Abstract
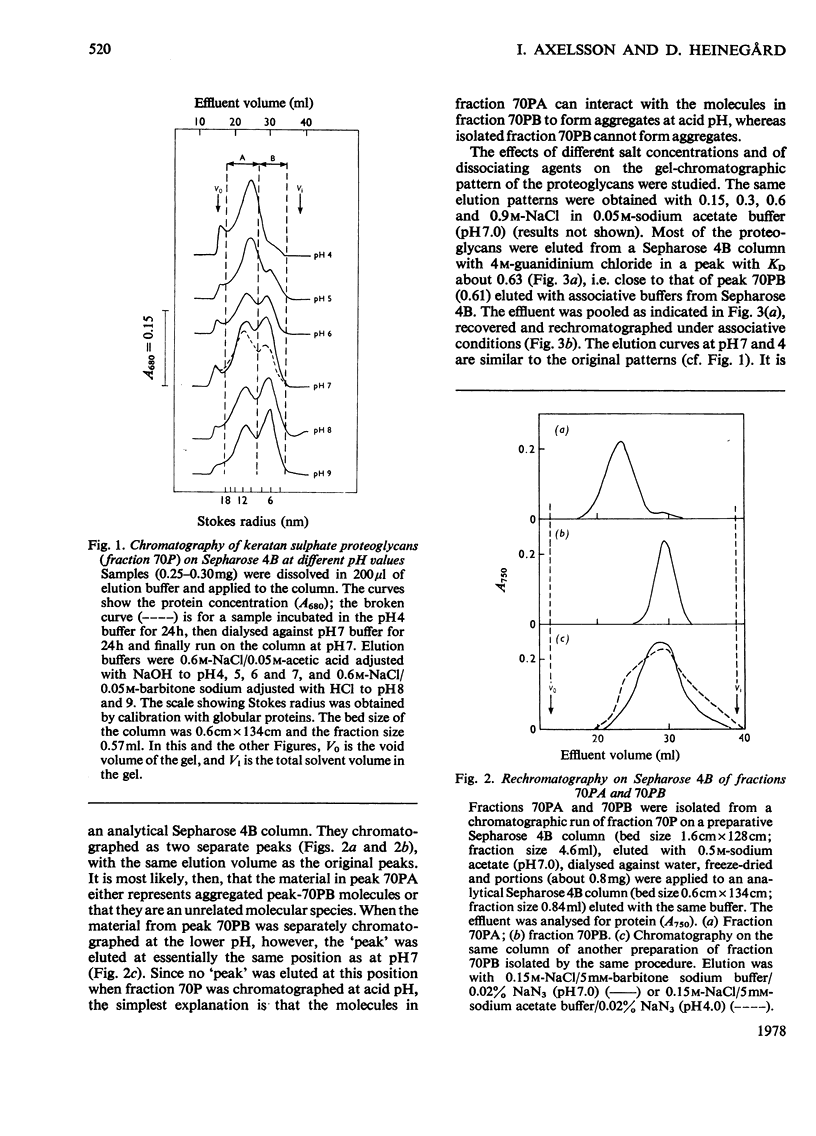
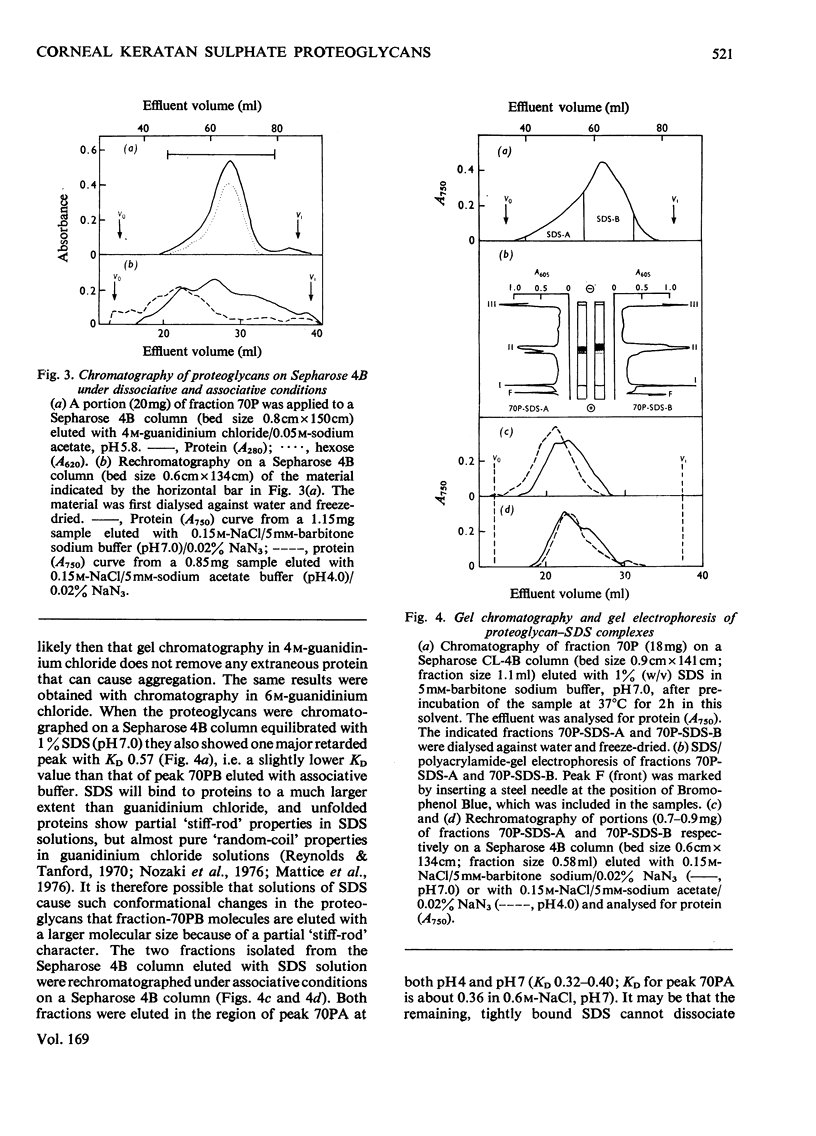
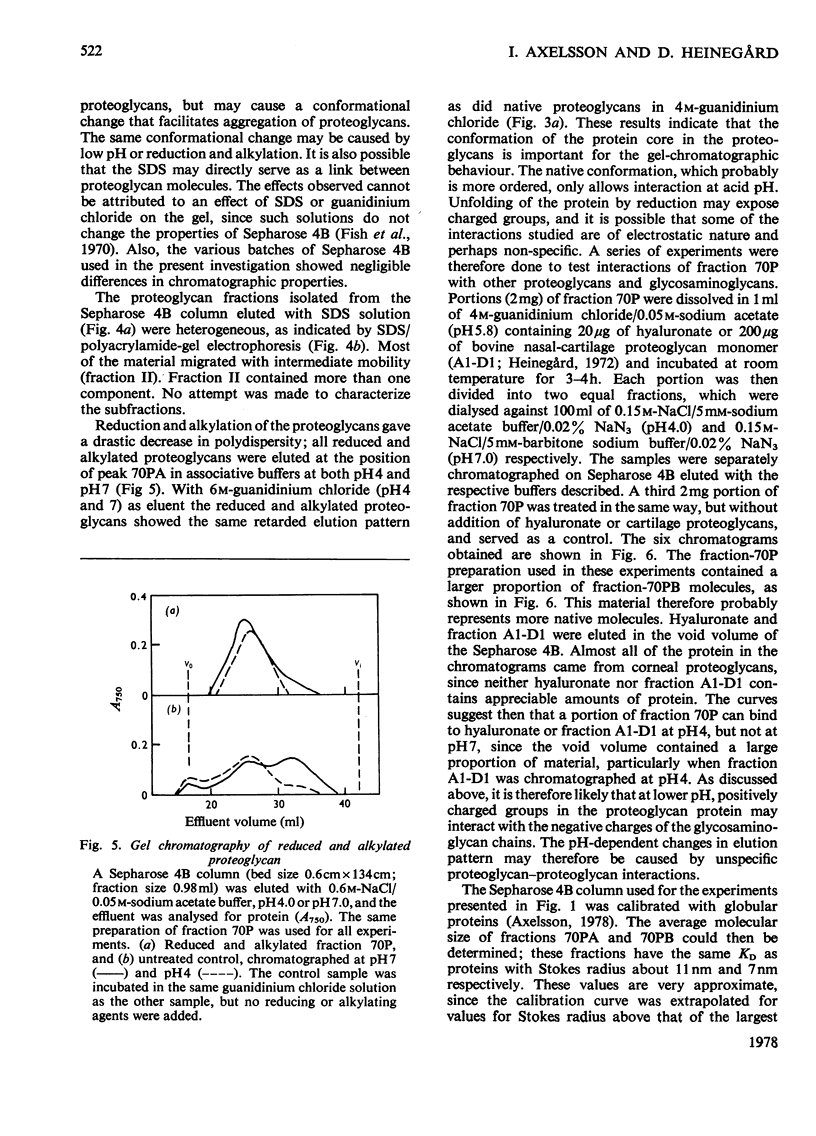
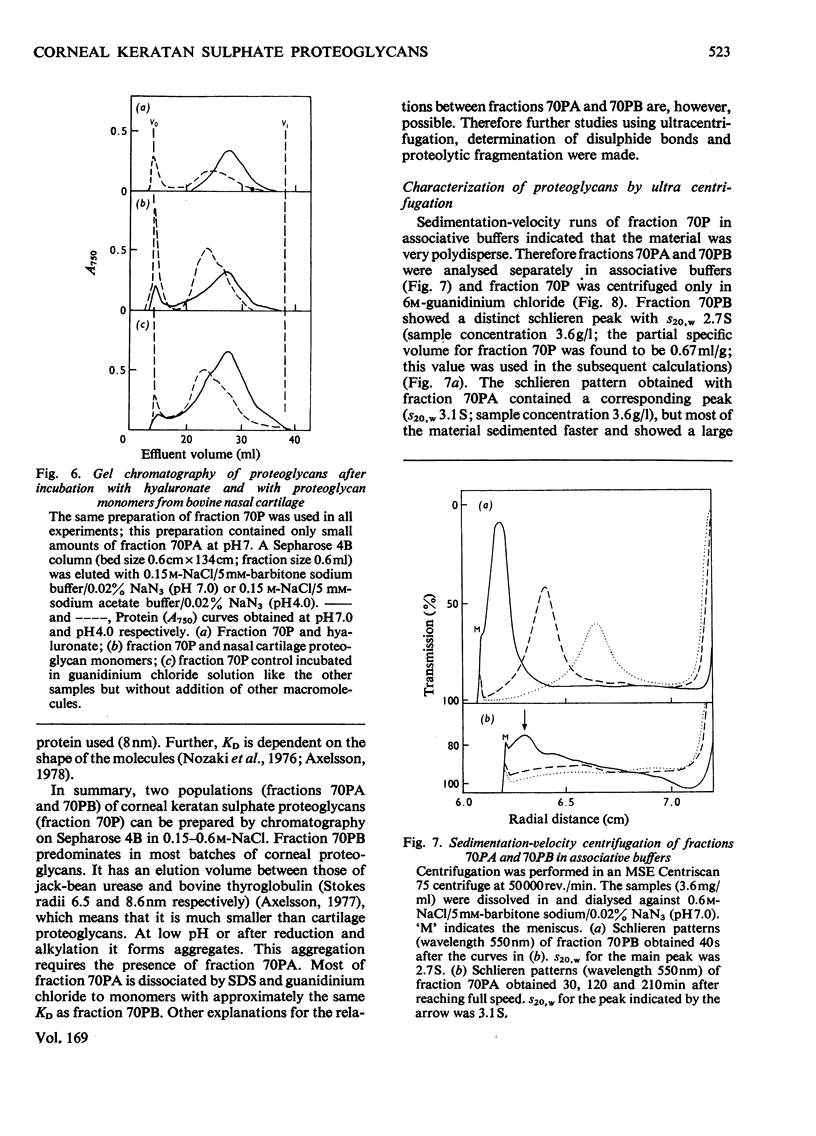
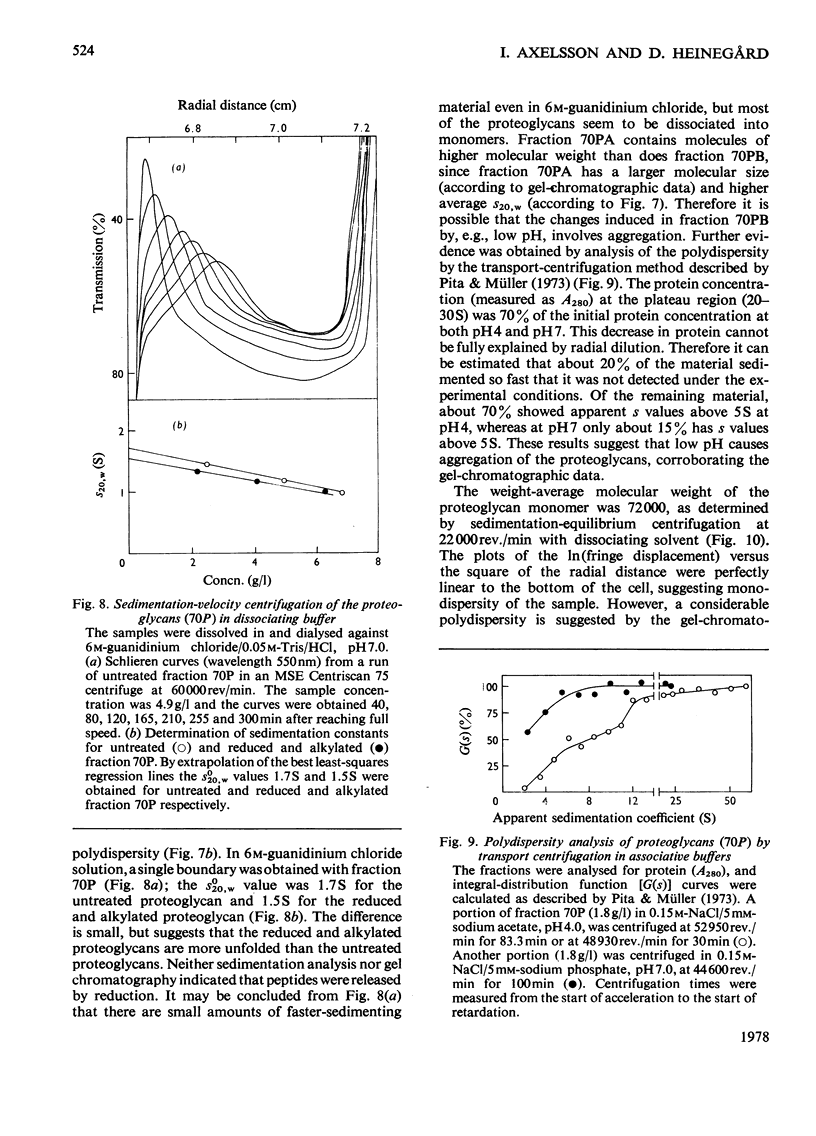
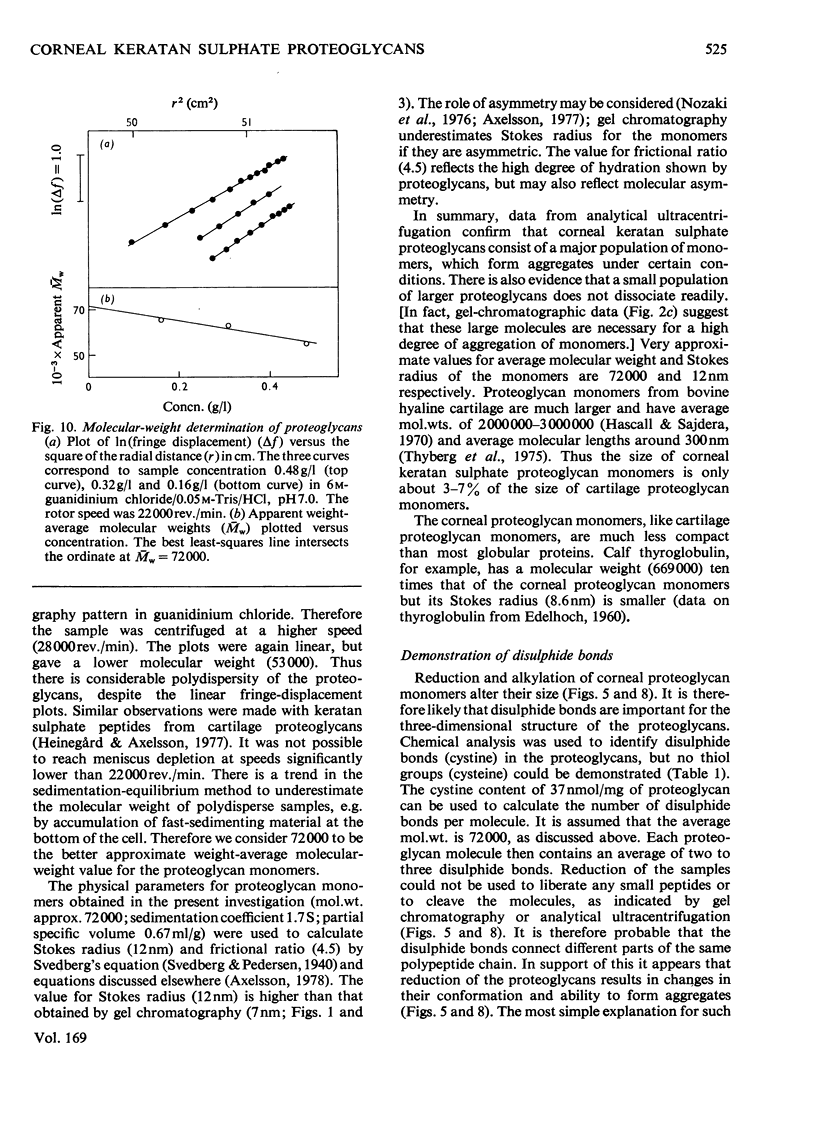
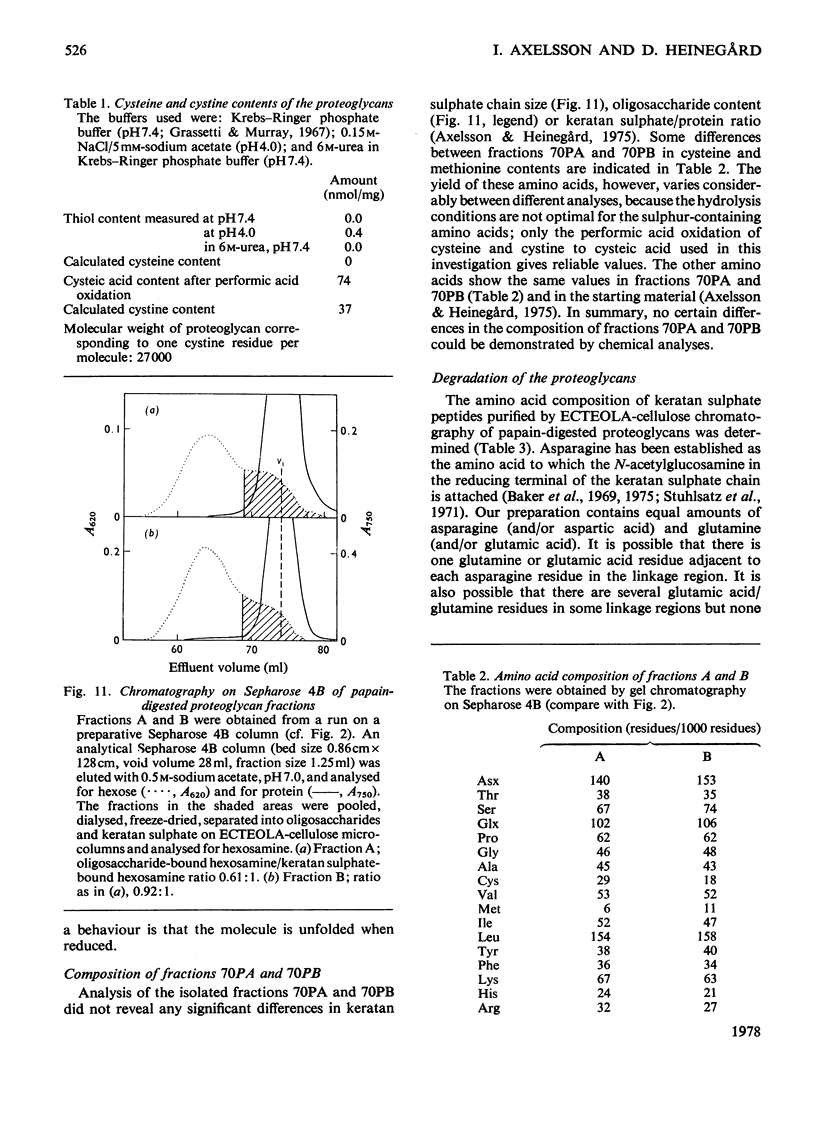
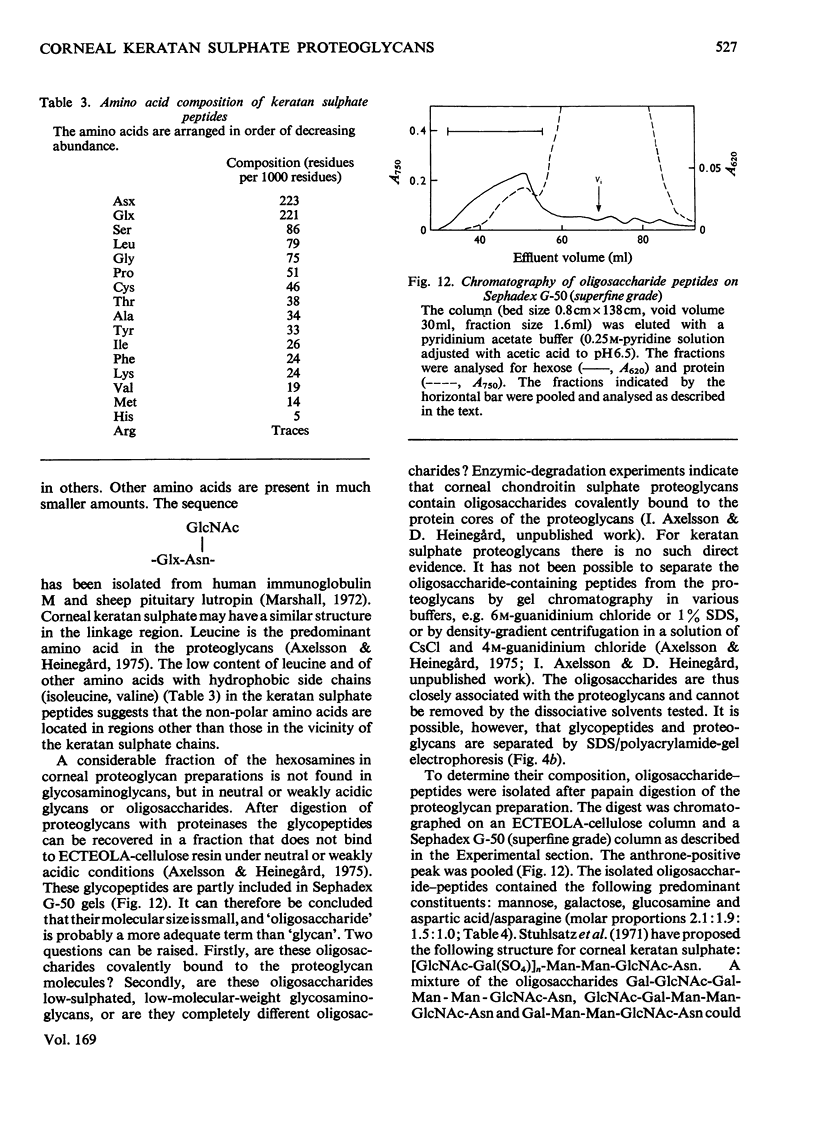
The keratan sulphate proteoglycans that can be prepared from bovine corneal stroma [Axelsson & Heinegård (1975) Biochem. J. 145, 491-500] were characterized by gel chromatography, gel electrophoresis and analytical ultracentrifugation in associative (0.6 M-NaCl) and dissociative (6M-guanidinum chloride) solvents. The proteoglycans aggreagated at low salt concentrations and pH. The weight-average molecular weight of the monomer proteoglycans was established. Keratan sulphate peptides and oligosaccharide peptides were isolated after proteolysis. Their composition indicated that both are linked to protein via asparagine residues. A tentative model for corneal keratan sulphate proteoglycans is suggested.