Abstract
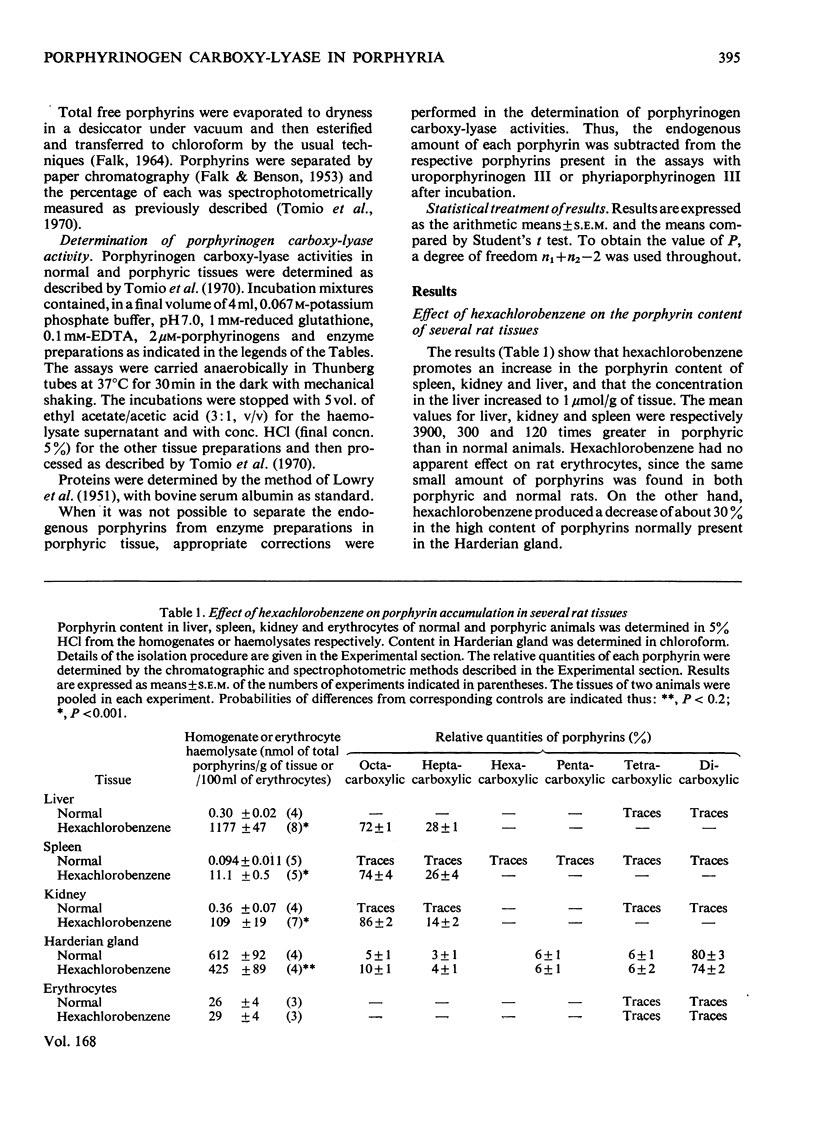
1. Qualitative and quantitative studies of the porphyrins and the porphyrinogen carboxylyase of the liver, spleen, kidney, harderian gland and erythrocytes from normal rats and from those hexachlorobenzene-induced porphyria were carried out. 2. Hexachlorobenzene has no effect on erythrocyte porphyrin content, but produces a decrease in that of Harderian gland and an increase in the porphyrin content of the kidney and spleen, and a marked increase in the liver (1 mumol/g of tissue). Octacarboxylic (isomer III) and heptacarboxylic porphyrins accumulated in kidney, spleen and liver, the former porphyrin being predominant. 3. Hexachlorobenzene has no effect on the activity of porphyrinogen carboxy-lase in erythrocytes; there is a slight decrease in enzyme activity in the Harderian gland, and a marked decrease in the liver and kidney enzyme activities. In the liver the removal of each carboxyl group from uroporphyrinogen III appears to be affected by this treatment. 4. The liver is the principal site of action of hexachlorobenzene, with the kidney next in decreasing order of effect, and erythropoietic tissue is unaffected. The marked decrease in porphyrinogen carboxy-lyase activities observed in liver and kidney could explain the high accumulation of octacarboxylic and heptacarboxylic porphyrins found in these tissues. 5. The results are discussed in relation to changes promoted by hexachlorobenzene in other enzymes of the haem pathway.
