Abstract
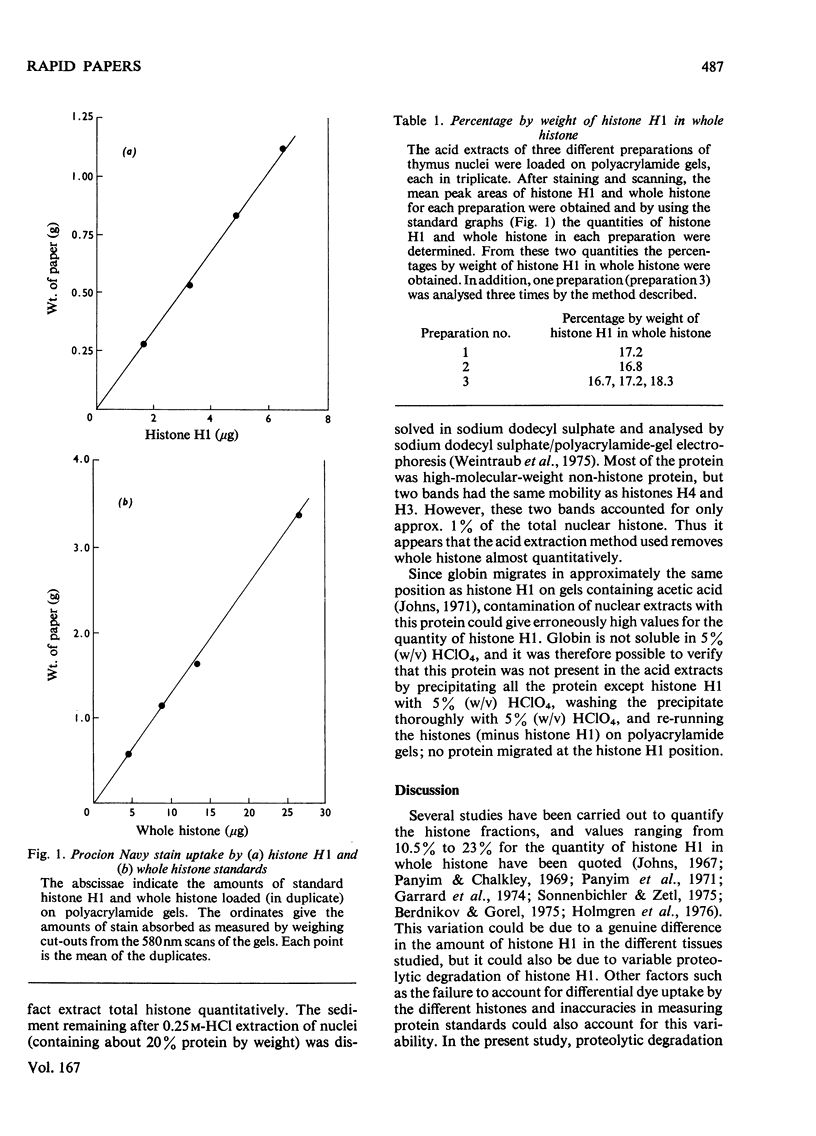
The relative quantity of histone H1 in rabbit thymus whole histone was determined to be 17.2% (w/w). This implies that there is, on average, one histone H1 molecule per nucleosome.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. P., Boseley P. G., Bradbury E. M., Ibel K. The subunit structure of the eukaryotic chromosome. Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):245–249. doi: 10.1038/253245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdinkov V. A., Gorel' F. L. Izuchenie kolichestvennykh sootnoshenii mezhdu gistonovymi fraktsiiami. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1975 Sep-Oct;9(5):699–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrard W. T., Pearson W. R., Wake S. K., Bonner J. Stoichiometry of chromatin proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):50–57. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90889-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Woodhead L., Johns E. W. The presence of high mobility group non-histone chromatin proteins in isolated nucleosomes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):85–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren P., Rasmuson B., Johansson T., Sundquist G. Histone content in relation to amount of heterochromatin and developmental stage in three species of Drosophila. Chromosoma. 1976 Feb 13;54(2):99–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00292833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard R. W., Matthew W. T., Dubowik D. A. Factors influencing the determination of DNA with indole. Anal Biochem. 1970 Nov;38(1):190–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke L. A rapid micromethod for the determination of nitrogen and phosphate in biological material. Anal Biochem. 1974 Oct;61(2):623–627. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90429-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joffe J., Keene M., Weintraub H. Histones H2a, H2b, H3, and H4 are present in equimolar amounts in chick erythroblasts. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1236–1238. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. W. The electrophoresis of histones in polyacrylamide gel and their quantitative determination. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):78–82. doi: 10.1042/bj1040078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkade J. M., Jr, Cole R. D. The resolution of four lysine-rich histones derived from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5790–5797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. I., Schjeide O. A. Micro estimation of RNA by the cupric ion catalyzed orcinol reaction. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):473–483. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N. The determination of nucleic acids. Methods Biochem Anal. 1966;14:113–176. doi: 10.1002/9780470110324.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Kornberg R. D. Action of micrococcal nuclease on chromatin and the location of histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):393–404. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Subunit structure of chromatin. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):249–251. doi: 10.1038/251249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Carlson R. D., Wright E. B., Olins D. E. Chromatin nu bodies: isolation, subfractionation and physical characterization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Dec;3(12):3271–3291. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.12.3271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Bilek D., Chalkley R. An electrophoretic comparison of vertebrate histones. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4206–4215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. The heterogeneity of histones. I. A quantitative analysis of calf histones in very long polyacrylamide gels. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):3972–3979. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenbichler J., Zetl I. The quantitative protein composition of calf thymus chromatin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 May;356(5):599–603. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.1.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Georgiev G. P. Heterogeneity of chromatin subunits in vitro and location of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):477–492. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Palter K., Van Lente F. Histones H2a, H2b, H3, and H4 form a tetrameric complex in solutions of high salt. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):85–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Simpson R. T. Removal of histone H1 exposes a fifty base pair DNA segment between nucleosomes. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3307–3314. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


