Abstract
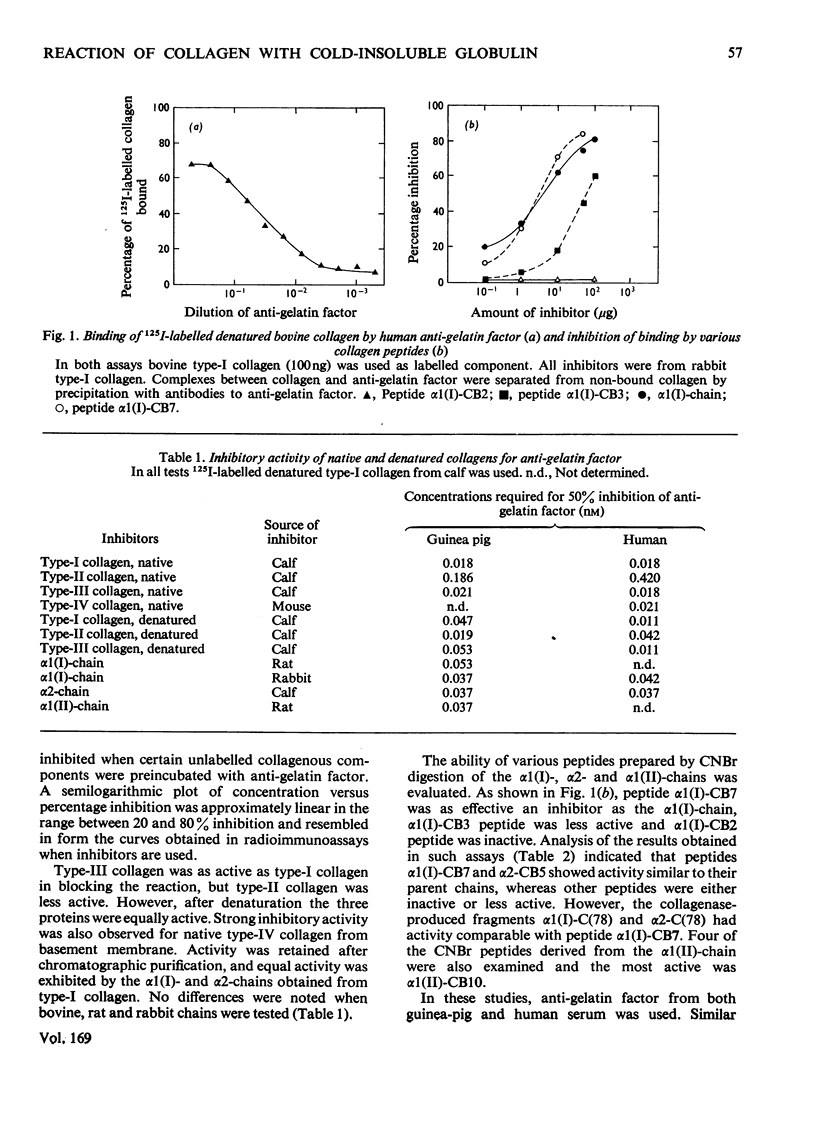
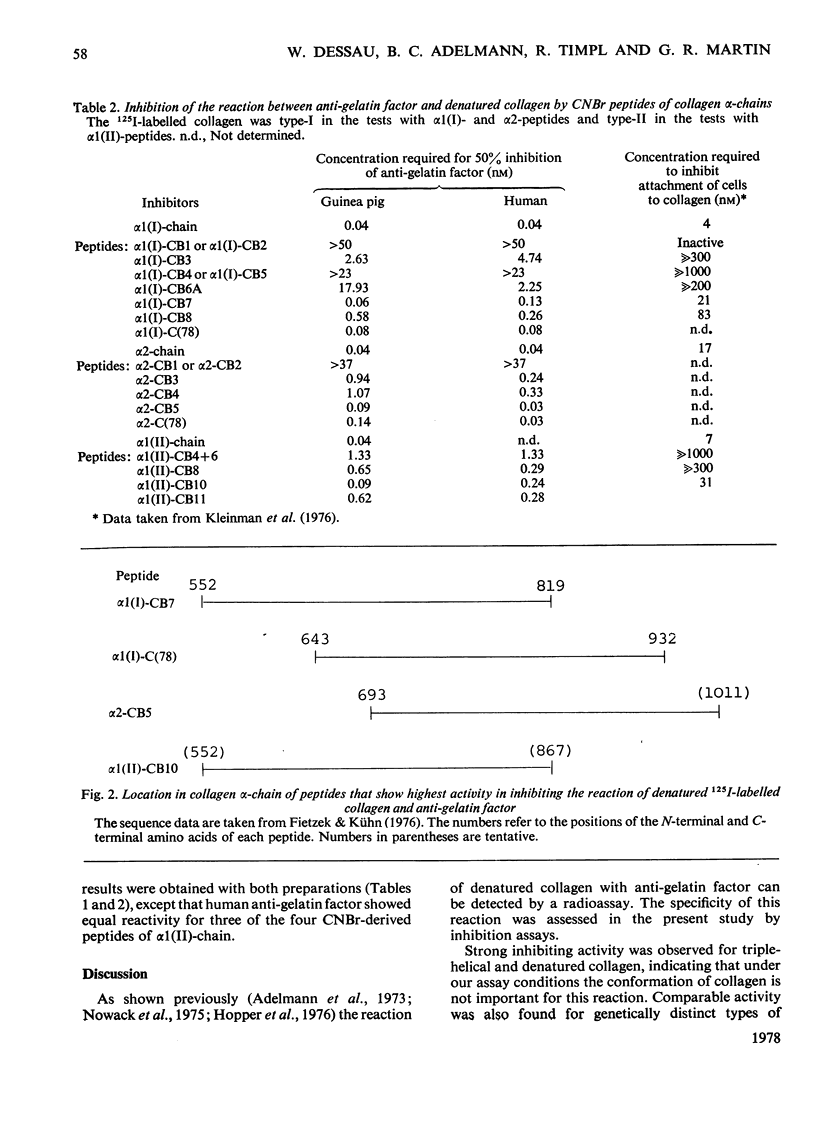
Anti-gelatin factor was prepared from guinea-pig and human serum by affinity chromatography on denatured type-I collagen. As shown previously, this component is related to cold-insoluble globulin. It reacted with 125I-labelled denatured collagen, and the reaction could be inhibited by preincubation with unlabelled collagenous components. In the inhibition assay comparable activities were observed for native and denatured type-I, -II, -III and -IV collagens. There was also no difference in reactivity between collagens of different species. The reactive sites in the collagen alpha-chains were located by inhibition assays on distinct CNBr- and collagenase-derived peptides. The results obtained with fragments from alpha1(I)-, alpha2- and alpha1(II)-chains indicate that the most active region is located between positions 643 and 819 of the alpha1-chain. Lower activities were found for other regions of collagen and may indicate that the factor has the potential to interact with several sites in the alpha-chains. The present data agree with observations by Kleinman, McGoodwin & Klebe [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. (1976) 72, 426-432] on the specificity of a serum factor promoting the attachment of fibroblasts to collagen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelmann B. C., Gentner G. J., Hopper K. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for collagen. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Dec;3(4):319–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker U., Timpl R. Cyanogen bromide peptides of the rabbit collagen a1-chain. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 15;27(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80415-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray J. P., Estess F., Bass J. A. Anticollagen antibodies following thermal trauma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Feb;130(2):394–398. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fietzek P. P., Kühn K. The primary structure of collagen. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1976;7:1–60. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363707-9.50007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fietzek P. P., Piez K. A. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha 2 chain of rat skin collagen. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):2129–2133. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T., Kühn K. Isolation and characterization of pepsin-treated type III collagen from calf skin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Nov;356(11):1793–1801. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.2.1793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Characterization of collagen peptides by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):510–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N. M. A comparison of membrane proteins of normal and transformed cells by lactoperoxidase labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):489–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper K. E., Adelmann B. C., Gentner G., Gay S. Recongnition by guinea-pig peritoneal exudate cells of conformationally different states of the collagen molecule. Immunology. 1976 Feb;30(2):249–259. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Humphryes K. C. Characterization of the external proteins of hamster fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):438–448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jilek F., Hörmann H. Cold-insoluble globulin, II. Plasminolysis of cold-insoluble globulin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Jan;358(1):133–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebe R. J. Isolation of a collagen-dependent cell attachment factor. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):248–251. doi: 10.1038/250248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGoodwin E. B. Localization of the cell attachment region in types I and II collagens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 20;72(2):426–432. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAURER P. H. I. Antigenicity of oxypolygelatin and gelatin in man. J Exp Med. 1954 Nov 1;100(5):497–513. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.5.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAURER P. H. II. Antigenicity of gelatin in rabbits and other species. J Exp Med. 1954 Nov 1;100(5):515–523. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.5.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Harris E. D., Jr, Chung E., Finch J. E., Jr, McCroskery P. A., Butler W. T. Cleavage of Type II and III collagens with mammalian collagenase: site of cleavage and primary structure at the NH2-terminal portion of the smaller fragment released from both collagens. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):787–792. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Lunde L. G. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha 1(II) chain of bovine and human cartilage collagen. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3153–3159. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Matukas V. J. Biosynthesis of collagen. The biochemist's view. Fed Proc. 1974 May;33(5):1197–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Structural studies on cartilage collagen employing limited cleavage and solubilization with pepsin. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4903–4909. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowack H., Hahn E., Timpl R. Specificity of the antibody response in inbred mice to bovine type I and type II collagen. Immunology. 1975 Oct;29(4):621–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin R. W., Gehron P., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Valentine T., Swarm R. A murine tumor producing a matrix of basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):204–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E. Plasma membrane glycoprotein which mediates adhesion of fibroblasts to collagen. Nature. 1976 Aug 5;262(5568):497–500. doi: 10.1038/262497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontz B., Meigel W., Rauterberg J., Kühn K. Localization of two species specific antigenic determinants on the peptide chains of calf skin collagen. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;16(1):50–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Vaheri A. Interaction of soluble fibroblast surface antigen with fribrinogen and fibrin. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):497–501. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff I., Timpl R., Pecker I., Steffen C. A two-component system of human serum agglutinating gelating-coated erythrocytes. Vital Health Stat 2. 1967 Jun;(24):443–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff I., Timpl R. Reaction of the human anti-gelatine factor with gelatine from different species and with collagen peptides. Vox Sang. 1968 Dec;15(6):459–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Weston J. A. Isolation of a major cell surface glycoprotein from fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3492–3496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., Rexrodt F., Wendt P., Kühn K. Isolation and characterization of cyanogen bromide-cleaved peptides from a collagenase digest of alpha 1-chain of calf skin collagen. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;16(1):143–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