Full text
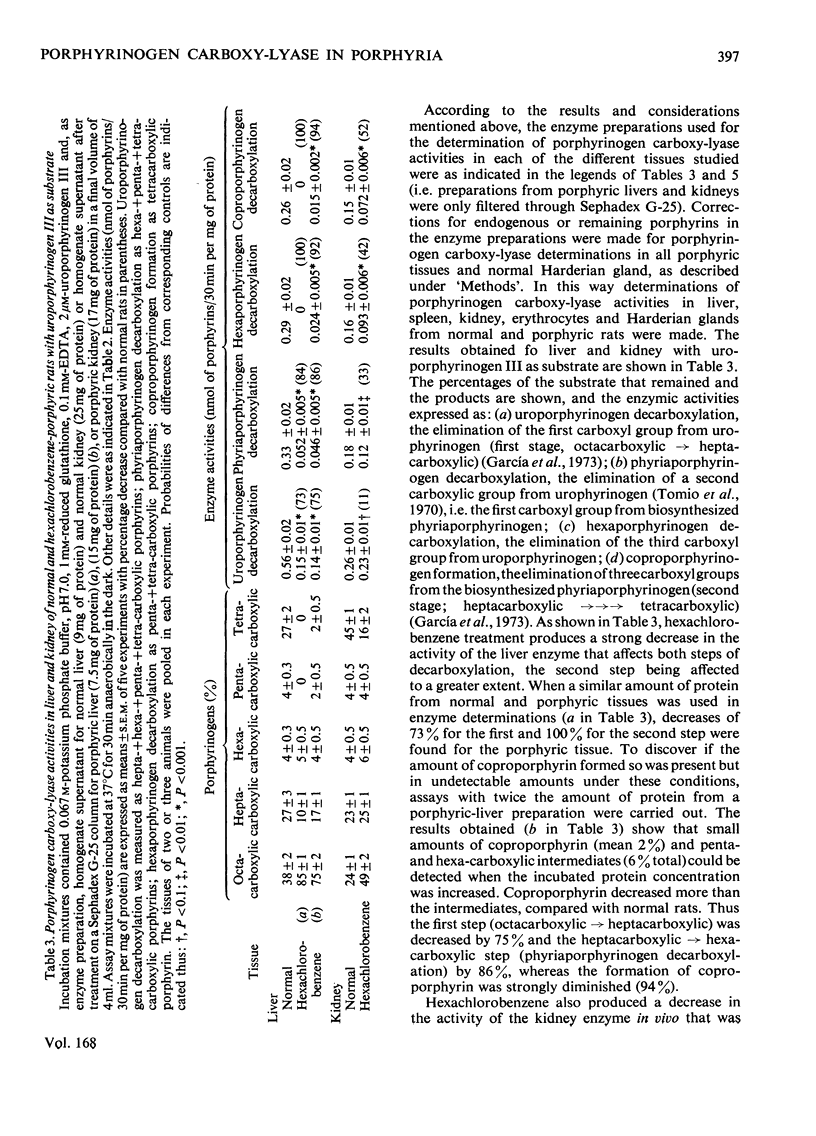
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CETINGIL A. I., OZEN M. A. Toxic porphyria. Blood. 1960 Jul;16:1002–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE MATTEIS F., PRIOR B. E., RIMINGTON C. Nervous and biochemical disturbances following hexachlorobenzene intoxication. Nature. 1961 Jul 22;191:363–366. doi: 10.1038/191363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdle E., Goldswain P., Spong N., Eales L. The pattern of porphyrin isomer accumulation and excretion in symptomatic porphyria. Clin Sci. 1970 Aug;39(2):147–158. doi: 10.1042/cs0390147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK J. E., BENSON A. Separation of uroporphyrin esters I and III by paper chromatography. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):101–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAJDOS A., GAJDOS-TOROK M. [Experimental prophyria observed in the white rat following intoxication with hexachlorobenzene]. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1961 Jun-Jul;6:549–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R. C., San Martin de Viale L. C., Tomio J. M., Grinstein M. Porphyrin biosynthesis. X. Porphyrinogen carboxy-lyase from avian erythrocytes: further properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 5;309(1):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOARE D. S., HEATH H. The biosynthesis of porphyrins from porphobilinogen by Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem J. 1959 Dec;73:679–690. doi: 10.1042/bj0730679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUZERALL D., GRANICK S. Porphyrin biosynthesis in erythrocytes. III. Uroporphyrinogen and its decarboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):1141–1162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez C. A., Mills G. C. Spectrophotofluorometric determination of porphyrins in urine. Clin Chem. 1971 Mar;17(3):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacht S., San Martín de Viale L. C., Grinstein M. Human porphyria cutanea tarda. Isolation and properties of the urinary porphyrins. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Mar;27(3):445–452. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90297-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCKNER R. K., SCHMID R. Acquired porphyria in man and rat due to hexachlorobenzene intoxication. Nature. 1961 Feb 11;189:499–499. doi: 10.1038/189499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIMINGTON C., SVEINSSON S. L. The spectrophotometric determination of uroporphyrin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1950;2(3):209–216. doi: 10.3109/00365515009049872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo G., Levin E. Y. Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase from mouse spleen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 23;230(2):330–341. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID R. Cutaneous porphyria in Turkey. N Engl J Med. 1960 Aug 25;263:397–398. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196008252630807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Martin de Viale L. C., Viale A. A., Nacht S., Grinstein M. Experimental porphyria induced in rats by hexachlorobenzene. A study of the porphyrins excreted by urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Apr;28(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90155-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Martín de Viale L. C., Grinstein M. Porphyrin biosynthesis. IV. 5- and 6-COOH porphyrinogens (type III) as normal intermediates in haem biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 16;158(1):79–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strik J. J. Chemical porphyria in Japanese quail (Coturnix c. Japonica). Enzyme. 1973;16(1):211–223. doi: 10.1159/000459383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strik J. J. Species differences in experimental porphyria caused by polyhalogenated aromatic compounds. Enzyme. 1973;16(1):224–230. doi: 10.1159/000459384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taljaard J. J., Shanley B. C., Deppe W. M., Joubert S. M. Porphyrin metabolism in experimental hepatic siderosis in the rat. 3. Effect of iron overload and hexachlorobenzene on liver haem biosynthesis. Br J Haematol. 1972 Nov;23(5):587–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomio J. M., García R. C., San Martín de Viale L. C., Grinstein M. Porphyrin biosynthesis. VII. Porphyrinogen carboxy-lyase from avian erythrocytes. Purification and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 11;198(2):353–363. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomio J. M., Grinstein M. Porphyrin biosynthesis. 5. Biosynthesis of protoporphyrin IX in Harderian glands. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Oct 17;6(1):80–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J. G., van der Maas H. L., Musch A., Ram E. Toxicity of hexachlorobenzene in Japanese quail with special reference to porphyria, liver damage, reproduction, and tissue residues. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1971 Apr;18(4):944–957. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(71)90240-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Viale L. C.S.M., García R. C., De Pisarev D. K., Tomio J. M., Grinstein M. Studies on uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase from chicken erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1969 Oct 21;5(2):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80317-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


