Abstract
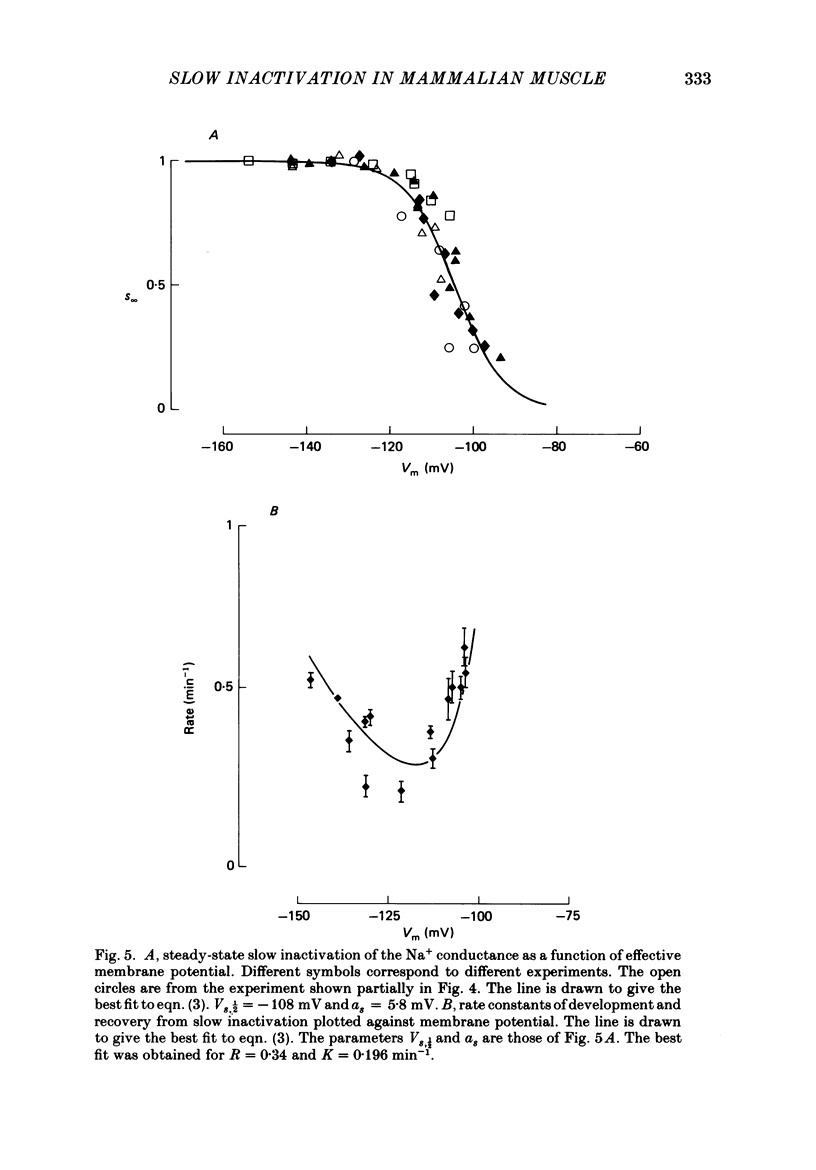
1. Voltage-clamp Na+ currents (INa) were measured in rat fast-twitch fibres using the loose-patch-clamp technique. Changes in the conditioning membrane potential produced slow changes in the peak INa elicited by short test depolarizations, due to a slow inactivation process. 2. Inactivation was increased by application of steady depolarizing potentials and was reversed by steady hyperpolarizations. These changes in peak INa could be well fitted by single-exponential functions with time constants in the range of 1-4 min. 3. The steady-state values of the maximum peak INa at any potential could be well fitted by a function identical to the one describing the fast inactivation process. This gave a potential of -108 mV at which 50% of the channels were closed due to slow inactivation. 4. The maximum peak current densities obtained with the slow inactivation fully removed were as large as 20 mA cm-2.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman W. J., Jr, Palti Y. The effects of external potassium and long duration voltage conditioning on the amplitude of sodium currents in the giant axon of the squid, Loligo pealei. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):589–606. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Marshall M. W. Sodium currents in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):223–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Roberts W. M., Ruff R. L. Voltage clamp of rat and human skeletal muscle: measurements with an improved loose-patch technique. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:751–768. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Stanfield P. R., Stühmer W. Lateral distribution of sodium and potassium channels in frog skeletal muscle: measurements with a patch-clamp technique. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:261–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Stanfield P. R., Stühmer W. Slow changes in currents through sodium channels in frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Caldwell J. H., Campbell D. T. Na channels in skeletal muscle concentrated near the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):588–590. doi: 10.1038/313588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Conti F. Structure of the squid axon membrane as derived from charge-pulse relaxation studies in the presence of absorbed lipophilic ions. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 15;59(2):91–104. doi: 10.1007/BF01875707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolte H. D., Lüderitz B. Einfluss von Insulin auf das Membranpotential bei alimentärem Kaliummangel Messungen am isolierten Rattenzwerchfell. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;301(3):254–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T. Slow mechanism for sodium permeability inactivation in myelinated nerve fibre of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):283–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y. Inactivation of sodium channels: second order kinetics in myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):573–596. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. A., Rojas E., Suarez-Isla B. A. Activation and inactivation characteristics of the sodium permeability in muscle fibres from Rana temporaria. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:297–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval A., Léoty C. Ionic currents in mammalian fast skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:403–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval A., Léoty C. Ionic currents in slow twitch skeletal muscle in the rat. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:23–41. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. M. Ultra-slow inactivation of the ionic currents through the membrane of myelinated nerve. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 5;426(2):232–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peganov E. M., Khodorov B. I., Shishkova L. D. Medlennaia natrievaia inaktivatsiia v membrane perekhvata Ranve. Rol' naruzhnogo kaliia. Biull Eksp Biol Med. 1973 Sep;76(9):15–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Inactivation in Myxicola giant axons responsible for slow and accumulative adaptation phenomena. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:531–549. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Slow inactivation of the sodium conductance in squid giant axons. Pronase resistance. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Stühmer W., Almers W. Effect of glucocorticoid treatment on the excitability of rat skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Nov 1;395(2):132–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00584726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdel R., Lehmann-Horn F. Membrane changes in cells from myotonia patients. Physiol Rev. 1985 Apr;65(2):310–356. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.2.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Pencek T. L., Davis F. A. Slow sodium inactivation in Myxicola axons. Evidence for a second inactive state. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):771–778. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85727-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Almers W. Photobleaching through glass micropipettes: sodium channels without lateral mobility in the sarcolemma of frog skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):946–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


