Abstract
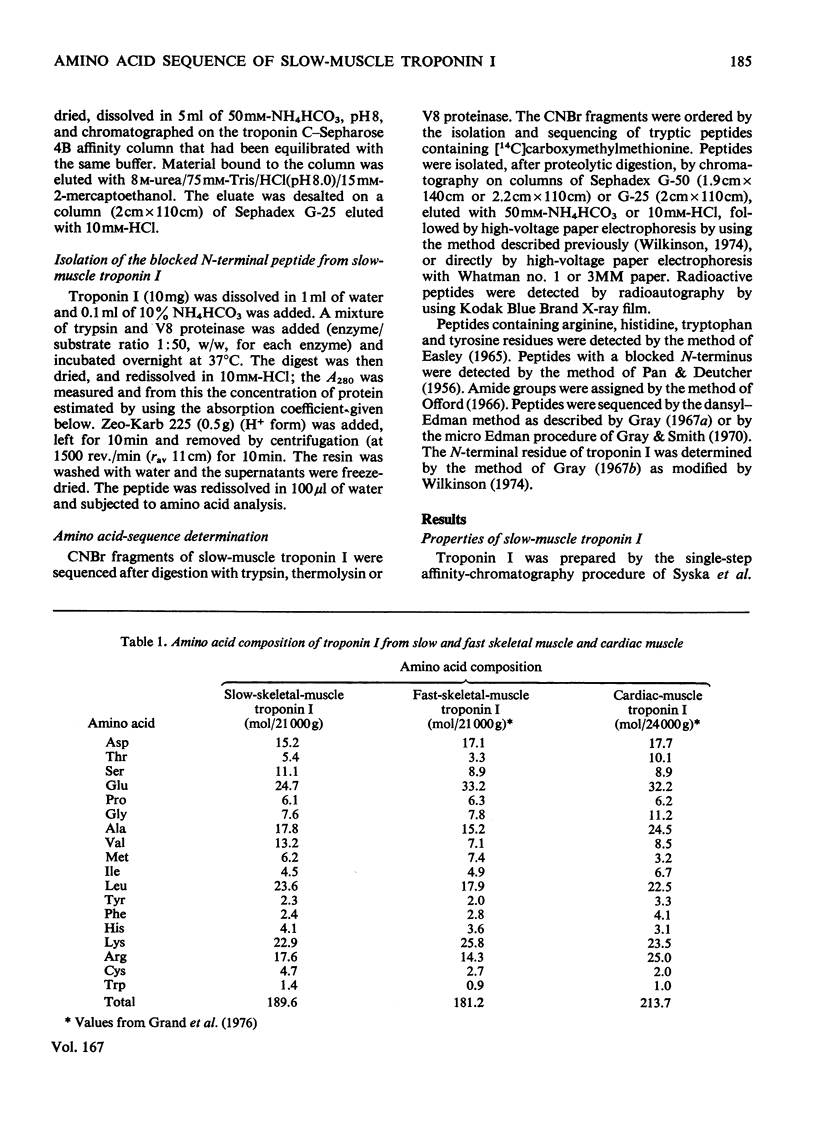
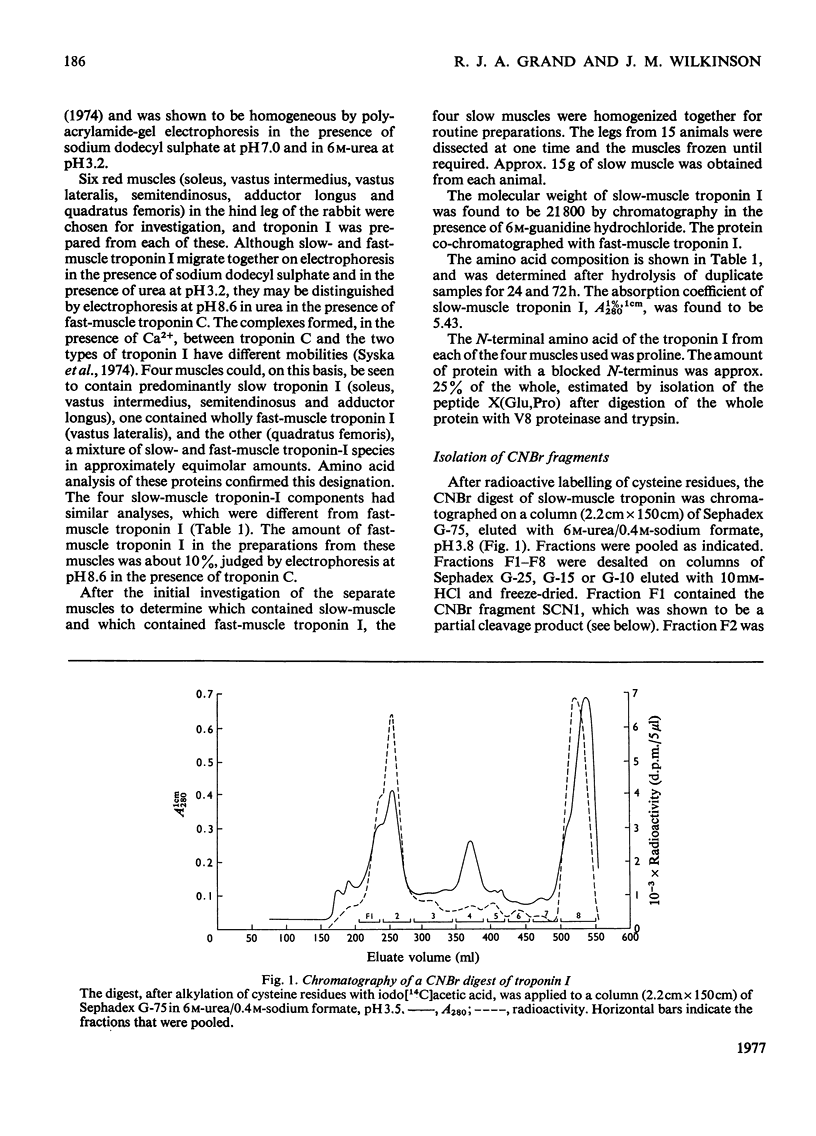
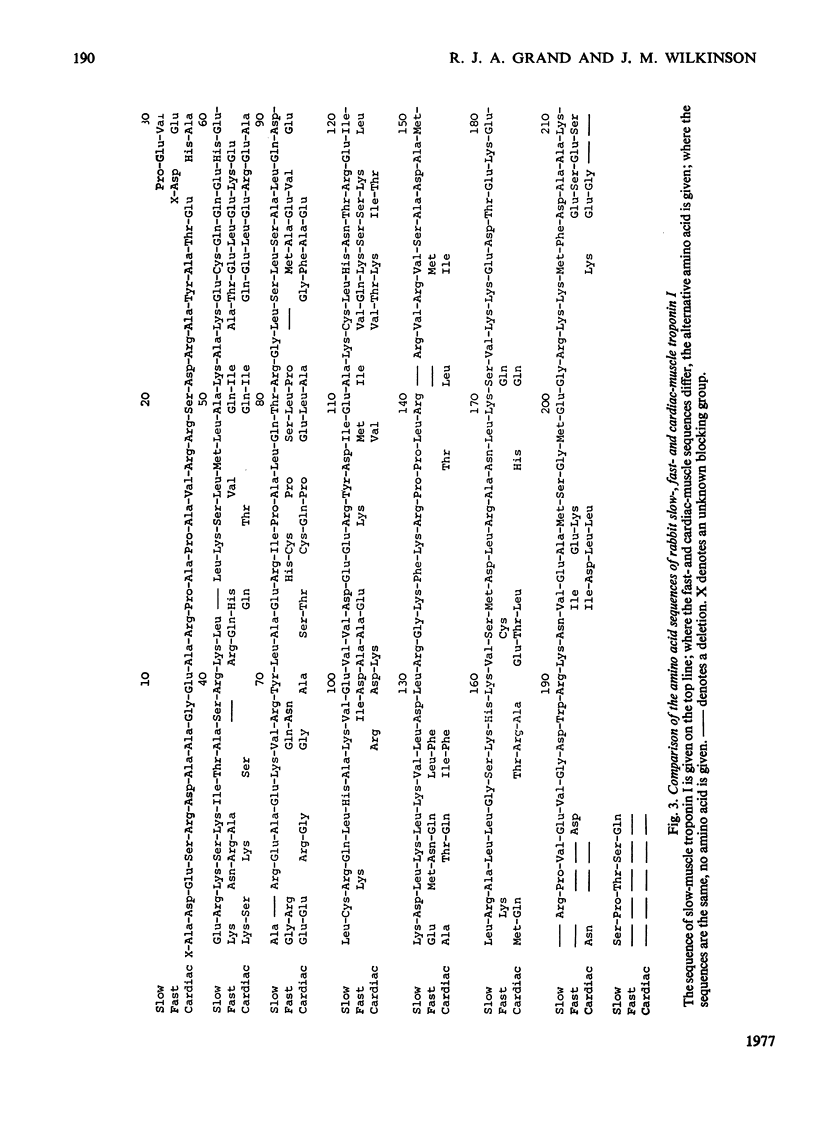
Troponin I was isolated from six red muscles in the hind leg of the rabbit. Soleus, semi-tendinosus, vastus intermedius and adductor longus muscles contained primarily slow-muscle troponin I, vastus lateralis contained fast-muscle troponin I and quadratus femoris contained a mixture of the two. The complete amino acid sequence of the troponin I from slow muscle was determined. Seven CNBr fragments were isolated and sequenced by using the dansyl–Edman technique after digestion with proteolytic enzymes. The CNBr fragments were ordered by isolation of tryptic peptides containing carboxy[14C]methyl-methionine. Direct evidence for the conjunction of residues 8 and 9 has not been obtained, and one of the carboxyl groups between residues 71 and 79 may carry an amide group. Slow-muscle troponin I is a single polypeptide chain of 184 residues with a mol.wt. of 21146. It has a net overall positive charge of 18 at pH7, and an absorption coefficient, A1%,1cm280, of 5.43. The protein was isolated with both a blocked and an unblocked N-terminus, although the nature of the blocking group was not determined. Proline was found to be the N-terminal amino acid. Two forms of the protein could also be distinguished by the presence of an extra two residues at the C-terminus. Comparison of sequences of troponin I from rabbit slow, fast and cardiac muscle shows that homology is most marked in the C-terminal half of the molecules. Towards the N-terminus the homology becomes much less marked. Detailed evidence on which the sequence is based has been deposited as Supplementary Publication SUP 50079 (32 pages) at the British Library (Lending Division), Boston Spa, Wetherby, West Yorkshire LS23 7BQ, U.K., from whom copies may be obtained in the terms given in Biochem. J. (1977), 161, 1.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amphlett G. W., Perry S. V., Syska H., Brown M. D., Vrbova G. Cross innervation and the regulatory protein system of rabbit soleus muscle. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):602–604. doi: 10.1038/257602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babul J., Stellwagen E. Measurement of protein concentration with interferences optics. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):216–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUMPTON M. J., WILKINSON J. M. AMINO ACID COMPOSITIONS OF HUMAN AND RABBIT GAMMA-GLOBULINS AND OF THE FRAGMENTS PRODUCED BY REDUCTION. Biochem J. 1963 Aug;88:228–234. doi: 10.1042/bj0880228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Potter J. D., Horn M. J., Wilshire G., Jackman N. The amino acid sequence of rabbit skeletal muscle troponin C: gene replication and homology with calcium-binding proteins from carp and hake muscle. FEBS Lett. 1973 Nov 1;36(3):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easley C. W. Combinations of specific color reactions useful in the peptide mapping technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 13;107(2):386–388. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S. Regulatory mechanism of muscle contraction with special reference to the Ca-troponin-tropomyosin system. Essays Biochem. 1974;10:1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Wilkinson J. M. The amino acid sequence of rabbit cardiac troponin I. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):633–641. doi: 10.1042/bj1590633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Smith J. F. Rapid sequence analysis of small peptides. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jan;33(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Weeks R. A., Perry S. V. Affinity-chromatographic isolation and some properties of troponin C from different muscle types. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 1;161(3):465–471. doi: 10.1042/bj1610465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Drapeau G. R. Staphylococcal protease: a proteolytic enzyme specific for glutamoyl bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3506–3509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Schaffer M. H., Stark G. R., Vanaman T. C. Specific chemical cleavage in high yield at the amino peptide bonds of cysteine and cystine residues. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6583–6591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V., Cole H. A. Phosphorylation of troponin and the effects of interactions between the components of the complex. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):733–743. doi: 10.1042/bj1410733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syska H., Perry S. V., Trayer I. P. A new method of preparation of troponin I (inhibitory protein) using affinity chromatography. Evidence for three different forms of troponin I in striated muscle. FEBS Lett. 1974 Apr 1;40(2):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syska H., Wilkinson J. M., Grand R. J., Perry S. V. The relationship between biological activity and primary structure of troponin I from white skeletal muscle of the rabbit. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):375–387. doi: 10.1042/bj1530375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Murray J. M. Molecular control mechanisms in muscle contraction. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jul;53(3):612–673. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.3.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G. Light chains from slow-twitch muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 15;66(1):157–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. A method for purifying methionine-containing peptides by radioactive labelling. FEBS Lett. 1969 Aug;4(3):170–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M., Grand R. J. The amino acid sequence of troponin I from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;149(2):493–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M., Perry S. V., Cole H. A., Trayer I. P. The regulatory proteins of the myofibril. Separation and biological activity of the components of inhibitory-factor preparations. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):215–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1270215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. The amino acid sequence of troponin C from chicken skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):254–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80769-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. The preparation and properties of the components of troponin B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 8;359(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eerd J. P., Takahshi K. Determination of the complete amino acid sequence of bovine cardiac troponin C. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):1171–1180. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


