Abstract
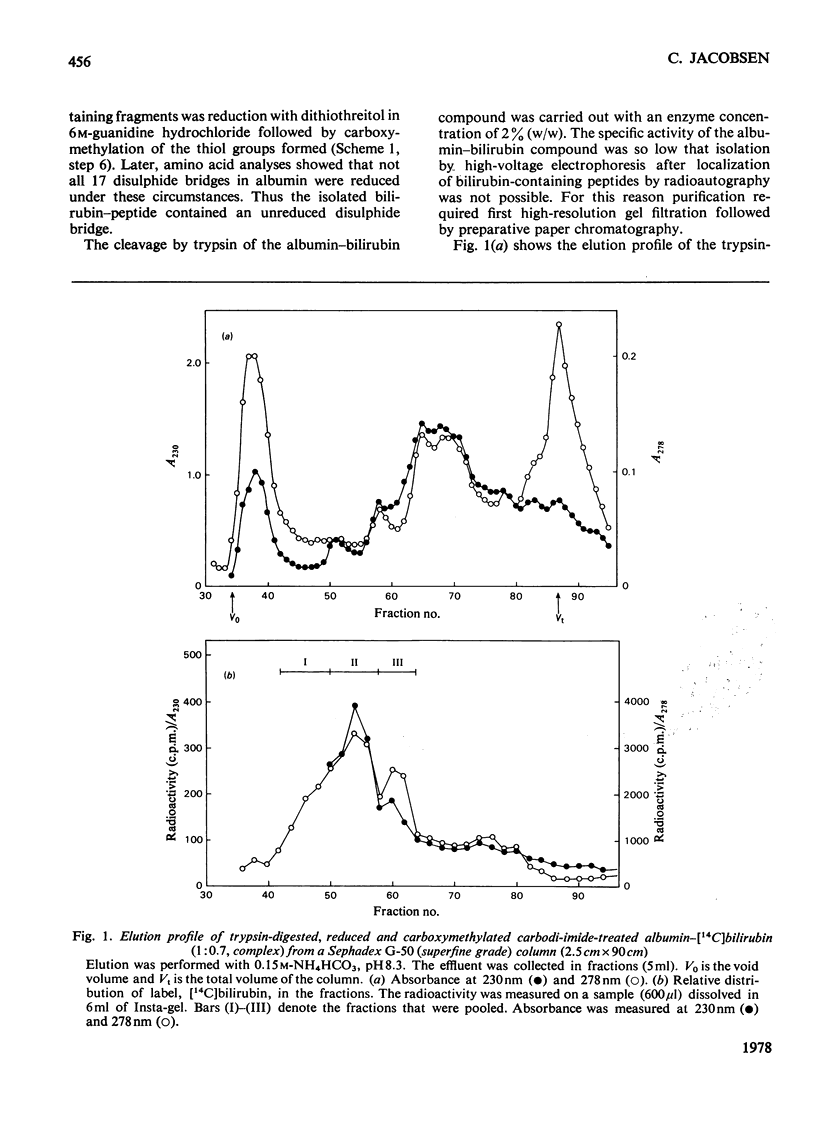
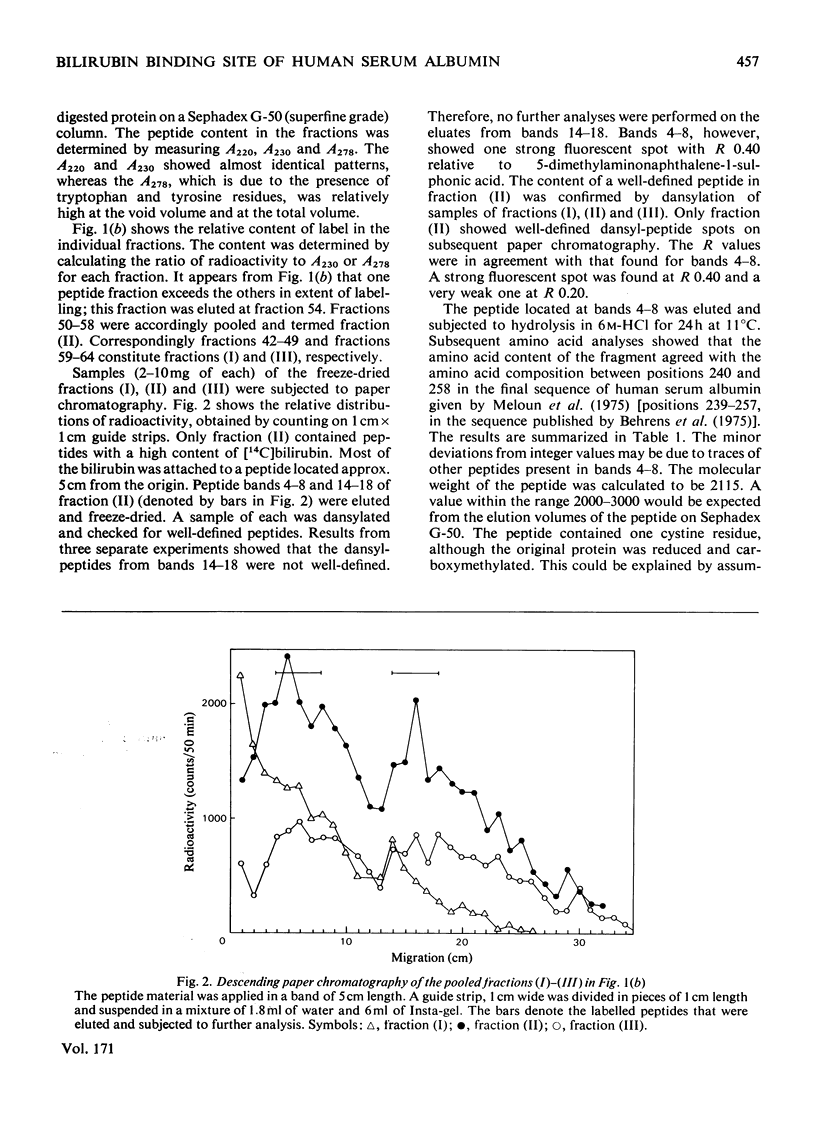
Bilirubin can be coupled covalently to albumin by using water-soluble carbodi-imide as coupling reagent. The optimal specificity in the attachment of bilirubin to the high-affinity site on the albumin molecule was obtained by treating an albumin-bilirubin complex with carbodi-imide in low concentrations and for a short period. The product was reduced, carboxymethylated and digested with trypsin. By fractionation on Sephadex G-50 (superfine grade) a peptide fraction containing most of the bilirubin label was isolated. Further purification by paper chromatography gave one peptide, consisting of residues 240-258. The peptide containined a single lysine residue, 240, and had an intact disulphide bridge. The results indicate that bilirubin is bound to lysine residue 240 at its high-affinity site on human serum albumin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. R., Weber G. Fluorescence polarization of the complexes of 1-anilino-8-naphthalenesulfonate with bovine serum albumin. Evidence for preferential orientation of the ligand. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):371–377. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodersen R., Funding L. Binding of bilirubin and long-chain fatty acids to human serum albumin with general remarks on displacement of firmly bound ligands. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 May;37(3):257–266. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Beaven G. H. Physical and binding properties of large fragments of human serum albumin. Biochem J. 1977 Jun 1;163(3):477–484. doi: 10.1042/bj1630477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heathcote J. G., Haworth C. An improved technique for the analysis of amino acids and related compounds on thin layers of cellulose. II. The quantitative determination of amino acids in protein hydrolysates. J Chromatogr. 1969 Aug 5;43(1):84–92. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)99169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen C. Chemical modification of the high-affinity bilirubin-binding site of human-serum albumin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jun 9;27(3):513–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen C. Covalent coupling of bilirubin to albumin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1976;8(3):295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1976.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen C. Trinitrophenylation of the bilirubin binding site of human serum albumin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1975;7(2):161–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1975.tb02427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. Binding of bilirubin to human serum albumin - determination of the dissociation constants. FEBS Lett. 1969 Oct 21;5(2):112–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. Studies of the affinity of human serum albumin for binding of bilirubin at different temperatures and ionic strength. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1977;9(3):235–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1977.tb03486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloun B., Morávek L., Kostka V. Complete amino acid sequence of human serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):134–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. G., Feldhoff R. C., Clute O. L., Peters T., Jr Fragments of bovine serum albumin produced by limited proteolysis. Conformation and ligand binding. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4578–4583. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler N. Use of the dansyl reaction in biochemical analysis. Methods Biochem Anal. 1970;18:259–337. doi: 10.1002/9780470110362.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallevik K. Reversible denaturation of human serum albumin by pH, temperature, and guanidine hydrochloride followed by optical rotation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2650–2655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxdal M. J., Konigsberg W. H., Henley W. L., Edelman G. M. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. II. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide fragments. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1959–1966. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


