Abstract
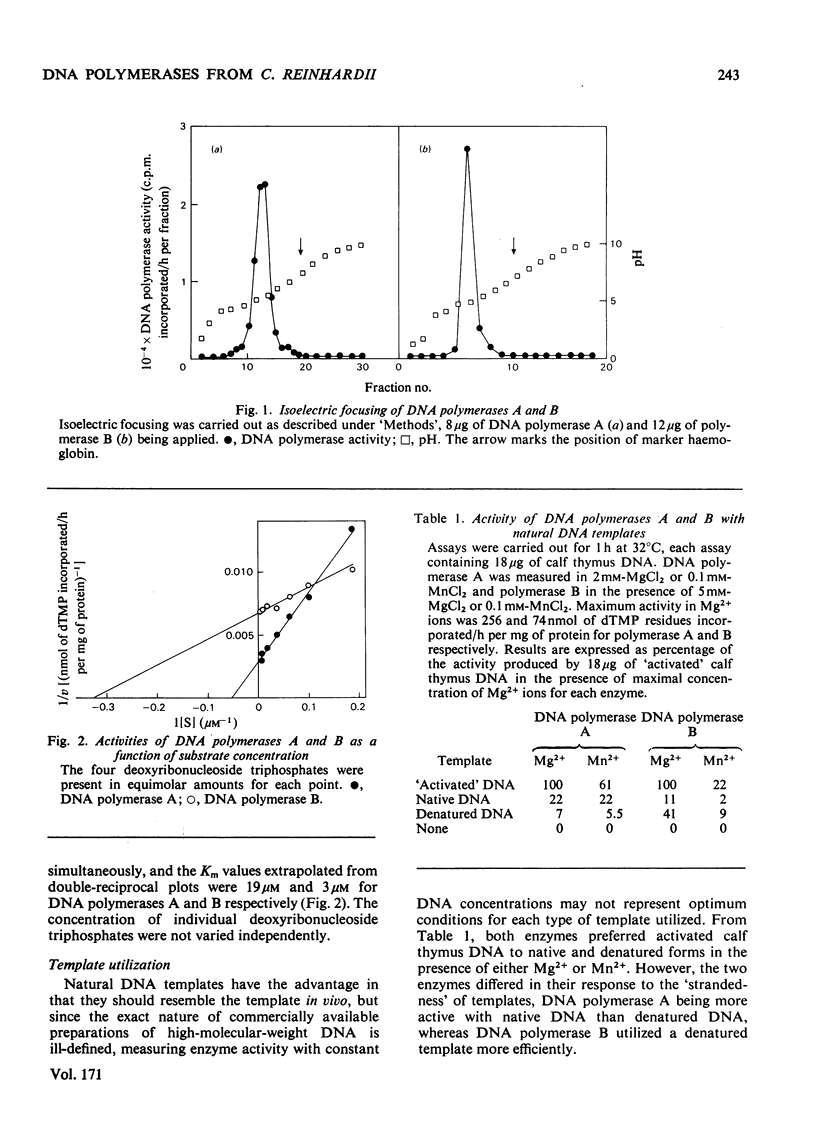
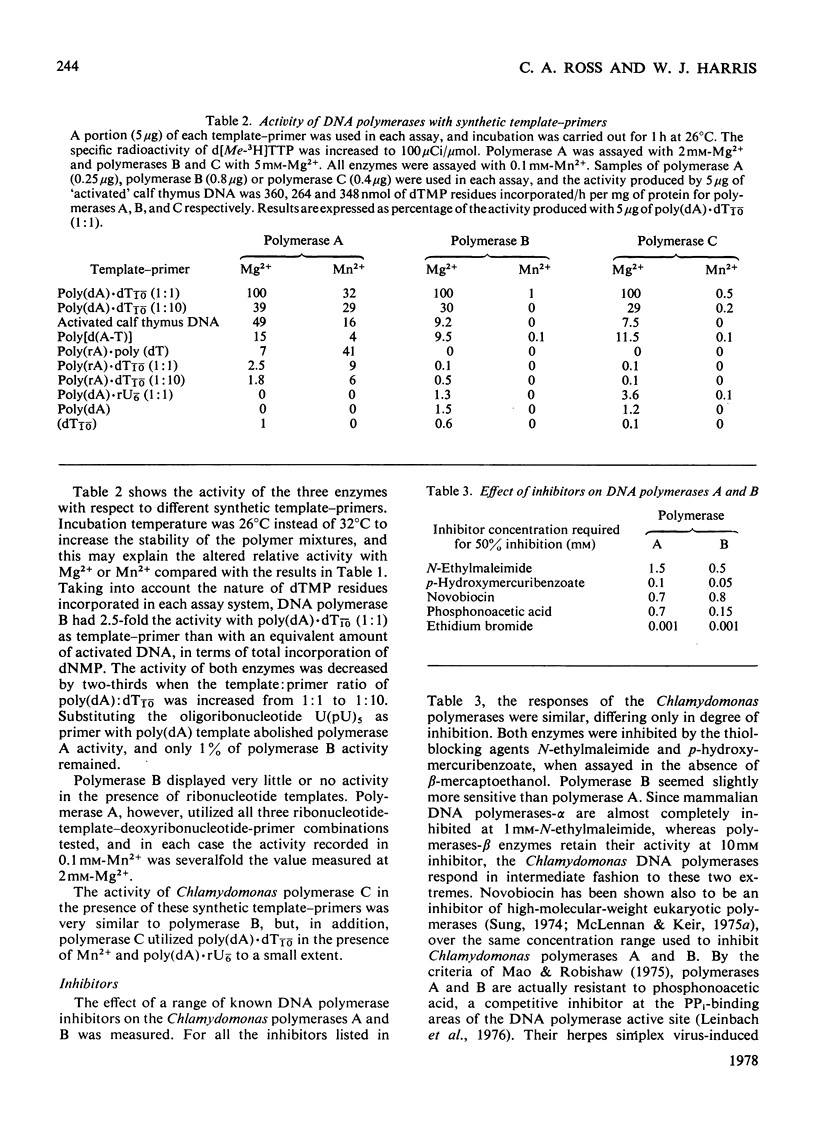
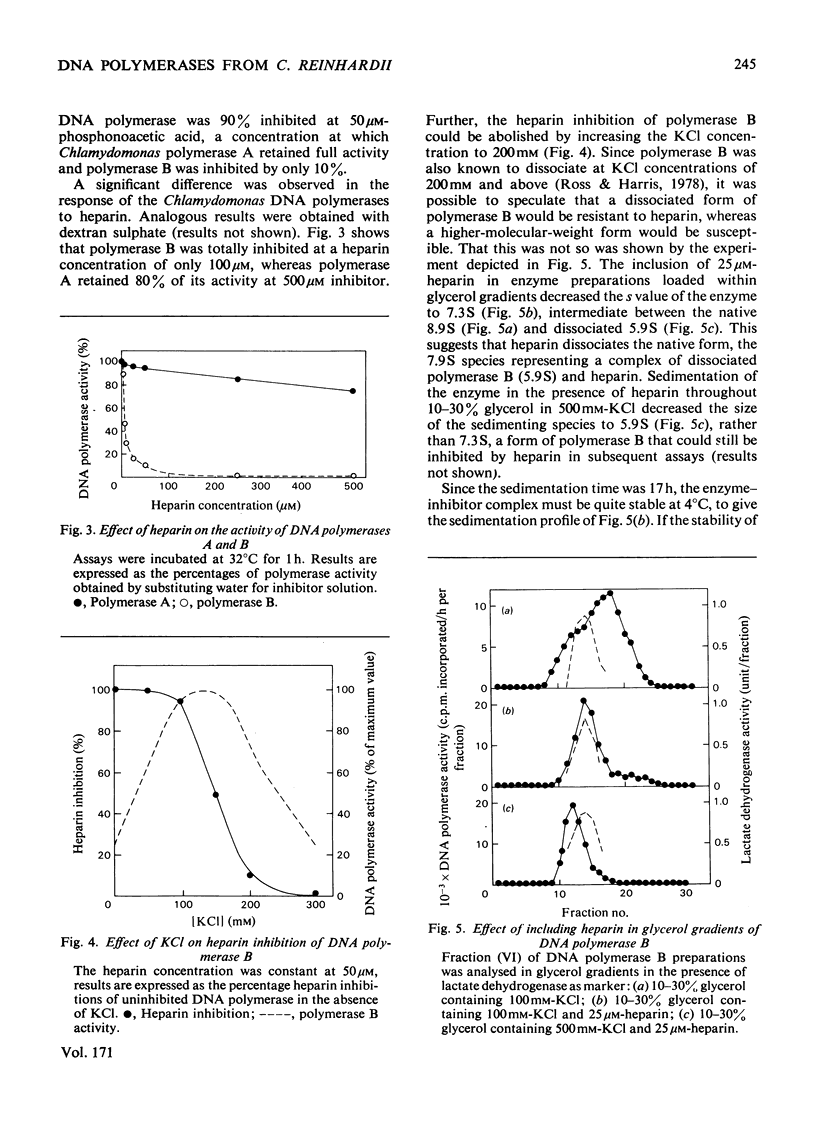
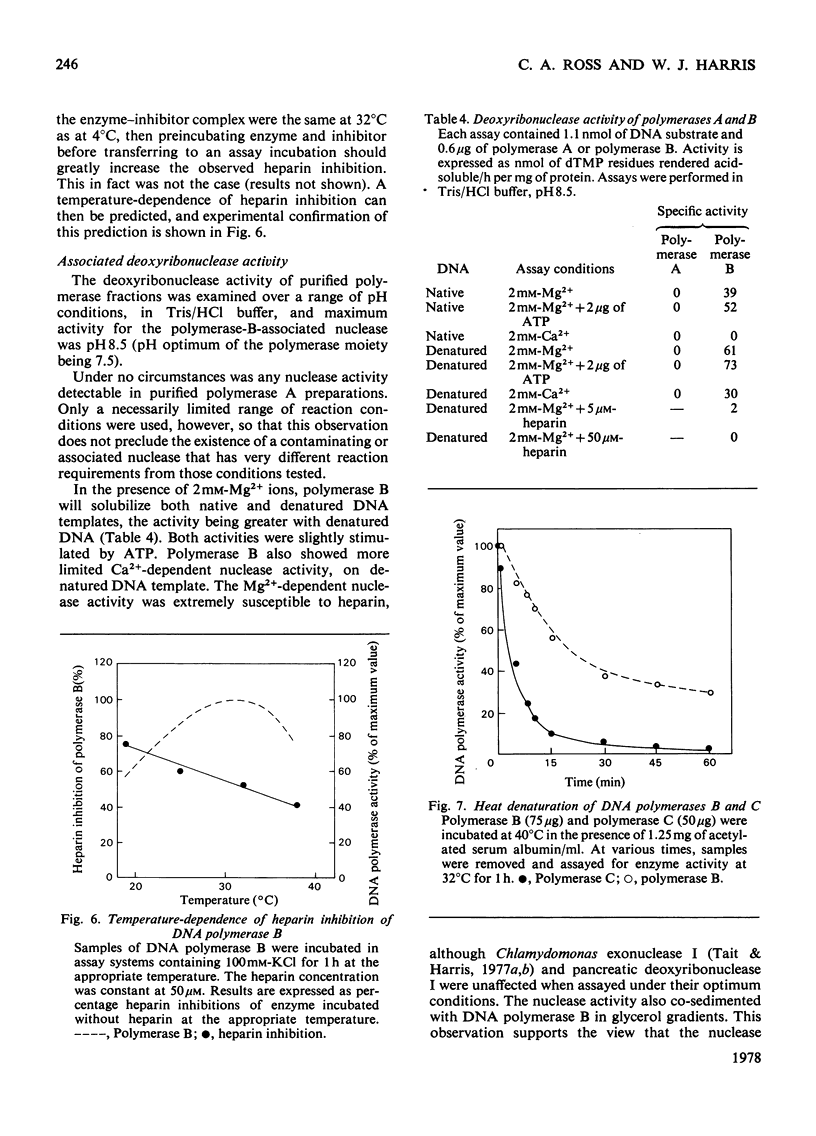
The properties of three DNA polymerase species A, B and C, purified from Chlamydomonas reinhardii were compared. DNA polymerases A and B have Km values with respect to deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates of 19 micron and 3 micron respectively. DNA polymerase A is most active with activated DNA, but will also use native DNA and synthetic RNA and DNA templates with DNA primers. DNA polymerase B is also most active with activated DNA, but will use denatured DNA and synthetic DNA templates. It is inactive with RNA templates. DNA polymerase B is completely inactive in the presence of 100 micron-heparin, which has no effect on DNA polymerase A activity. Heparin dissociates DNA polymerase B into subunits that are still catalytically active, but which heparin inhibited. DNA polymerase B possesses deoxyribonuclease activity that is inhibited by 5 micron-heparin, suggesting that the deoxyribonuclease is an integral part of the DNA polymerase moiety. DNA polymerase A is devoid of nuclease activity. DNA polymerase C is similar to DNA polymerase B in all these properties, though it is more active with RNA primers and has greater heat-sensitivity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks G. R., Holloman W. K., Kairis M. V., Spanos A., Yarranton G. T. A DNA polymerase from Ustilago maydis. 1. Purification and properties of the polymerase activity. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 2;62(1):131–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks G. R., Yarranton G. T. A DNA polymerase from Ustilago maydis. 2. Properties of the associated deoxyribonuclease activity. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 2;62(1):143–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollum F. J. Mammalian DNA polymerases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1975;15(0):109–144. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes J. J., Downey K. M., Black V. L., So A. G. A new mammalian DNA polymerase with 3' to 5' exonuclease activity: DNA polymerase delta. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2817–2823. