Abstract
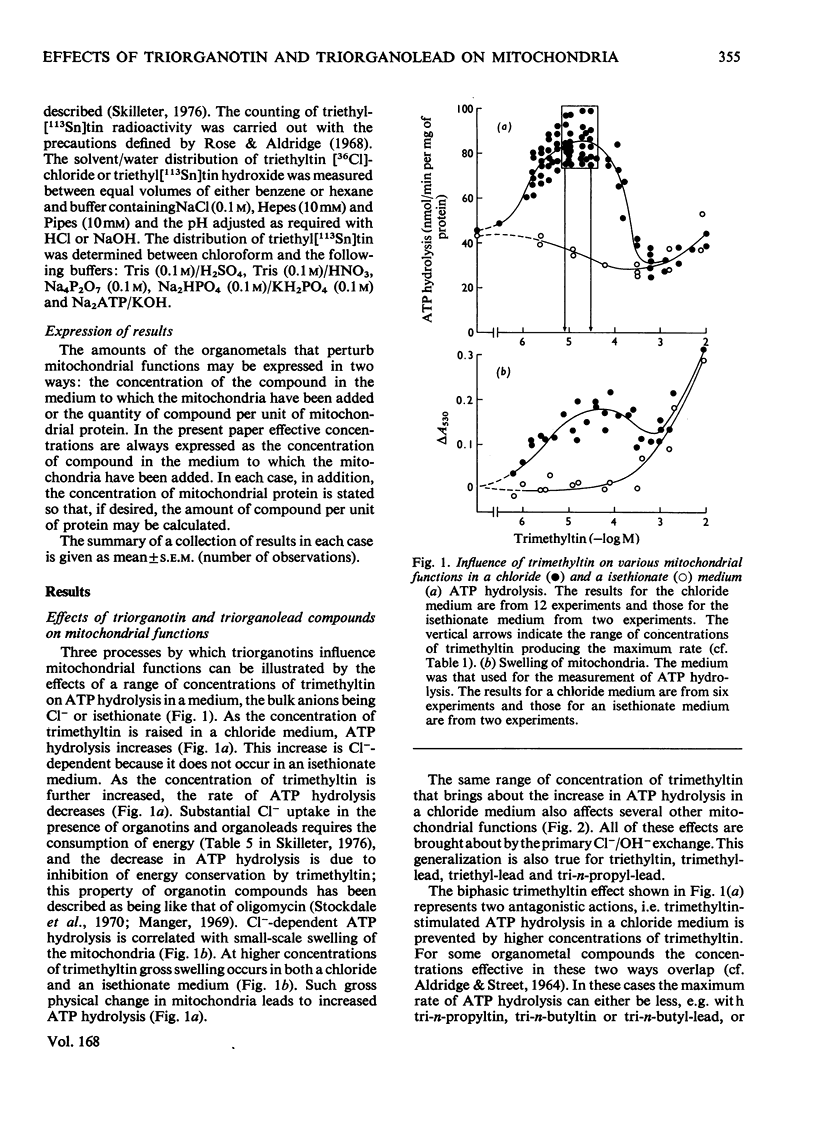
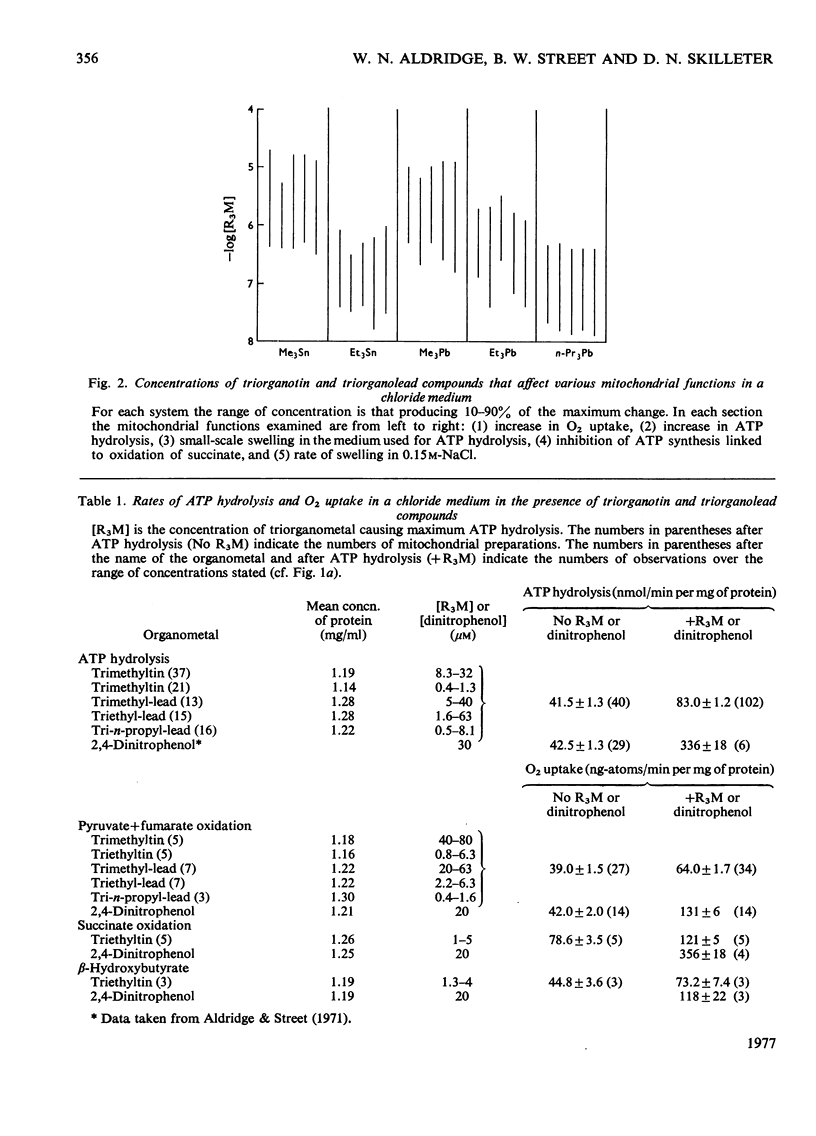
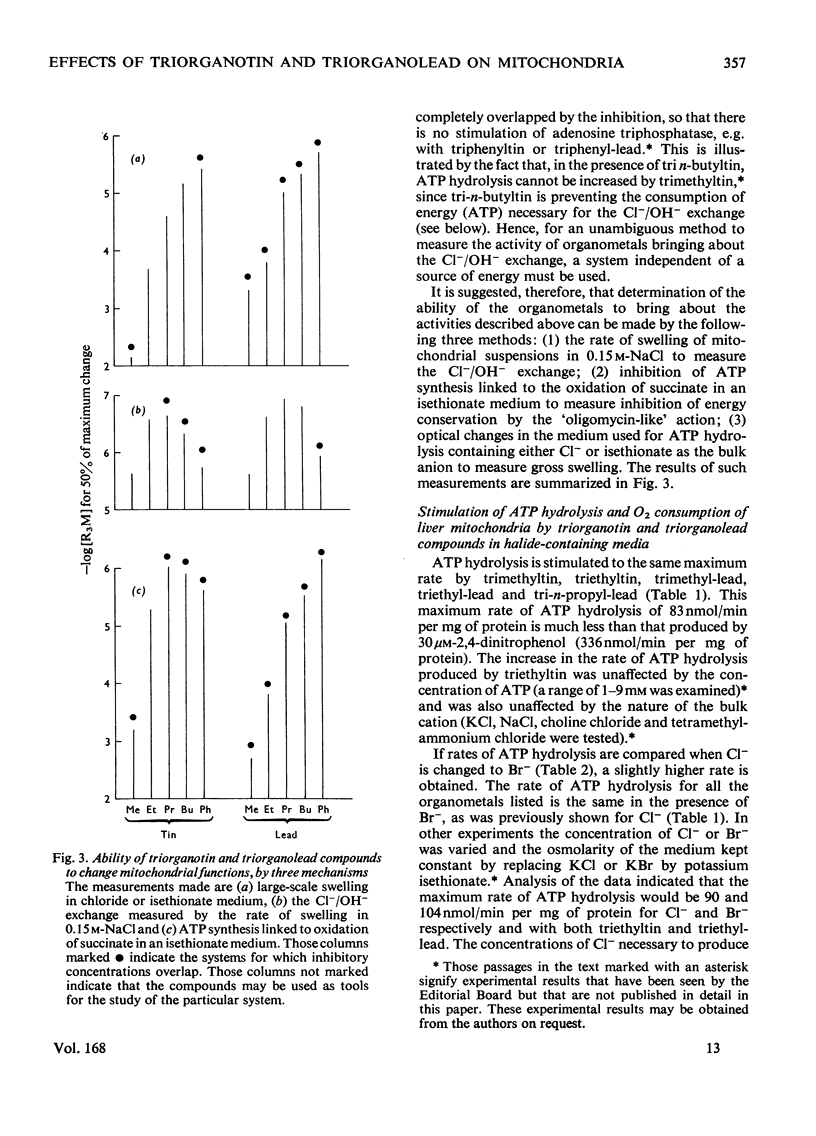
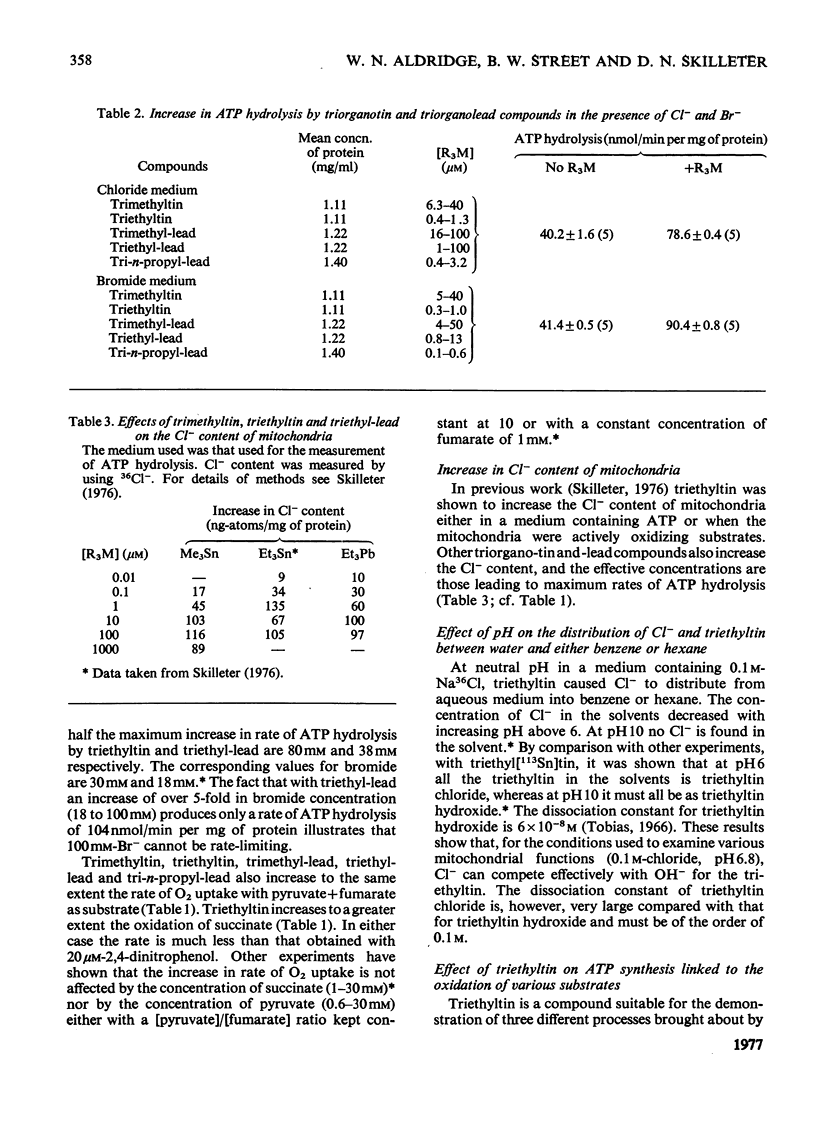
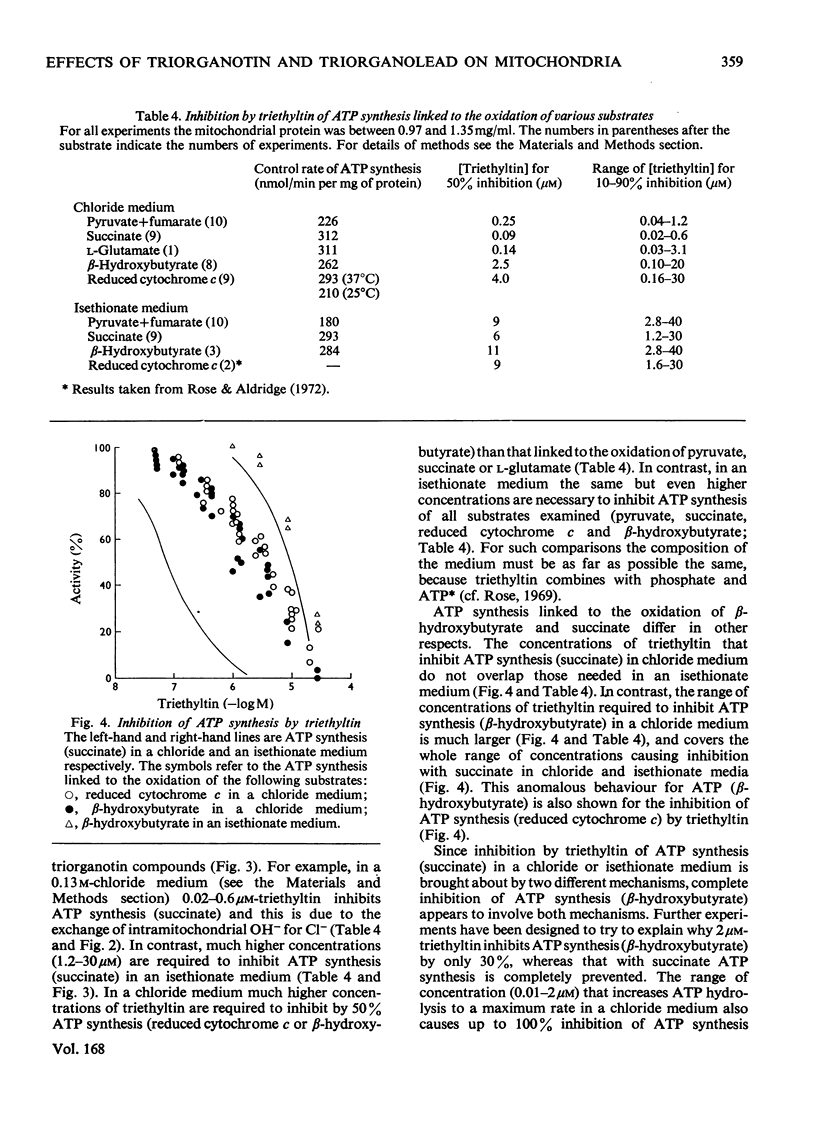
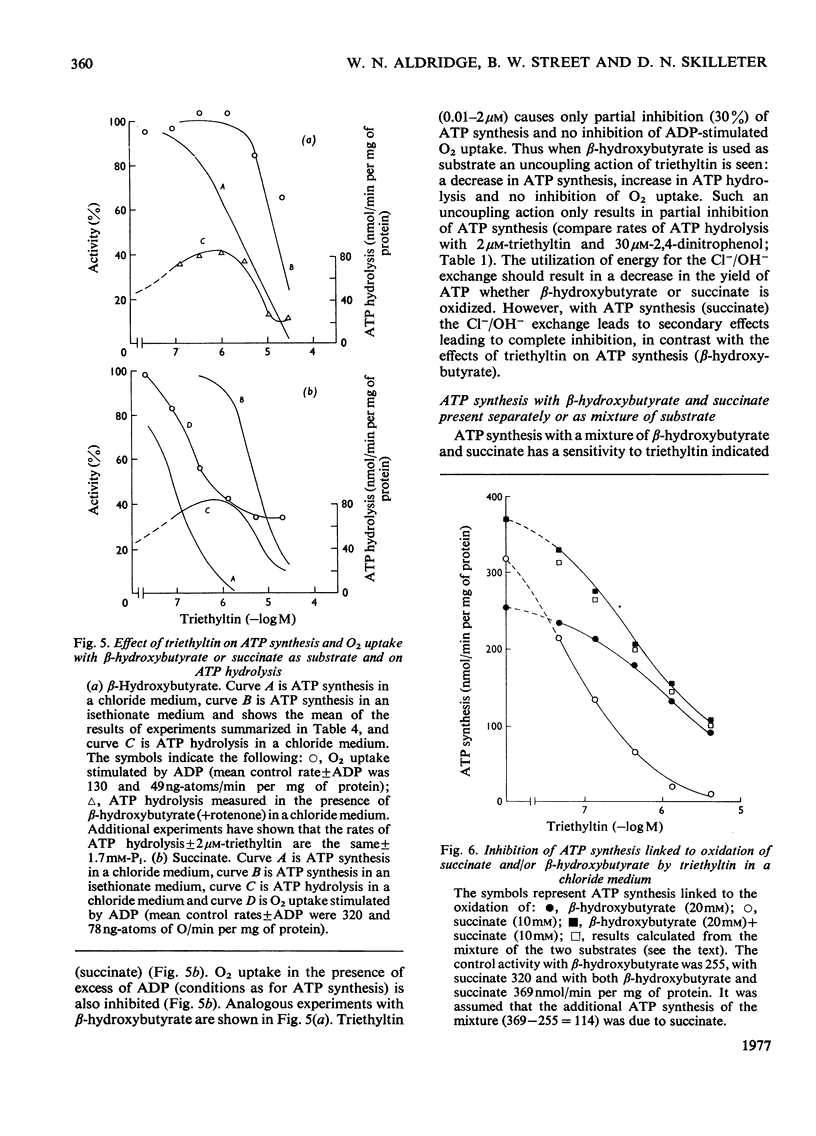
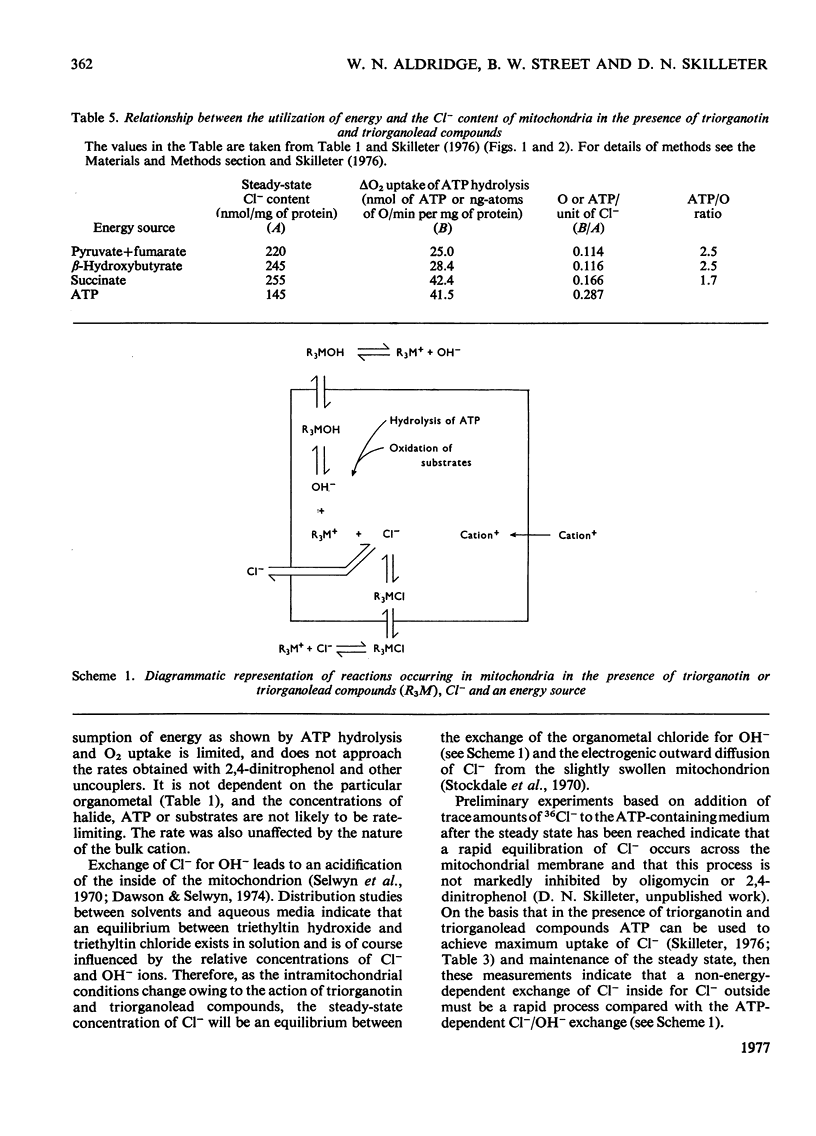
1. Each of five triorganotin and five triorganolead compounds was shown to perturb mithochondrial functions in three different ways. One is dependent and two are independent of Cl- in the medium. 2. Structure-activity relationships for the three interactions are described, and compounds suitable as tools for the separate study of each process are defined. 3. In a Cl- -containing medium trimethyltin, triethyltin, trimethyl-lead, triethyl-lead and tri-n-propyl-lead all produce the same maximum rate of ATP hydrolysis and O2 uptake; this rate is much less than that produced by uncoupling agents such as 2,4-dinitrophenol. 4. Increase in ATP hydrolysis and O2 uptake are measures on energy ultilization when triogranotin and triorganolead compounds bring about an exchange of external C1- for intramitochondrial OH- ions. Possible rate-limiting steps in this process are discussed. 5. In a C1- -containing medium ATP synthesis linked to the oxidation of beta-hydroxybutyrate or reduced cytochrone c is less inhibited by triethyltin or triethyl-lead than is ATP synthesis linked to the oxidation of succinate, pyruvate or L-glutamate. 