Abstract
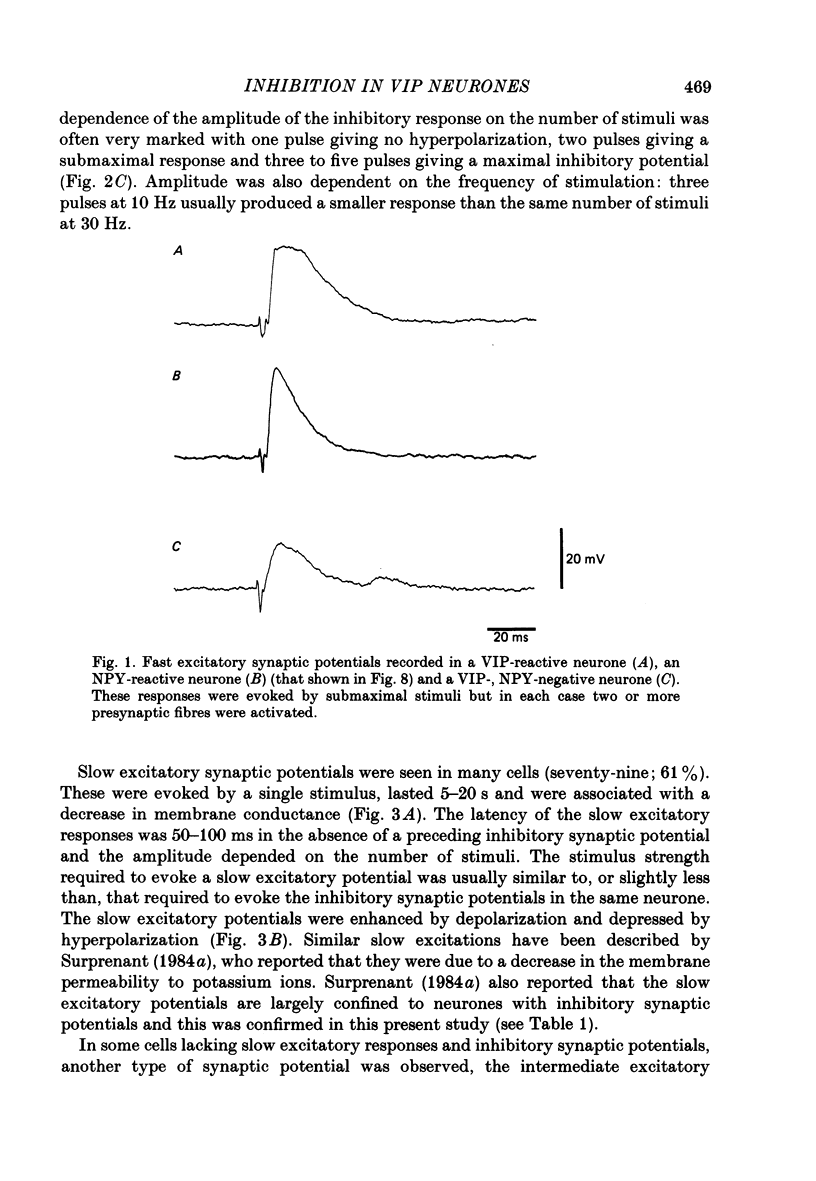
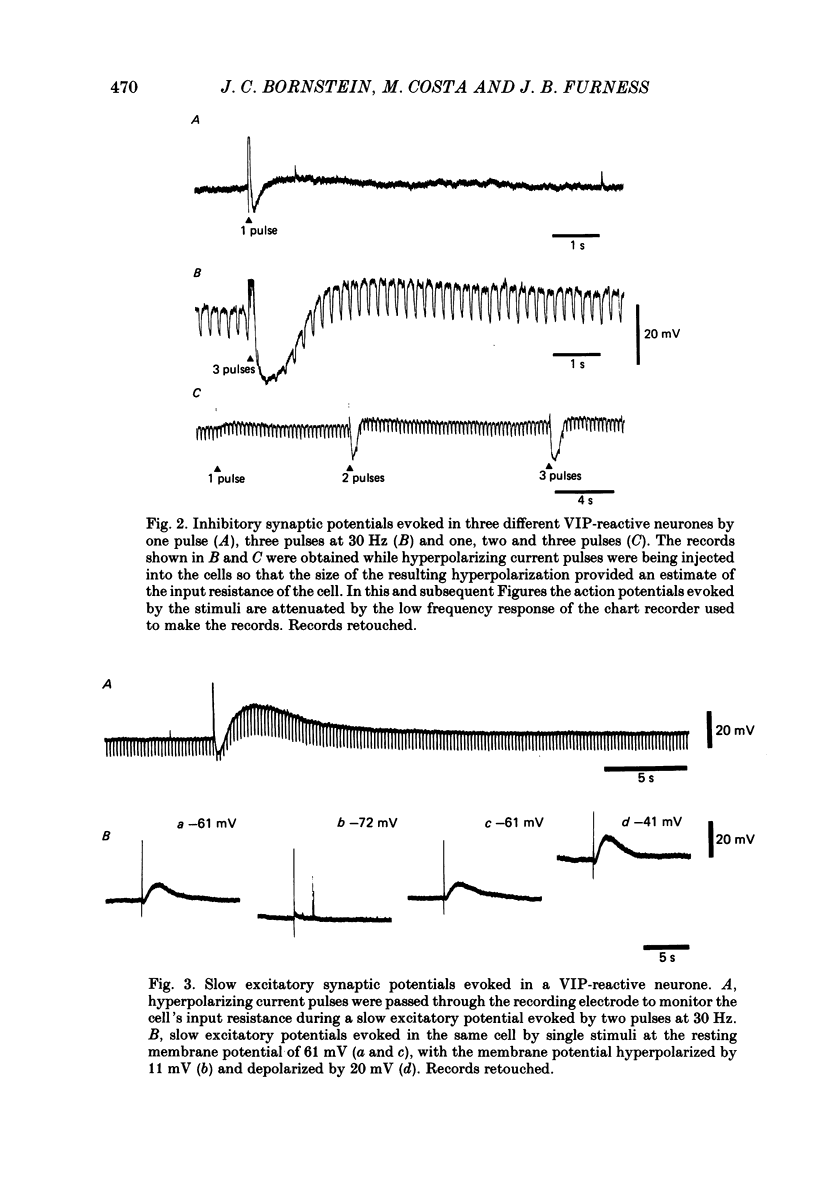
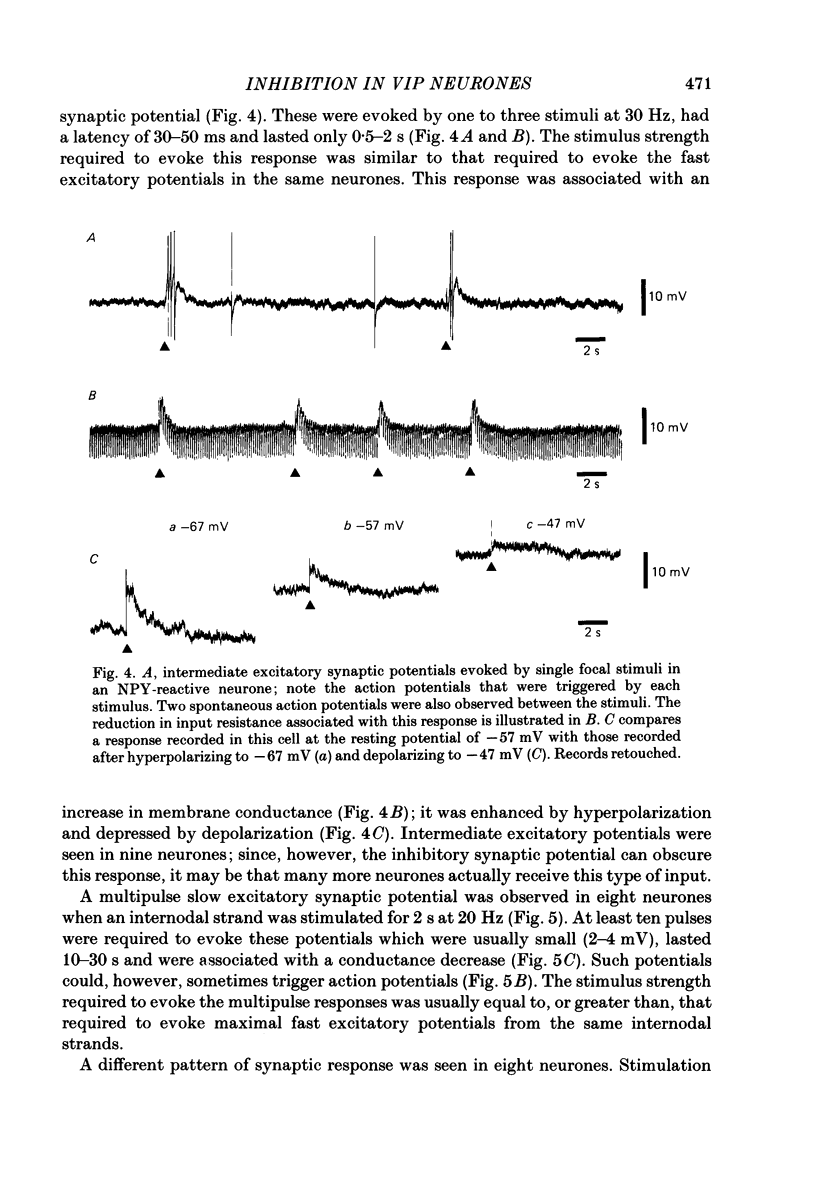
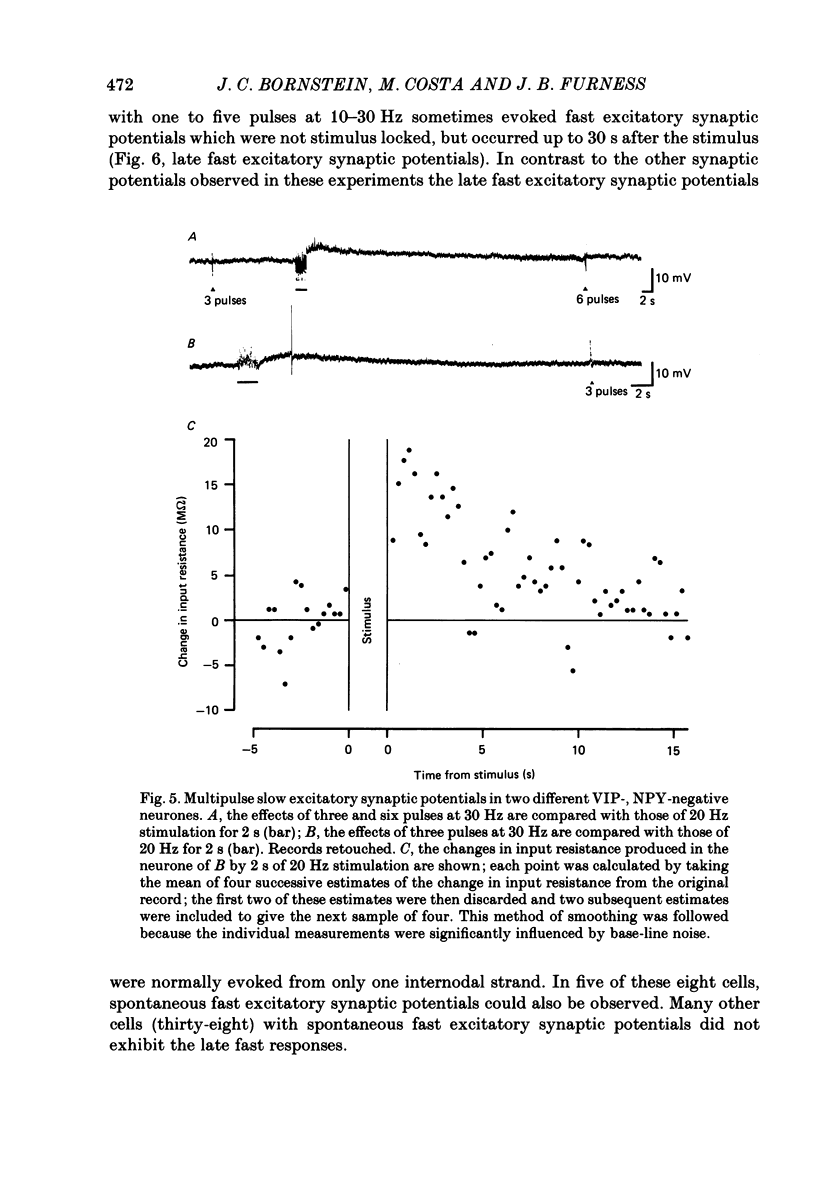
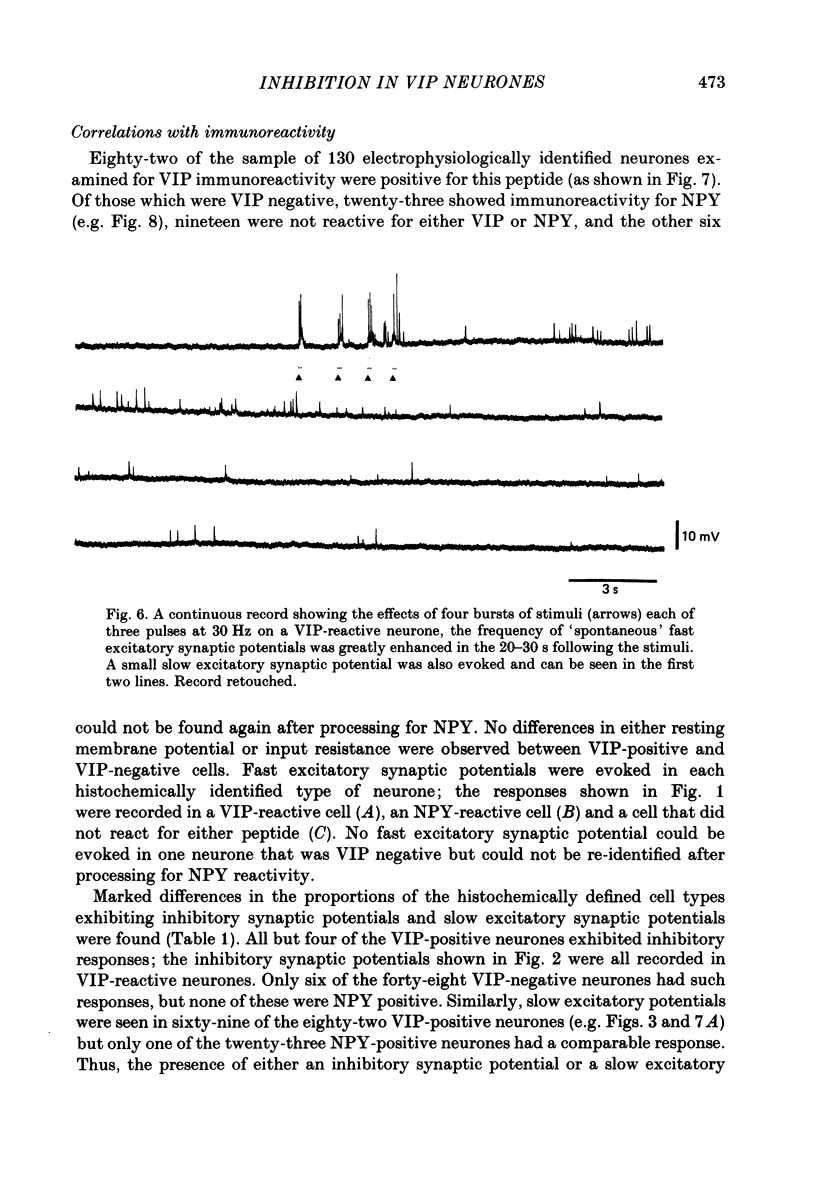
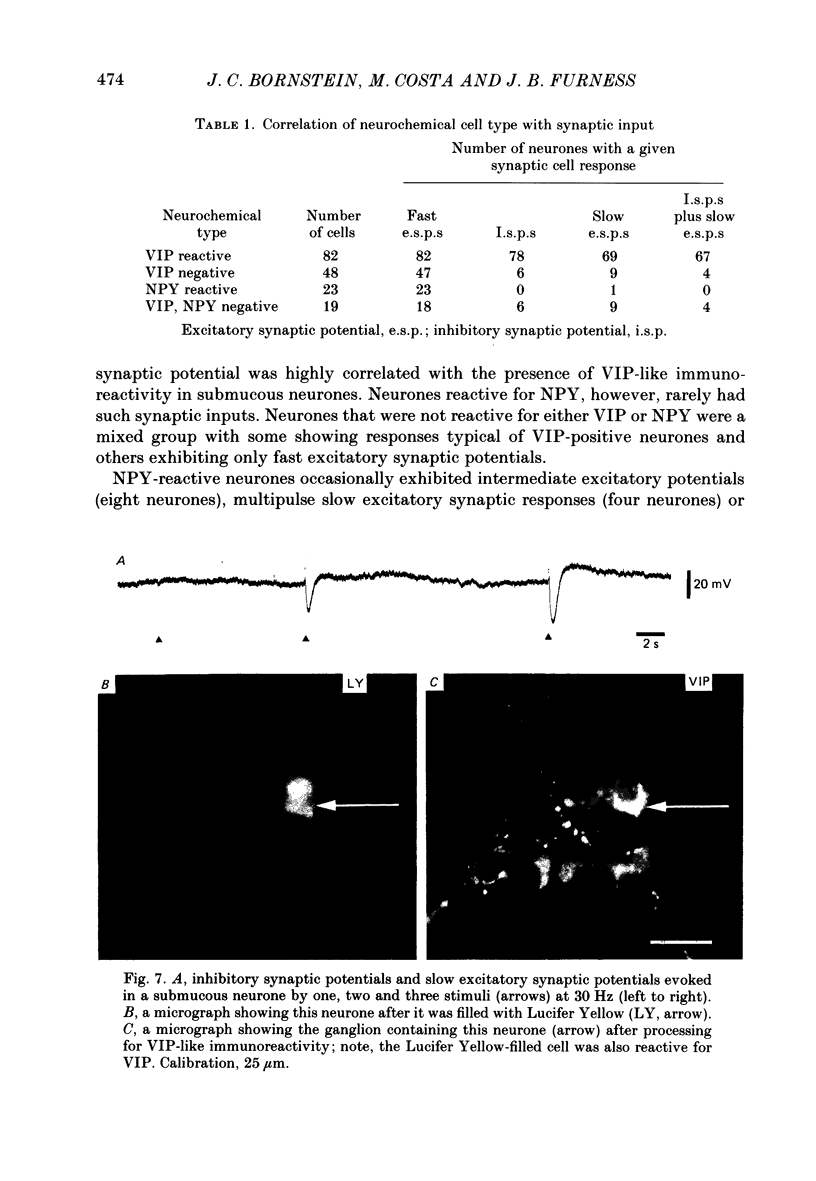
1. Electrophysiological recordings were made from neurones in the submucous plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine, and these neurones were classified according to their synaptic inputs. 2. The neurones from which recording were made were filled during the recording period with the fluorescent dye, Lucifer Yellow, so they could be re-identified after processing for immunohistochemical localization of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). 3. The presence or absence of VIP-like immunoreactivity was determined for a total of 130 neurones whose synaptic inputs had been fully characterized and eighty-two were found to be VIP reactive. After the VIP reactivity had been assessed, the preparations were reprocessed to reveal immunoreactivity for neuropeptide Y (NPY) and a further twenty-three