Abstract
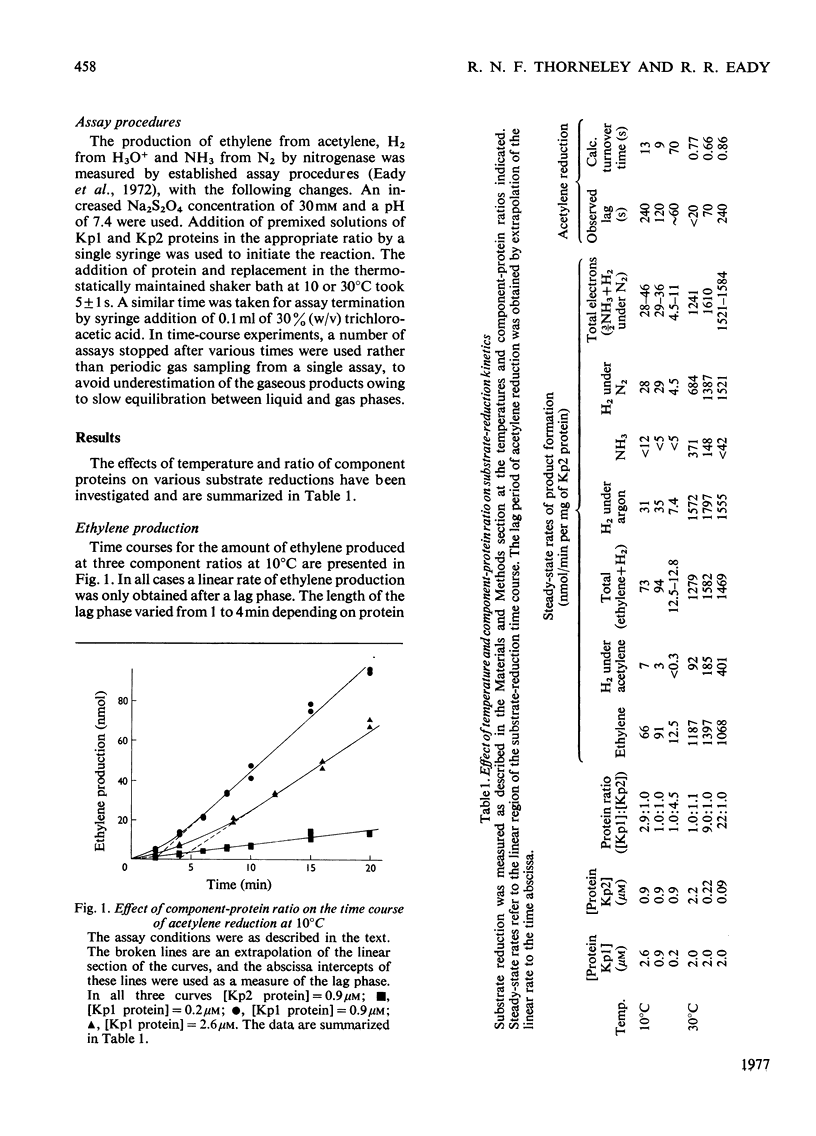
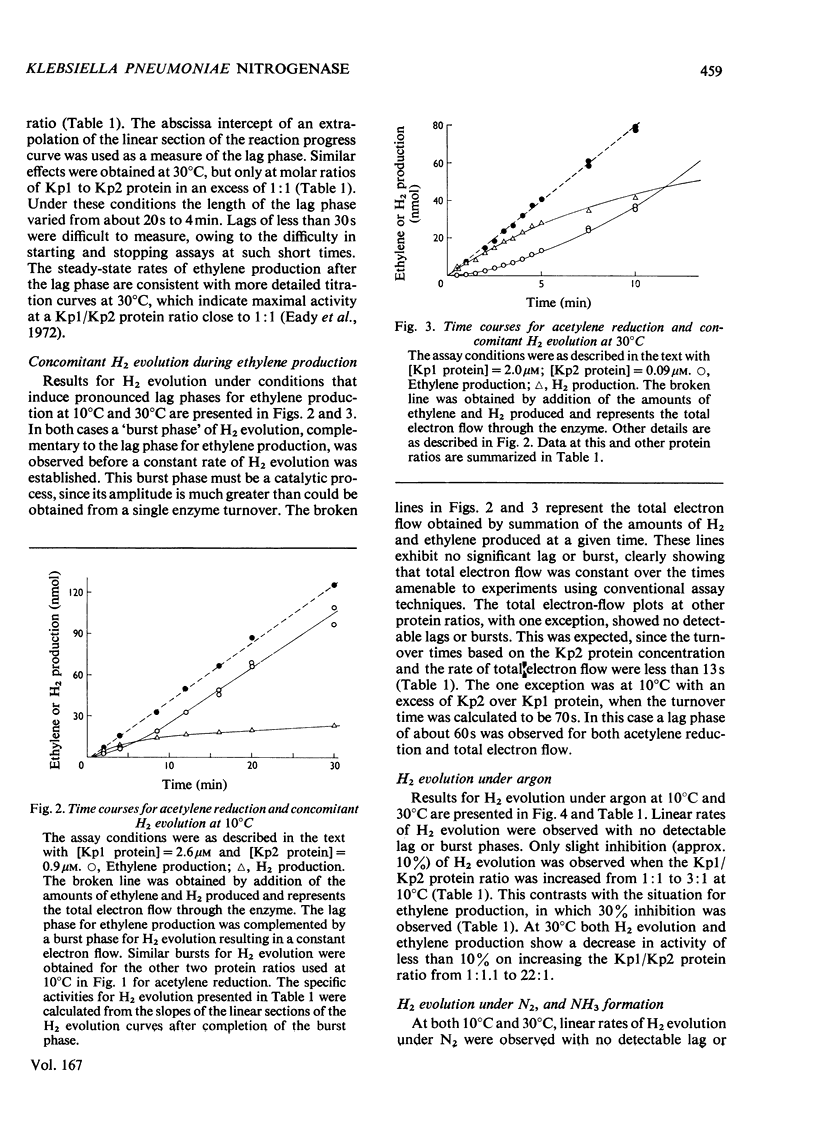
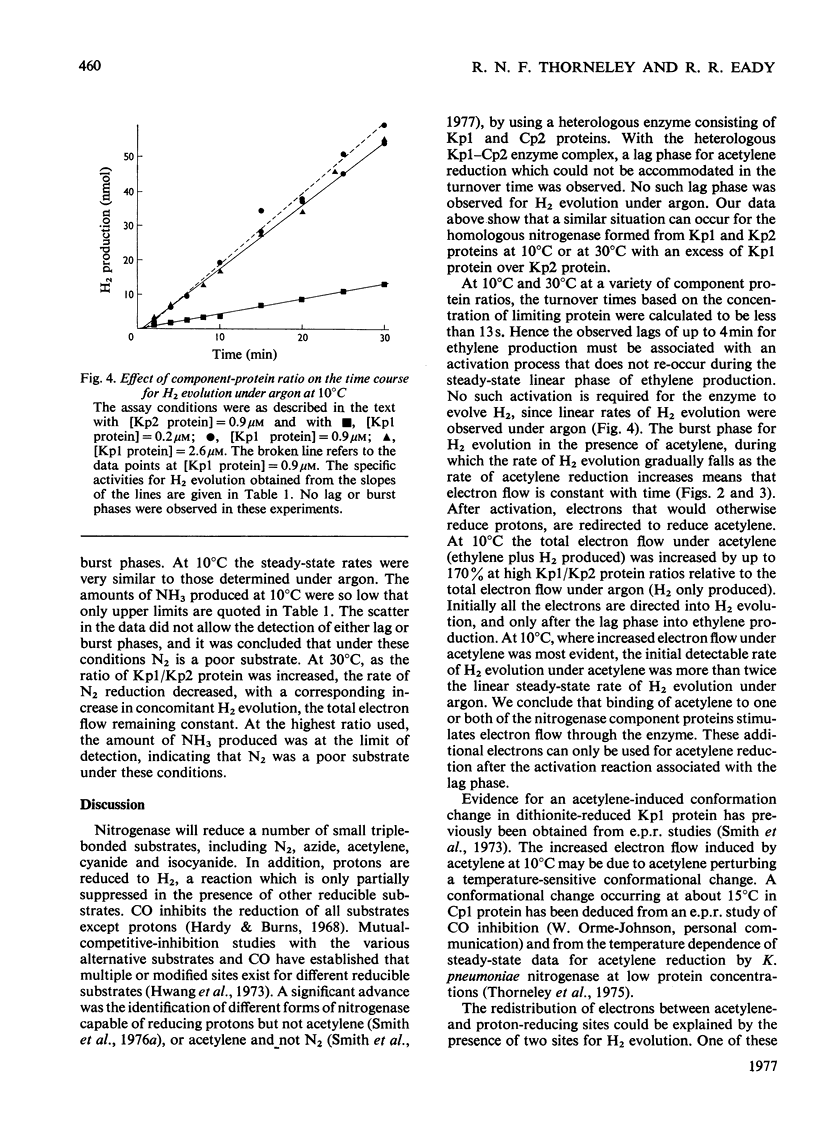
Non-linear rates of acetylene reduction and concomitant H2 evolution were observed for the nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae at 10 degrees C. A lag phase of 1-4 min, dependent on the ratio of Mo-Fe protein to Fe protein present, occurred before linear rates of acetylene reduction were achieved. A complementary burst phase for concomitant H2 evolution in the presence of acetylene was also observed. When the proton was the only reducible substrate present, linear rates of H2 evolution were observed. N2 was a poor substrate under these conditions. Similar lag and burst phases occurred at 30 degrees C, but only when a large molar excess of Mo-Fe protein with respect to Fe protein was present. The results at 10 degrees C show that the binding of acetylene to the enzyme stimulates electron flow, but that these electrons, which initially reduce protons, can only reduce acetylene after a lag phase that cannot be accommodated in the turnover time calculated under steady-state conditions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eady R. R., Smith B. E., Cook K. A., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):655–675. doi: 10.1042/bj1280655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C. Kinetic aspects of regulation of metabolic processes. The hysteretic enzyme concept. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5788–5799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J. C., Chen C. H., Burris R. H. Inhibition of nitrogenase-catalyzed reductions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):256–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljones T., Burris R. H. ATP hydrolysis and electron transfer in the nitrogenase reaction with different combinations of the iron protein and the molybdenum-iron protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 12;275(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Evans H. J. Hydrogen evolution: A major factor affecting the efficiency of nitrogen fixation in nodulated symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis L. C., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. VI. Acetylene reduction assay: Dependence of nitrogen fixation estimates on component ratio and acetylene concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 19;384(2):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Lowe D. J., Bray R. C. Studies by electron paramagnetic resonance on the catalytic mechanism of nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):331–341. doi: 10.1042/bj1350331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Thorneley R. N., Eady R. R., Mortenson L. E. Nitrogenases from Klebsiella pneumoniae and Clostridium pasteurianum. Kinetic investigations of cross-reactions as a probe of the enzyme mechanism. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):439–447. doi: 10.1042/bj1570439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Eady R. R., Yates M. G. Nitrogenases of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Azotobacter chroococum. Complex formation between the component proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 22;403(2):269–284. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Mortenson L. E. The nitrogen-fixing complex of bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 31;416(1):1–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(75)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


