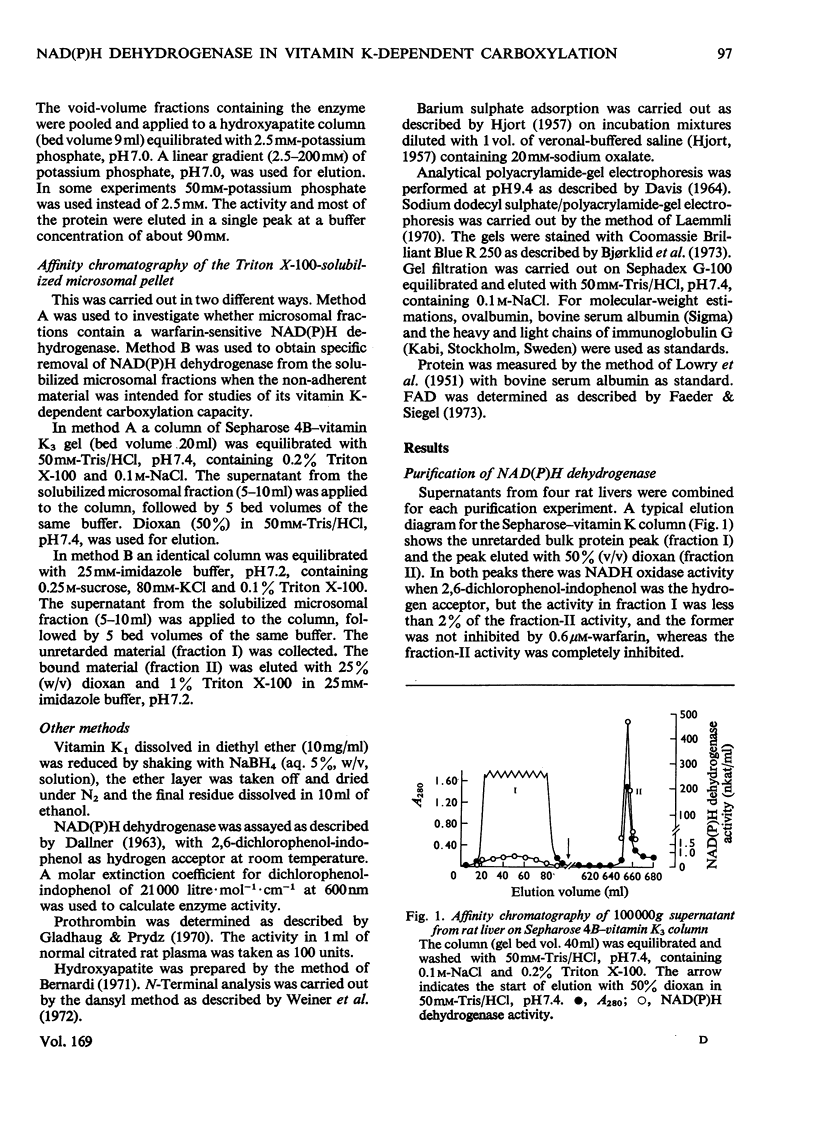
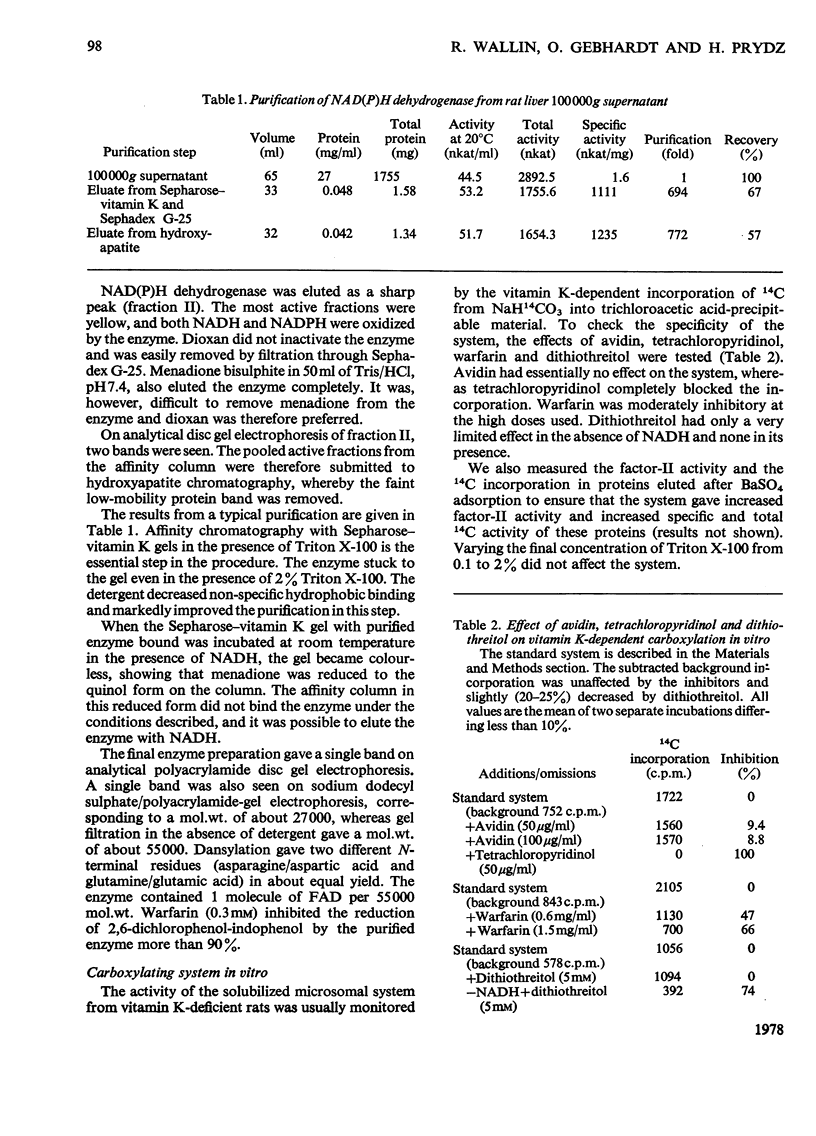
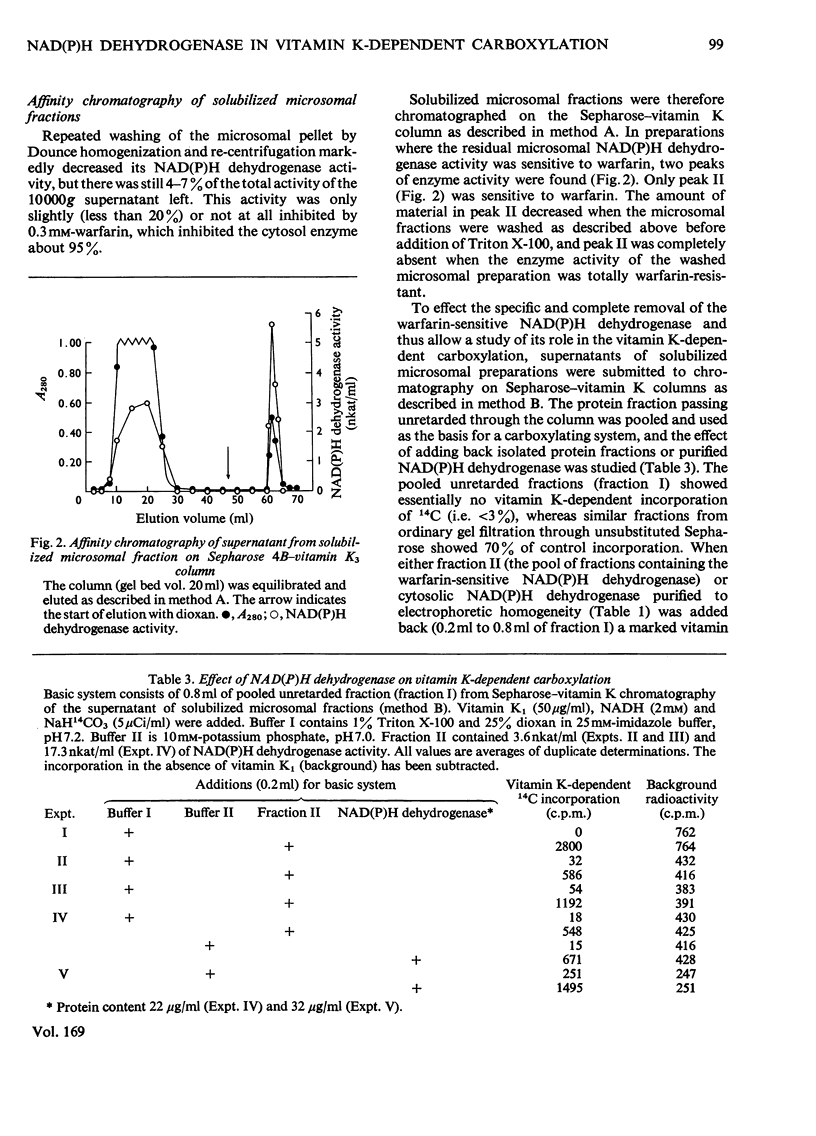
Abstract
A simple three-step method was established for the purification of NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) ('DT-diaphorase', EC 1.6.99.2) from rat liver by affinity chromatography with a recovery of above 50%. The final enzyme preparation was purified about 750-fold and was electrophoretically homogeneous. Gel filtration showed that the enzyme had a mol.wt. of about 55 000, and one molecule of FAD was found per 55 000 mol.wt. Sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis gave a mol.wt. of about 27 000. Two N-terminal amino acids, asparagine/aspartic acid and glutamine/glutamic acid, were found in about equal yield, suggesting the presence of two non-identical polypeptide chains in the enzyme. NAD(P)H dehydrogenase was selectively removed by this affinity-chromatographic method from a microsomal carboxylation system. The system, which was solubilized by detergent and is dependent on vitamin K (2-methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthaquinone or analogues with other side chains), lost its activity on the removal of the enzyme. The activity can be completely restored to the system by adding purified cytoplasmic NAD(P)H dehydrogenase or by using the quinol form of vitamin K1 (2-methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthaquinol).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell R. G., Stark P. Inhibition of prothrombin synthesis and epoxidation of vitamin K1 by anticoagulants in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 20;72(2):619–625. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorklid E., Storm E., Prydz H. The protein component of human brain thromboplastin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):969–976. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung G. C., Delaney R., Mack D., Johnson B. C. Partial purification and characterization of the enzyme which converts precursor liver protein to factor X. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 29;386(2):556–566. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90299-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERNSTER L., DANIELSON L., LJUNGGREN M. DT diaphorase. I. Purification from the soluble fraction of rat-liver cytoplasm, and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 9;58:171–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90997-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Sadowski J. A., Suttie J. W. A new carboxylation reaction. The vitamin K-dependent incorporation of H-14-CO3- into prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4744–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Solubilization and properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6238–6243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faeder E. J., Siegel L. M. A rapid micromethod for determination of FMN and FAD in mixtures. Anal Biochem. 