Abstract
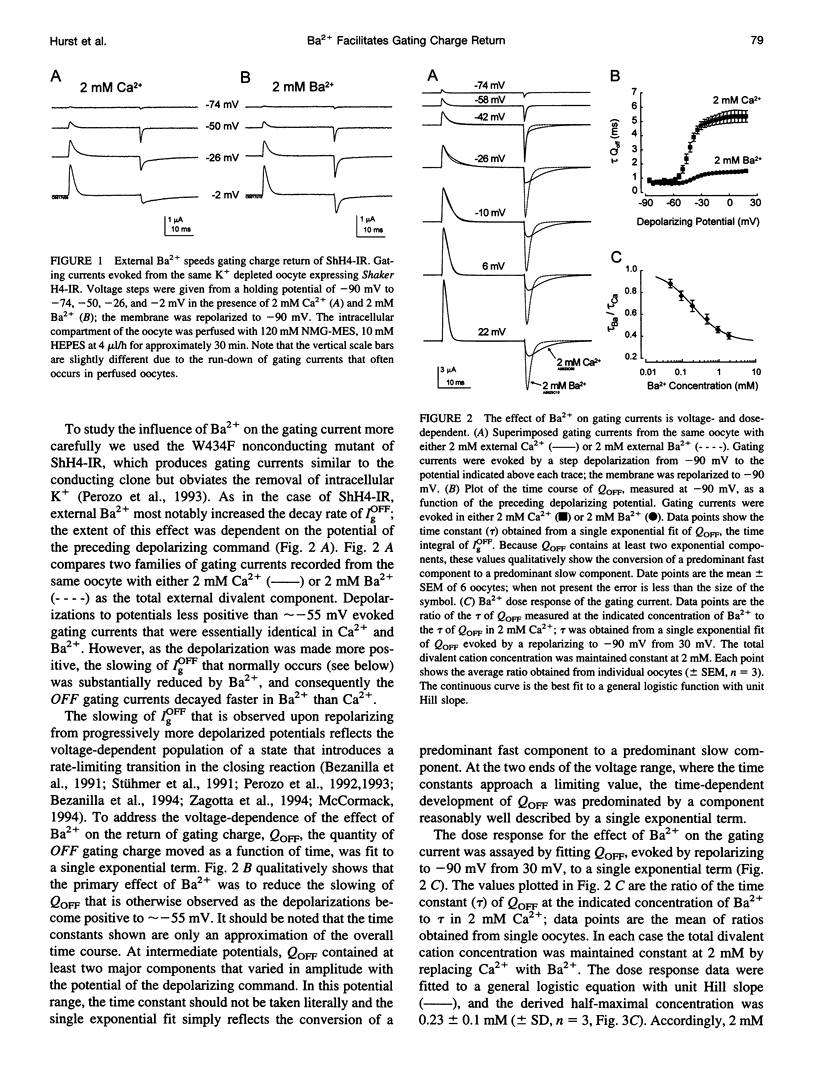
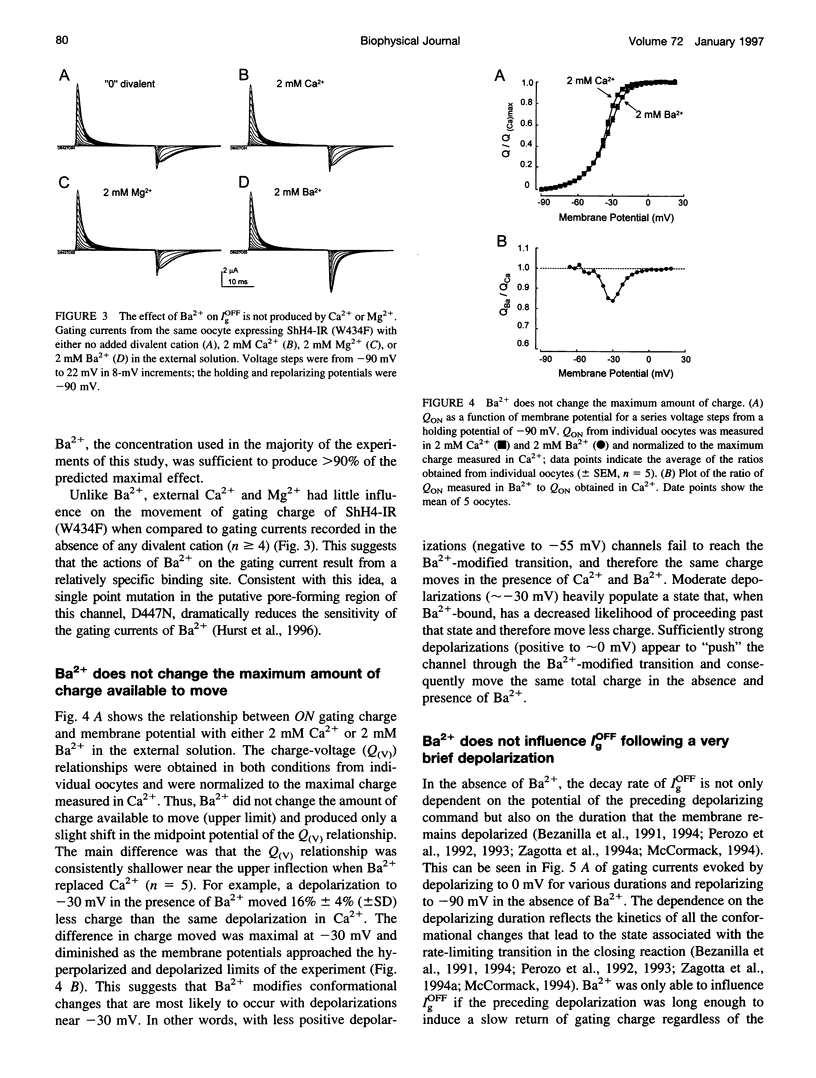
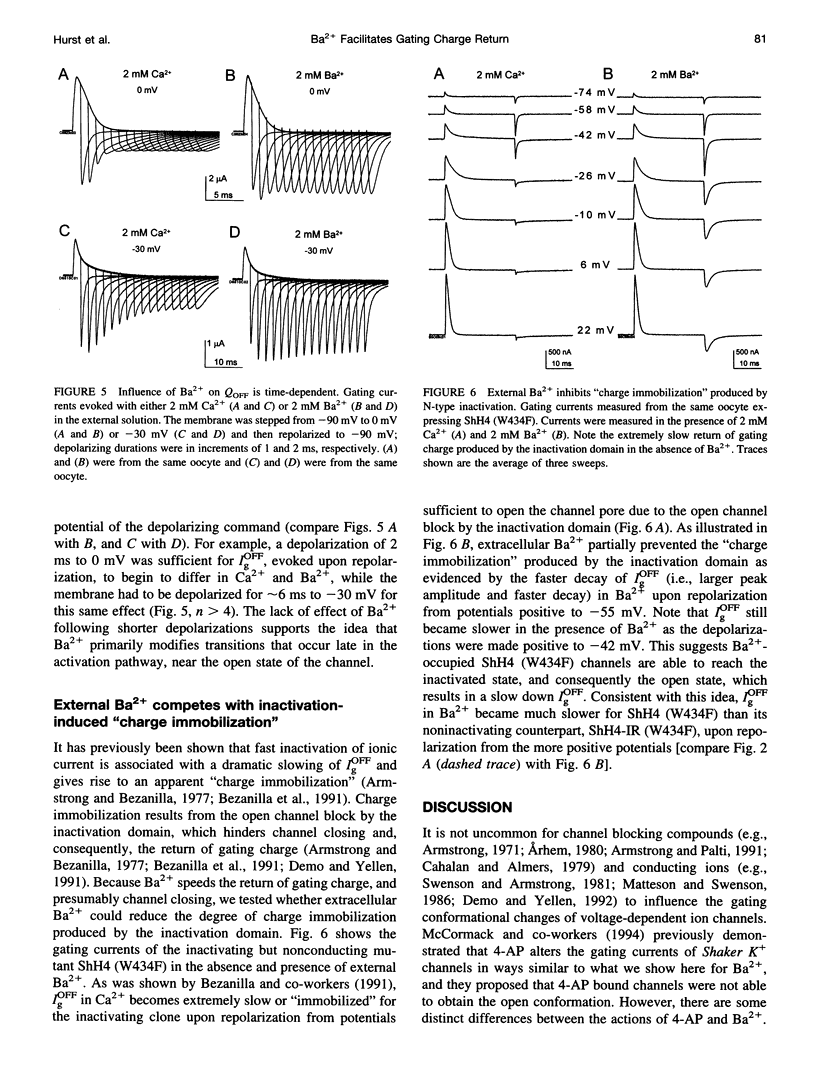
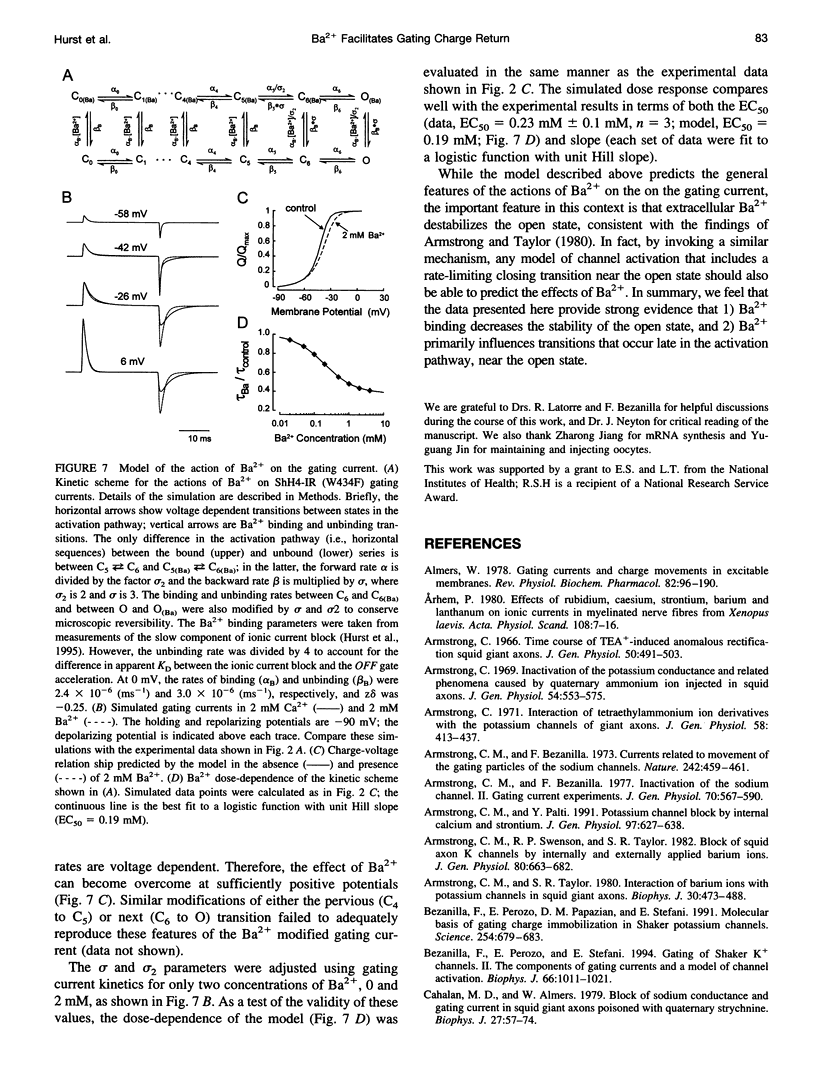
External Ba2+ speeds the OFF gating currents (IgOFF) of Shaker K+ channels but only upon repolarization from potentials that are expected to open the channel pore. To study this effect we used a nonconducting and noninactivating mutant of the Shaker K+ channel, ShH4-IR (W434F). External Ba2+ slightly decreases the quantity of ON gating charge (QON) upon depolarization to potentials near -30 mV but has little effect on the quantity of charge upon stepping to more hyperpolarized or depolarized potentials. More strikingly, Ba2+ significantly increases the decay rate of IgOFF upon repolarization to -90 mV from potentials positive to approximately -55 mV. For Ba2+ to have this effect, the depolarizing command must be maintained for a duration that is dependent on the depolarizing potential (> 4 ms at -30 mV and > 1 ms at 0 mV). The actions of Ba2+ on the gating current are dose-dependent (EC50 approximately 0.2 mM) and are not produced by either Ca2+ or Mg2+ (2 mM). The results suggest that Ba2+ binds to a specific site on the Shaker K+ channel that destabilizes the open conformation and thus facilitates the return of gating charge upon repolarization.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W. Gating currents and charge movements in excitable membranes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;82:96–190. doi: 10.1007/BFb0030498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arhem P. Effects of rubidium, caesium, strontium, barium and lanthanum on ionic currents in myelinated nerve fibres from Xenopus laevis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Jan;108(1):7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Currents related to movement of the gating particles of the sodium channels. Nature. 1973 Apr 13;242(5398):459–461. doi: 10.1038/242459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):567–590. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the potassium conductance and related phenomena caused by quaternary ammonium ion injection in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):553–575. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Palti Y. Potassium channel block by internal calcium and strontium. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Mar;97(3):627–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Swenson R. P., Jr, Taylor S. R. Block of squid axon K channels by internally and externally applied barium ions. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Nov;80(5):663–682. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.5.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Taylor S. R. Interaction of barium ions with potassium channels in squid giant axons. Biophys J. 1980 Jun;30(3):473–488. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85108-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Time course of TEA(+)-induced anomalous rectification in squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Nov;50(2):491–503. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Perozo E., Papazian D. M., Stefani E. Molecular basis of gating charge immobilization in Shaker potassium channels. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):679–683. doi: 10.1126/science.1948047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Perozo E., Stefani E. Gating of Shaker K+ channels: II. The components of gating currents and a model of channel activation. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1011–1021. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80882-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Almers W. Block of sodium conductance and gating current in squid giant axons poisoned with quaternary strychnine. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85202-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay J. R. Asymmetric modulation and blockade of the delayed rectifier in squid giant axons by divalent cations. Biophys J. 1995 Nov;69(5):1773–1779. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80047-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., Inoue I., Kukita F., Stühmer W. Pressure dependence of sodium gating currents in the squid giant axon. Eur Biophys J. 1984;11(2):137–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00276629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. L., Kehl S. J. Changes of activation and inactivation gating of the transient potassium current of rat pituitary melanotrophs caused by micromolar Cd2+ and Zn2+. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;73(1):36–42. doi: 10.1139/y95-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demo S. D., Yellen G. Ion effects on gating of the Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel correlate with occupancy of the pore. Biophys J. 1992 Mar;61(3):639–648. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81869-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demo S. D., Yellen G. The inactivation gate of the Shaker K+ channel behaves like an open-channel blocker. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):743–753. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C., Brodwick M. S. Effects of barium on the potassium conductance of squid axon. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jun;75(6):727–750. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.6.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Armstrong C. M. Divalent cations and the activation kinetics of potassium channels in squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jun;79(6):965–996. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Armstrong C. M. Slowing of sodium channel opening kinetics in squid axon by extracellular zinc. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jun;79(6):935–964. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.6.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grissmer S., Cahalan M. D. Divalent ion trapping inside potassium channels of human T lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Apr;93(4):609–630. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Radke H. K., Tamkun M. M., Lovinger D. M. Modulation of gating of cloned rat and human K+ channels by micromolar Zn2+. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;43(3):482–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Biophysical and molecular mechanisms of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):533–538. doi: 10.1126/science.2122519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst R. S., Latorre R., Toro L., Stefani E. External barium block of Shaker potassium channels: evidence for two binding sites. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Dec;106(6):1069–1087. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.6.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst R. S., Toro L., Stefani E. Molecular determinants of external barium block in Shaker potassium channels. FEBS Lett. 1996 Jun 10;388(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00516-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Rojas E. Characteristics of the sodium gating current in the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;233(1):28P–30P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren G., Liman E. R., Logothetis D. E., Nadal-Ginard B., Hess P. Gating mechanism of a cloned potassium channel expressed in frog oocytes and mammalian cells. Neuron. 1990 Jan;4(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90442-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez G. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Evidence that the S6 segment of the Shaker voltage-gated K+ channel comprises part of the pore. Nature. 1994 Jan 13;367(6459):179–182. doi: 10.1038/367179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Barneo J., Hoshi T., Heinemann S. H., Aldrich R. W. Effects of external cations and mutations in the pore region on C-type inactivation of Shaker potassium channels. Receptors Channels. 1993;1(1):61–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Swenson R. P., Jr External monovalent cations that impede the closing of K channels. J Gen Physiol. 1986 May;87(5):795–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack K., Joiner W. J., Heinemann S. H. A characterization of the activating structural rearrangements in voltage-dependent Shaker K+ channels. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Latorre R., Reisin I. Coupling of voltage-dependent gating and Ba++ block in the high-conductance, Ca++-activated K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Sep;90(3):427–449. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Miller C. Discrete Ba2+ block as a probe of ion occupancy and pore structure in the high-conductance Ca2+ -activated K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Nov;92(5):569–586. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.5.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Pelleschi M. Multi-ion occupancy alters gating in high-conductance, Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Apr;97(4):641–665. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.4.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perozo E., MacKinnon R., Bezanilla F., Stefani E. Gating currents from a nonconducting mutant reveal open-closed conformations in Shaker K+ channels. Neuron. 1993 Aug;11(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perozo E., Papazian D. M., Stefani E., Bezanilla F. Gating currents in Shaker K+ channels. Implications for activation and inactivation models. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):160–171. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81802-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Bullock J. O. Modifications of sodium channel gating in Myxicola giant axons by deuterium oxide, temperature, and internal cations. Biophys J. 1979 Aug;27(2):193–208. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85211-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoppa N. E., McCormack K., Tanouye M. A., Sigworth F. J. The size of gating charge in wild-type and mutant Shaker potassium channels. Science. 1992 Mar 27;255(5052):1712–1715. doi: 10.1126/science.1553560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slesinger P. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. The S4-S5 loop contributes to the ion-selective pore of potassium channels. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song L., Magleby K. L. Testing for microscopic reversibility in the gating of maxi K+ channels using two-dimensional dwell-time distributions. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80458-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spires S., Begenisich T. Modulation of potassium channel gating by external divalent cations. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Oct;104(4):675–692. doi: 10.1085/jgp.104.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spires S., Begenisich T. Voltage-independent gating transitions in squid axon potassium channels. Biophys J. 1995 Feb;68(2):491–500. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80210-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Toro L., Perozo E., Bezanilla F. Gating of Shaker K+ channels: I. Ionic and gating currents. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):996–1010. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80881-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg I. Z. Frequencies of paired open-closed durations of ion channels. Method of evaluation from single-channel recordings. Biophys J. 1987 Jul;52(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83187-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg I. Z. Relationship between statistical properties of single ionic channel recordings and the thermodynamic state of the channels. J Theor Biol. 1987 Jan 7;124(1):71–87. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(87)80253-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Conti F., Stocker M., Pongs O., Heinemann S. H. Gating currents of inactivating and non-inactivating potassium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1991 May;418(4):423–429. doi: 10.1007/BF00550881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Jr, Armstrong C. M. K+ channels close more slowly in the presence of external K+ and Rb+. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):427–429. doi: 10.1038/291427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taglialatela M., Drewe J. A., Brown A. M. Barium blockade of a clonal potassium channel and its regulation by a critical pore residue. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;44(1):180–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talukder G., Harrison N. L. On the mechanism of modulation of transient outward current in cultured rat hippocampal neurons by di- and trivalent cations. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Jan;73(1):73–79. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.73.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollmuth L. P. Mechanism of Ba2+ block of M-like K channels of rod photoreceptors of tiger salamanders. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Jan;103(1):45–66. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Voltage-dependent gating of Shaker A-type potassium channels in Drosophila muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jan;95(1):29–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., Aldrich R. W. Shaker potassium channel gating. III: Evaluation of kinetic models for activation. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Feb;103(2):321–362. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., Dittman J., Aldrich R. W. Shaker potassium channel gating. II: Transitions in the activation pathway. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Feb;103(2):279–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


