Abstract
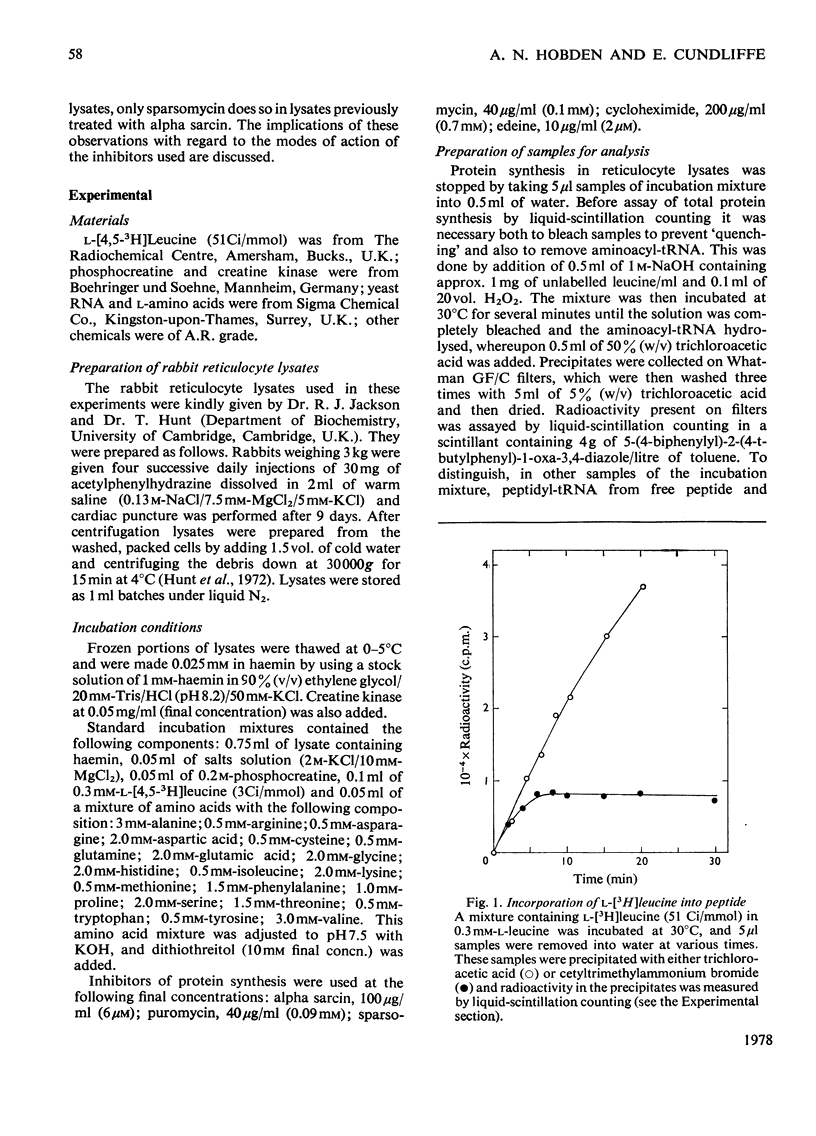
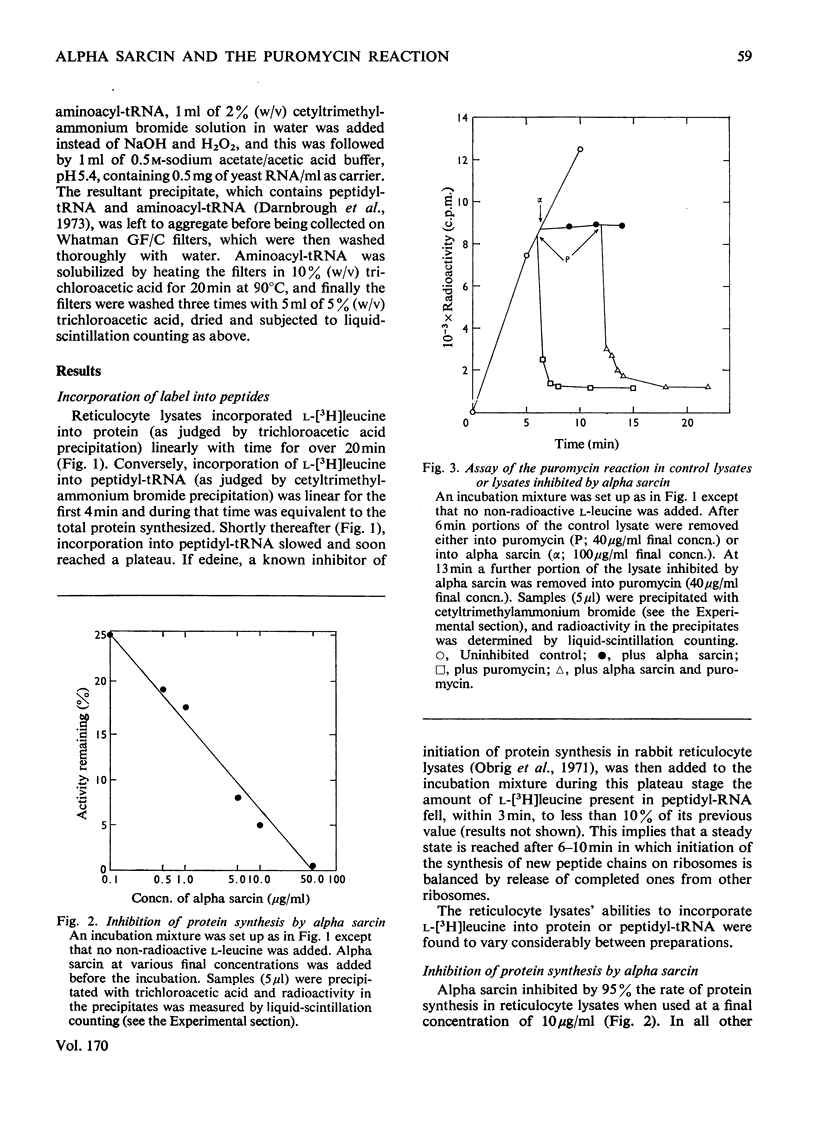
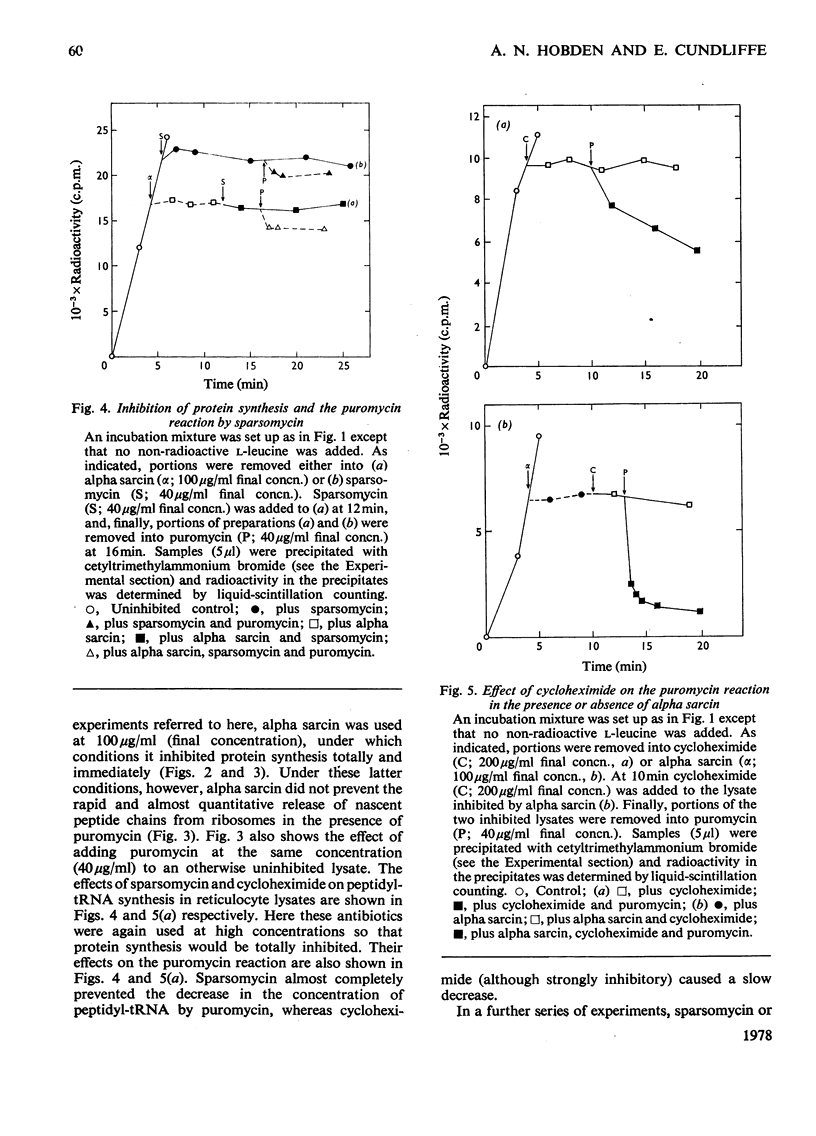
A new technique was developed for measuring the amount of peptidyl-tRNA in a protein-synthesizing system in vitro. By this technique the course of the puromycin reaction may be followed and the modes of action of various inhibitors of protein synthesis readily determined. We conclude that the polypeptide alpha sarcin inhibits the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA into the ribosomal 'A' site, that sparsomycin inhibits the peptidyl transferase reaction and that cycloheximide may block translocation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baglioni C. Inhibition of protein synthesis in reticulocytes by antibiotics. 3. Mechanism of action of sparsomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 21;129(3):642–645. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baliga B. S., Cohen S. A., Munro H. N. Effect of cycloheximide on the reaction of puromycin with polysome-bound peptidyl-tRNA. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jun 27;8(5):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E., McQuillen K. Bacterial protein synthesis: the effects of antibiotics. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E. The mode of action of thiostreption in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):912–917. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90798-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnbrough C., Legon S., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. Initiation of protein synthesis: evidence for messenger RNA-independent binding of methionyl-transfer RNA to the 40 S ribosomal subunit. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):379–403. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90511-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. H., Mitsugi K. Inhibition by sparsomycin and other antibiotics of the puromycin-induced release of polypeptide from ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):383–391. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T., Vanderhoff G., London I. M. Control of globin synthesis: the role of heme. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENNINGS J. C., OLSON B. H., ROGA V., JUNEK A. J., SCHUURMANS D. M. ALPHA SARCIN, A NEW ANTITUMOR AGENT. II. FERMENTATION AND ANTITUMOR SPECTRUM. Appl Microbiol. 1965 May;13:322–326. doi: 10.1128/am.13.3.322-326.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolchine G., Reiss-Husson F. Comparative studies on two reaction center preparations from Rhodopseudomonas speheroides Y. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80881-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W., Hardesty B. The mechanism of cycloheximide inhibition of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 15;36(4):625–630. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90351-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON B. H., GOERNER G. L. ALPHA SARCIN, A NEW ANTITUMOR AGENT. I. ISOLATION, PURIFICATION, CHEMICAL COMPOSITION, AND THE IDENTITY OF A NEW AMINO ACID. Appl Microbiol. 1965 May;13:314–321. doi: 10.1128/am.13.3.314-321.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T., Irvin J., Culp W., Hardesty B. Inhibition of peptide initiation on reticulocyte ribosomes by edeine. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 15;21(1):31–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUURMANS D. M., DUNCAN D. T., OLSON B. H. A BIOAUTOGRAPHIC SYSTEM EMPLOYING MAMMALIAN CELL STRAINS, AND ITS APPLICATION TO ANTITUMOR ANTIBIOTICS. Cancer Res. 1964 Jan;24:83–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUT R. R., MONRO R. E. THE PUROMYCIN REACTION AND ITS RELATION TO PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:63–72. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