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri L. F., Modak M. J., Marcus S. L. Evidence for allosterism in in vitro DNA synthesis on RNA templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):858–862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crerar M., Pearlman R. E. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Tetrahymena pyriformis. Purification and properties of the major activity in exponentially growing cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3123–3131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. M., Kado C. I. High molecular weight deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from crown gall tumor cells of periwinkle (Vinca rosea). Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):688–697. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer R. J., Coffey D. S. The interaction of natural and synthetic polyanions with mammalian nucleo. I. DNA synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 14;224(2):553–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus L. H., Kitron N. Inhibition and dissociation of mammalian polymeric DNA polymerase by heparin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):414–419. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Reno J. M., Lee L. F., Isbell A. F., Boezi J. A. Mechanism of phosphonoacetate inhibition of herpesvirus-induced DNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):426–430. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo K. Y., Bessman M. J. An antimutator deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. II. In vitro and in vivo studies of its temperature sensitivity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2480–2486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis L. W., Rossomando E. F., Chang L. M. DNA polymerase of Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):469–477. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E. Mode of inhibition of herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase by phosphonoacetate. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5475–5479. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan A. G., Keir H. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of Euglena gracilis. Primer-template utilization of and enzyme activities associated with the two deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of high molecular weight. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):239–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1510239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan A. G., Keir H. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of Euglena gracilis. Purification and properties of two distinct deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of high molecular weight. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):227–238. doi: 10.1042/bj1510227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzyczka N., Poland R. L., Bessman M. J. Studies on the biochemical basis of spontaneous mutation. I. A comparison of the deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of mutator, antimutator, and wild type strains of bacteriophage T4. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7116–7122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera R. M., Bonhoeffer E. Replication of Escherichia coli requires DNA polymerase I. Nature. 1974 Aug 9;250(5466):513–514. doi: 10.1038/250513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Harris W. J. DNA polymerases from Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Purification and properties. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):231–240. doi: 10.1042/bj1710231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougeon F., Brun G., da Costa Maia J. C., Chapeville F. Primer requirement and template specificity of a DNA polymerase of chick embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1229–1233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahai Srivastava B. I., Grace J. T., Jr A 7S DNA polymerase in the cytoplasmic fraction from higher plant. Life Sci. 1974 May 16;14(10):1947–1954. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90411-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S., Weissbach A. HeLa cell R-deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases. Separation and characterization of two enzymatic activities. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5809–5815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalker D. M., Mosbaugh D. W., Meyer R. R. Novikoff hepatoma deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. Purification and properties of a homogeneous beta polymerase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):3114–3121. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. C. Effect of novobiocin on DNA-dependent DNA polymerases from developing rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 15;361(1):115–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait G. C., Harris W. J. A deoxyribonuclease from Chlamydomonas reinhardii. 1. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 16;75(2):357–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait G. C., Harris W. J. A deoxyribonuclease from Chlamydomonas reinhardii. 2. Substrate specificity, mode of action and products. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 16;75(2):365–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyemura D., Lehman I. R. Biochemical characterization of mutant forms of DNA polymerase I from Escherichia coli. I. The polA12 mutation. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):4078–4084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Zillig W., Palm P., Fuchs E. Initiation of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis and the effect of heparin on RNA polymerase. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Dec;3(2):194–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A. Vertebrate DNA polymerases. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger E. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases from yeast. Further purification and characterization of DNA-dependent DNA polymerases A and B. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):41–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger U., Wintersberger E. Studies on deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases from yeast. 1. Parial purification and properties of two DNA polymerases from mitochondria-free cell extracts. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Mar 1;13(1):11–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Recondo A. M., Abadiedebat J. Regenerating rat liver DNA polymerases: disimilitude or relationship between nuclear and cytoplasmic enzymes? Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Aug;3(8):1823–1837. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.8.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


