Abstract
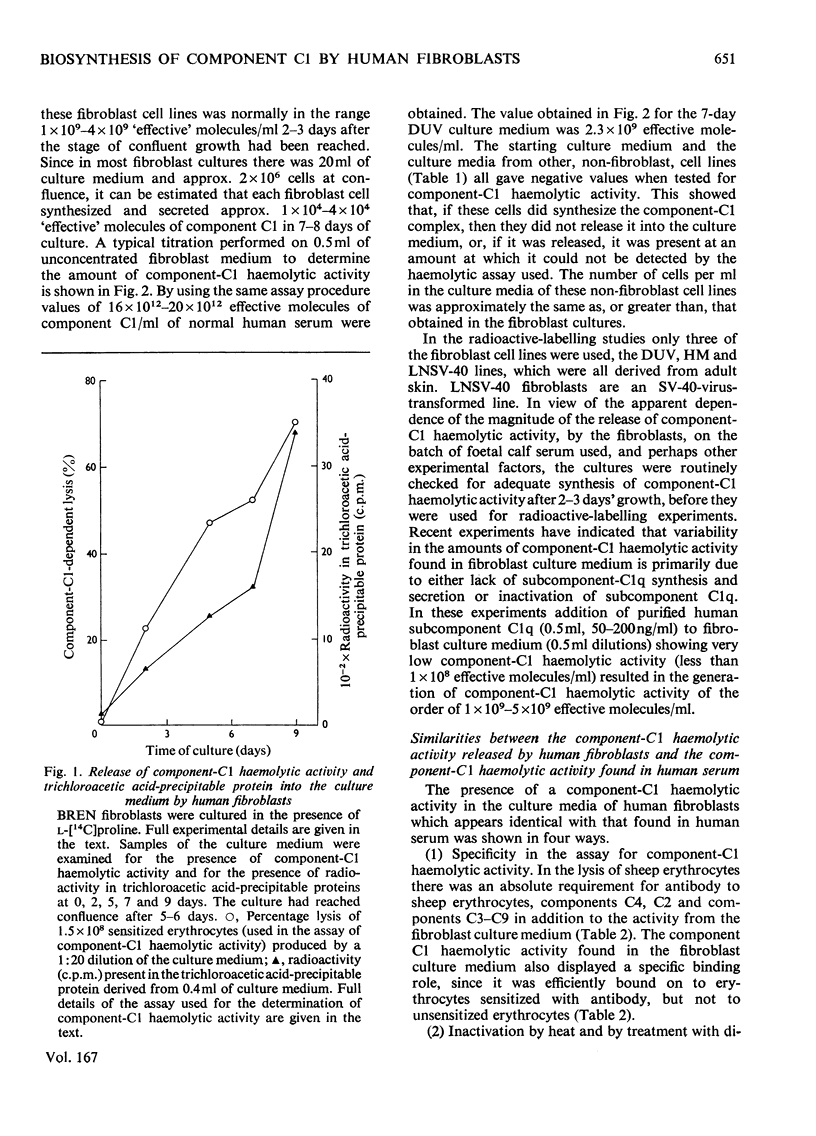
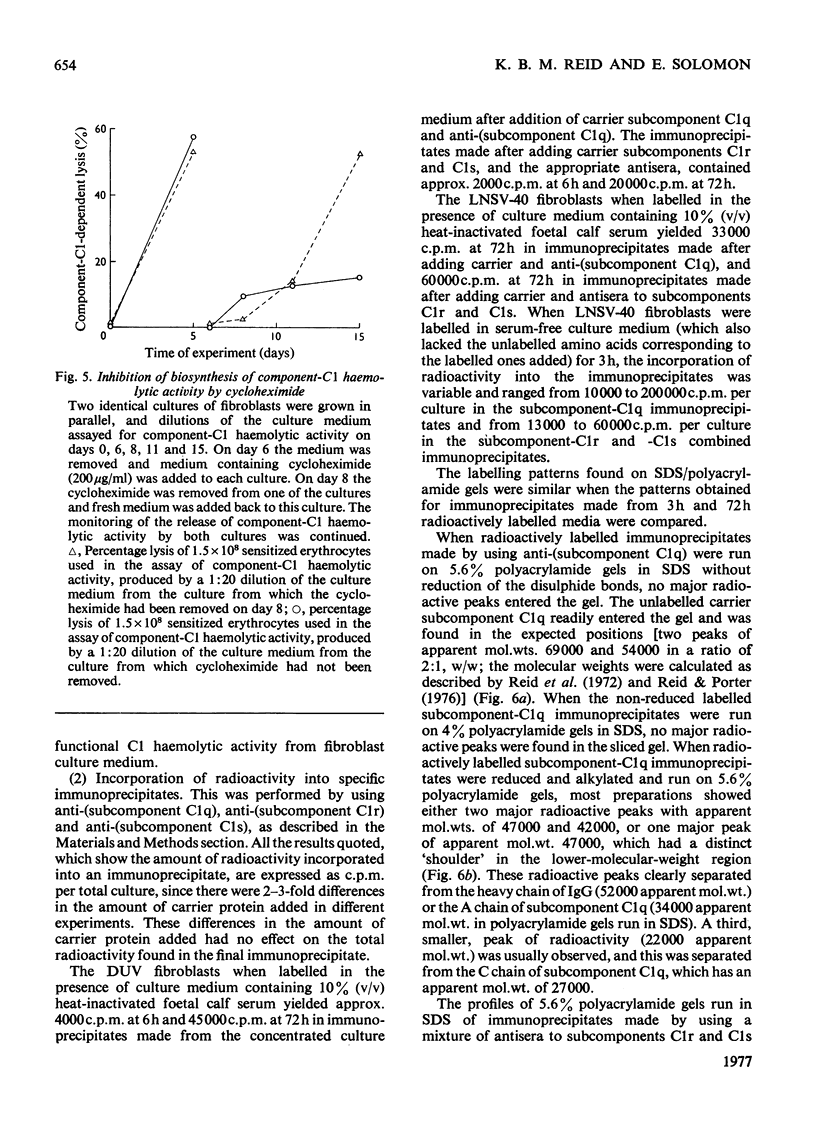
1. Haemolytic activity corresponding to that of the first component of complement (C1) was synthesized and secreted by all nine human fibroblast cell lines examined. No activity was found in the culture media of a variety of other human cell lines. 2. The component-C1 haemolytic activity secreted by the fibroblast lines behaved in an identical manner, in most respects, with that of the component-C1 haemolytic activity of human serum. The component-C1 haemolytic activity secreted by fibroblasts, however, was less susceptible to inhibition by rabbit fragment F(ab′)2 anti-(human subcomponent C1q) than was the component-C1 haemolytic activity of human serum. 3. Biosynthesis of fibroblast component-C1 haemolytic activity was inhibited by the presence of cycloheximide and regained on its removal. 4. Incorporation of radioactivity into proteins secreted by the fibroblasts and release of component-C1 haemolytic activity by the fibroblasts both increased in a linear manner until several days after the cultures had reached a state of confluent growth. 5. Radioactivity was incorporated into subcomponents C1q, C1r and C1s, as judged by the formation of specific immunoprecipitates and by absorption with immune aggregates. 6. The immunoprecipitates formed by using antisera against subcomponents C1r and C1s were run on polyacrylamide gels in sodium dodecyl sulphate, and this provided convincing physiochemical evidence for the biosynthesis of these subcomponents de novo. 7. The results obtained with immunoprecipitates formed by using anti-(subcomponent C1q) suggest that subcomponent C1q may be synthesized and secreted by fibroblast cell lines in vitro, in a form with a higher molecular weight than that of subcomponent C1q which is isolated by conventional techniques of protein fractionation from fresh serum.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Adnani M. S., McGee J. O. Clq production and secretion by fibroblasts. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):145–146. doi: 10.1038/263145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing D. H., Spurlock S. E., Bern M. M. Synthesis of the first component of complement by primary cultures of human tumors of the colon and urogenital tract and comparable normal tissue. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Sep;4(3):341–351. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky-Doyle B., Leonard K. R., Reid K. B. Circular-dichroism and electron-microscopy studies of human subcomponent C1q before and after limited proteolysis by pepsin. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):279–286. doi: 10.1042/bj1590279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Click E. M., Harper E., Bornstein P. Interchain disulfide bonds in procollagen are located in a large nontriple-helical COOH-terminal domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calcott M. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C1q protein of human complement. