Abstract
In order to determine the role of the carotid bodies on the ventilatory control characteristics during the non-steady-state phase of exercise in man, six normal males performed cycle ergometry with four repetitions of a 6 min, constant-load work bout at inspired O2 fractions (FI,O2) of 0.12, 0.15, 0.21, 0.30 and 1.00. Each test began with unloaded pedalling; this was followed by a constant load which was 90% of the subject's anaerobic threshold at FI,O2 = 0.12. Ventilation (VE), CO2 output (VCO2) and O2 uptake (VO2) were determined breath-by-breath during the test and the time constants of response (tau VE, tau VCO2 and tau VO2) were established by least-squares techniques, following interpolation (1 s), temporal alignment and averaging of the four responses. In each subject, tau VE and tau VCO2 increased as functions of increasing FI,O2, and were inverse functions of the proportional contribution to VE of peripheral chemoreceptor drive (as estimated from hyperoxic-transition or 'Dejours' tests). tau VE averaged 40 s at FI,O2 = 0.12 and 112 s at FI,O2 = 1.00, each response being well fitted by a single exponential. However, tau VO2 was not significantly affected by the alterations in FI,O2. Although there was no discernible peripheral chemosensitivity at FI,O2 = 0.30 or 1.00, the tau VE increased appreciably between these inspirates. We therefore conclude that the peripheral chemoreceptors are important, but not exclusive determinants of the exponential response characteristics during the non-steady-state phase of the exercise hyperpnoea in man. This supports the contention of a component of the control being humorally mediated even during moderate exercise.
Full text
PDF

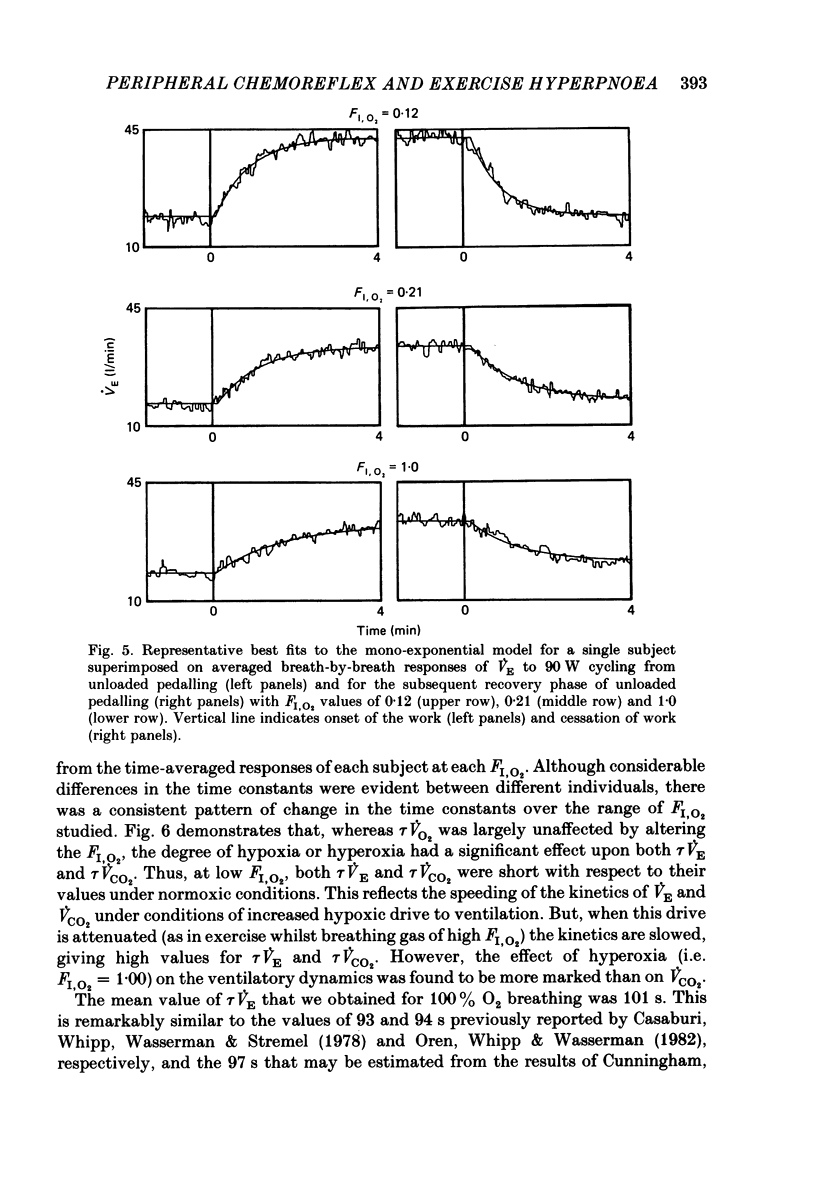
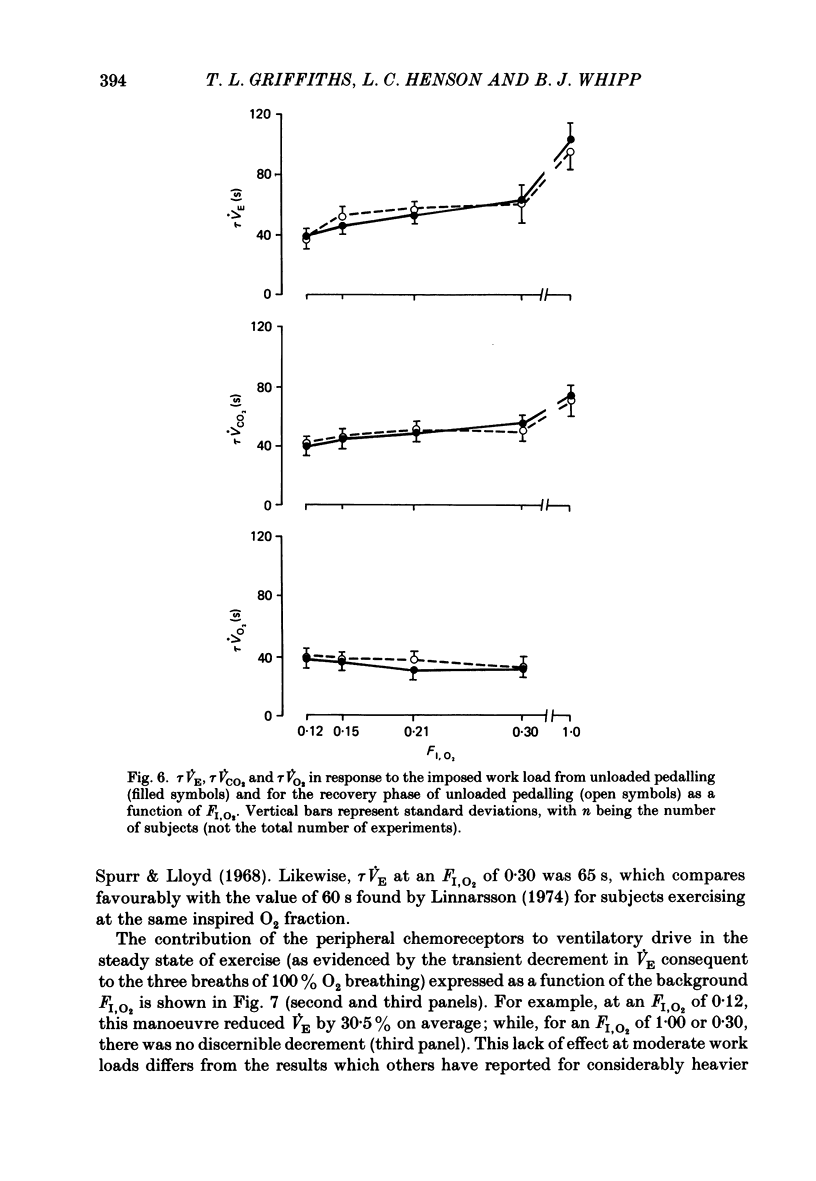
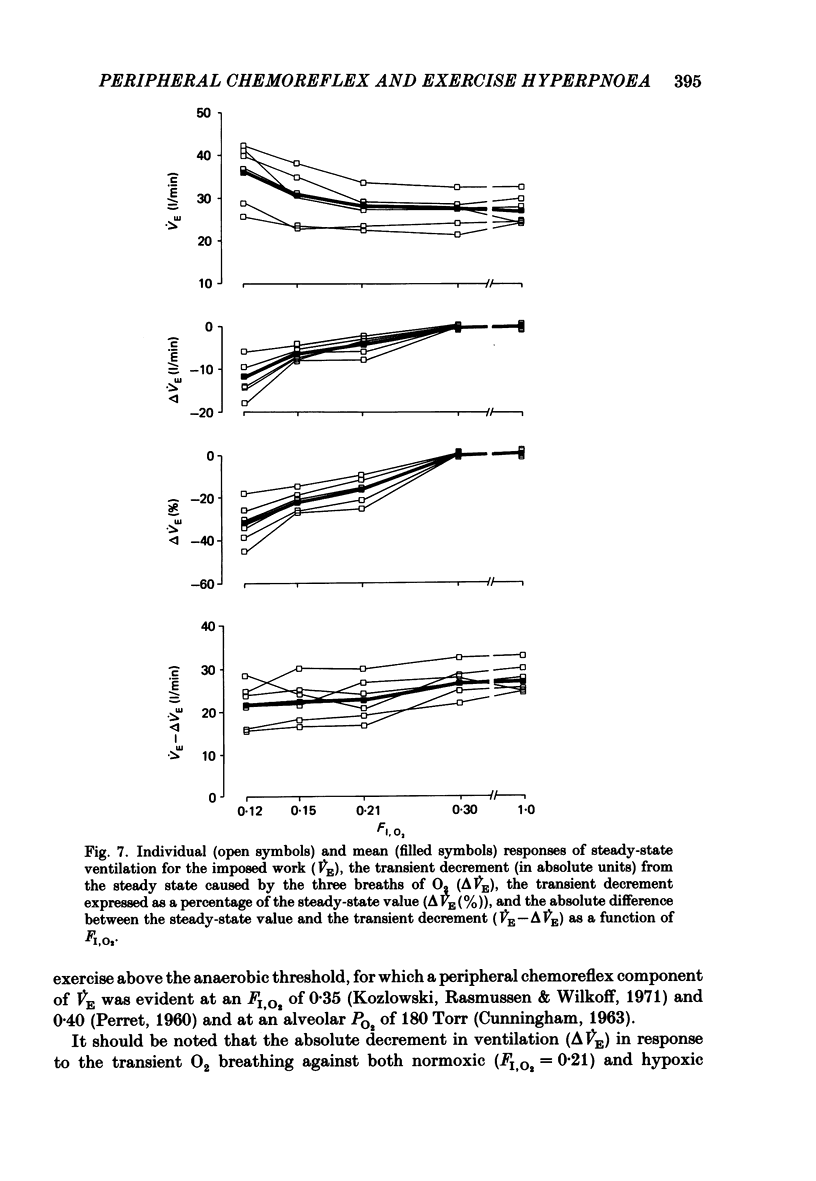
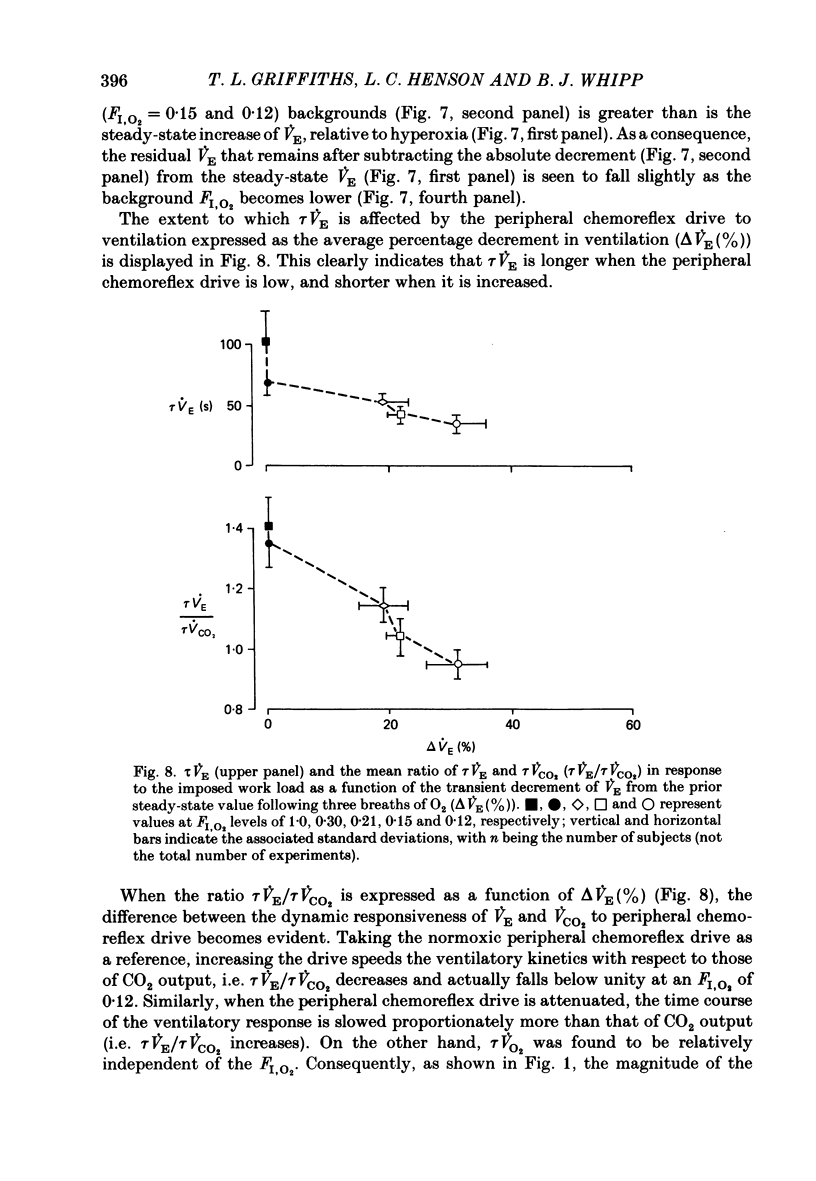







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams L., Frankel H., Garlick J., Guz A., Murphy K., Semple S. J. The role of spinal cord transmission in the ventilatory response to exercise in man. J Physiol. 1984 Oct;355:85–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal D., Milhorn H. T., Jr, Lee L. Y. Role of the carotid chemoreceptors in the hyperpnea of exercise in the cat. Respir Physiol. 1976 Apr;26(2):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(76)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker H. K., Struikenkamp R. S., De Vries G. A. Dynamics of ventilation, heart rate, and gas exchange: sinusoidal and impulse work loads in man. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Feb;48(2):289–301. