Abstract
Human liver extracts contain an activating protein which is required for hexosaminidase A-catalysed hydrolysis of the N-acetylgalactosaminyl linkage of GM2 ganglioside [N-acetylgalactosaminyl-(N-acetylneuraminyl) galactosylglucosylceramide]. A partially purified preparation of human liver hexosaminidase A that is substantially free of GM2 ganglioside hydrolase activity is used to assay the activating protein. The proceudres of heat and alcohol denaturation, ion-exchange chromatography and gel filtration were used to purify the activating protein over 100-fold from crude human liver extracts. When the purified activating protein is analysed by polyacrylamide-gel disc electrophoresis, two closely migrating protein bands are seen. When purified activating protein is used to reconstitute the GM2 ganglioside hydrolase activity, the rate of reaction is proportional to the amount of hexosaminidase A used. The activation is specific for GM2 ganglioside and and hexosaminidase A. The activating protein did not stimulate hydrolysis of asialo-GM2 ganglioside by either hexosaminidase A or B. Hexosaminidase B did not catalyse hydrolysis of GM2 ganglioside with or without the activator. Kinetic experiments suggest the presence of an enzyme–activator complex. The dissociation constant of this complex is decreased when higher concentrations of substrate are used, suggesting the formation of a ternary complex between enzyme, activator and substrate. Determination of the molecular weight of the activating protein by gel-filtration and sedimentation-velocity methods gave values of 36000 and 39000 respectively.
Full text
PDF

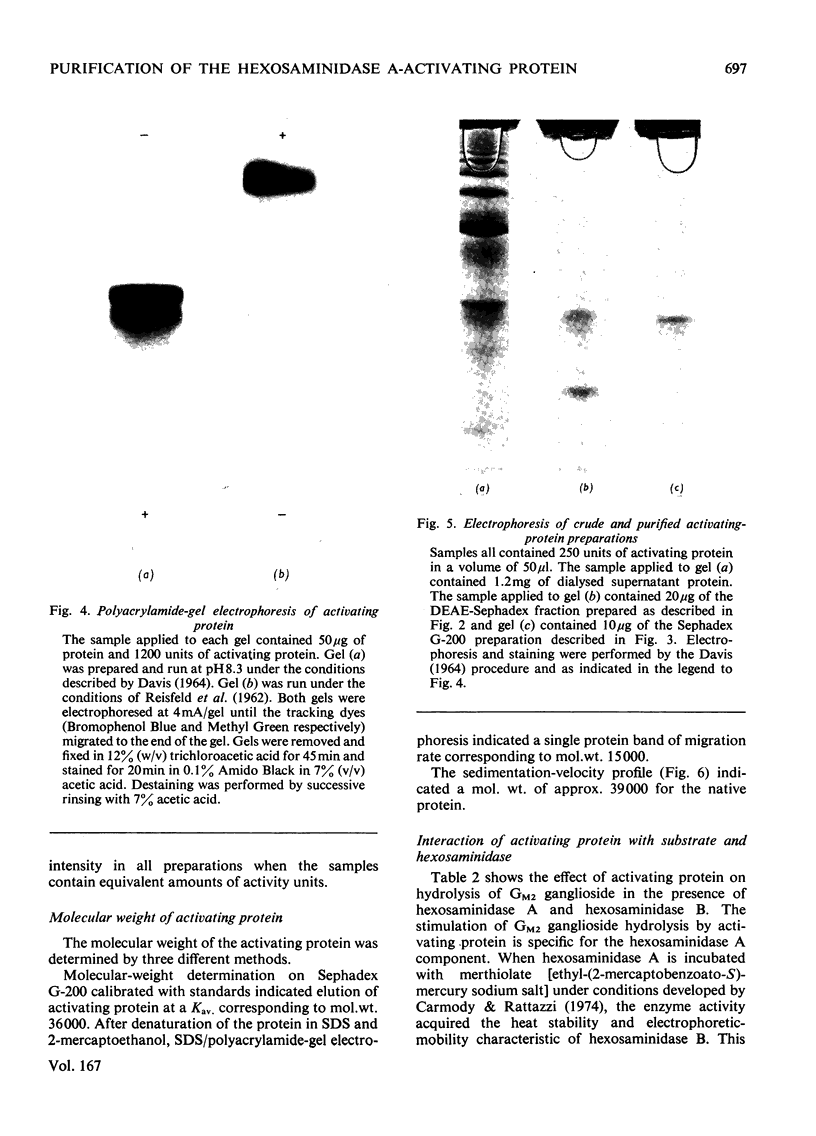
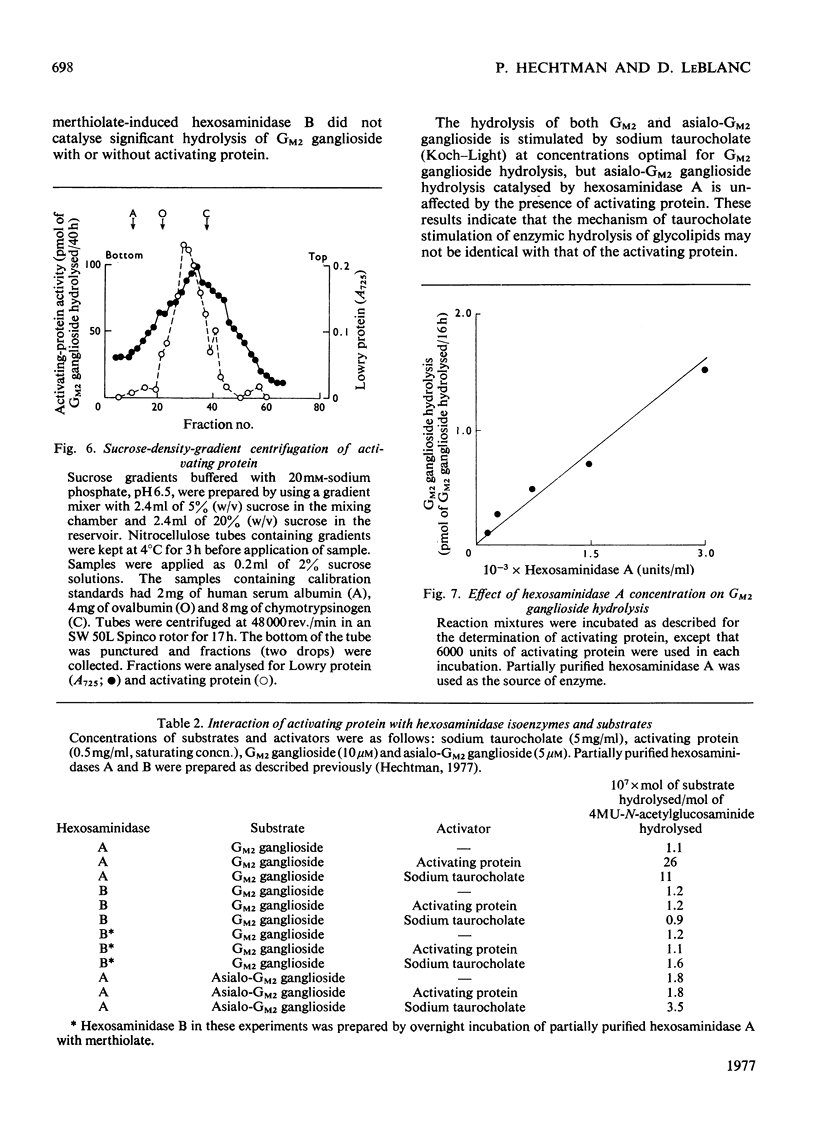



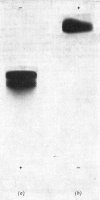
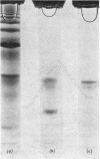
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
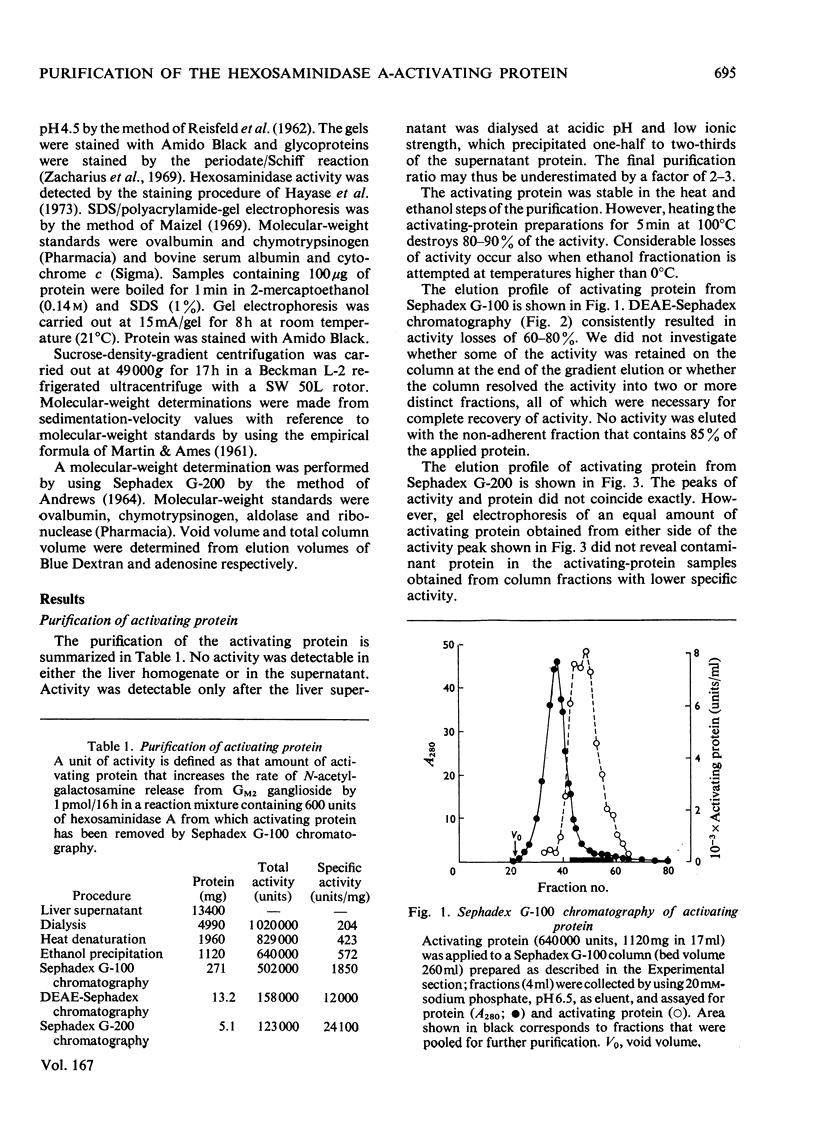
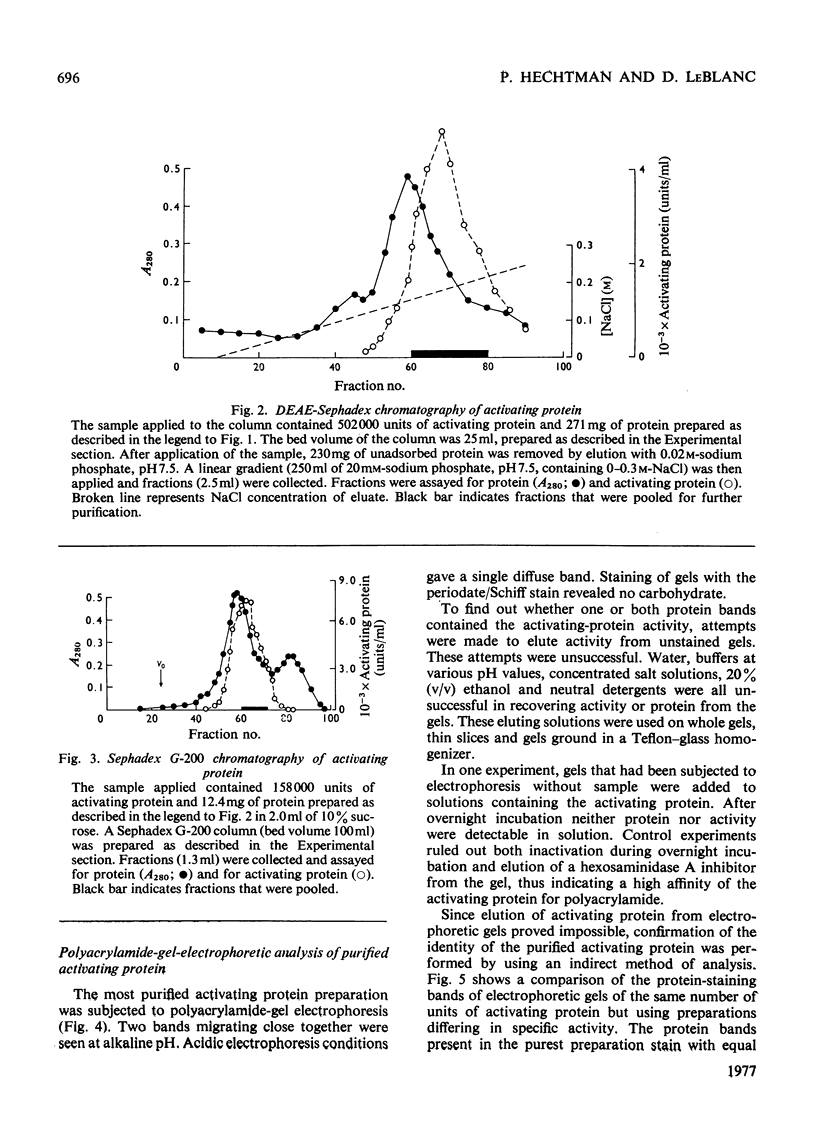
