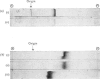
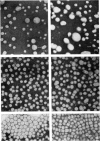
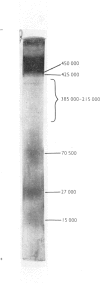
Abstract
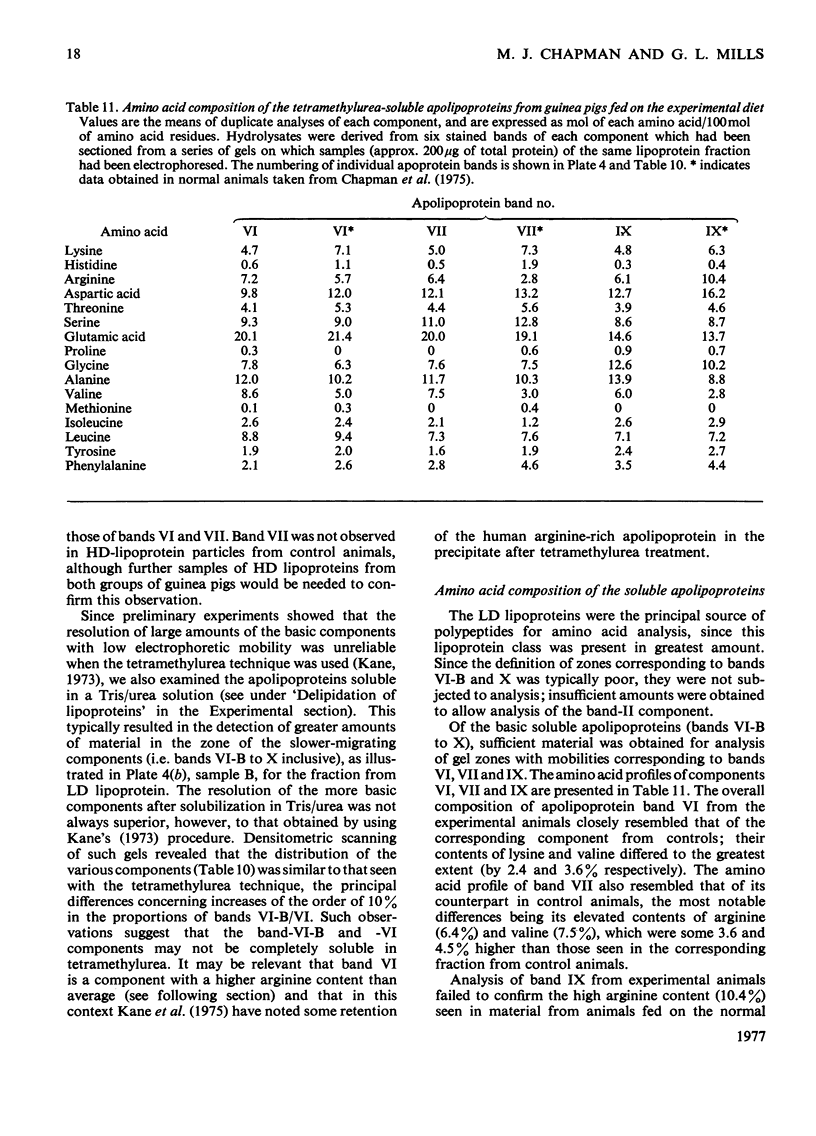
1. Hypercholesterolaemia was induced in male guinea pigs after 6 days on a chow diet supplemented with 1.6% (w/w) cholesterol and 15% (w/w) corn oil. Both the VLD (very-low-density) and LD (low-density) lipoproteins were increased in cholesterol-fed animals, although the low concentrations of HD (high-density) lipoproteins remained essentially unchanged. LD lipoproteins of d 1.019-1.100 were the major class, accounting for 74% of the total substances of d less than 1.100. 2. Both VLD and LD lipoproteins exhibited alterations in their chemical composition, physical properties and apolipoprotein content. The VLD lipoproteins in cholesterolaemic animals were rich in cholesterol (25.9%), deficient in protein (4.9%) and exhibited electrophoretic mobility greater than that of beta-globulin; their average particle size (64.5 nm) was larger than that in controls (46.3 nm). The LD lipoproteins in animals fed on the experimental diet were also richer in cholesterol (53.1%) and of larger diameter (24.3 nm) than in the control group (41.1% and 21.4 nm respectively). 3. The apolipoprotein-B content of both VLD and LD lipoproteins was elevated in cholesterolaemic animals, particularly in the VLD class, where it represented 74.8% of the total protein moiety. 4. Apo-VLD lipoprotein exhibited an increase from 6 to 19% in its complement of tetramethylurea-soluble apolipoproteins with low electrophoretic mobility (relative mobility less than 0.29); this was primarily accounted for by apolipoproteins characterized by high arginine (7.2 and 6.4% respectively) and glutamic acid (20.1 and 20.0% respectively) contents. 5. By contrast, there was little change in the soluble apolipoproteins of LD lipoproteins in hypercholesterolaemic animals.6. These studies show the response of the guinea pig to dietary fat and cholesterol to be distinct from that elicited by similar stimuli in the rabbit, rat, pig and dog.
