Abstract
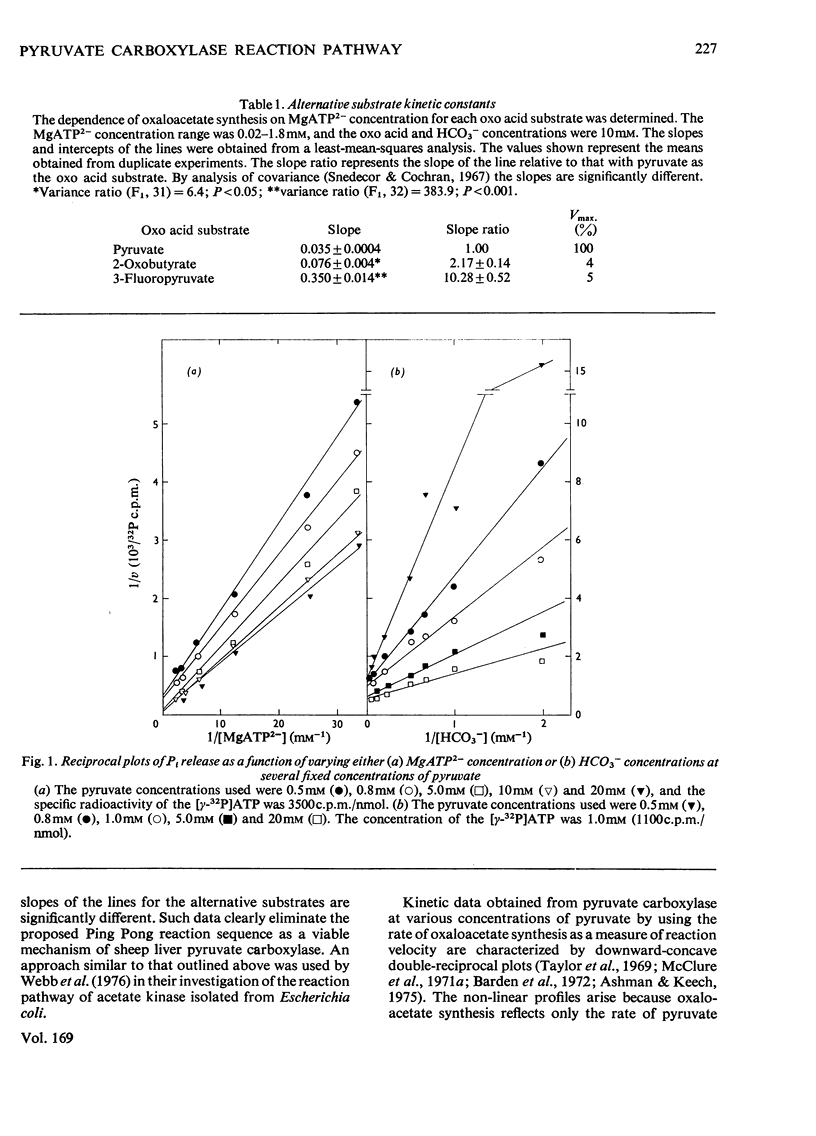
The reaction pathway catalysed by pyruvate carboxylase was re-examined by using two independent experimental approaches not previously applied to this enzyme. To avoid the variable stoicheiometry associated with oxaloacetate formation, the reaction rate was measured by following release of Pi. Initial velocities, when plotted as a function of varying concentrations of either MgATP2- or HCO3-, at fixed concentrations of pyruvate, gave in double-reciprocal-form families of straight intersecting lines. Further, when the reaction velocity was determined as a function of varying MgATP2- concentrations by using pyruvate, 3-fluoropyruvate and 2-oxobutyrate as alternative carboxyl-acceptor substrates, the slopes of the double-reciprocal plots were significantly different. Both results support a sequential reaction pathway.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashman L. K., Keech D. B. Sheep kidney pyruvate carboxylase. Studies on the coupling of adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis and CO2 fixation. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):14–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barden R. E., Fung C. H., Utter M. F., Scrutton M. C. Pyruvate carboxylase from chicken liver. Steady state kinetic studies indicate a "two-site" ping-pong mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1323–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. F., Walsh C. Studies on the intramolecular and intermolecular kinetic isotope effects in pyruvate carboxylase catalysis. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3749–3754. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easterbrook-Smith S. B., Hudson P. J., Goss N. H., Keech D. B., Wallace J. C. Pyruvate carboxylase: mechanism on the second partial reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Oct;176(2):709–720. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easterbrook-Smith S. B., Wallace J. C., Keech D. B. Pyruvate carboxylase: affinity labelling of the magnesium adenosine triphosphate binding site. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 2;62(1):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEECH D. B., UTTER M. F. PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE. II. PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2609–2614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Lardy H. A., Cleland W. W. Rat liver pyruvate carboxylase. 3. Isotopic exchange studies of the first partial reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3584–3590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Lardy H. A., Wagner M., Cleland W. W. Rat liver pyruvate carboxylase. II. Kinetic studies of the forward reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3579–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mildvan A. S., Scrutton M. C., Utter M. F. Pyruvate carboxylase. VII. A possible role for tightly bound manganese. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3488–3498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON M. S., GREENE R. C. MEASUREMENT OF LOW ENERGY BETA-EMITTERS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF EMULSIONS. Anal Chem. 1965 Jun;37:854–857. doi: 10.1021/ac60226a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed G. H., Scrutton M. C. Pyruvate carboxylase from chicken liver. Magnetic resonance studies of the effect of substrates and inhibitors on the environment of the bound manganese. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6156–6162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCRUTTON M. C., KEECH D. B., UTTER M. F. PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE. IV. PARTIAL REACTIONS AND THE LOCUS OF ACTIVATION BY ACETYL COENZYME A. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:574–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H., Nielsen J., Keech D. B. Substrate activation of pyruvate carboxylase by pyruvate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Nov 20;37(5):723–728. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90951-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Tipton K. F. Pig liver pyruvate carboxylase. The reaction pathway for the carboxylation of pyruvate. Biochem J. 1974 May;139(2):311–320. doi: 10.1042/bj1390311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Tipton K. F. Pig liver pyruvate carboxylase. The reaction pathway for the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate. Biochem J. 1974 May;139(2):321–329. doi: 10.1042/bj1390321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb B. C., Todhunter J. A., Purich D. L. Studies on the kinetic mechanism and the phosphoryl-enzyme compound of the Escherichia coli acetate kinase reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Mar;173(1):282–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


