Abstract
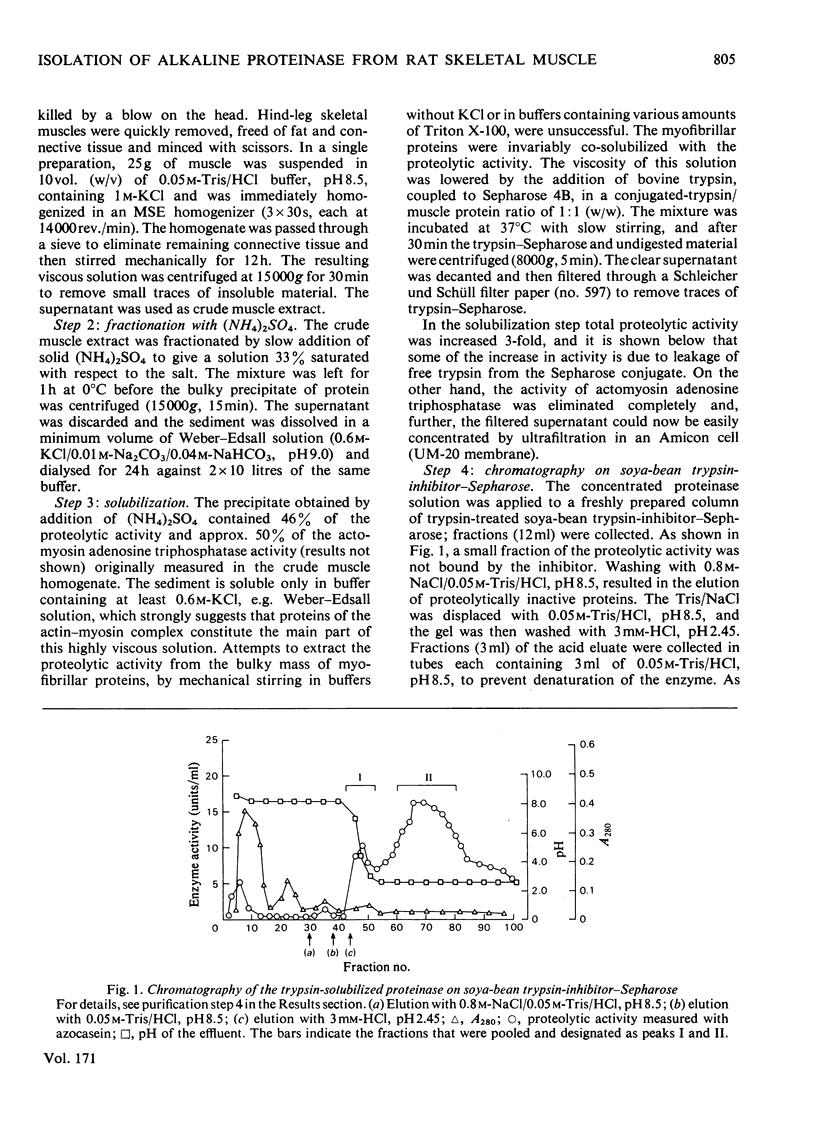
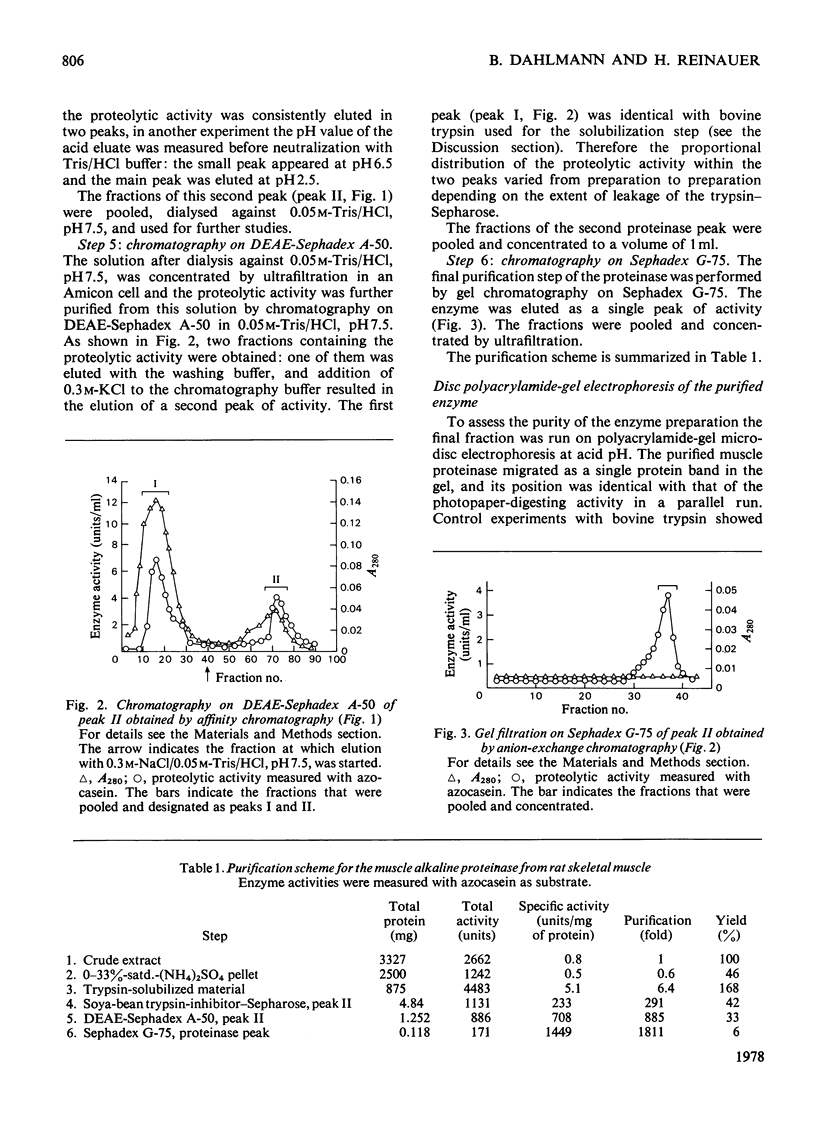
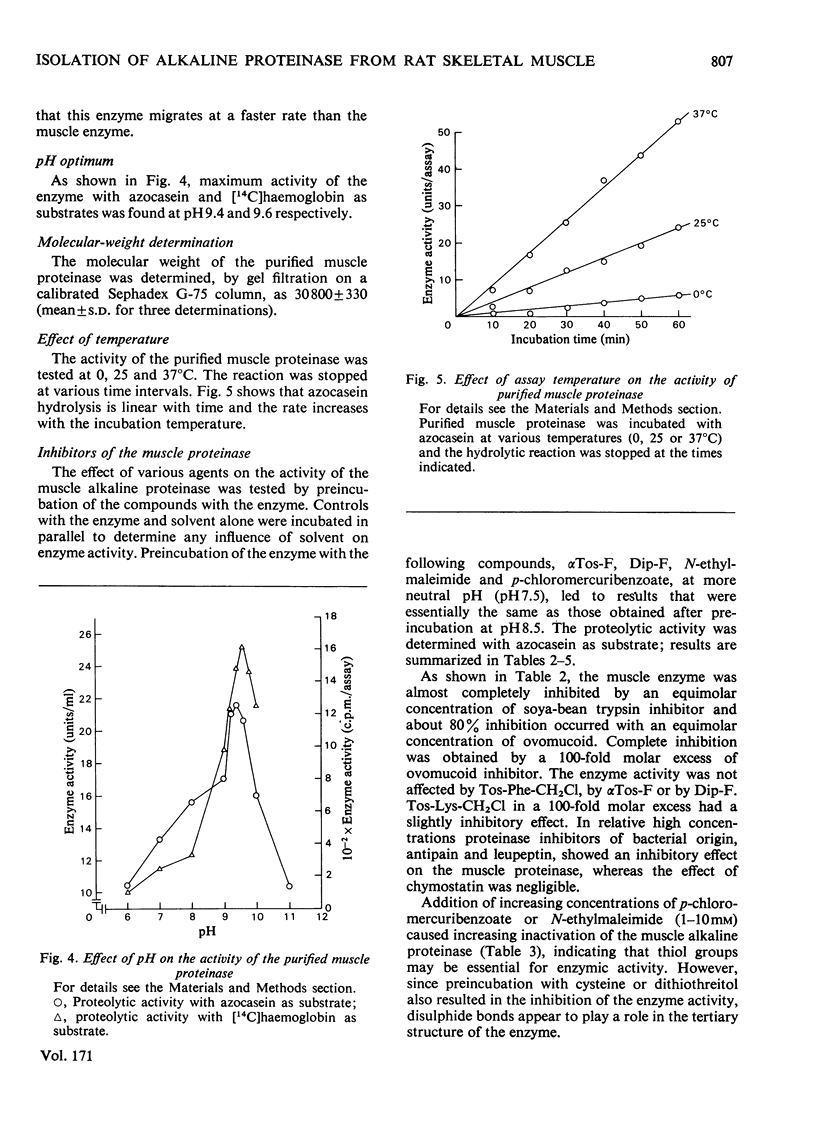
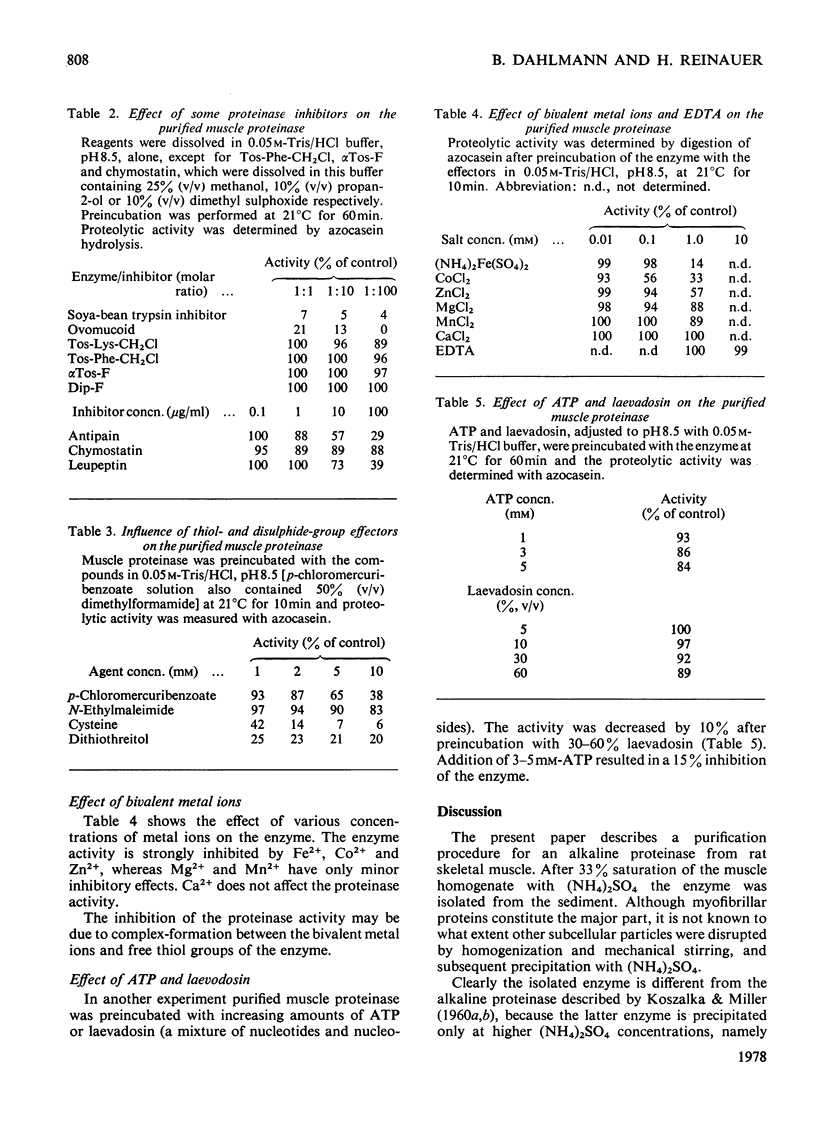
1. Rat skeletal muscle was homogenized in 0.05M-Tris/HCl, pH 8.5, containing 1M-KCl. Myofibrillar proteins were precipitated by addition of (NH4)2SO4 (33% saturation). 2. The alkaline proteolytic activity that was precipitated with the myofibrillar proteins was solubilized with trypsin (conjugated to Sepharose) and further purified by affinity chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography and gel filtration. 3. The purified enzyme migrates as a single band in polyacrylamide-disc electrophoresis, and has optimum hydrolytic activity with azocasein and [14C]haemoglobin as substrates at pH 9.4 and 9.6 respectively. Its apparent molecular weight, as determined by gel filtration on Sephadex G-75, is 30800. 4. The purified alkaline proteinase is strongly inhibited by equimolar amounts of soya-bean trypsin inhibitor and ovomucoid, whereas di-isopropyl phosphorofluoidate and alpha-toluenesulphonyl fluoride have no effect. On the other hand N-ethylmaleimide and p-chloromercuribenzoate have inhibitory effects on the enzyme activity. 