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 29;11(18):3443–3450. doi: 10.1021/bi00768a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R. Biosynthesis of complement. Adv Immunol. 1976;22:67–118. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60548-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R., Borsos T., Rapp H. J. In vitro synthesis of the first component of complement by guinea pig small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1158–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R., Gordon J. M., Rapp H. J., Borsos T. Synthesis of the first component of guinea pig complement by columnar epithelial cells of the small intestine. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):788–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Girardi A. J., Koprowski H. Assignment of the T-antigen gene of simian virus 40 to human chromosome C-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3617–3620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler L. I., Morris N. P., Fessler J. H. Procollagen: biological scission of amino and carboxyl extension peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4905–4909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Porter R. R., Sim R. B. The unactivated form of the first component of human complement, C1. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1570541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P., Barnstable C., Jones E., Bodmer W. F., Crumpton M. J., Snary D. Production of specific antisera to human B lymphocytes. Tissue Antigens. 1976 Feb;7(2):105–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1976.tb01039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Cooper N. R. Studies on human plasma C1 inactivator-enzyme interactions. I. Mechanisms of interaction with C1s, plasmin, and trypsin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):593–604. doi: 10.1172/JCI107967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surgace IgM specificity on cells derived from a Burkitt's lymphoma. Lancet. 1967 Nov 18;2(7525):1068–1070. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90340-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., NAFF G. B., TODD E. W., PENSKY J., HINZ C. F. Chromatographic resolution of the first component of human complement into three activities. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:983–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. W., Murphy D. G., Cristofalo V. J., Toji L. H., Greene A. E., Dwight S. A. Characterization of a new human diploid cell strain, IMR-90. Science. 1977 Apr 1;196(4285):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.841339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowack H., Olsen B. R., Timpl R. Characterization of the amino-terminal segment in type III procollagen. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 1;70(1):205–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen B. R., Hoffmann H., Prockop D. J. Interchain disulfide bonds at the COOH-terminal end of procollagen synthesized by matrix-free cells from chick embryonic tendon and cartilage. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90516-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. A collagen-like amino acid sequence in a polypeptide chain of human C1q (a subcomponent of the first component of complement). Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):189–203. doi: 10.1042/bj1410189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Complement fixation by the F(ab')2-fragment of pepsin-treated rabbit antibody. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):649–658. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Isolation, by partial pepsin digestion, of the three collagen-like regions present in subcomponent Clq of the first component of human complement. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):5–17. doi: 10.1042/bj1550005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Lowe D. M., Porter R. R. Isolation and characterization of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, from human and rabbit sera. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):749–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1300749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. Subunit composition and structure of subcomponent C1q of the first component of human complement. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):19–23. doi: 10.1042/bj1550019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Sim R. B., Faiers A. P. Inhibition of the reconstitution of the haemolytic activity of the first component of human complement by a pepsin-derived fragment of subcomponent C1q. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):239–245. doi: 10.1042/bj1610239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Porter R. R., Reid K. B., Gigli I. The structure and enzymic activities of the C1r and C1s subcomponents of C1, the first component of human serum complement. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):219–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1630219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Bobrow M., Goodfellow P. N., Bodmer W. F., Swallow D. M., Povey S., Noël B. Human gene mapping using an X/autosome translocation. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Mar;2(2):125–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01542626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stecher V. J., Morse J. H., Thorbecke G. J. Sites of production of primate serum proteins associated with complement system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):433–438. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumilowicz J. J., Nichols W. W., Cholon J. J., Greene A. E. Definition of a continuous human cell line derived from neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 1970 Aug;30(8):2110–2118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. F., Sanger C. Properties of a cell line from human adenocarcinoma of the rectum. Br J Cancer. 1977 Jun;35(6):785–794. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