1973 May;53(1):332–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90442-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Shia M. Some characteristics of a vitamin K-dependent carboxylating system from rat liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):647–654. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardot J. M., Mack D. O., Floyd R. A., Johnson B. C. Evidence for vitamin K semiquinone as the functional form of vitamin K in the liver vitamin K-dependent protein carboxylation reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):655–662. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladhaug A., Prydz H. Purification of the coagulation factors VII and X from human serum. Some properties of factor VII. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 21;215(1):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90392-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander P. M., Ernster L. Studies on the reaction mechanism of DT diaphorase. Action of dead-end inhibitors and effects of phospholipids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Aug;169(2):560–567. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoda S., Nakamura W., Hayashi K. Properties and reaction mechanism of DT diaphorase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6416–6423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. F., Eisen H. N. Preparation and characterization of antibodies to menadione. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 31;13(27):5547–5552. doi: 10.1021/bi00724a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. P., Fausto A., Houser R. M., Gardner E. J., Olson R. E. Effect of vitamin K homologues on the conversion of preprothrombin to prothrombin in rat liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 20;72(2):589–597. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind C., Rase B., Ernster L., Townsend M. G., Martin A. D. Strain differences in liver DT diaphorase activities. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):147–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAERKI F., MARTIUS C. [Vitamin K reductase, from cattle and ratliver]. Biochem Z. 1961;334:293–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARITIUS C., STRUFE R. Phyllochinonreduktase; vorläufige Mitteilung. Biochem Z. 1954;326(1):24–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. O., Suen E. T., Girardot J. M., Miller J. A., Delaney R., Johnson B. C. Soluble enzyme system for vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3269–3276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Morris H. R., Dell A. Primary structure of the vitamin K-dependent part of prothrombin. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80723-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martius C., Ganser R., Viviani A. The enzymatic reduction of K-vitamins incorporated in the membrane of liposomes. FEBS Lett. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):13–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prydz H. Vitamin K--dependent clotting factors. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1977 Summer;4(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rase B., Bartfai T., Ernster L. Purification of DT-diaphorase by affinity chromatography. Occurrence of two subunits and nonlinear Dixon and Scatchard plots of the inhibition by anticoagulants. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Feb;172(2):380–386. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren P., Laliberte R. E., Bell R. G. Effects of warfarin, phenylindanedione, tetrachloropyridinol, and chloro-vitamin K1 on prothrombin synthesis and vitamin K metabolism in normal and warfarin-resistant rats. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 May;10(3):373–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski J. A., Esmon C. T., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Requirements of the rat liver microsomal enzyme system. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2770–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. V., Suttie J. W. The vitamin K dependent, in vitro production of prothrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1397–1402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Fernlund P., Egan W., Roepstorff P. Vitamin K dependent modifications of glutamic acid residues in prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2730–2733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Hageman J. M. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Development of a peptide substrate. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5827–5830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Jackson C. M. Prothrombin structure, activation, and biosynthesis. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):1–70. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeer C., Soute B. A., Govers-Riemslag J., Hemker H. C. In vitro prothrombin synthesis from a purified precursor protein. I. Development of a bovine liver cell-free system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 22;444(3):926–930. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Platt T., Weber K. Amino-terminal sequence analysis of proteins purified on a nanomole scale by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3242–3251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