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach G., Suzuki K. Heterogeneity of human hepatic H-acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminidose. A activity toward natural glycosphingolipid substrates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1328–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmody P. J., Rattazzi M. C. Conversion of human hexosaminidase A to hexosaminidase "B" by crude Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase preparations: merthiolate is the active factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 5;371(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90160-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus J. C., Poenaru L., Svennerholm L. Absence of hexosaminidase A and B in a normal adult. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 9;292(2):61–63. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501092920201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Jatzkewitz H. The activator of cerebroside sulphatase. Purification from human liver and identification as a protein. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 May;356(5):605–613. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.1.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohwein Y. Z., Gatt S. Enzymatic hydrolysis of sphingolipids. VI. Hydrolysis of ceramide glycosides by calf brain beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2783–2787. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAMMACK D. B. PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF OX-BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. Biochem J. 1963 Aug;88:373–383. doi: 10.1042/bj0880373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M. W., Rigby M. Glucocerebrosidase: stoichiometry of association between effector and catalytic proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 27;397(1):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90199-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayase K., Reisher S. R., Kritchevsky D. Microheterogeneity of N-acetyl- -D-hexosaminidase of bull epididymis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Feb;142(2):466–470. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechtman P. Characterization of an activating factor required for hydrolysis of Gm2 ganglioside catalyzed by hexosaminidase A. Can J Biochem. 1977 Apr;55(4):315–324. doi: 10.1139/o77-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. W., O'Brien J. S. Gaucher's disease: deficiency of 'acid' -glucosidase and reconstitution of enzyme activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2810–2813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. W., O'Brien J. S., Radin N. S., Erickson J. S. Glucocerebrosidase: reconstitution of activity from macromolecular components. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;131(1):173–176. doi: 10.1042/bj1310173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEABACK D. H., WALKER P. G. Studies on glucosaminidase. 4. The fluorimetric assay of N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:151–156. doi: 10.1042/bj0780151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Li Y. T. An activator stimulating the enzymic hydrolysis of sphingoglycolipids. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1159–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Wan C. C., Mazzotta M. Y., Li Y. T. Requirement of an activator for the hydrolysis of sphingoglycolipids by glycosidases of human liver. Carbohydr Res. 1974 May;34(1):189–193. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)80383-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. T., Mazzotta M. Y., Wan C. C., Orth R., Li S. C. Hydrolysis of Tay-Sachs ganglioside by beta-hexosaminidase A of human liver and urine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7512–7515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Norden G. W., Miller A. L., Frost R. G., Kelly T. E. Ganglioside GM2 N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminidase and asialo GM2 (GA2) N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminidase; studies in human skin fibroblasts. Clin Genet. 1977 Mar;11(3):171–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb01296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada S., Veath M. L., O'Brien J. S. Juvenile GM2 gangliosidosis: partial deficiency of hexosaminidase A. J Pediatr. 1970 Dec;77(6):1063–1065. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Sep;10:613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K. The hydrolysis of Tay-Sachs ganglioside (TSG) by human N-acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminidase A. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec 18;11(5):342–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80564-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K., Wässle W. Anreicherung und Charakterisierung zweier Formen der menschlichen N-acetyl- -D-hexosaminidase. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Aug;352(8):1119–1133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallman J. F., Brady R. O. The catabolism of Tay-Sachs ganglioside in rat brain lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7570–7575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S., MacDougall B. G. Juvenile Sandhoff disease: some properties of the residual hexosaminidase in cultured fibroblasts. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Sep;28(5):489–495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Wenger, Sattler M., Clark C. Effect of bile salts on lactosylceramide beta-galactosidase activities in human brain, liver and cultured skin fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 17;409(3):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]