5. Bivalent metal ions (Fe2+, Co2+, Zn2+, Mg2+, Mn2+) diminish the proteolytic activity, at 1mM concentrations. Ca2+ ions and the metal-ion-chelating agent EDTA are without effect on enzyme activity. 6. The enzyme is part of the alkaline proteolytic activity that appears to be associated with myofibrillar proteins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cuatrecasas P., Wilchek M., Anfinsen C. B. Selective enzyme purification by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):636–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann B., Jany K. D. A rapid and sensitive detection of proteolytic enzymes after electrophoresis. J Chromatogr. 1975 Jul 2;110(1):175–177. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)91224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C., Heinemann M. A., Kitabchi A. E. Purification of insulin-specific protease by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jany K. D. Studies on the digestive enzymes of the stomachless bonefish Carassius auratus gibelio (Bloch): endopeptidases. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1976;53(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(76)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSZALKA T. R., MILLER L. L. Proteolytic activity of rat skeletal muscle. I. Evidence for the existence of an enzyme active optimally at pH 8.5 to 9.0. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:665–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSZALKA T. R., MILLER L. L. Proteolytic activity of rat skeletal muscle. II. Purification and properties of an enzyme active optimally at pH 8.5 to 9.0. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:669–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katunuma N., Kominami E., Kobayashi K., Banno Y., Suzuki K. Studies on new intracellular proteases in various organs of rat. 1. Purification and comparison of their properties. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 3;52(1):37–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M., Khassis S., Shafrir E. Determination of trypsin by its accelerating effect on the onset of trypsinogen activation. Anal Biochem. 1974 Mar;58(1):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Laskowski M., Jr The reactive site of trypsin inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 10;241(17):3955–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Steffen E. The soybean trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz) is a doubleheaded inhibitor. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 May;356(5):617–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. S., Losty T., Wierbicki E. Assay of proteolytic enzyme activity using a 14C-labeled hemoglobin. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jul;42(1):214–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röthig H. J., Stiller N., Dahlmann B., Reinauer H. Insulin effect on proteolytic activities in rat skeletal muscle. Horm Metab Res. 1978 Mar;10(2):101–104. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


