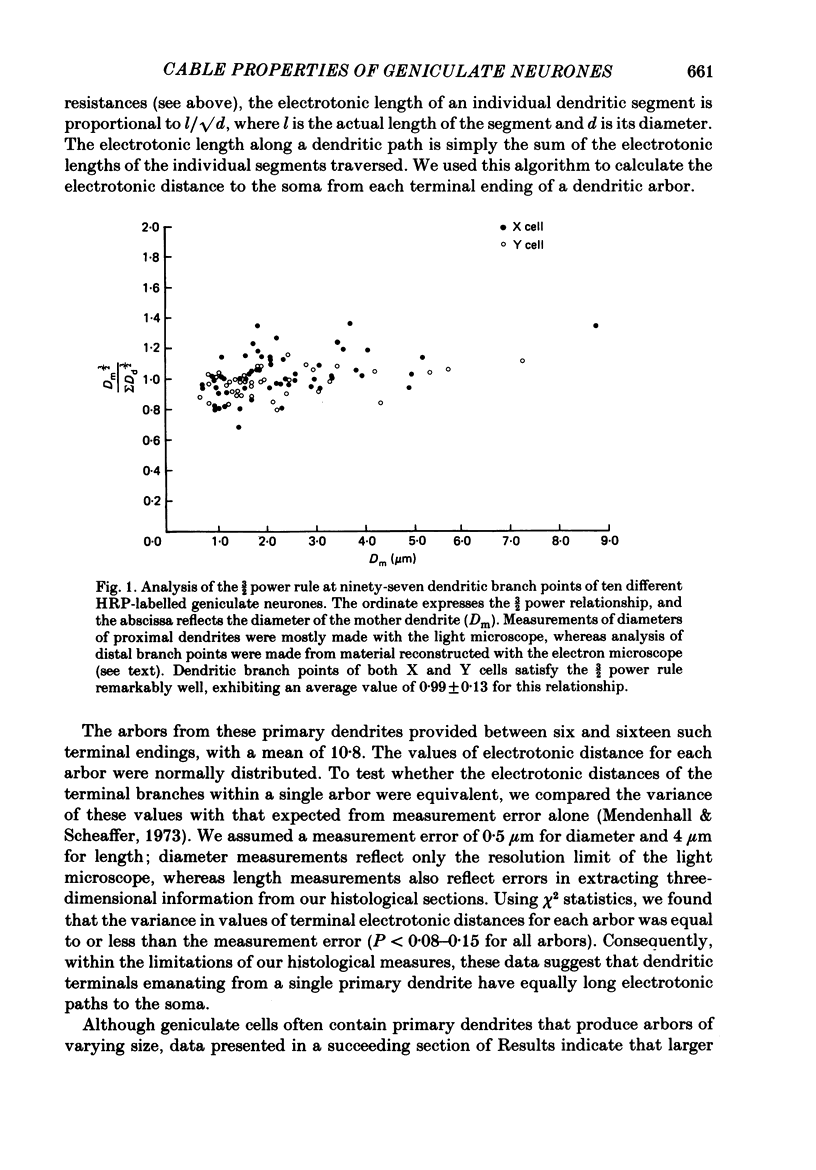
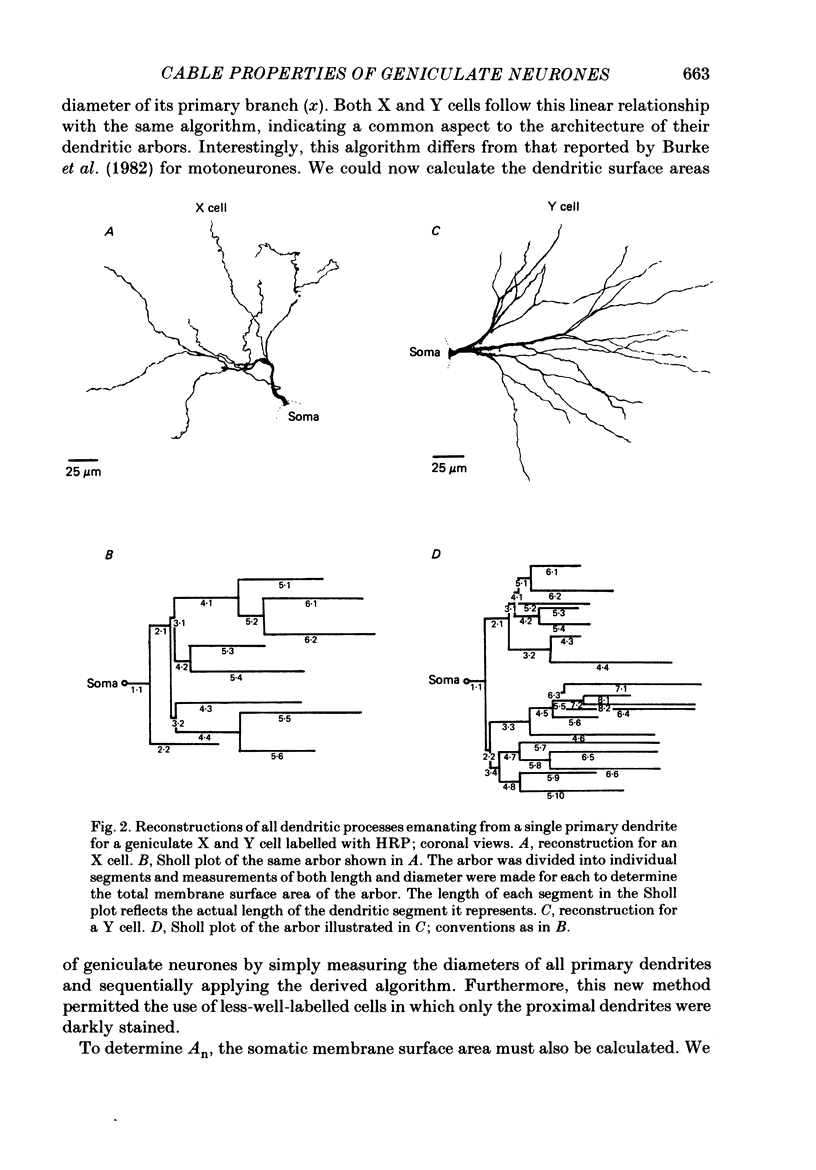
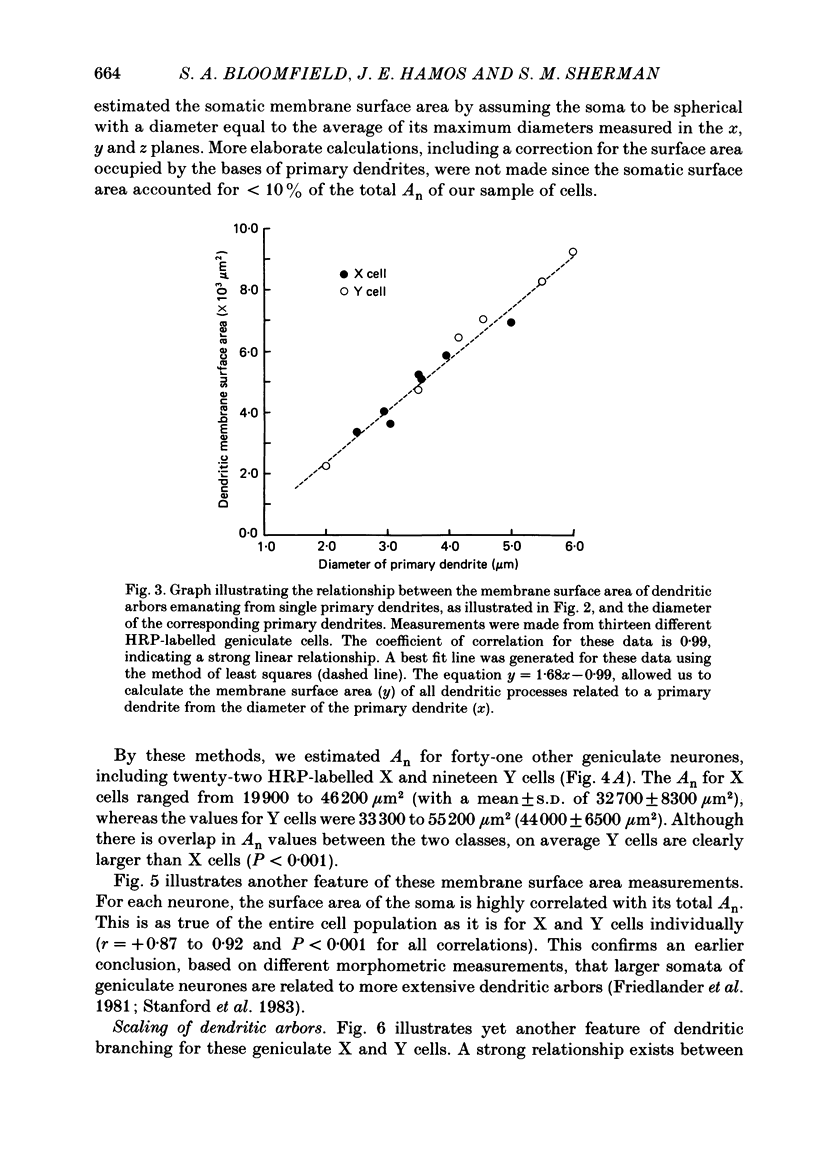
Abstract
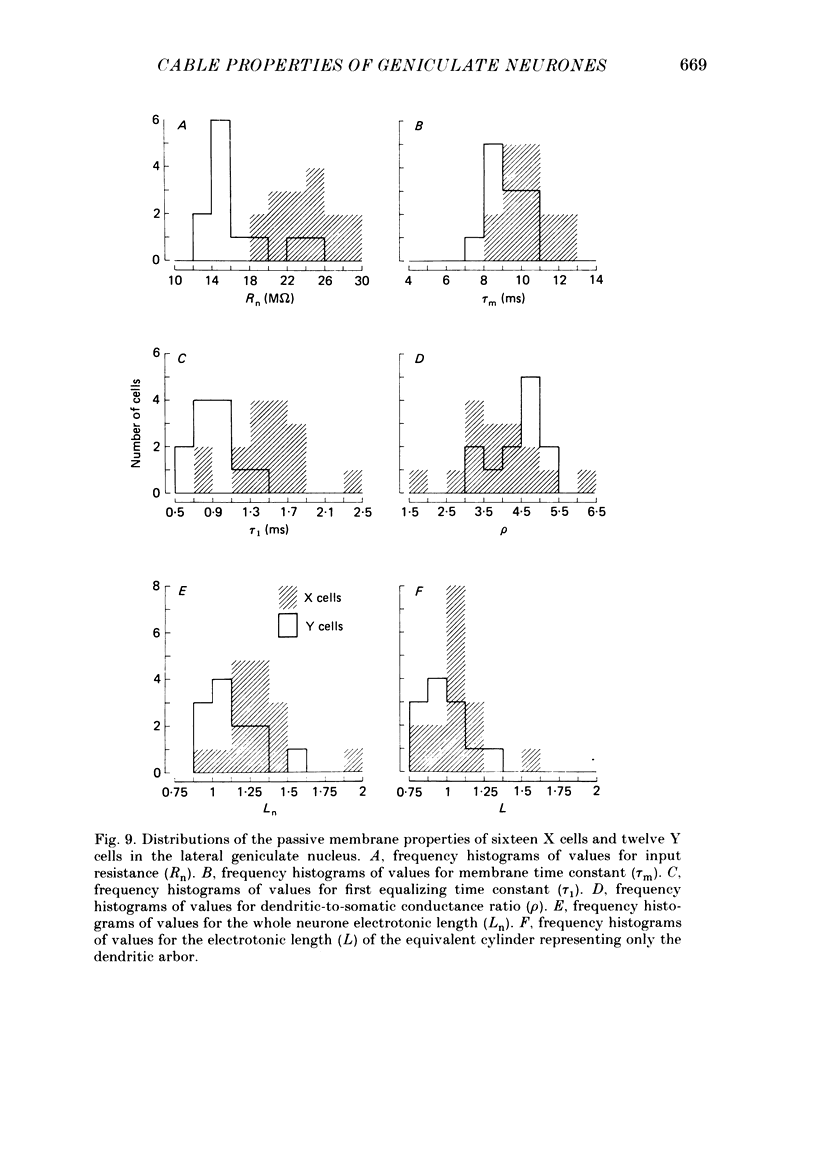
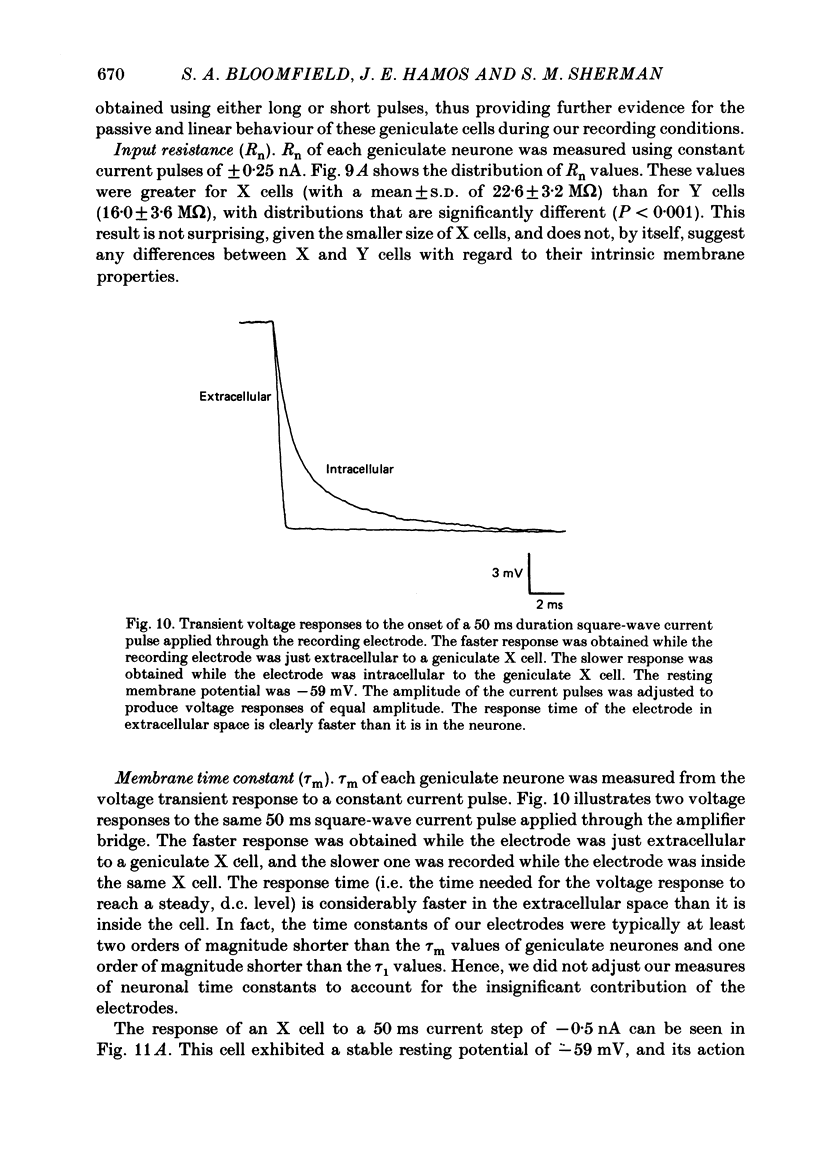
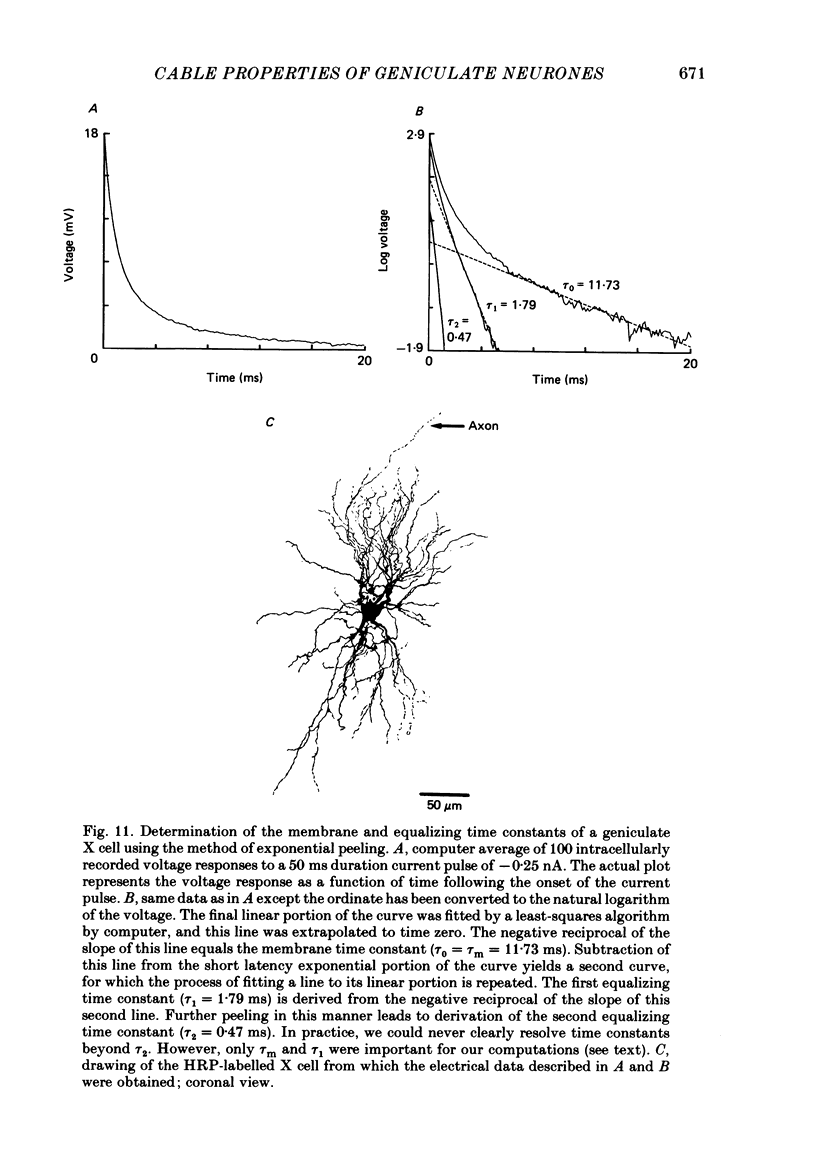
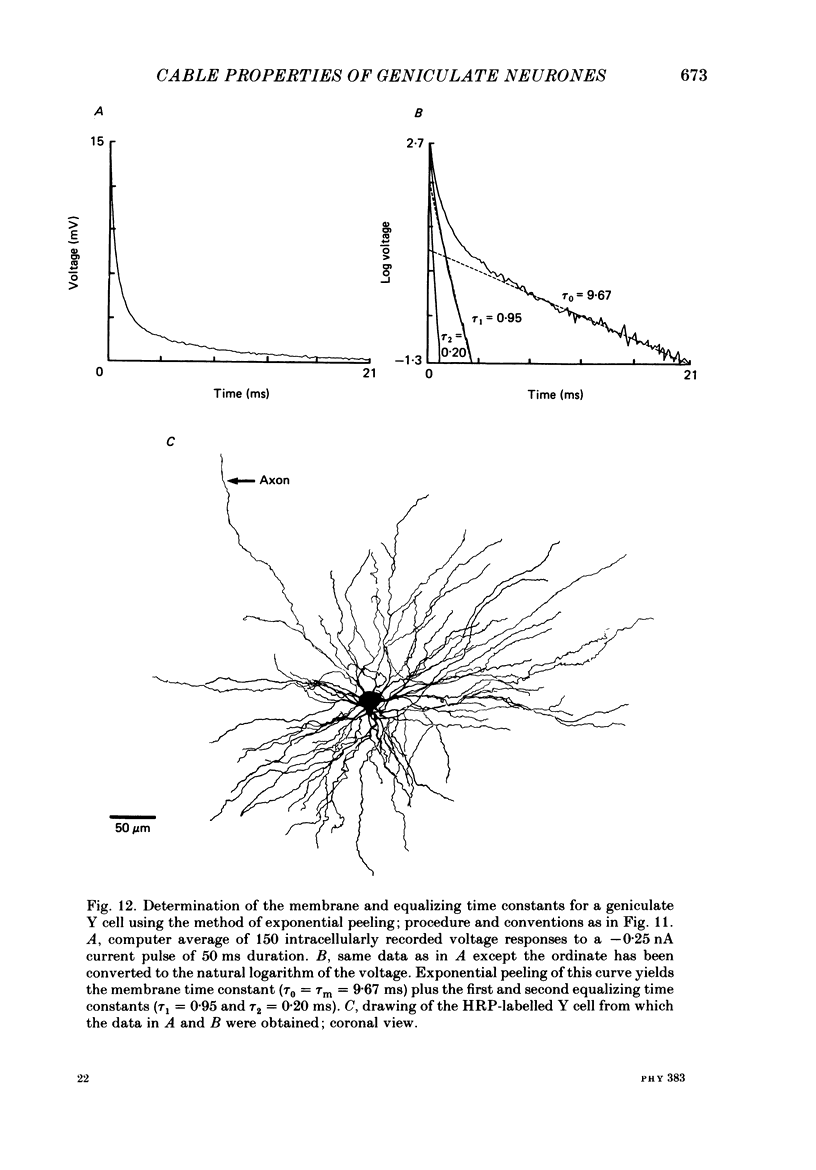
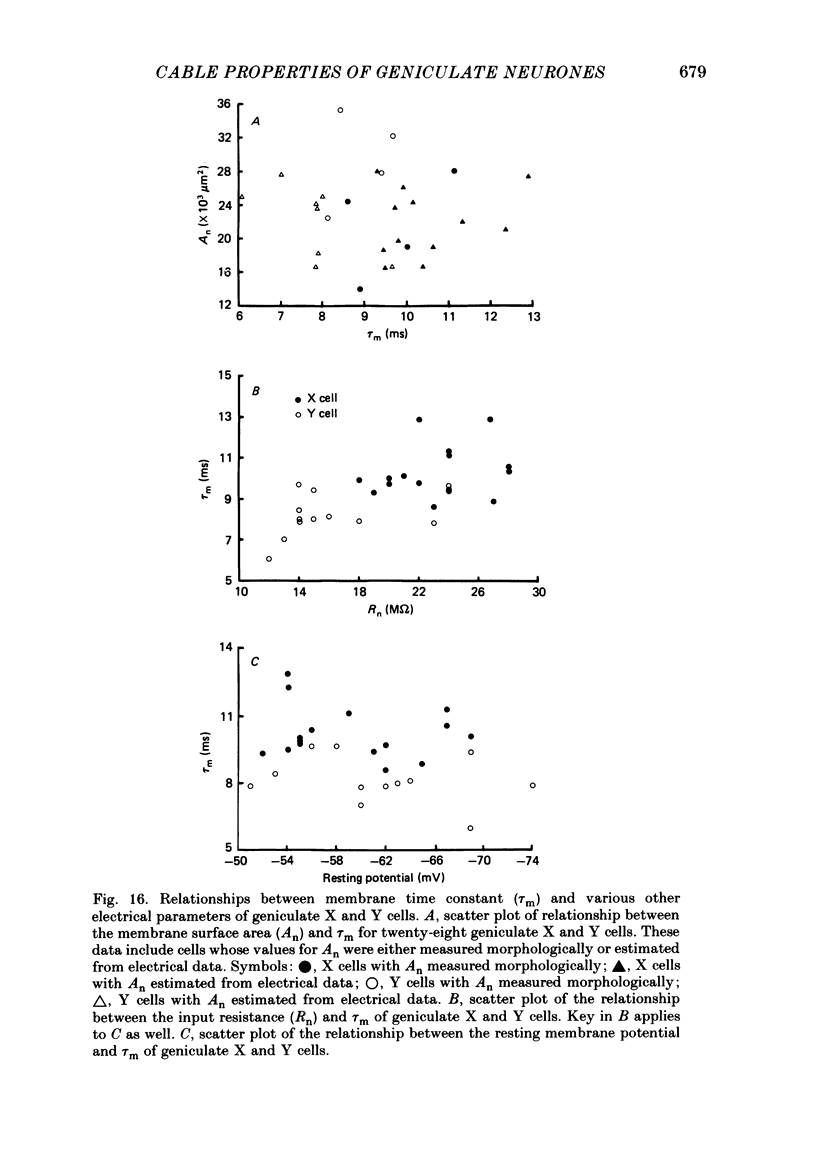
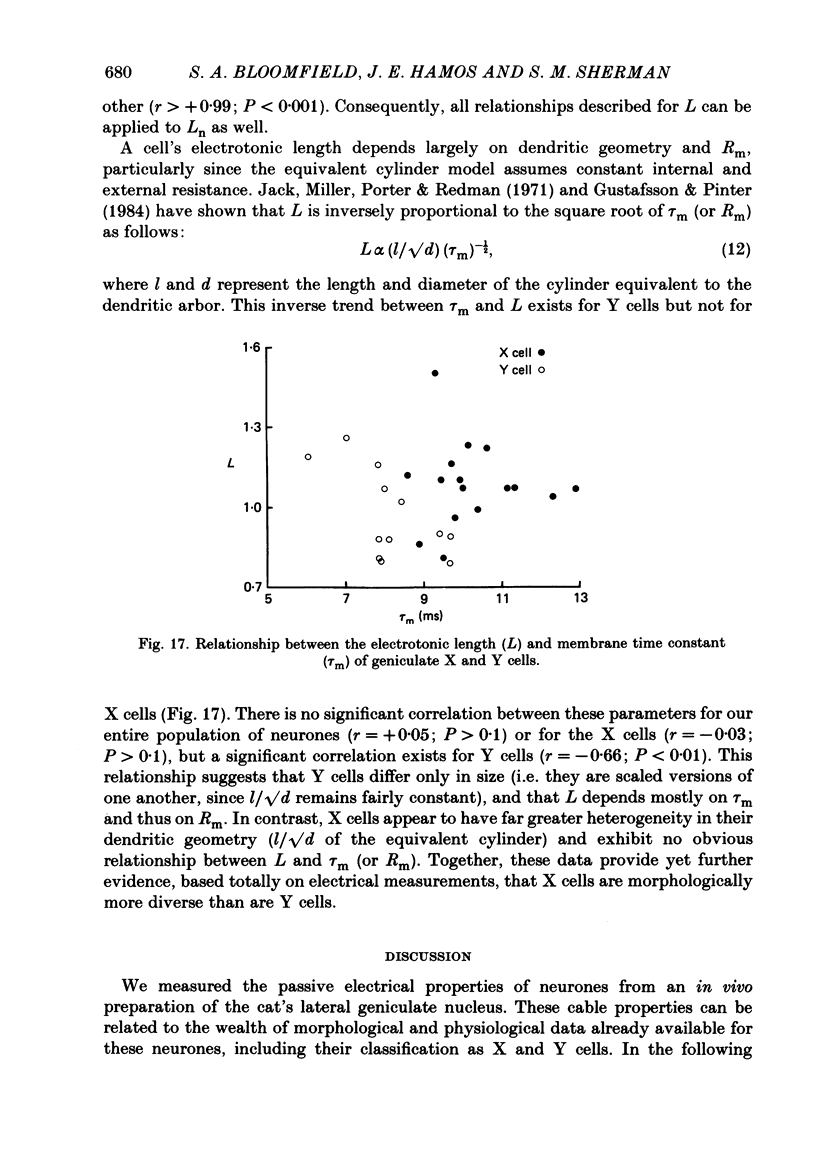
1. We used an in vivo preparation of the cat to study the passive cable properties of sixteen X and twelve Y cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus. Cells were modelled as equivalent cylinders according to Rall's formulations (Rall, 1959a, 1969, 1977). We injected intracellular current pulses into these geniculate neurones, and we analysed the resulting voltage transients to obtain the cable parameters of these cells. In addition, fifty-four physiologically characterized neurones were labelled with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and analysed morphologically. 2. Analysis of HRP-labelled geniculate neurones showed that the dendritic branching pattern of these cells adheres closely to the 3/2 power rule. That is, at each branch point, the diameter of the parent branch raised to the 3/2 power equals the sum of the diameters of the daughter dendrites after each is raised to the 3/2 power. Furthermore, preliminary data indicate that the dendritic terminations emanating from each primary dendrite occur at the same electrotonic distance from the soma. These observations suggest that both X and Y cells meet the geometric constraints necessary for reduction of their dendritic arbors into equivalent cylinders. 3. We found a strong linear relationship between the diameter of each primary dendrite and the membrane surface area of the arbor emanating from it. We used this relationship to derive an algorithm for determining the total somatic and dendritic membrane surface area of an X and Y cell simply from knowledge of the diameters of its soma and primary dendrites. 4. Both geniculate X and Y cells display current-voltage relationships that were linear within +/- 20 mV of the resting membrane potential. This meant that we could easily remain within the linear voltage range during the voltage transient analyses. 