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Band D. M., Wolff C. B., Ward J., Cochrane G. M., Prior J. Respiratory oscillations in arterial carbon dioxide tension as a control signal in exercise. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):84–85. doi: 10.1038/283084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaver W. L., Wasserman K., Whipp B. J. On-line computer analysis and breath-by-breath graphical display of exercise function tests. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Jan;34(1):128–132. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.34.1.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgard G. E., Forster H. V., Byrnes B., Stanek K., Klein J., Manohar M. Cerebrospinal fluid acid-base balance during muscular exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Jul;45(1):94–101. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black A. M., Torrance R. W. Respiratory oscillations in chemoreceptor discharge in the control of breathing. Respir Physiol. 1971 Nov;13(2):221–237. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(71)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUNNINGHAM D. J. Some quantitative aspects of the regulation of human respiration in exercise. Br Med Bull. 1963 Jan;19:25–30. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casaburi R., Whipp B. J., Wasserman K., Beaver W. L., Koyal S. N. Ventilatory and gas exchange dynamics in response to sinusoidal work. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Feb;42(2):300–301. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.42.2.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casaburi R., Whipp B. J., Wasserman K., Stremel R. W. Ventilatory control characteristics of the exercise hyperpnea as discerned from dynamic forcing techniques. Chest. 1978 Feb;73(2 Suppl):280–283. doi: 10.1378/chest.73.2_supplement.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross B. A., Davey A., Guz A., Katona P. G., MacLean M., Murphy K., Semple S. J., Stidwill R. The ph oscillations in arterial blood during exercise; a potential signal for the ventilatory response in the dog. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:57–73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross B. A., Davey A., Guz A., Katona P. G., MacLean M., Murphy K., Semple S. J., Stidwill R. The role of spinal cord transmission in the ventilatory response to electrically induced exercise in the anaesthetized dog. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:37–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEJOURS P. Control of respiration by arterial chemoreceptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Jun 24;109:682–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEJOURS P., LABROUSSE Y., RAYNAUD J., TEILLAC A. Stimulus oxygène chémoréflexe de la ventilation à basse altitude (50 m) chez l'homme. I. Au repos. J Physiol (Paris) 1957 Jan-Mar;49(1):115–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. O., Lahiri S. Absence of carotid chemoreceptor response during hypoxic exercise in the cat. Respir Physiol. 1973 Jun;18(1):92–100. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey J. A., Mitchell G. S., Smith C. A. Exercise and chemoreception. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Feb;129(2 Pt 2):S31–S34. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.2P2.S31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L. Maintenance of respiration by central neural feedback mechanisms. Fed Proc. 1977 Sep;36(10):2400–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L., Millhorn D. E., Waldrop T. G. Exercise hyperpnea and locomotion: parallel activation from the hypothalamus. Science. 1981 Feb 20;211(4484):844–846. doi: 10.1126/science.7466362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L. The importance of timing on the respiratory effects of intermittent carotid body chemoreceptor stimulation. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):319–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hník P., Hudlická O., Kucera J., Payne R. Activatioof muscle afferents by nonproprioceptive stimuli. Am J Physiol. 1969 Nov;217(5):1451–1457. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.5.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holton P., Wood J. B. The effects of bilateral removal of the carotid bodies and denervation of the carotid sinuses in two human subjects. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(2):365–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda Y., Watanabe S., Hashizume I., Satomura Y., Hata N., Sakakibara Y., Severinghaus J. W. Hypoxic chemosensitivity in asthmatic patients two decades after carotid body resection. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Apr;46(4):632–638. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.4.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughson R. L., Inman M. D. Gas exchange analysis of immediate CO2 storage at onset of exercise. Respir Physiol. 1985 Mar;59(3):265–278. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(85)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughson R. L., Morrissey M. Delayed kinetics of respiratory gas exchange in the transition from prior exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Apr;52(4):921–929. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.4.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. L., Jurkowski J. E. Body carbon dioxide storage capacity in exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Apr;46(4):811–815. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.4.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. L. Use of exercise in testing respiratory control mechanisms. Chest. 1976 Jul;70(1 Suppl):169–173. doi: 10.1378/chest.70.1_supplement.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski S., Rasmussen B., Wilkoff W. G. The effect of high oxygen tensions on ventilation during severe exercise. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Mar;81(3):385–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugliani R., Whipp B. J., Seard C., Wasserman K. Effect of bilateral carotid-body resection on ventilatory control at rest and during exercise in man. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov;285(20):1105–1111. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111112852002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey D. I., Mitchell J. H. Reflex cardiovascular and respiratory responses originating in exercising muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(1):173–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto Y., Nakazono Y., Hiura T., Abe Y. Cardiorespiratory dynamics during sinusoidal and impulse exercise in man. Jpn J Physiol. 1983;33(6):971–986. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.33.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIELSEN M., SMITH H. Studies on the regulation of respiration in acute hypoxia; with a appendix on respiratory control during prolonged hypoxia. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952 Feb 12;24(4):293–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldenburg F. A., McCormack D. W., Morse J. L., Jones N. L. A comparison of exercise responses in stairclimbing and cycling. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Mar;46(3):510–516. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.3.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren A., Whipp B. J., Wasserman K. Effect of acid-base status on the kinetics of the ventilatory response to moderate exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Apr;52(4):1013–1017. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.4.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRET C. [Hyperoxia and regulation of ventilation during muscular exercise]. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1960;18:72–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce D. H., Milhorn H. T., Jr Dynamic and steady-state respiratory responses to bicycle exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Jun;42(6):959–967. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.42.6.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior J. G., Powlson M., Cochrane G. M., Wolff C. B. Ventilatory changes during exercise and arterial PCO2 oscillations in chronic airway obstruction patients. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Jun;58(6):1942–1948. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.6.1942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders K. B. Oscillations of arterial CO2 tension in a respiratory model: some implications for the control of breathing in exercise. J Theor Biol. 1980 May 7;84(1):163–179. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(80)81042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockley R. A. The contribution of the reflex hypoxic drive to the hyperpnoea of exercise. Respir Physiol. 1978 Oct;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(78)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange-Petersen E., Whipp B. J., Drysdale D. B., Cunningham D. J. Carotid arterial blood gas oscillations and the phase of the respiratory cycle during exercise in man: testing a model. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;99:335–342. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4009-6_36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson G. D., Ward D. S., Bellville J. W. Posthyperventilation isocapnic hyperpnea. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Apr;40(4):592–596. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.4.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibes U., Hemmer B., Böning D. Heart rate and ventilation in relation to venous [K+], osmolality, pH, PCO2, PO2, [orthophosphate], and [lactate] at transition from rest to exercise in athletes and non-athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1977 Jan 14;36(2):127–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00423120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. G., Larson C. P., Jr, Hickey R. F., Ehrenfeld W. K., Severinghaus J. W. Effect of carotid endarterectomy on carotid chemoreceptor and baroreceptor function in man. N Engl J Med. 1970 Apr 9;282(15):823–829. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197004092821501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. A., Whipp B. J., Koyal S., Wasserman K. Influence of body CO2 stores on ventilatory dynamics during exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Sep;55(3):742–749. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.3.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman D. H., Whipp B. J. Coupling of ventilation to pulmonary gas exchange during nonsteady-state work in men. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Feb;54(2):587–593. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.2.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman K., Van Kessel A. L., Burton G. G. Interaction of physiological mechanisms during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Jan;22(1):71–85. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman K., Whipp B. J., Koyal S. N., Cleary M. G. Effect of carotid body resection on ventilatory and acid-base control during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Sep;39(3):354–358. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.3.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman M. L., Wasserman K., Huntsman D. J., Whipp B. J. Ventilation and gas exchange during phasic hindlimb exercise in the dog. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 May;46(5):878–884. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.5.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp B. J., Ward S. A., Lamarra N., Davis J. A., Wasserman K. Parameters of ventilatory and gas exchange dynamics during exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Jun;52(6):1506–1513. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.6.1506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp B. J., Wasserman K. Carotid bodies and ventilatory control dynamics in man. Fed Proc. 1980 Jul;39(9):2668–2673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter B. Bilateral carotid body resection for asthma and emphysema. A new surgical approach without hypoventilation or baroreceptor dysfunction. Int Surg. 1972 Jun;57(6):458–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAMOTO W. S., EDWARDS M. W., Jr Homeostasis of carbon dioxide during intravenous infusion of carbon dioxide. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Sep;15:807–818. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.5.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. H., Woolcock A. J. Changes in arterial blood gas tensions during unsteady-state exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Jan;44(1):93–96. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.44.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


