Abstract
1. Neuropeptide tyrosine (neuropeptide Y, NPY), a recently isolated endogenous brain peptide, reduces the extracellular population spike evoked by stimulation of stratum radiatum in area CA1 of the in vitro rat hippocampal slice, without reducing the antidromically evoked population spike. To test the hypothesis that NPY acts presynaptically, intracellular recordings were made of pyramidal neurones of area CA1 in vitro. 2. Bath application of 10(-6) M-NPY causes a long-lasting (1-1.5 h), reversible reduction of the orthodromically evoked excitatory post-synaptic potential (e.p.s.p.) recorded intracellularly from CA1 pyramidal neurones. This effect on the e.p.s.p. was dependent upon the concentration of NPY. 3. The resting membrane potential, slope input resistance, and action potential threshold, amplitude and duration of the CA1 pyramidal neurones were not affected by NPY. 4. The responses of CA1 pyramidal neurones to ionophoretic pulses of glutamate, applied to the dendrites during synaptic blockade, was also unaffected by NPY. 5. The evidence supports the hypothesis that NPY acts presynaptically in the CA1 region of hippocampus to reduce excitatory input to the pyramidal neurones.
Full text
PDF


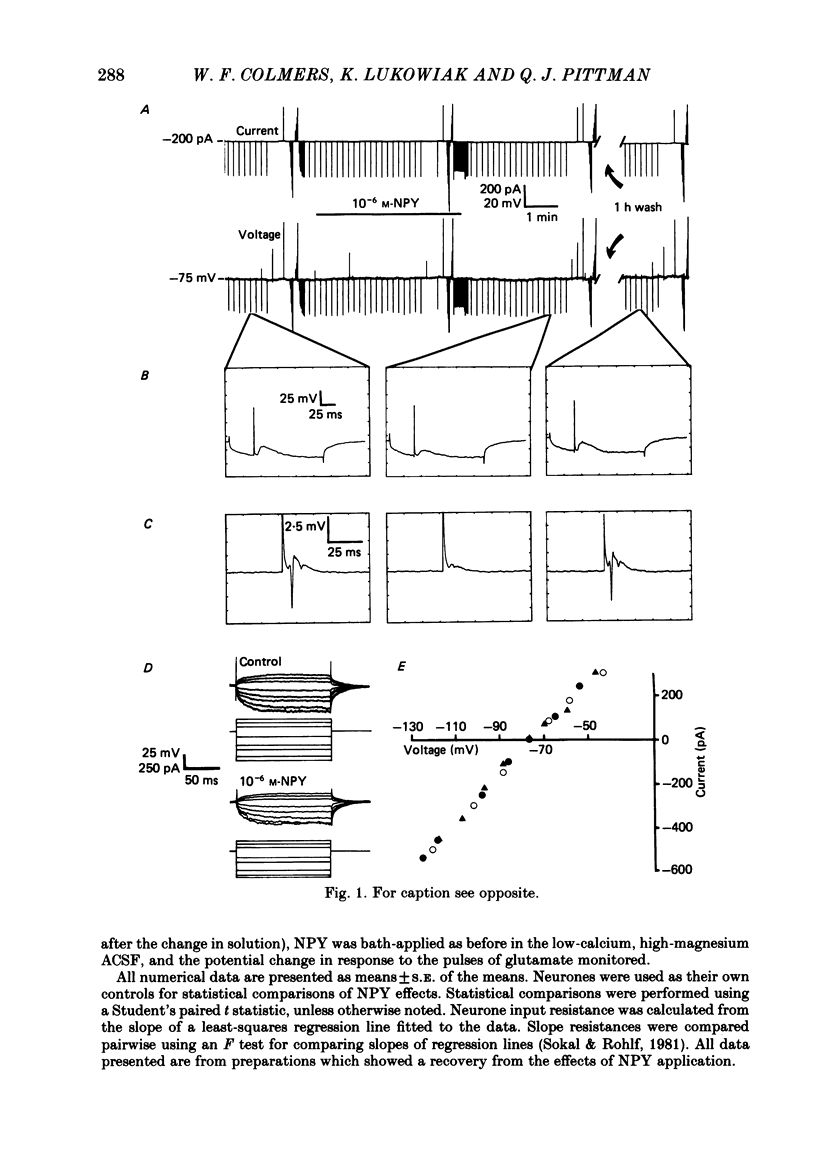

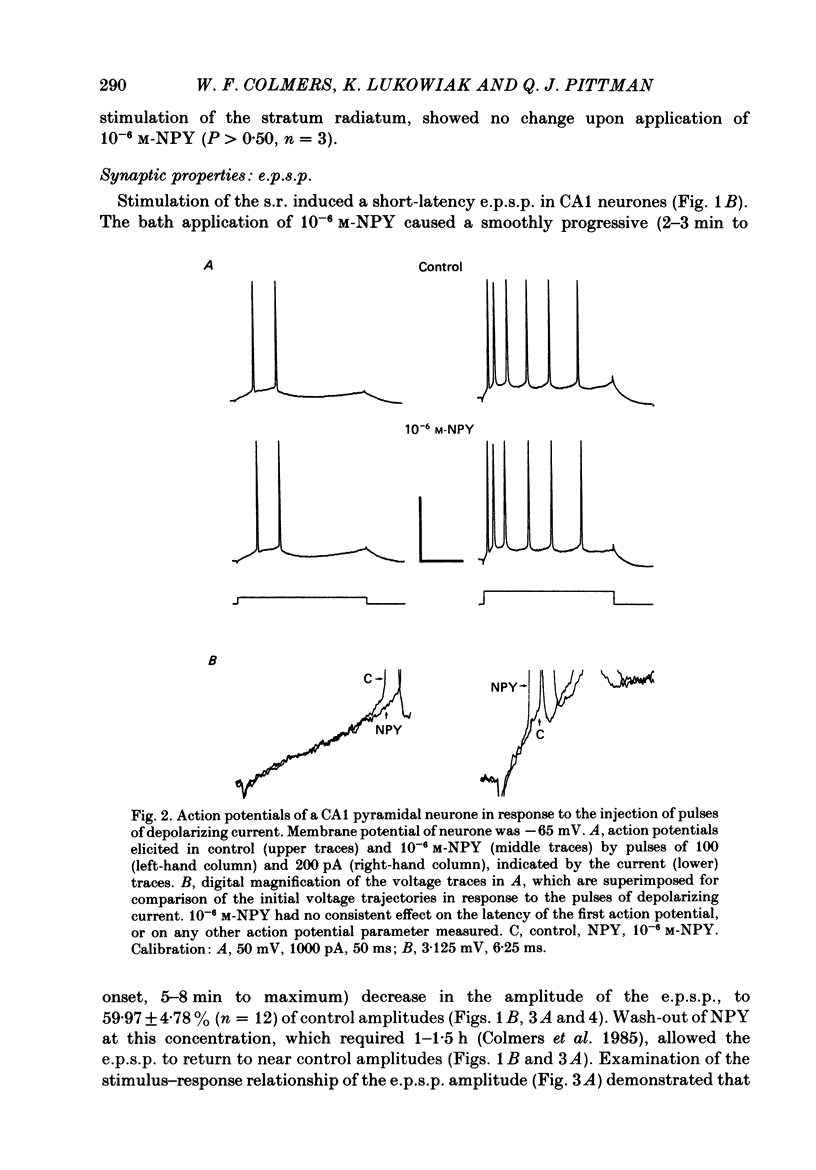
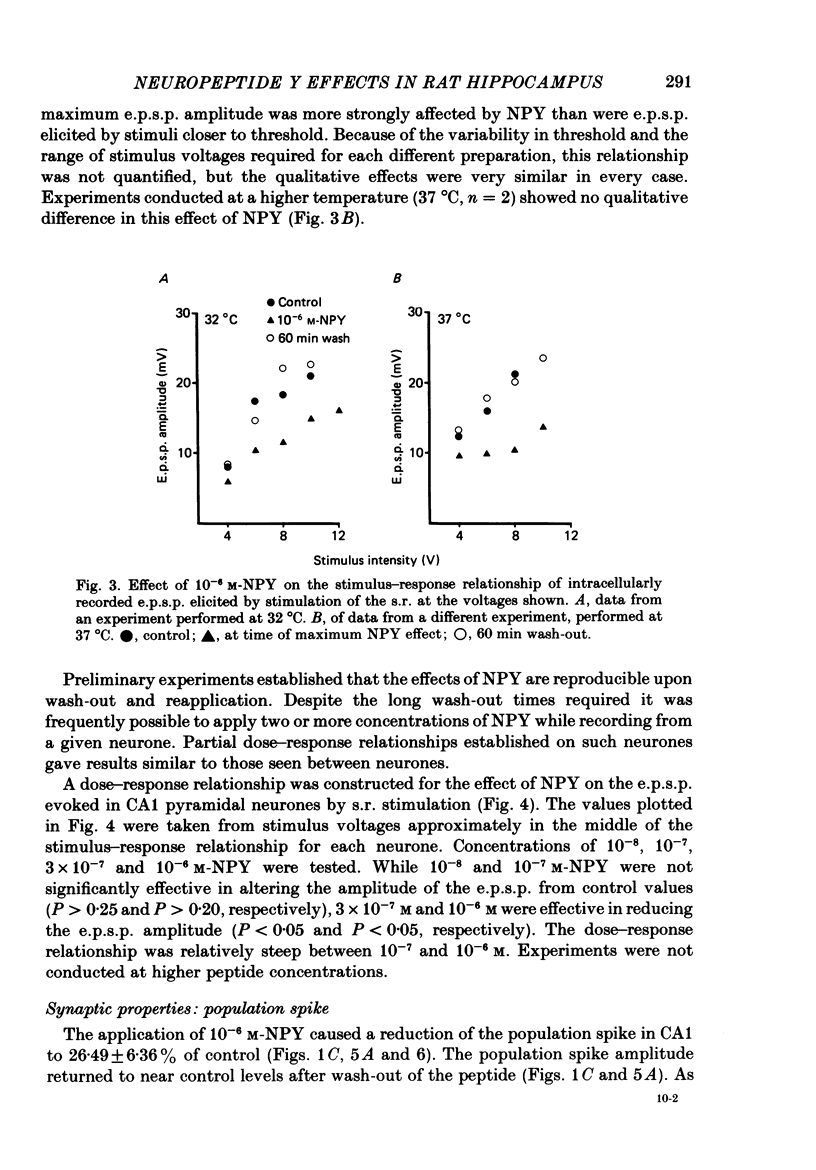
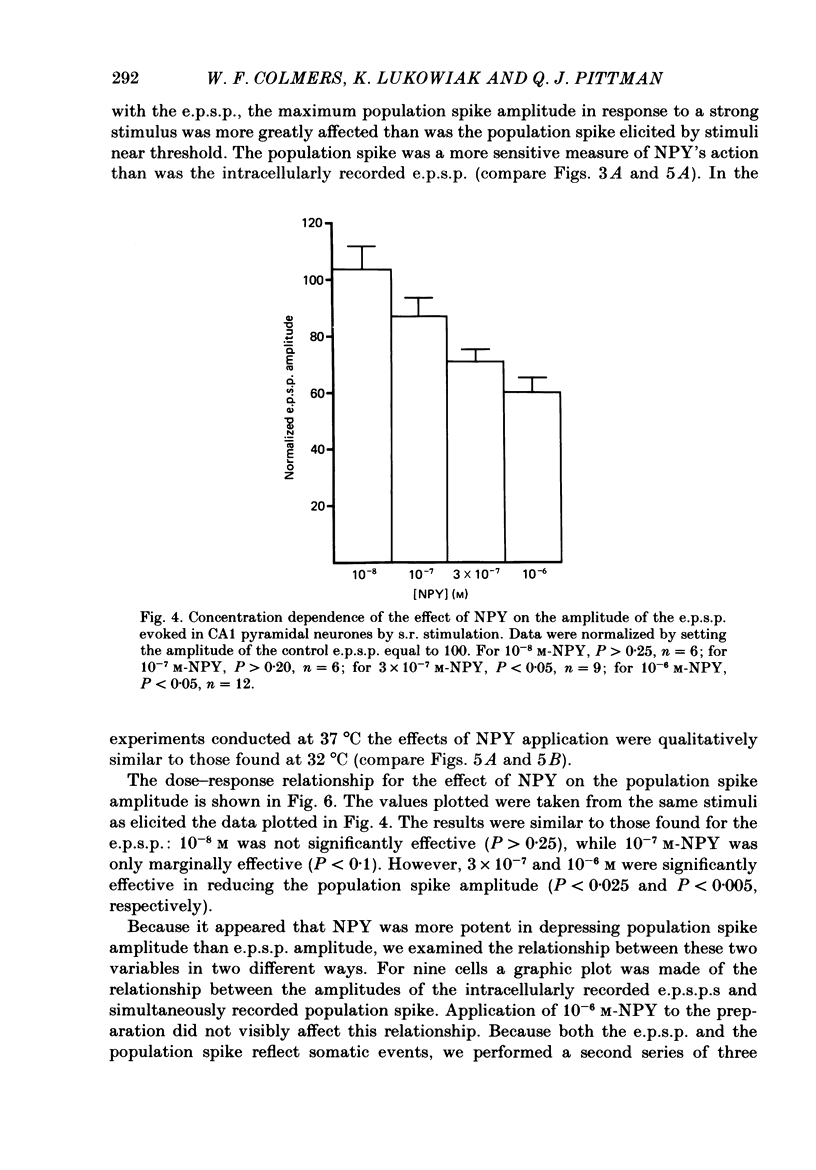