Full text
PDF



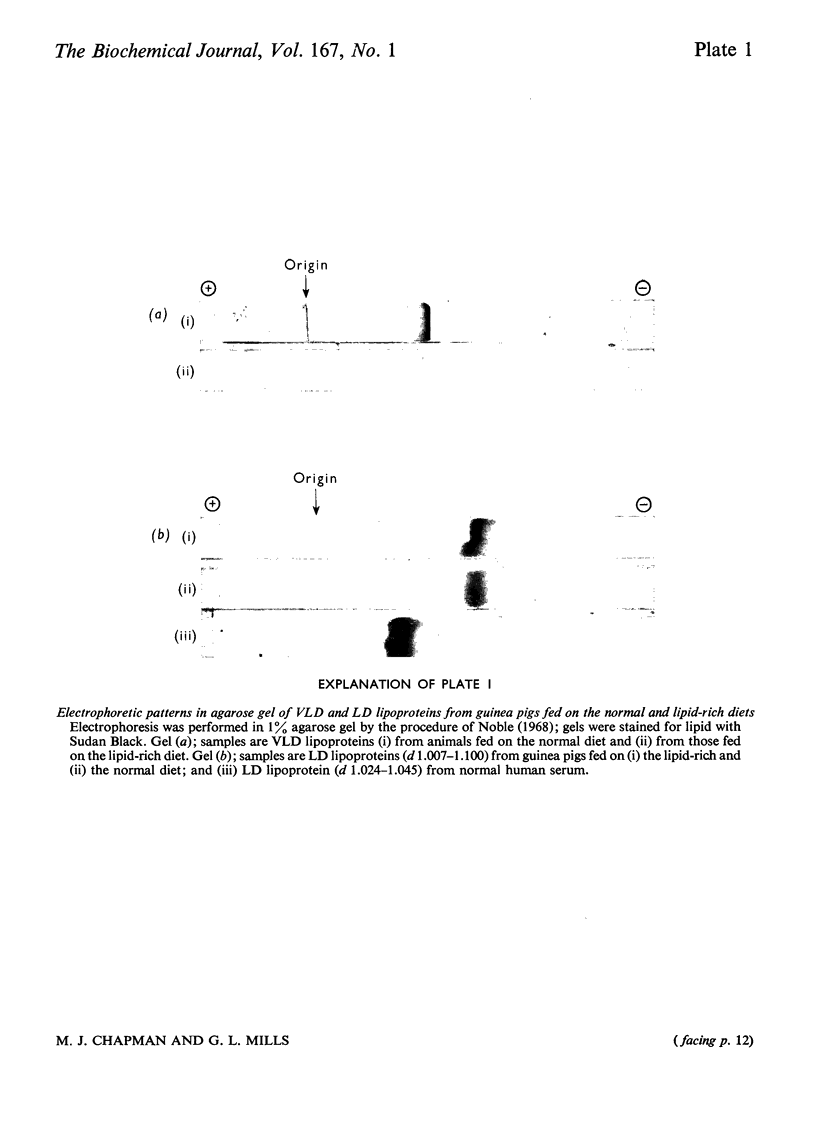


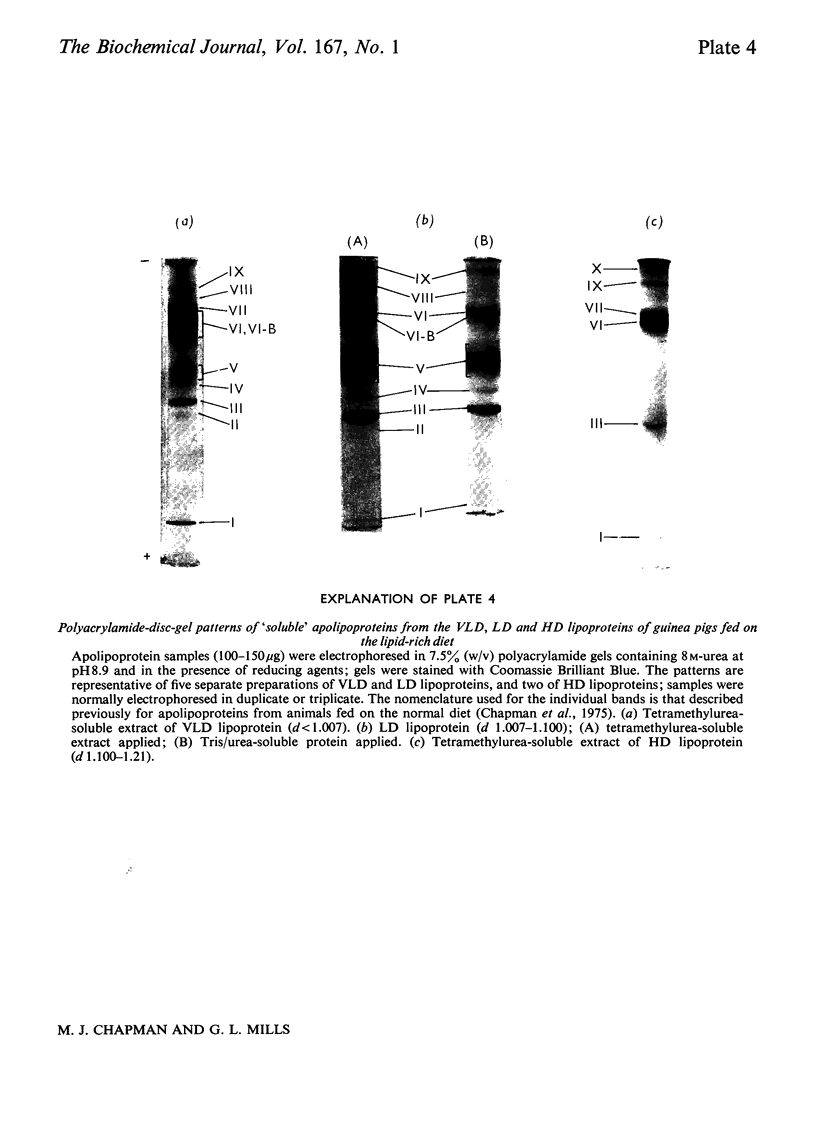
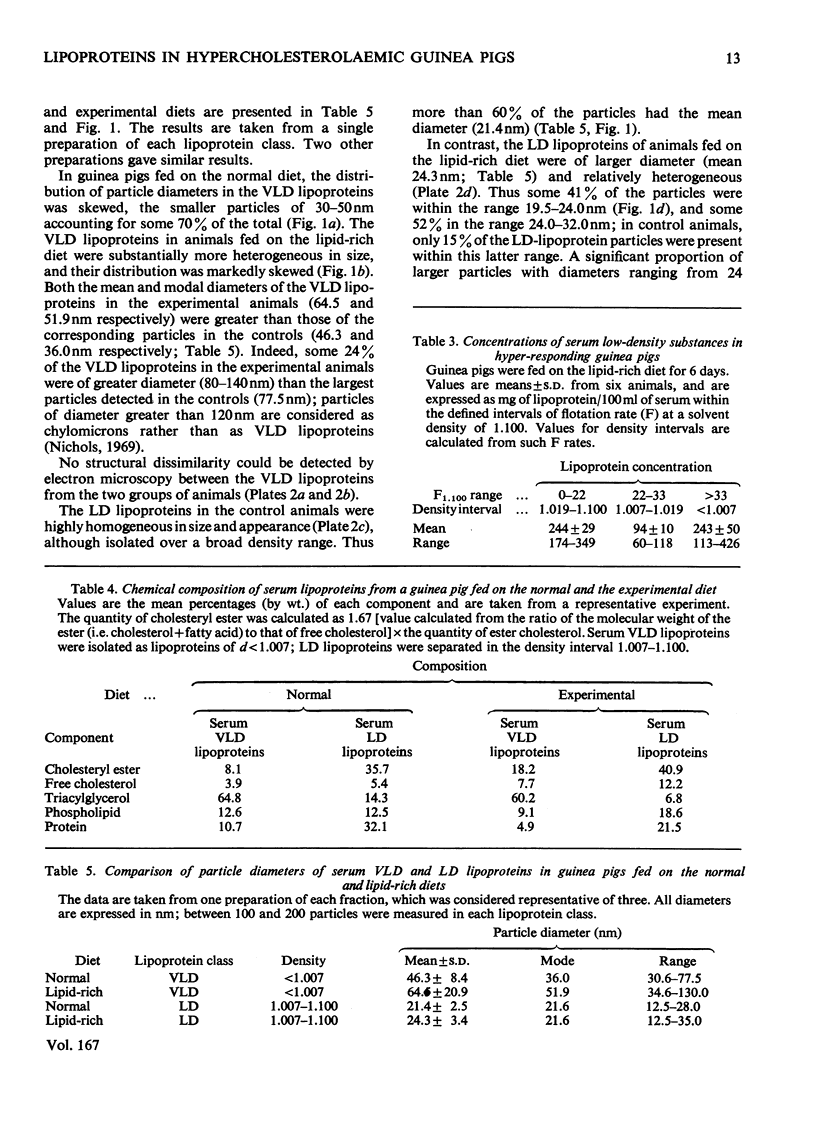
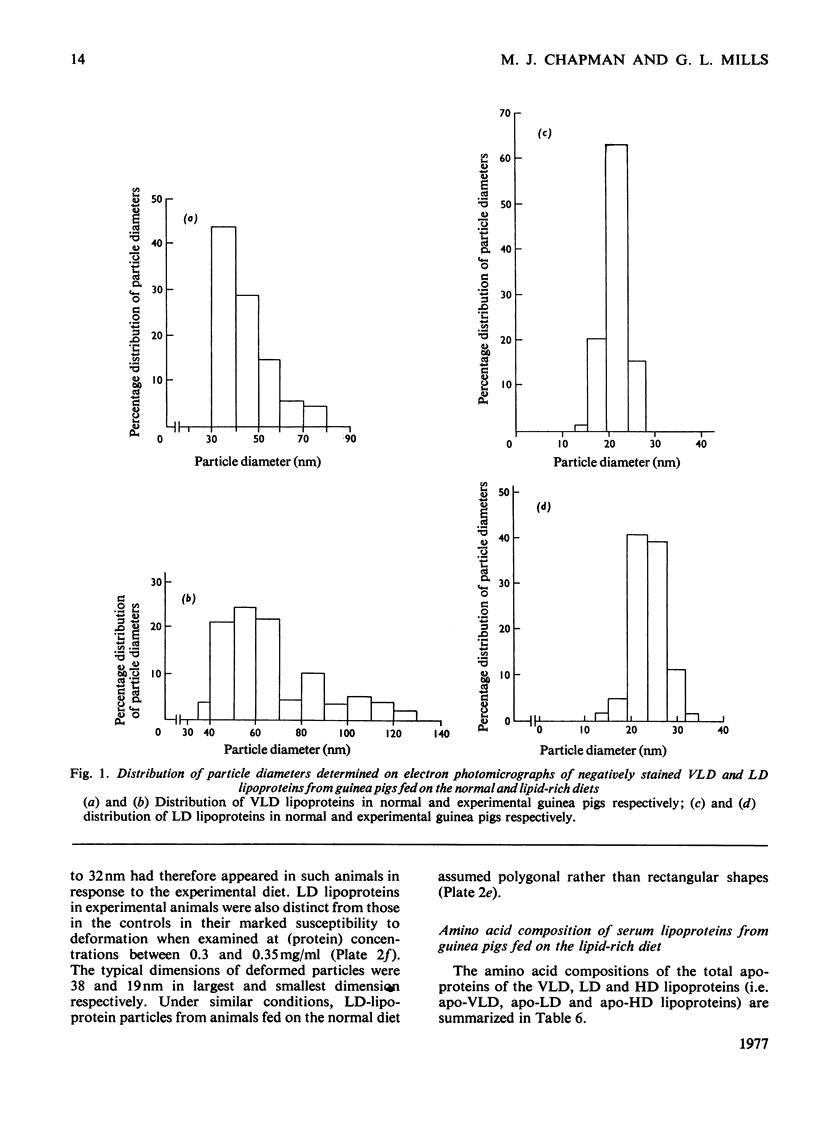


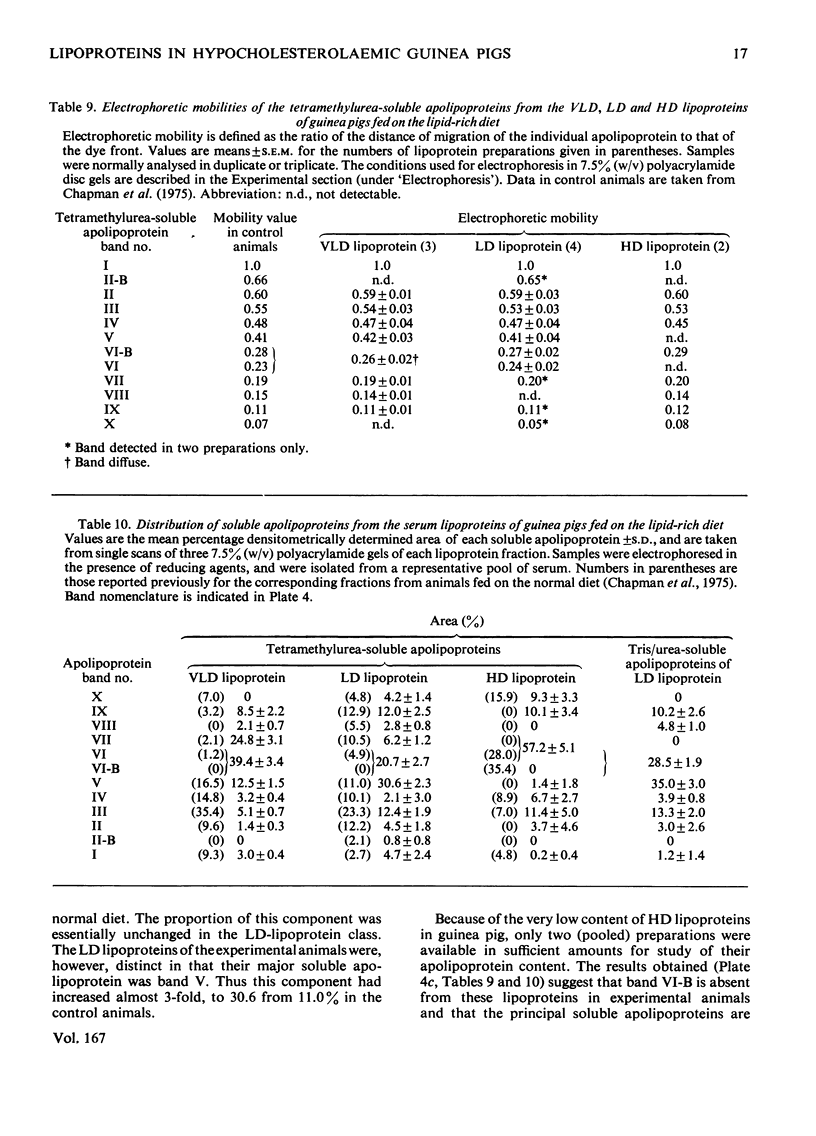



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borensztajn J., Rone M. S., Kotlar T. J. The inhibition in vivo of lipoprotein lipase (clearing-factor lipase) activity by triton WR-1339. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):539–543. doi: 10.1042/bj1560539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Studies of the proteins in human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5687–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G., Bosch V., Arreaza C., Mendez H. C. Early changes in plasma lipoprotein structure and biosynthesis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jan;14(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. J., Goldstein S. Comparison of the serum low density lipoprotein and of its apoprotein in the pig, rhesus monkey and baboon with that in man. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Nov-Dec;25(2-3):267–291. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. J., Mills G. L., Ledford J. H. The distribution and partial characterization of the serum apolipoproteins in the guinea pig. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;149(2):423–436. doi: 10.1042/bj1490423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. J., Mills G. L., Taylaur C. E. The effect of a lipid-rich diet on the properties and composition of lipoprotein particles from the Golgi apparatus of guinea-pig liver. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):177–185. doi: 10.1042/bj1310177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABAR P., WILLIAMS C. A., Jr Méthode immuno-électrophorétique d'analyse de mélanges de substances antigéniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 May;17(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P. Primary dysbetalipoproteinemia: predominance of a specific apoprotein species in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2015–2019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill E. G., Silbernick C. L. Development of hyperbetalipoproteinemia in pigs fed atherogenic diet. Lipids. 1975 Jan;10(1):41–43. doi: 10.1007/BF02532192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston L. L. Amino acid analysis of stained bands from polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. A rapid electrophoretic technique for identification of subunit species of apoproteins in serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):350–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Sata T., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Apoprotein composition of very low density lipoproteins of human serum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1622–1634. doi: 10.1172/JCI108245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasser N. L., Roheim P. S., Edelstein D., Eder H. A. Serum lipoproteins of normal and cholesterol-fed rats. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jan;14(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H. Canine lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. I. Isolation and characterization of plasma lipoproteins from control dogs. Circ Res. 1974 Nov;35(5):713–721. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.5.