Abstract
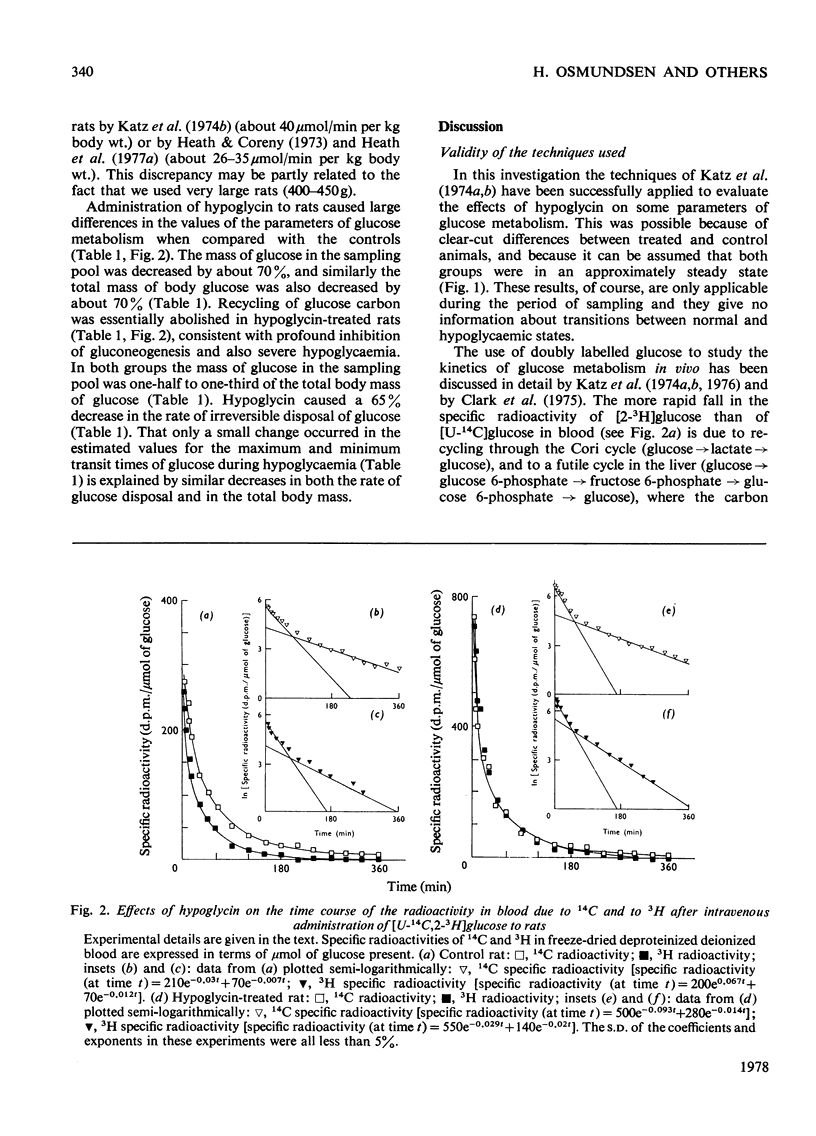
1. The kinetics of glucose metabolism were evaluated in rats deprived of food 15-21 h after the administration of hypoglycaemic doses of hypoglycin (100 mg/kg body wt.) by following changes in the specific radioactivities of 14C and 3H in blood glucose after an intravenous dose of [U-14C,2-3H]glucose [Katz, Rostami & Dunn (1974) Biochem. J. 142, 161-170]. 2. During this time, recycling of glucose through the Cori cycle was virtually abolished, the rate of irreversible disposal of glucose and its total body mass were both decreased by about 70%, whereas there was little effect on the mean transit time for glucose. 3. It was concluded that hypoglycaemia is due to inhibition of gluconeogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins G. L. A versatile digital computer program for non-linear regression analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 21;252(3):405–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billington D., Osmundsen H., Sherrat H. S. The time-course of the changes in the concentrations of some volatile fatty acids after administration of hypoglycin to rats. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(1):102–105. doi: 10.1042/bst0040102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler R., Corredor C., Brendel K. Hypoglycin and hypoglycin-like compounds. Pharmacol Rev. 1969 Jun;21(2):105–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D., Lee D., Rognstad R., Katz J. Futile cycles in isolated perfused rat liver and in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):212–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corredor C., Brendel K., Bressler R. Studies of the mechanism of the hypoglycemic action of 4-pentenoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2299–2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENG P. C., PATRICK S. J. Studies of the action of hypoglycin-A, an hypoglycaemic substance. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Jun;13(2):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D. F., Barton R. N. The design of experiments using isotopes for the determination of the rates of disposal of blood-borne substrates in vivo with special reference to glucose, ketone bodies, free fatty acids and proteins. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):503–518. doi: 10.1042/bj1360503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D. F., Corney P. L. The effects of starvation, environmental temperature and injury on the rate of disposal of glucose by the rat. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):519–530. doi: 10.1042/bj1360519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D. F., Frayn K. N., Rose J. G. Glucose turnover in the post-absorptive rat and the effects of halothane anaesthesia. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 15;162(3):653–657. doi: 10.1042/bj1620653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D. F., Frayn K. N., Rose J. G. Rates of glucose utilization and glucogenesis in rats in the basal state induced by halothane anaesthesia. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 15;162(3):643–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1620643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L., Hers H. G. On the use of (3H, 14C)labelled glucose in the study of the so-called "futile cycles" in liver and muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 4;58(3):532–539. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Dunn A., Chenoweth M., Golden S. Determination of synthesis, recycling and body mass of glucose in rats and rabbits in vivo 3H-and 14C-labelled glucose. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;142(1):171–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1420171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Golden S., Dunn A., Chenoweth M. Estimation of glucose turnover in rats in vivo with tritium labeled glucoses. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Dec;357(10):1387–1394. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.2.1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Rostami H., Dunn A. Evaluation of glucose turnover, body mass and recycling with reversible and irreversible tracers. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;142(1):161–170. doi: 10.1042/bj1420161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean E. A. Improved method for isolation of hypoglycins A and B from fruit of Blighia sapida. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;26(8):639–640. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1974.tb10678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean E. A., Rainford I. J. Inhibition of gluconeogenesis in vitro by a metabolite of hypoglycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 5;320(3):557–560. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., Hems R., Weidemann M. J., Speake R. N. The fate of isotopic carbon in kidney cortex synthesizing glucose from lactate. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):242–249. doi: 10.1042/bj1010242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmundsen H., Sherratt H. S. A novel mechanism for inhibition of beta-oxidation by methylenecyclopropylacetyl-CoA, a metabolite of hypoglycin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 15;55(1):38–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80951-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPOVIC V., POPOVIC P. Permanent cannulation of aorta and vena cava in rats and ground squirrels. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Jul;15:727–728. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick S. J. Effects of phenfromin and hypoglycin on gluconeogenesis of rat tissues. Can J Biochem. 1966 Jan;44(1):27–33. doi: 10.1139/o66-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognstad R., Clark D. G., Katz J. Relationship between isotopic reversibility and futile cycles in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):1149–1156. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90812-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Sherratt H. S. Biochemical effects of the hypoglycaemic compound pent-4-enoic acid and related non-hypoglycaemic fatty acids. Carbohydrate metabolism. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):521–527. doi: 10.1042/bj1100521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherratt H. S. Hypoglycin and related hypoglycaemic compounds. Br Med Bull. 1969 Sep;25(3):250–255. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley H., Sherratt A., Osmundsen H. On the mechanisms of some pharmacological actions of the hypoglycaemic toxins hypoglycin and pent-4-enoic acid. A way out of the present confusion. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Apr 1;25(7):743–750. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton R. A. Simple and reliable method for serial sampling of blood from rats. J Pharm Sci. 1975 Jan;64(1):112–114. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600640123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hoof F., Hue L., De Barsy T., Jacquemin P., Devos P., Hers H. G. Glycogen storage diseases. Biochimie. 1972;54(5):745–752. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Holt C., Von Holt M., Böhm H. Metabolic effects of hypoglycin and methylenecyclopropaneacetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 3;125(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