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANSETH A. Studies on corneal polysaccharides. III. Topographic and comparative biochemistry. Exp Eye Res. 1961 Dec;1:106–115. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(61)80015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonopoulos C. A., Fransson L. A., Heinegård D., Gardell S. Chromatography of glycosaminoglycans on ECTEOLA-cellulose columns. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 9;148(1):158–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90291-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson I., Heinegård D. Fractionation of proteoglycans from bovine corneal stroma. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):491–500. doi: 10.1042/bj1450491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. R., Cifonelli J. A., Rodén L. The linkage of corneal keratan sulfate to protein. Connect Tissue Res. 1975;3(2):149–156. doi: 10.3109/03008207509152173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettelheim F. A., Plessy B. The hydration of proteoglycans of bovine cornea. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 13;381(1):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90202-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryce C. F., Crichton R. R. The subunit structure of horse spleen apoferritin. I. The molecular weight of the subunit. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4198–4205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervenka C. H. Long-column meniscus depletion sedimentation equilibrium technique for the analytical ultracentrifuge. Anal Biochem. 1970 Mar;34:24–29. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELHOCH H. The properties of thyroglobulin. I. The effects of alkali. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1326–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassetti D. R., Murray J. F., Jr Determination of sulfhydryl groups with 2,2'- or 4,4'-dithiodipyridine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Mar;119(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiling H., Stuhlsatz H. W. Struktur und Stoffwechsel von Glykosaminoglykan-Proteinen. I. Die Keratansulfat-Peptide der Rinder-Cornea. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1966;345(4):236–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Physical properties and polydispersity of proteoglycan from bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):4920–4930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Axelsson I. Distribution of keratan sulfate in cartilage proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1971–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Extraction, fractionation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine tracheal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratky O., Leopold H., Stabinger H. The determination of the partial specific volume of proteins by the mechanical oscillator technique. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:98–110. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENT T. C., ANSETH A. Studies on corneal polysaccharides. II. Characterization. Exp Eye Res. 1961 Dec;1:99–105. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(61)80014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Fish W. W., Cox A. C., Tanford C. Single-chain nature of human serum transferrin. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1348–1354. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D. Glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:673–702. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattice W. L., Riser J. M., Clark D. S. Conformational properties of the complexes formed by proteins and sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4264–4272. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczar E., Moczar M., Robert L. Isolation and characterisation of the glycopeptides of the structural glycoprotein of corneal stroma. Life Sci. 1969 Jul 15;8(14):757–762. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Schechter N. M., Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Use of gel chromatography for the determination of the Stokes radii of proteins in the presence and absence of detergents. A reexamination. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3884–3890. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pita J. C., Müller F. J. Ultracentrifugal study of polydisperse and paucidisperse biological systems using capillary microcells. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2656–2665. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisler E., Haik Y., Eisenberg H. Bovine serum albumin and aqueous guanidine hydrochloride solutions. Preferential and absolute interactions and comparison with other systems. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 25;16(2):197–203. doi: 10.1021/bi00621a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. The gross conformation of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5161–5165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdera S. W., Hascall V. C. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. A comparison of low and high shear extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):77–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhlsatz H. W., Kisters R., Wollmer A., Greiling H. Zur Struktur von Proteoglykanen aus der Cornea. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Feb;352(2):289–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Lohmander S., Heinegård D. Proteoglycans of hyaline cartilage: Electron-microscopic studies on isolated molecules. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):157–166. doi: 10.1042/bj1510157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