5. X and Y cells clearly differ in terms of many of their electrical properties, including input resistance, membrane time constant and electrotonic length. The difference in input resistance between X and Y cells cannot be attributed solely to the smaller average size of X cells, but it also reflects a higher specific membrane resistance (Rm) of the X cells. Furthermore, X cells exhibit electrotonic lengths slightly larger than those of Y cells, but both neuronal types display electrotonic lengths of roughly 1. This indicates that even the most distally located innervation to these cells should have considerable influence on their somatic and axonal responses.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF








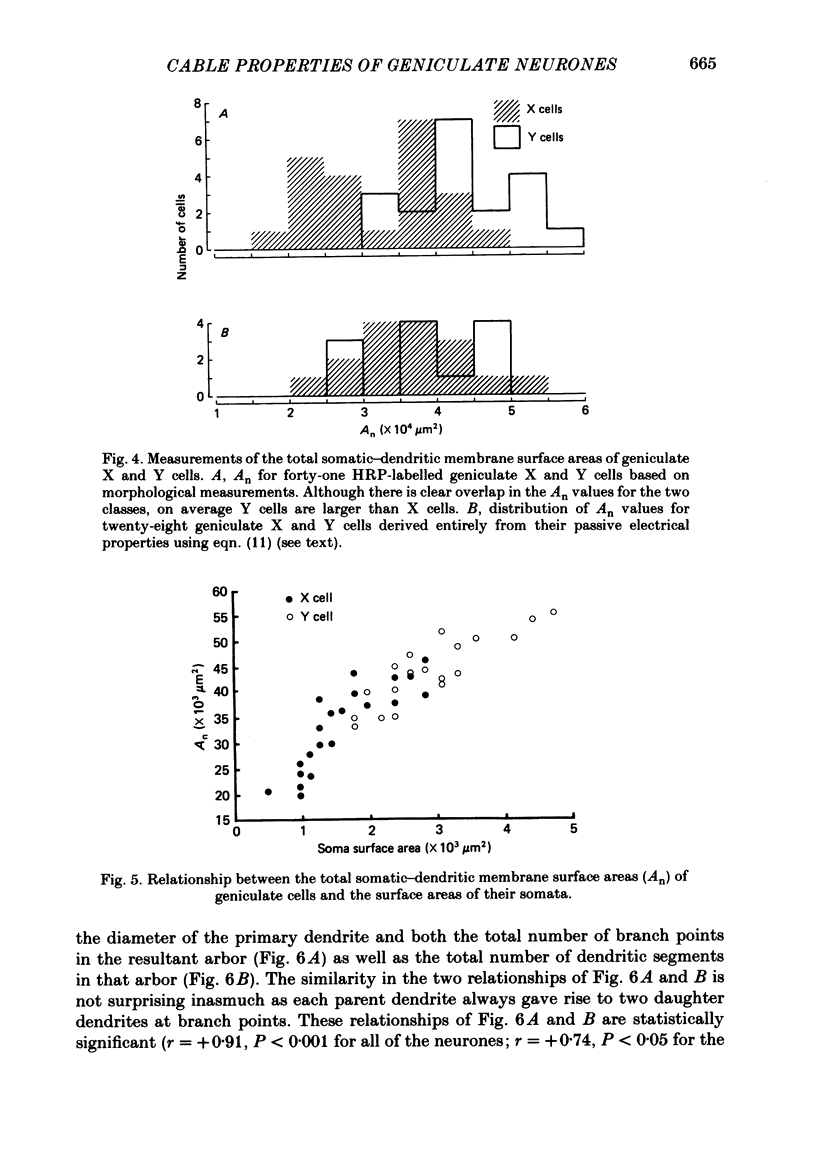
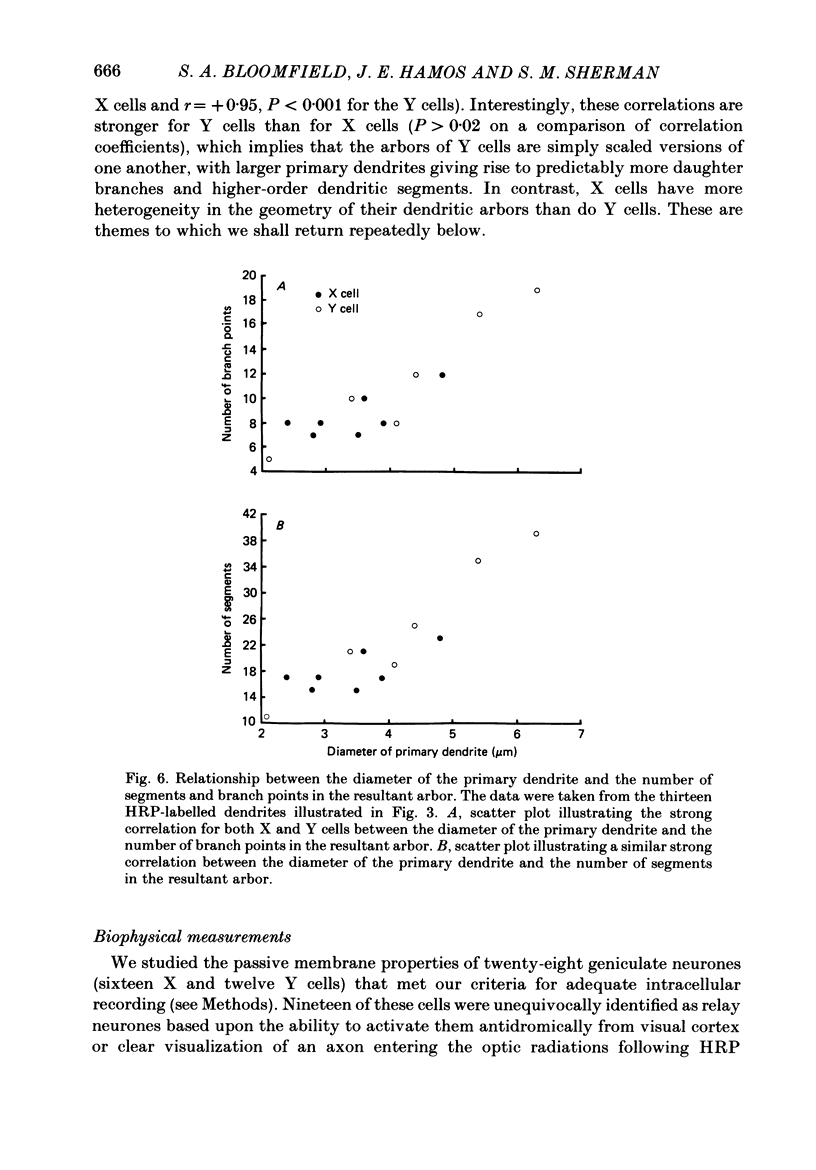
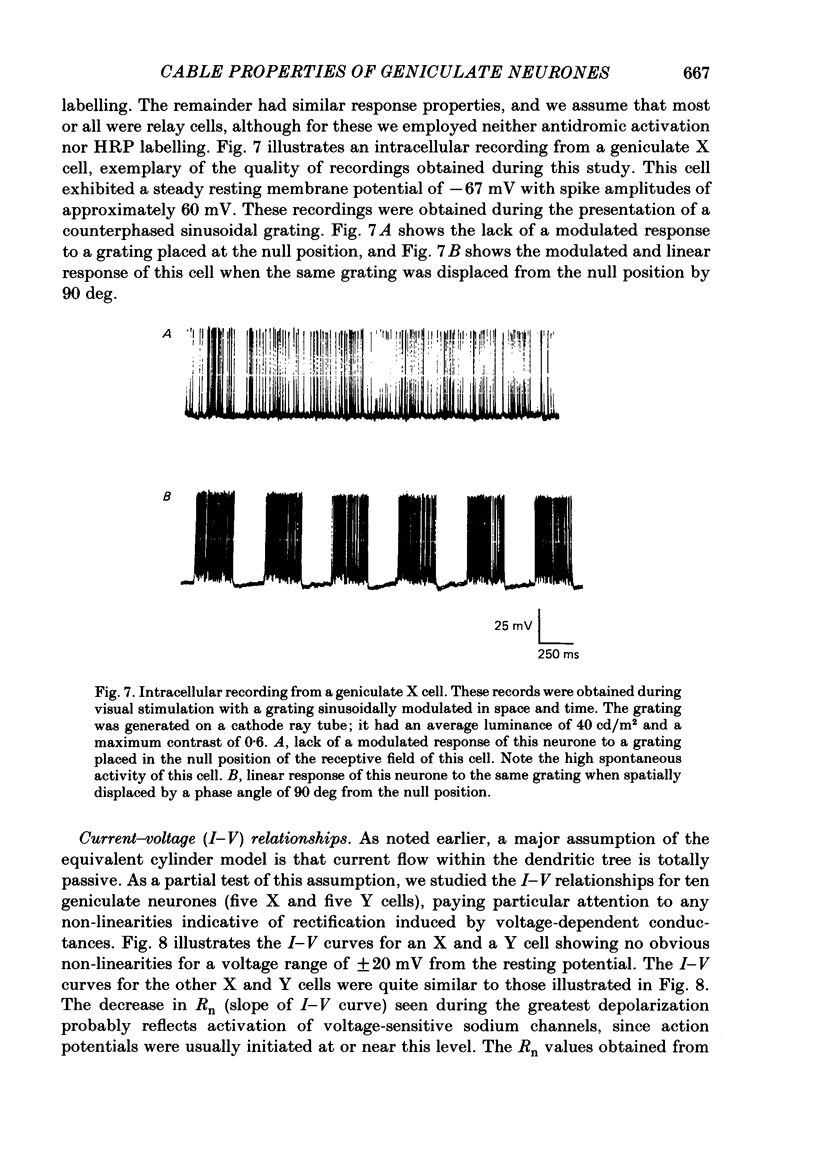
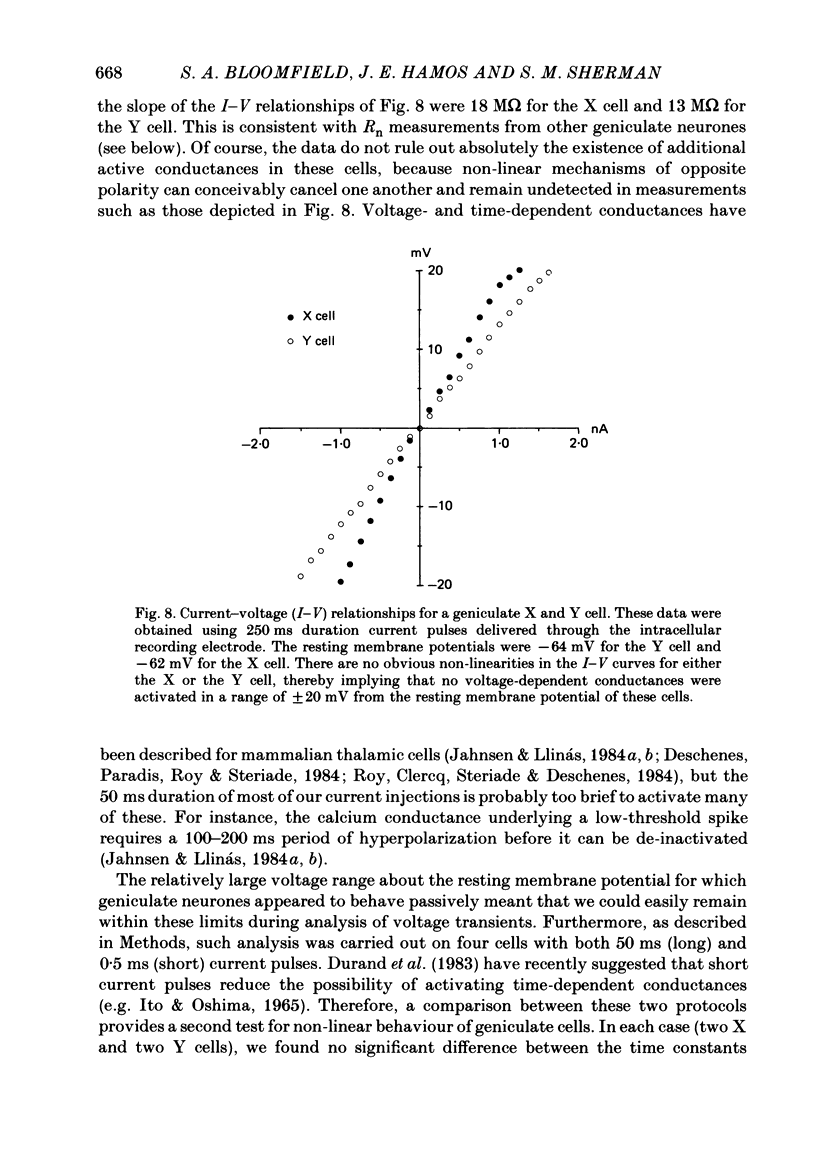














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C. Technical considerations on the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker. Neuroscience. 1977;2(1):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlsén G., Lindström S., Lo F. S. Inhibition from the brain stem of inhibitory interneurones of the cat's dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:593–609. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Crill W. E. Specific membrane properties of cat motoneurones. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):301–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y., Krnjević K., Reiffenstein R. J., Reinhardt W. Inhibitory conductance changes and action of gamma-aminobutyrate in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2445–2463. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E. Direct observations on the contacts made between Ia afferent fibres and alpha-motoneurones in the cat's lumbosacral spinal cord. J Physiol. 1981;313:121–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Fricke R. A., Perkel D. H. Passive electrical constants in three classes of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Oct;46(4):812–827. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.4.