Abstract
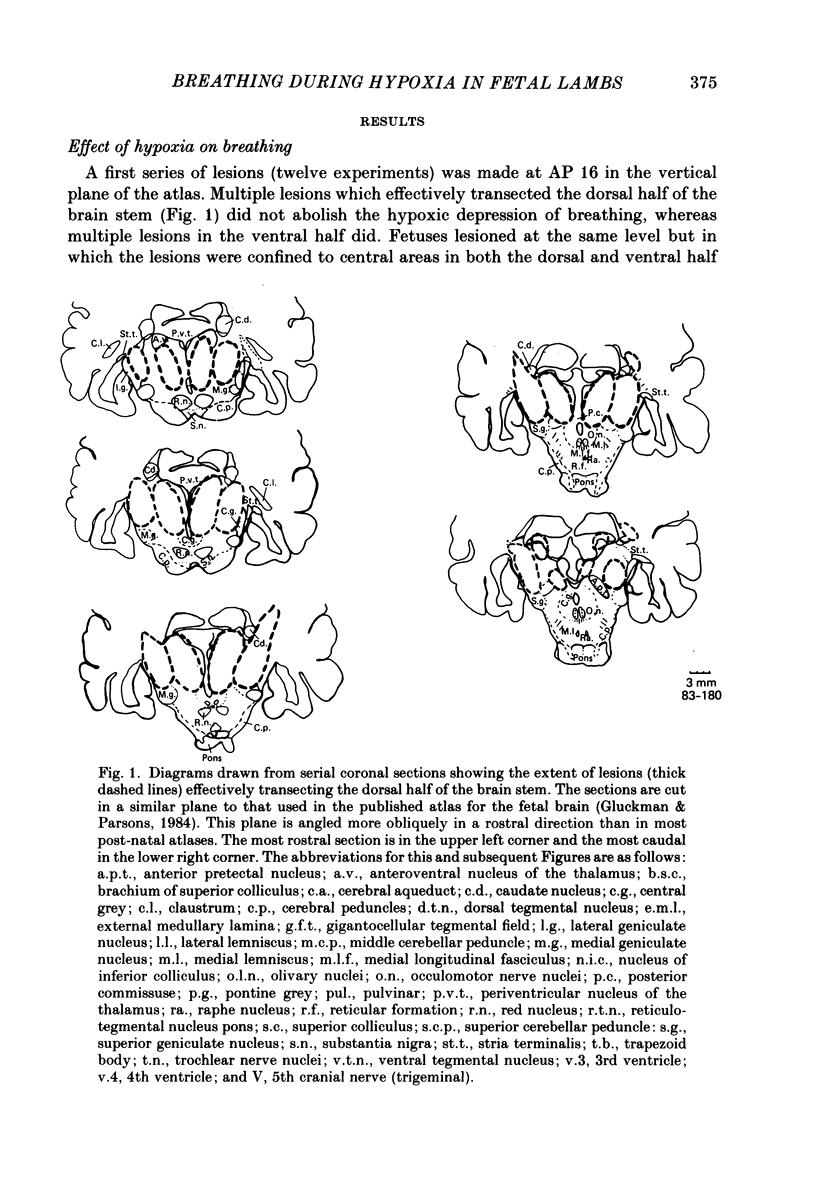
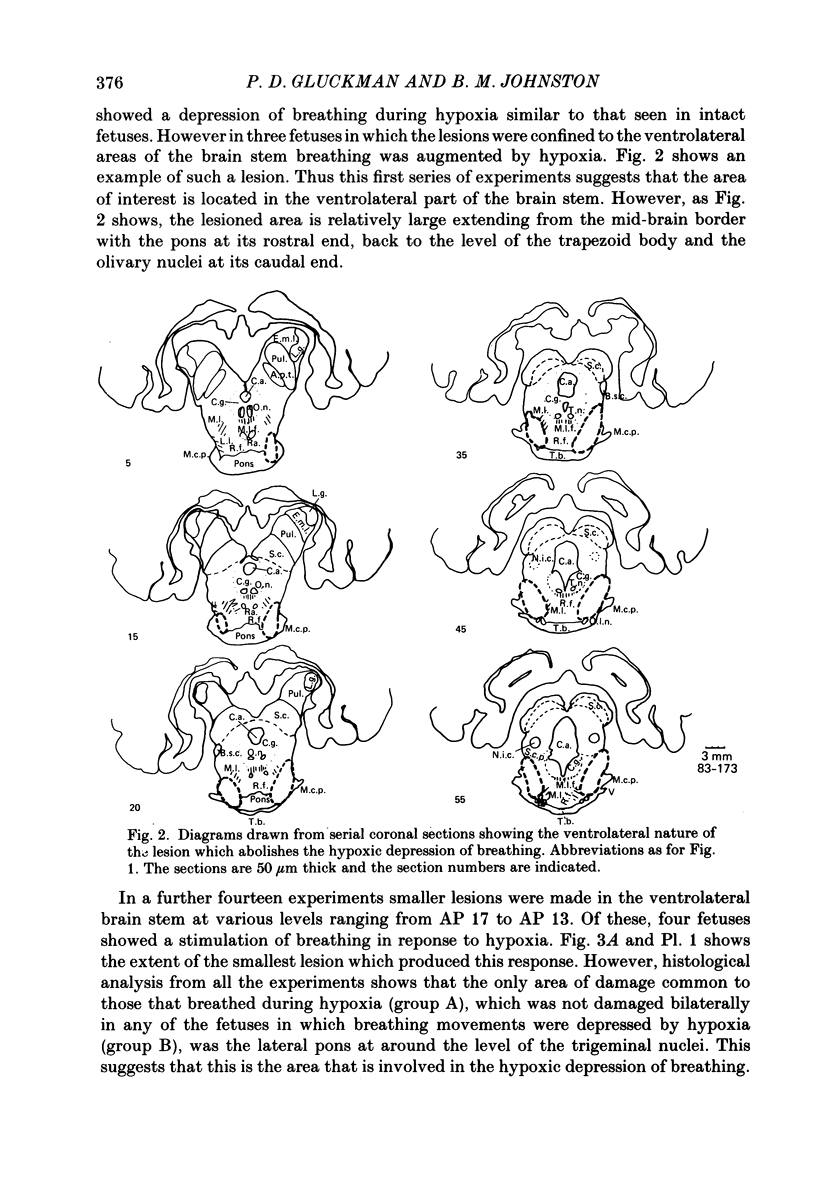
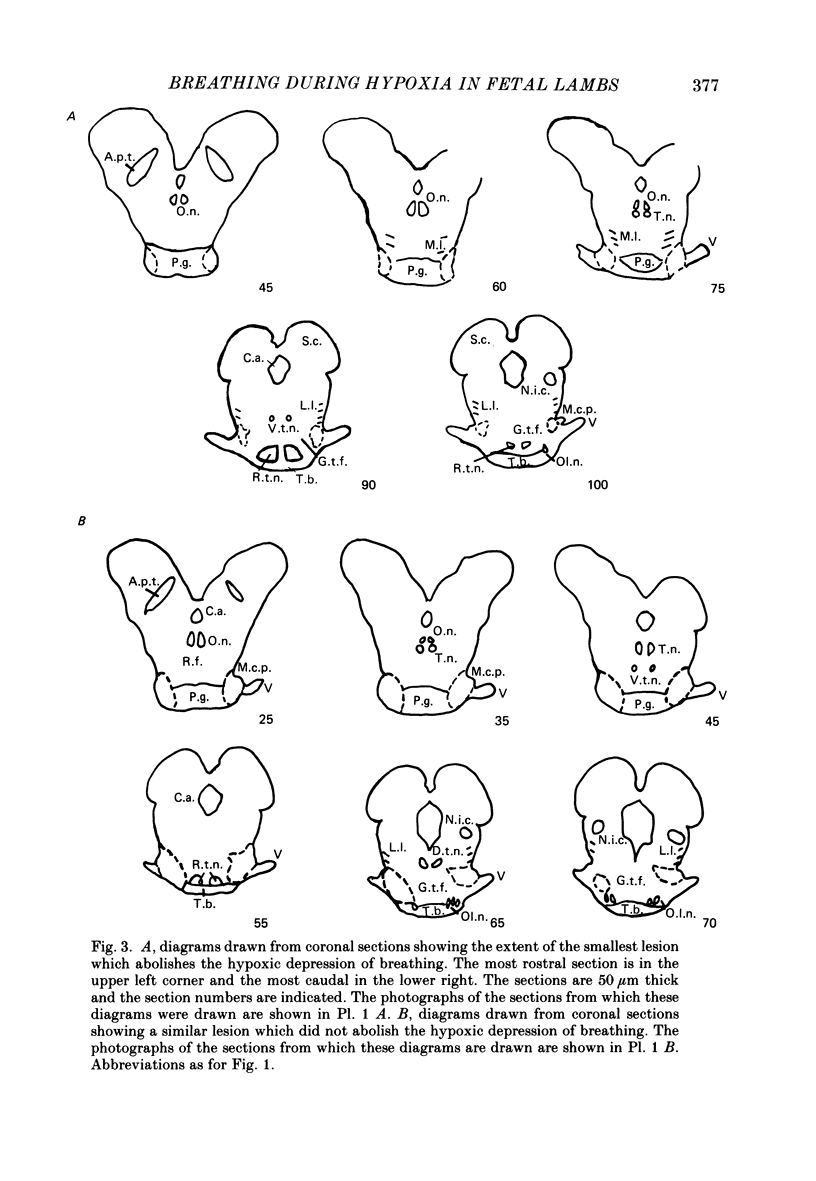
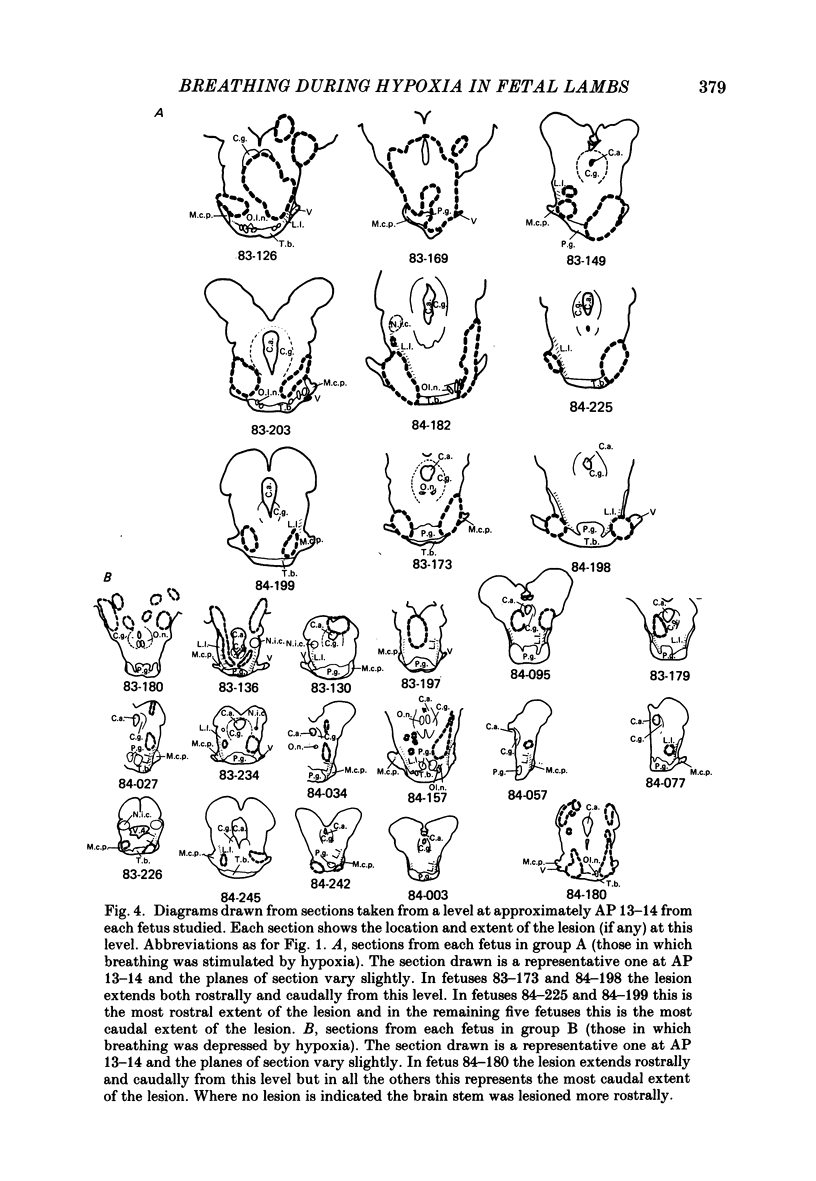
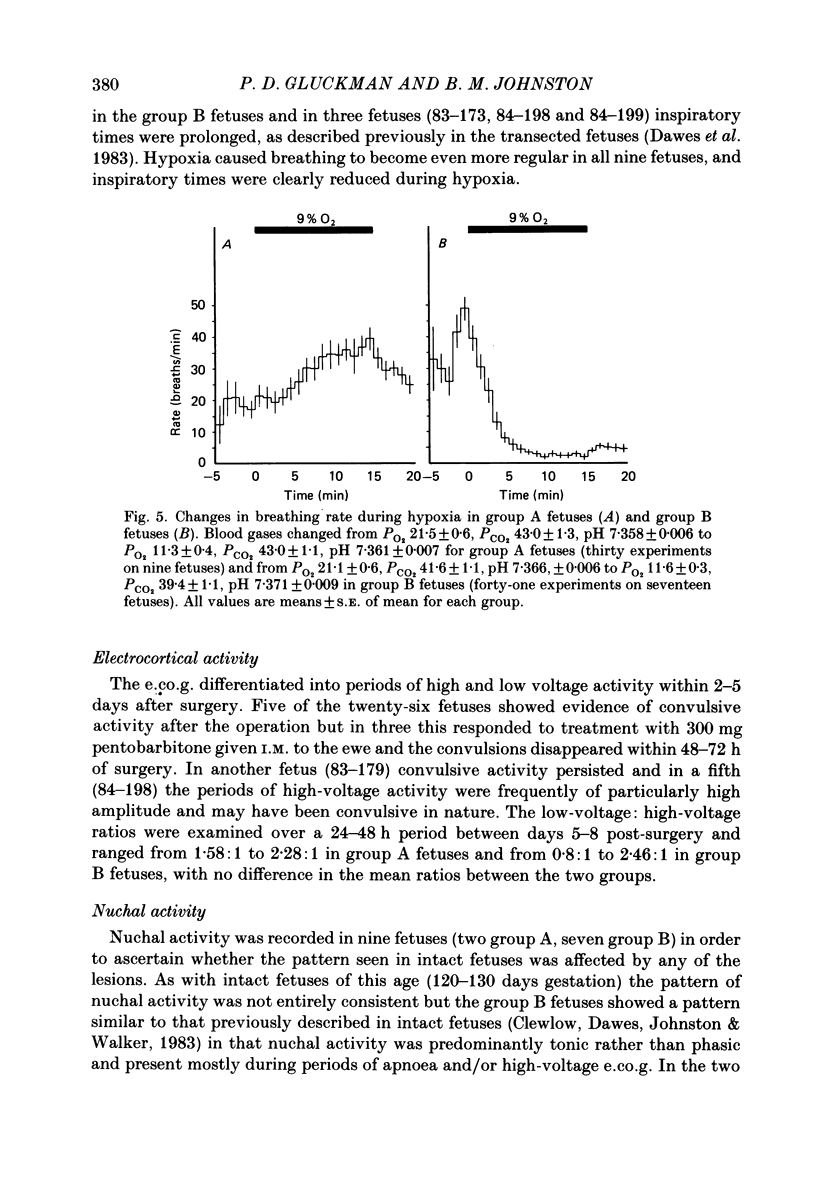
1. The effects of stereotaxically placed lesions made throughout the mid-brain and upper pons were studied in chronically instrumented fetal lambs from 120 days gestation, after recovery in utero. 2. Isocapnic hypoxia caused an increase in the rate and depth of breathing movements in fetuses in which bilateral lesions encompassed the upper lateral pons in the region of and slightly rostral to the principal sensory and motor nuclei of the trigeminal nerve. 3. Fetal lambs with lesions which did not bilaterally encompass the upper lateral pons showed the normal fetal depressive response to hypoxia. 