6. The inhibition of ATP synthesis linked to the oxidation of both beta-hydroxybutyrate and reduced cytochrome c consists of two processes: one is a limited uncoupling and is C1- -dependent and the other is a C1- -independent inhibition of the energy-conservation system. 7. The different sensitivities to inhibition by triethyltin of mitochondrial functions involving the oxidation of beta-hydroxybutyrate and succinate are compared and discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N., CREMER J. E., THRELFALL C. J. Trialkylleads and oxidative phosphorylation: a study of the action of trialkylleads upon rat liver mitochondria and rat brain cortex slices. Biochem Pharmacol. 1962 Sep;11:835–846. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(62)90179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N., CREMER J. E. The biochemistry of organo-tin compounds; diethyltin dichloride and triethyltin sulphate. Biochem J. 1955 Nov;61(3):406–418. doi: 10.1042/bj0610406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N., THRELFALL C. J. Trialkyltins and oxidative phosphorylation. The [32P]phosphate-adenosine triphosphate-exchange reaction. Biochem J. 1961 May;79:214–219. doi: 10.1042/bj0790214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N. The biochemistry of organotin compounds: trialkyltins and oxidative phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):367–376. doi: 10.1042/bj0690367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Street B. W. Oxidative phosphorylation. Biochemical effects and properties of trialkyltins. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):287–297. doi: 10.1042/bj0910287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Street B. W. Oxidative phosphorylation. The relation between the specific binding of trimethylytin and triethyltin to mitochondria and their effects on various mitochondrial functions. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):221–234. doi: 10.1042/bj1240221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Street B. W. Oxidative phosphorylation. The specific binding of trimethyltin and triethyltin to rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):171–179. doi: 10.1042/bj1180171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMER J. E. The metabolism in vitro of tissue slices from rats given triethyltin compounds. Biochem J. 1957 Sep;67(1):87–96. doi: 10.1042/bj0670087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. O., Palmer J. M. The influence of pH on the inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation and electron transport by triethyltin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 7;245(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. P., Selwyn M. J. The action of trialkyltin compounds on mitochondrial respiration. The effect of pH. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;138(3):349–357. doi: 10.1042/bj1380349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-O S., Graven S. N., Lardy H. A. Potassium Ion-dependent hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate induced by nigericin in mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2925–2932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. J., Bangham J. A., Zukovic B. Equilibration of chloride and pyruvate distributions between liver mitochondria and medium mediated by organo-tin salts. FEBS Lett. 1973 Feb 1;29(3):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. J., Manger J. R. Intersubstrate competitions and evidence for compartmentation in mitochondria. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(4):617–628. doi: 10.1042/bj1130617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. J., Manger J. R. Intramitochondrial substrate concentration as a factor controlling metabolism. The role of interanion competition. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(2):239–246. doi: 10.1042/bj1090239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. J., van Dam K., Pressman B. C. Dependence of uptake of succinate by mitochondria on energy and its relation to potassium retention. Nature. 1967 Mar 18;213(5081):1126–1127. doi: 10.1038/2131126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEHNINGER A. L., SUDDUTH H. C., WISE J. B. D-beta-Hydroxybutyric dehydrogenase of muitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2450–2455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock E. A. The action of triethyltin on the respiration of rat brain cortex slices. J Neurochem. 1976 May;26(5):887–892. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb06469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE K. E., BRODY T. M. The effect of triethyltin on oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase activation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 May;6:125–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORET V., PINNA L. A., SPERTI S., LORINI M., SILIPRANDI N. ON THE MECHANISM OF MITOCHONDRIAL PHOSPHORYLATION OF PHOSVITIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 16;82:603–605. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90451-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger J. R. The effect of triethyltin on mitochondrial ion accumulation. FEBS Lett. 1969 Dec 30;5(5):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80349-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Stoichiometry of proton translocation through the respiratory chain and adenosine triphosphatase systems of rat liver mitochondria. Nature. 1965 Oct 9;208(5006):147–151. doi: 10.1038/208147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Translocation of some anions cations and acids in rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):149–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker V. H. Uncouplers of rat-liver mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1965 Dec;97(3):658–662. doi: 10.1042/bj0970658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. S., Aldridge W. N. Oxidative phosphorylation. The effect of anions on the inhibition by triethyltin of various mitochondrial functions, and the relationship between this inhibition and binding of triethyltin. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):51–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1270051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. S., Aldridge W. N. The interaction of triethyltin with components of animal tissues. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):821–828. doi: 10.1042/bj1060821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. S. Evidence for histidine in the triethyltin-binding site of rat haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(2):129–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1110129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SONE N., HAGIHARA B. INHIBITORY ACTION OF TRIALKYLTIN COMPOUNDS ON OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN MITOCHONDRIA. J Biochem. 1964 Aug;56:151–156. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn M. J., Dawson A. P., Stockdale M., Gains N. Chloride-hydroxide exchange across mitochondrial, erythrocyte and artificial lipid membranes mediated by trialkyl- and triphenyltin compounds. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):120–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilleter D. N. The decrease of mitochondrial substrate uptake caused by trialkyltin and trialkyl-lead compounds in chloride media and its relevance to inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):465–471. doi: 10.1042/bj1460465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilleter D. N. The influence of adenine nucleotides and oxidizable substrates on triethyltin-mediated chloride uptake by rat liver mitochondria in potassium chloride media. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 15;154(2):271–276. doi: 10.1042/bj1540271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottocasa G. L., Kuylenstierna B., Ernster L., Bergstrand A. An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):415–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockdale M., Dawson A. P., Selwyn M. J. Effects of trialkyltin and triphenyltin compounds on mitochondrial respiration. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Aug;15(2):342–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADKINS C. L., LEHNINGER A. L. The oxidation state of the respiratory carriers and the partial reactions of oxidation phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):681–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Neupert W. Functional and biogenetical heterogeneity of the inner membrane of rat-liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb 15;25(2):379–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulf R. G., Byington K. H. On the structure-activity relationships and mechanism of organotin induced, nonenergy dependent swelling of liver mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Mar;167(1):176–185. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