neurones (none of which were reactive for VIP) were found to be reactive for this peptide. Of the remaining twenty-five neurones, nineteen were not reactive for either VIP or NPY and six could not be re-identified after reprocessing. 4. Electrical stimulation of internodal strands evoked excitatory synaptic potentials lasting 20-30 ms (fast responses) in all but one of the 130 neurones studied. 5. Almost all the VIP-reactive neurones (seventy-eight of eighty-two cells) exhibited inhibitory synaptic potentials, ranging in amplitude from 2 to 30 mV and lasting 150-1500 ms, but few of the VIP-negative neurones had such responses (six of forty-eight cells). No inhibitory synaptic potentials could be evoked in any of the NPY-reactive neurones. 6. Most VIP-reactive neurones (sixty-nine) had a slow excitatory synaptic potential which could be evoked by a single stimulus, lasted 5-20 s and was associated with an increase in input resistance. Only one NPY-reactive neurone had a slow excitatory potential, but such potentials were seen in nine of the nineteen VIP-negative, NPY-negative neurones. 7. In nine of the twenty-three NPY-reactive neurones a single stimulus evoked an excitatory synaptic potential (intermediate excitatory synaptic potential) lasting 500-1500 ms and associated with a fall in the input resistance. None of the VIP-negative, NPY-negative neurones exhibited the intermediate excitatory potentials but it was not possible to determine whether such potentials could be evoked in VIP-reactive neurones because the inhibitory synaptic potentials would obscure such events. 8. It is concluded that neurochemically distinct populations of submucous neurones can be distinguished physiologically on the basis of the differing combinations of types of synaptic input they receive.
Full text
PDF



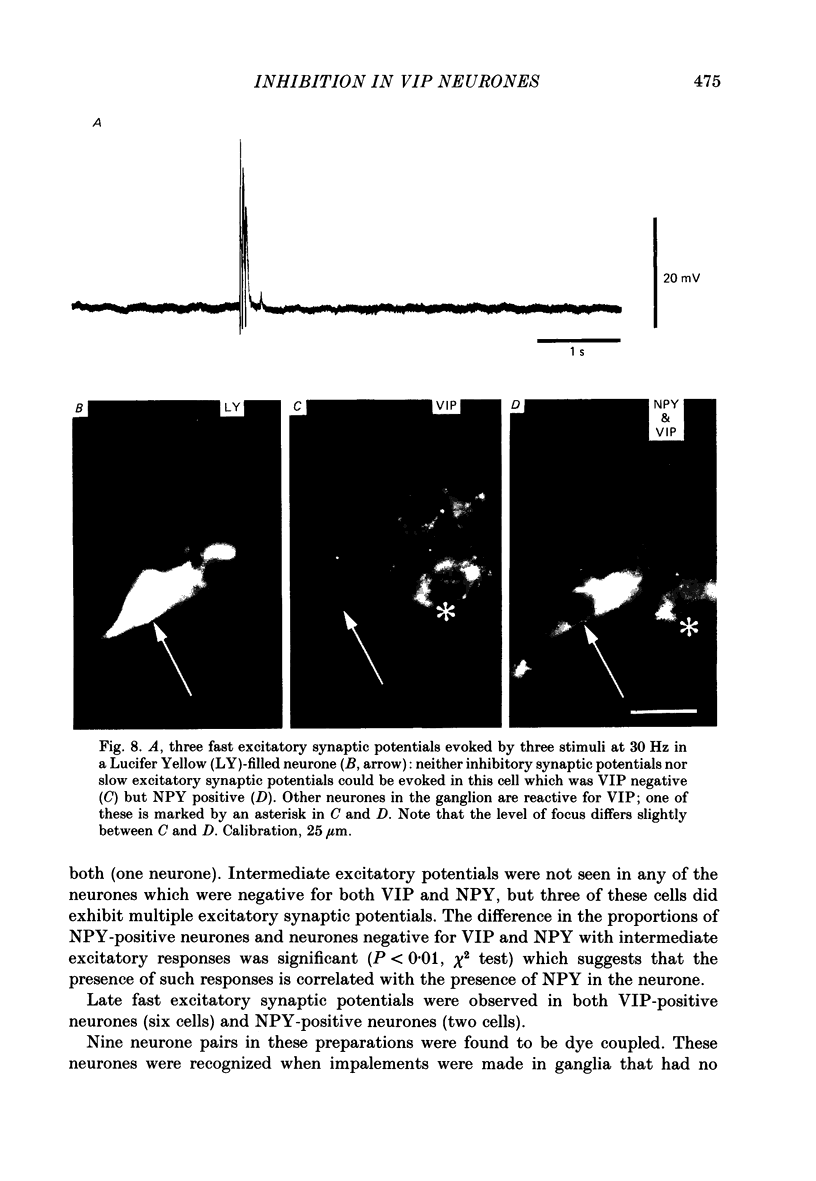


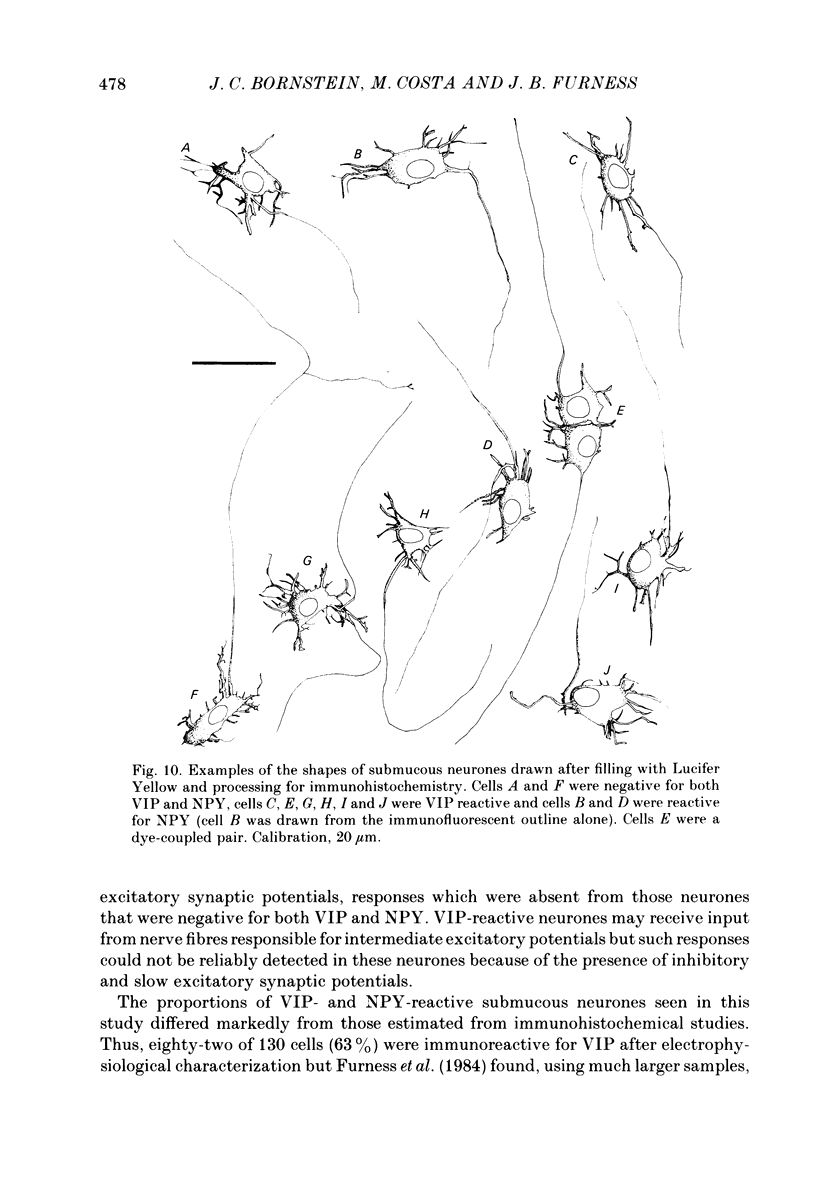




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bornstein J. C., Costa M., Furness J. B., Lang R. J. Electrophysiological analysis of projections of enteric inhibitory motoneurones in the guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:61–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein J. C., Costa M., Furness J. B., Lees G. M. Electrophysiology and enkephalin immunoreactivity of identified myenteric plexus neurones of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:313–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J. Influence of enteric cholinergic neurons on mucosal transport in guinea pig ileum. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 1):G263–G267. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.3.G263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Buffa R., Furness J. B., Solcia E. Immunohistochemical localization of polypeptides in peripheral autonomic nerves using whole mount preparations. Histochemistry. 1980 Feb;65(2):157–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00493164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B. Somatostatin is present in a subpopulation of noradrenergic nerve fibres supplying the intestine. Neuroscience. 1984 Nov;13(3):911–919. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B. The origins, pathways and terminations of neurons with VIP-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience. 1983 Apr;8(4):665–676. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erde S. M., Sherman D., Gershon M. D. Morphology and serotonergic innervation of physiologically identified cells of the guinea pig's myenteric plexus. J Neurosci. 1985 Mar;5(3):617–633. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-03-00617.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M., Emson P. C., Håkanson R., Moghimzadeh E., Sundler F., Taylor I. L., Chance R. E. Distribution, pathways and reactions to drug treatment of nerves with neuropeptide Y- and pancreatic polypeptide-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig digestive tract. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;234(1):71–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00217403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M., Freeman C. G. Absence of tyrosine hydroxylase activity and dopamine beta-hydroxylase immunoreactivity in intrinsic nerves of the guinea-pig ileum. Neuroscience. 