4. None of the lesions induced permanent continuous breathing as previously described in mid-brain transected fetuses, although periods of continuous breathing lasting several hours were seen at times in some fetuses with lesions in the upper lateral pons. 5. It is concluded that an area in the lateral pons close to areas with well known involvement in respiratory control is involved in the hypoxic depression of breathing in the fetal lamb.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertrand F., Hugelin A., Vibert J. F. Quantitative study of anatomical distribution of respiration related neurons in the pons. Exp Brain Res. 1973 Feb 28;16(4):383–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00233430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Järhult J. The effect of somatostatin on pancreatic endocrine responses mediated via the parasympathetic innervation in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:29–38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., Dawes G. S., Fisher R., Pinter S., Robinson J. S. Foetal respiratory movements, electrocortical and cardiovascular responses to hypoxaemia and hypercapnia in sheep. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):599–618. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewlow F., Dawes G. S., Johnston B. M., Walker D. W. Changes in breathing, electrocortical and muscle activity in unanaesthetized fetal lambs with age. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:463–476. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. I. Neurogenesis of respiratory rhythm in the mammal. Physiol Rev. 1979 Oct;59(4):1105–1173. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.4.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Fox H. E., Leduc B. M., Liggins G. C., Richards R. T. Respiratory movements and rapid eye movement sleep in the foetal lamb. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(1):119–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Gardner W. N., Johnston B. M., Walker D. W. Effects of hypercapnia on tracheal pressure, diaphragm and intercostal electromyograms in unanaesthetized fetal lambs. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:461–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier H., Bertrand F. Respiratory effects of pneumotaxic center lesions and subsequent vagotomy in chronic cats. Respir Physiol. 1975 Jan;23(1):71–85. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(75)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John W. M., Glasser R. L., King R. A. Rhythmic respiration in awake vagotomized cats with chronic pneumotaxic area lesions. Respir Physiol. 1972 Jun;15(2):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(72)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]