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T., Brewer H. B., Jr, Assmann G. Swine lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. Changes in the plasma lipoproteins and apoproteins induced by cholesterol feeding. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2817–2823. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. Canine lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. II. Characterization of the plasma lipoproteins associated with atherogenic and nonatherogenic hyperlipidemia. Circ Res. 1974 Nov;35(5):722–733. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.5.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills G. L., Chapman M. J., McTaggart F. Some effects of diet on guinea pig serum lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 23;260(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills G. L., Taylaur C. E., Chapman M. J. Low-density lipoproteins in patients homozygous for familial hyperbetalipoproteinaemia. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Sep;51(3):221–231. doi: 10.1042/cs0510221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols A. V. Functions and interrelationships of different classes of plasma lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1128–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCANU A., ORIENTE P. Triton hyperlipemia in dogs. I. In vitro effects of the detergent on serum lipoproteins and chylomcrons. J Exp Med. 1961 Apr 1;113:735–757. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.4.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOTZ M. C., SCANU A., PAGE I. H. Effect of triton on lipoprotein lipase of rat plasma. Am J Physiol. 1957 Feb;188(2):399–402. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.188.2.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Hansma H., Ostwald R. Characterization of guinea pig plasma lipoproteins: the appearance of new lipoproteins in response to dietary cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1972 Sep;13(5):624–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V. G., Shore B., Hart R. G. Changes in apolipoproteins and properties of rabbit very low density lipoproteins on induction of cholesteremia. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1579–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]