1979;4(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M., Gibbins I. L., Llewellyn-Smith I. J., Oliver J. R. Neurochemically similar myenteric and submucous neurons directly traced to the mucosa of the small intestine. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;241(1):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00214637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M., Keast J. R. Choline acetyltransferase- and peptide immunoreactivity of submucous neurons in the small intestine of the guinea-pig. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;237(2):329–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00217152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M. Types of nerves in the enteric nervous system. Neuroscience. 1980;5(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McKirdy H. C. Synaptic potentials recorded from neurones of the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):369–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Silinsky E. M. Some effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine and noradrenaline on neurones in the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):817–832. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe P. R., Provis J. C., Furness J. B., Costa M., Chalmers J. P. Residual catecholamines in extrinsically denervated guinea-pig ileum. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1981 Jul;8(4):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1981.tb00736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keast J. R., Furness J. B., Costa M. Investigations of nerve populations influencing ion transport that can be stimulated electrically, by serotonin and by a nicotinic agonist. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;331(2-3):260–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00634247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keast J. R., Furness J. B., Costa M. Origins of peptide and norepinephrine nerves in the mucosa of the guinea pig small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1984 Apr;86(4):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees G. M., Gray M. J. A method for simultaneous visualization and electrophysiological recording of enteric neurones with intracellular fluorescent markers. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1982;71:169–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Surprenant A. Inhibitory synaptic potentials resulting from alpha 2-adrenoceptor activation in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:17–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves T. A., Jr, Hayward J. N. Intracellular dye-marked enkephalin neurons in the magnocellular preoptic nucleus of the goldfish hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):6009–6011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.6009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. Slow excitatory synaptic potentials recorded from neurones of guinea-pig submucous plexus. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:343–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. Two types of neurones lacking synaptic input in the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:363–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]