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Perkel D. H., Norris J. C., Peacock J. H. Electrotonic structure and specific membrane properties of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):1–15. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Dum R. P., Fleshman J. W., Glenn L. L., Lev-Tov A., O'Donovan M. J., Pinter M. J. A HRP study of the relation between cell size and motor unit type in cat ankle extensor motoneurons. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Jul 20;209(1):17–28. doi: 10.1002/cne.902090103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland B. G., Dubin M. W., Levick W. R. Sustained and transient neurones in the cat's retina and lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(2):473–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. Function of the thalamic reticular complex: the searchlight hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4586–4590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschênes M., Paradis M., Roy J. P., Steriade M. Electrophysiology of neurons of lateral thalamic nuclei in cat: resting properties and burst discharges. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Jun;51(6):1196–1219. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.6.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmond N. L., Levy W. B. Dendritic caliber and the 3/2 power relationship of dentate granule cells. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Aug 20;227(4):589–596. doi: 10.1002/cne.902270410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D., Carlen P. L., Gurevich N., Ho A., Kunov H. Electrotonic parameters of rat dentate granule cells measured using short current pulses and HRP staining. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Nov;50(5):1080–1097. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.5.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egger M. D., Egger L. D. Quantitative morphological analysis of spinal motoneurons. Brain Res. 1982 Dec 16;253(1-2):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90669-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellias S. A., Stevens J. K. The dendritic varicosity: a mechanism for electrically isolating the dendrites of cat retinal amacrine cells? Brain Res. 1980 Sep 