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P., ECCLES J. C., LOYNING Y. PATHWAY OF POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITION IN THE HIPPOCAMPUS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jul;27:608–619. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.4.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Bloom S. R., Ghatei M. A., Rossor M. N., Roberts G. W., Crow T. J., Tatemoto K., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in human brain. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):584–586. doi: 10.1038/306584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers H. E., Ferris C. F. Neuropeptide Y: role in light-dark cycle entrainment of hamster circadian rhythms. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Sep 7;50(1-3):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alger B. E., Nicoll R. A. Pharmacological evidence for two kinds of GABA receptor on rat hippocampal pyramidal cells studied in vitro. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:125–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Adrian T. E., Tatemoto K., Polak J. M., Hughes J., Bloom S. R. Two novel related peptides, neuropeptide Y (NPY) and peptide YY (PYY) inhibit the contraction of the electrically stimulated mouse vas deferens. Neuropeptides. 1982 Dec;3(2):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(82)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen Y. S., Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Tatemoto K., Crow T. J., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):877–879. doi: 10.1126/science.6136091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Bliss T. V., Skrede K. K. Unit analysis of hippocampal polulation spikes. Exp Brain Res. 1971;13(2):208–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00234086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
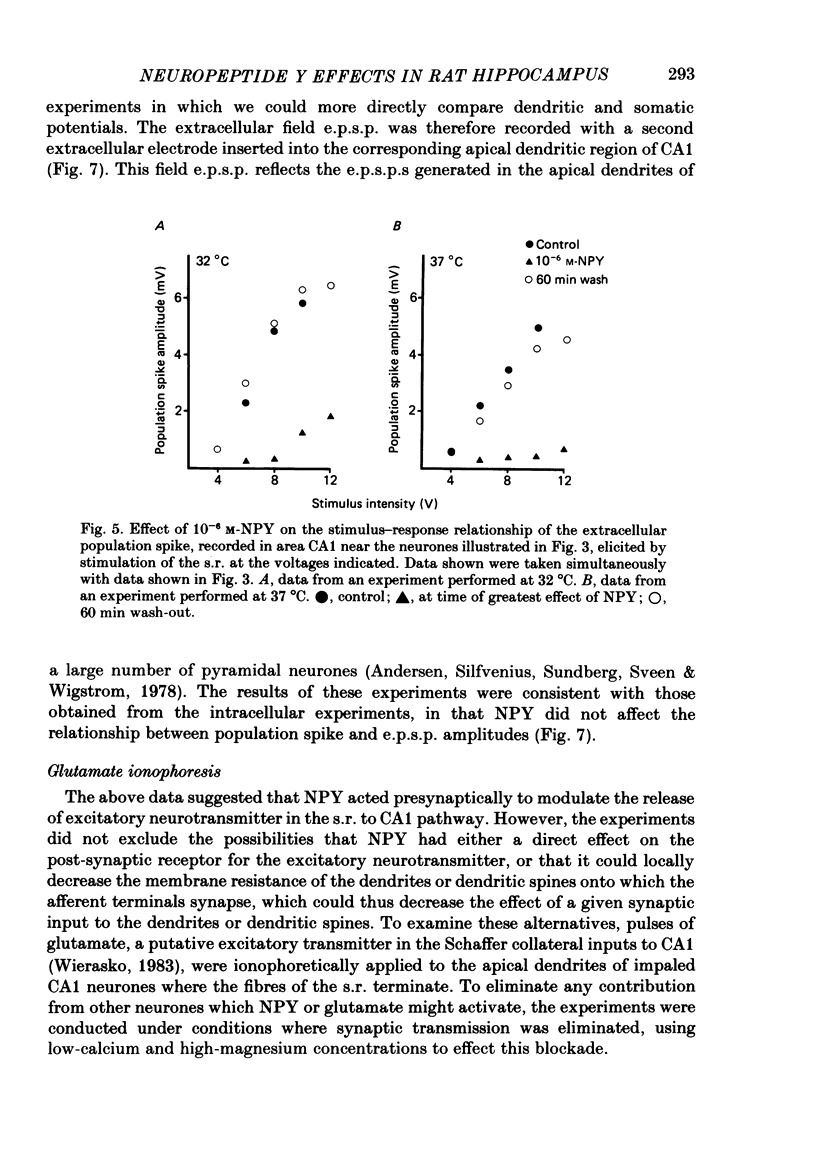
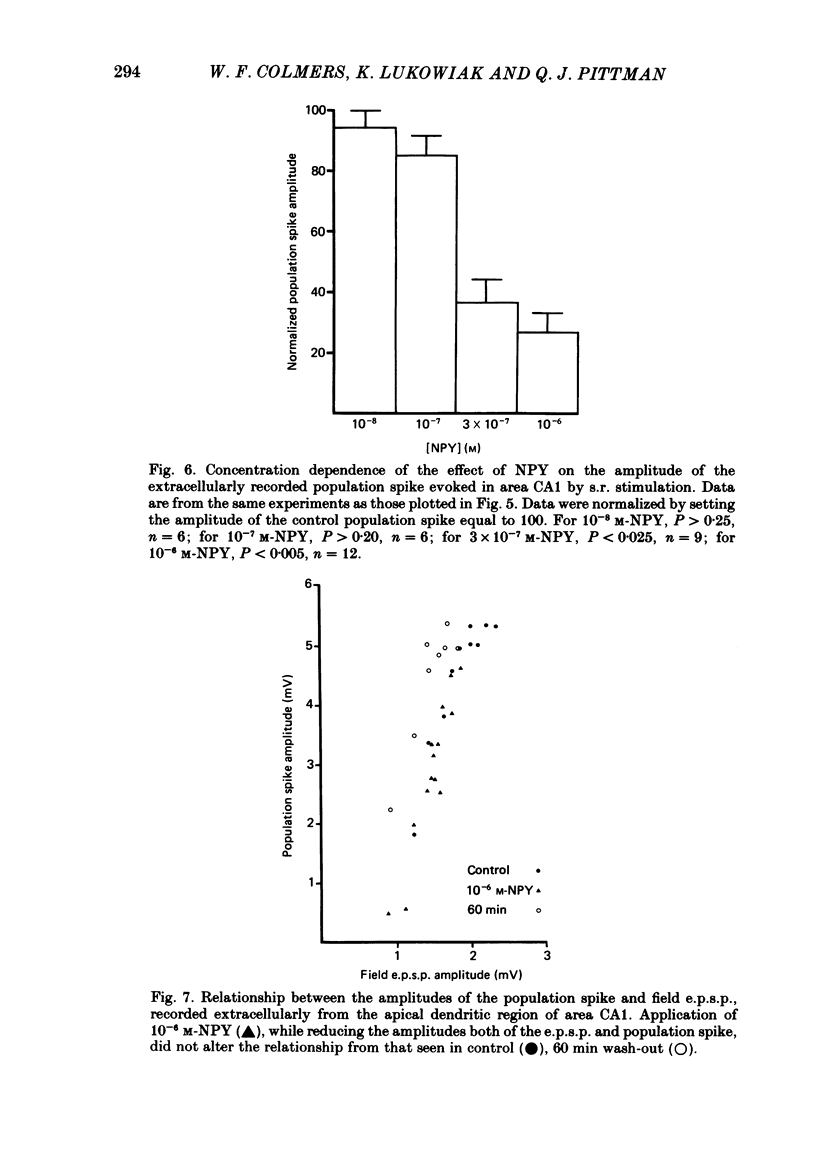
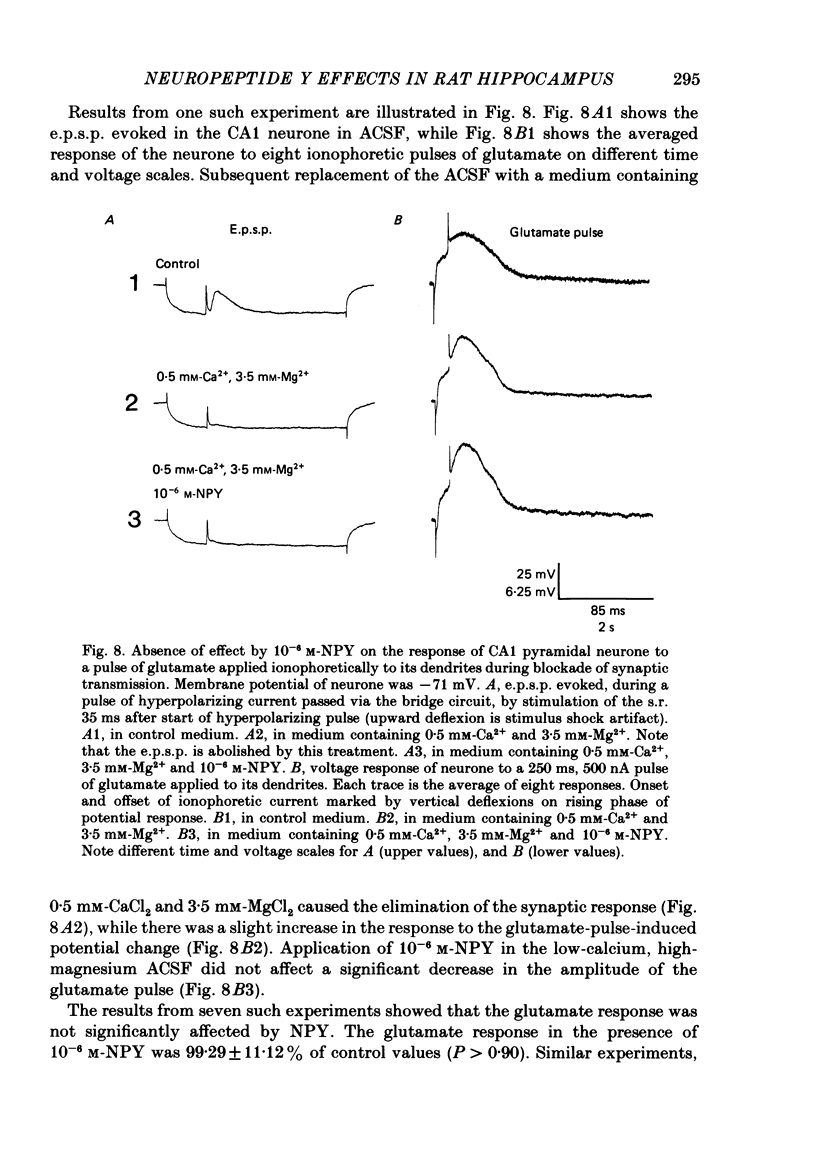
- Andersen P., Silfvenius H., Sundberg S. H., Sveen O., Wigström H. Functional characteristics of unmyelinated fibres in the hippocampal cortex. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 7;144(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Sundberg S. H., Sveen O., Swann J. W., Wigström H. Possible mechanisms for long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices from guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:463–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. A., Vallejo M., Lightman S. L. Cardiovascular effects of neuropeptide Y in the nucleus tractus solitarius of rats: relationship with noradrenaline and vasopressin. Peptides. 1985 May-Jun;6(3):421–425. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chronwall B. M., Chase T. N., O'Donohue T. L. Coexistence of neuropeptide Y and somatostatin in rat and human cortical and rat hypothalamic neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Dec 21;52(3):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chronwall B. M., DiMaggio D. A., Massari V. J., Pickel V. M., Ruggiero D. A., O'Donohue T. L. The anatomy of neuropeptide-Y-containing neurons in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1985 Aug;15(4):1159–1181. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colmers W. F., Lukowiak K., Pittman Q. J. Neuropeptide Y reduces orthodromically evoked population spike in rat hippocampal CA1 by a possibly presynaptic mechanism. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90880-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Ekblad E., Håkanson R., Wahlestedt C. Neuropeptide Y potentiates the effect of various vasoconstrictor agents on rabbit blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Emson P., McCulloch J., Tatemoto K., Uddman R. Neuropeptide Y: cerebrovascular innervation and vasomotor effects in the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 23;43(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Edvinsson L., Wahlestedt C., Uddman R., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Neuropeptide Y co-exists and co-operates with noradrenaline in perivascular nerve fibers. Regul Pept. 1984 Apr;8(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt B. J., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Goldstein M. Differential co-existence of neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines in the central nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1984 Feb;11(2):443–462. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe K., Agnati L. F., Härfstrand A., Zini I., Tatemoto K., Pich E. M., Hökfelt T., Mutt V., Terenius L. Central administration of neuropeptide Y induces hypotension bradypnea and EEG synchronization in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jun;118(2):189–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J., Polak J. M., Allen J. M., Huang W. M., Sheppard M. N., Tatemoto K., Bloom S. R. High concentrations of a novel peptide, neuropeptide Y, in the innervation of mouse and rat heart. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 May;32(5):467–472. doi: 10.1177/32.5.6546942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Jones E. G., DeFelipe J., Schmechel D., Brandon C., Emson P. C. Neuropeptide-containing neurons of the cerebral cortex are also GABAergic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6526–6530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Jones E. G., Emson P. C. Morphology, distribution, and synaptic relations of somatostatin- and neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive neurons in rat and monkey neocortex. J Neurosci. 1984 Oct;4(10):2497–2517. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-10-02497.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalra S. P., Crowley W. R. Norepinephrine-like effects of neuropeptide Y on LH release in the rat. Life Sci. 1984 Sep 10;35(11):1173–1176. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90187-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hua X. Y., Franco-Cereceda A. Effects of neuropeptide Y (NPY) on mechanical activity and neurotransmission in the heart, vas deferens and urinary bladder of the guinea-pig. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984 Aug;121(4):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Stjarne L. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) depresses the secretion of 3H-noradrenaline and the contractile response evoked by field stimulation, in rat vas deferens. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984 Mar;120(3):477–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Pancreatic polypeptide family (APP, BPP, NPY and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Goldstein M. High levels of neuropeptide Y in peripheral noradrenergic neurons in various mammals including man. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 2;42(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90401-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVicar B. A., Dudek F. E. Local synaptic circuits in rat hippocampus: interactions between pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1980 Feb 17;184(1):220–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90602-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Actions of noradrenaline recorded intracellularly in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurones, in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:221–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlethaler M., Charpak S., Dreifuss J. J. Contrasting effects of neurohypophysial peptides on pyramidal and non-pyramidal neurones in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1984 Aug 6;308(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90921-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohhashi T., Jacobowitz D. M. The effects of pancreatic polypeptides and neuropeptide Y on the rat vas deferens. Peptides. 1983 May-Jun;4(3):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(83)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman Q. J., Siggins G. R. Somatostatin hyperpolarizes hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. Brain Res. 1981 Sep 28;221(2):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90791-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E. K. Prolonged non-adrenergic inhibition of cardiac vagal action following sympathetic stimulation: neuromodulation by neuropeptide Y? Neurosci Lett. 1985 Mar 15;54(2-3):117–121. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(85)80065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Lundberg J. M. Evidence for specific neuropeptide Y-binding sites in rat brain synaptosomes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Dec 15;107(1):105–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley B. G., Leibowitz S. F. Neuropeptide Y injected in the paraventricular hypothalamus: a powerful stimulant of feeding behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3940–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler F., Moghimzadeh E., Håkanson R., Ekelund M., Emson P. Nerve fibers in the gut and pancreas of the rat displaying neuropeptide-Y immunoreactivity. Intrinsic and extrinsic origin. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;230(3):487–493. doi: 10.1007/BF00216194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


