactation. Neuroscience. 1984 Jan;11(1):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90222-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodosis D. T., Poulain D. A. Evidence that oxytocin-secreting neurones are involved in the ultrastructural reorganisation of the rat supraoptic nucleus apparent at lactation. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;235(1):217–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00213745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodosis D. T., Poulain D. A., Vincent J. D. Possible morphological bases for synchronisation of neuronal firing in the rat supraoptic nucleus during lactation. Neuroscience. 1981;6(5):919–929. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90173-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita H., Inenaga K., Kawata M., Sano Y. Phasically firing neurons in the supraoptic nucleus of the rat hypothalamus: immunocytochemical and electrophysiological studies. Neurosci Lett. 1983 May 27;37(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90509-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