8;196(2):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90401-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald R., Chase R. An improved method for plotting retinal landmarks and focusing the eyes. Vision Res. 1971 Jan;11(1):95–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(71)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote W. E., Mordes J. P., Colby C. L., Harrison T. A. Differential effect of midbrain stimulation on X-sustained and Y-transient neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Brain Res. 1977 May 20;127(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M. J., Lin C. S., Stanford L. R., Sherman S. M. Morphology of functionally identified neurons in lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jul;46(1):80–129. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillery R. W. The organization of synaptic interconnections in the laminae of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;96(1):1–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00321474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Pinter M. J. Relations among passive electrical properties of lumbar alpha-motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:401–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Integrative action in the cat's lateral geniculate body. J Physiol. 1961 Feb;155:385–398. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamos J. E., Van Horn S. C., Raczkowski D., Uhlrich D. J., Sherman S. M. Synaptic connectivity of a local circuit neurone in lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):618–621. doi: 10.1038/317618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein S., Shapley R. M. Linear and nonlinear spatial subunits in Y cat retinal ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):265–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann K. P., Stone J., Sherman S. M. Relay of receptive-field properties in dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1972 Jul;35(4):518–531. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.4.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey A. L., Sur M., Uhlrich D. J., Sherman S. M. Projection patterns of individual X- and Y-cell axons from the lateral geniculate nucleus to cortical area 17 in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Mar 8;233(2):159–189. doi: 10.1002/cne.902330203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iansek R., Redman S. J. An analysis of the cable properties of spinal motoneurones using a brief intracellular current pulse. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):613–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Oshima T. Electrical behaviour of the motoneurone membrane during intracellularly applied current steps. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(3):607–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Miller S., Porter R., Redman S. J. The time course of minimal excitory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurones by group Ia afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J. An electrical description of the motoneurone, and its application to the analysis of synaptic potentials. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):321–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H., Llinás R. Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:205–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H., Llinás R. Ionic basis for the electro-responsiveness and oscillatory properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:227–247. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., Powell T. P. An electron microscopic study of the mode of termination of cortico-thalamic fibres within the sensory relay nuclei of the thalamus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 11;172(1027):173–185. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan E., Marcus S., So Y. T. Effects of dark adaptation on spatial and temporal properties of receptive fields in cat lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:561–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Poggio T. A theoretical analysis of electrical properties of spines. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Jul 22;218(1213):455–477. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. Understanding the intrinsic circuitry of the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus: electrical properties of the spine-triad arrangement. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Sep 23;225(1240):365–390. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauth J. The interpretation of significance tests for independent and dependent samples. J Neurosci Methods. 1983 Dec;9(4):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(83)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuter F., Richter D. W., Camerer H., Senekowitsch R. Morphological and electrical description of medullary respiratory neurons of the cat. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Nov 25;372(1):7–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00582200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennie P. Parallel visual pathways: a review. Vision Res. 1980;20(7):561–594. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(80)90115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. F., Bloomfield S. A. Electroanatomy of a unique amacrine cell in the rabbit retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3069–3073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Lux H. D. Some electrical measurements of motoneuron parameters. Biophys J. 1970 Jan;10(1):55–73. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86285-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Branching dendritic trees and motoneuron membrane resistivity. Exp Neurol. 1959 Nov;1:491–527. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Time constants and electrotonic length of membrane cylinders and neurons. Biophys J. 1969 Dec;9(12):1483–1508. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86467-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy J. P., Clercq M., Steriade M., Deschênes M. Electrophysiology of neurons of lateral thalamic nuclei in cat: mechanisms of long-lasting hyperpolarizations. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Jun;51(6):1220–1235. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.6.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. J., Sherman S. M. Nasotemporal overlap in visual field projected to lateral geniculate nucleus in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1971 May;34(3):453–466. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. J. The projection of the visual field to the lateral geniculate and medial interlaminar nuclei in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1971 Sep;143(1):101–108. doi: 10.1002/cne.901430107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarthy P. V., Bridges C. D., Kretzer F. L., Lam D. M. Lectin receptors on cells isolated from the turtle retina. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Nov 10;202(4):561–569. doi: 10.1002/cne.902020408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedivec M. J., Capowski J. J., Mendell L. M. Morphology of HRP-injected spinocervical tract neurons: effect of dorsal rhizotomy. J Neurosci. 1986 Mar;6(3):661–672. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-03-00661.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapley R., Lennie P. Spatial frequency analysis in the visual system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1985;8:547–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.08.030185.002555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. M., Koch C. The control of retinogeniculate transmission in the mammalian lateral geniculate nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1986;63(1):1–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00235642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. M., Spear P. D. Organization of visual pathways in normal and visually deprived cats. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):738–855. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer W. Control of thalamic transmission by corticofugal and ascending reticular pathways in the visual system. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jul;57(3):386–420. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.3.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer W. The effect of mesencephalic reticular stimulation on intracellular potentials of cat lateral geniculate neurons. Brain Res. 1973 Oct 26;61:35–54. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90514-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So Y. T., Shapley R. Spatial tuning of cells in and around lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat: X and Y relay cells and perigeniculate interneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):107–120. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanford L. R., Friedlander M. J., Sherman S. M. Morphological and physiological properties of geniculate W-cells of the cat: a comparison with X- and Y-cells. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Sep;50(3):582–608. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.3.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., Dreher B., Leventhal A. Hierarchical and parallel mechanisms in the organization of visual cortex. Brain Res. 1979 Dec;180(3):345–394. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(79)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sur M., Sherman S. M. Retinogeniculate terminations in cats: morphological differences between X and Y cell axons. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):389–389. doi: 10.1126/science.7123239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara N., Murakami F., Hultborn H. Electrical constants of neurons of the red nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1975 Jul 11;23(1):49–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00238728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. A., Schwartzkroin P. A. Steady-state electrotonic analysis of intracellularly stained hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Jul;44(1):184–199. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.44.1.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Cullheim S. A quantitative light microscopic study of the dendrites of cat spinal gamma -motoneurons after intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Nov 10;202(4):585–596. doi: 10.1002/cne.902020410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Kellerth J. O. Electrophysiological and morphological measurements in cat gastrocnemius and soleus alpha-motoneurones. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 30;307(1-2):167–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. R., Friedlander M. J., Sherman S. M. Fine structural morphology of identified X- and Y-cells in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Jun 22;221(1225):411–436. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]