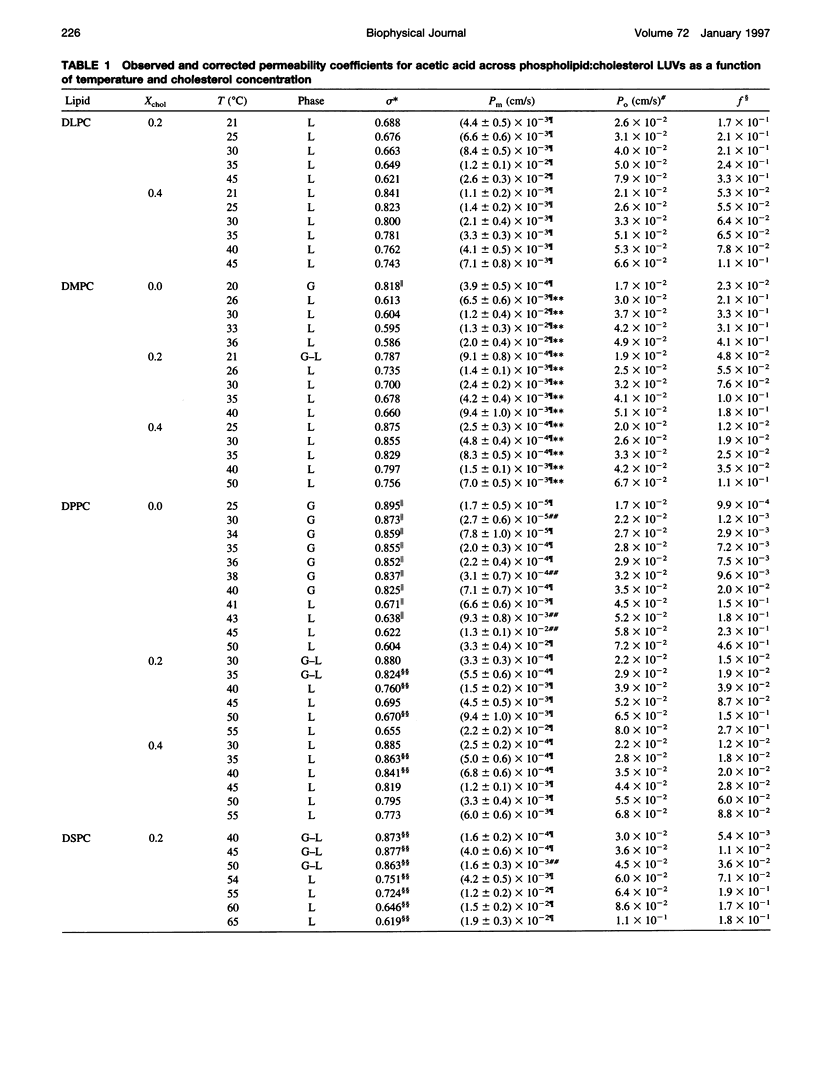
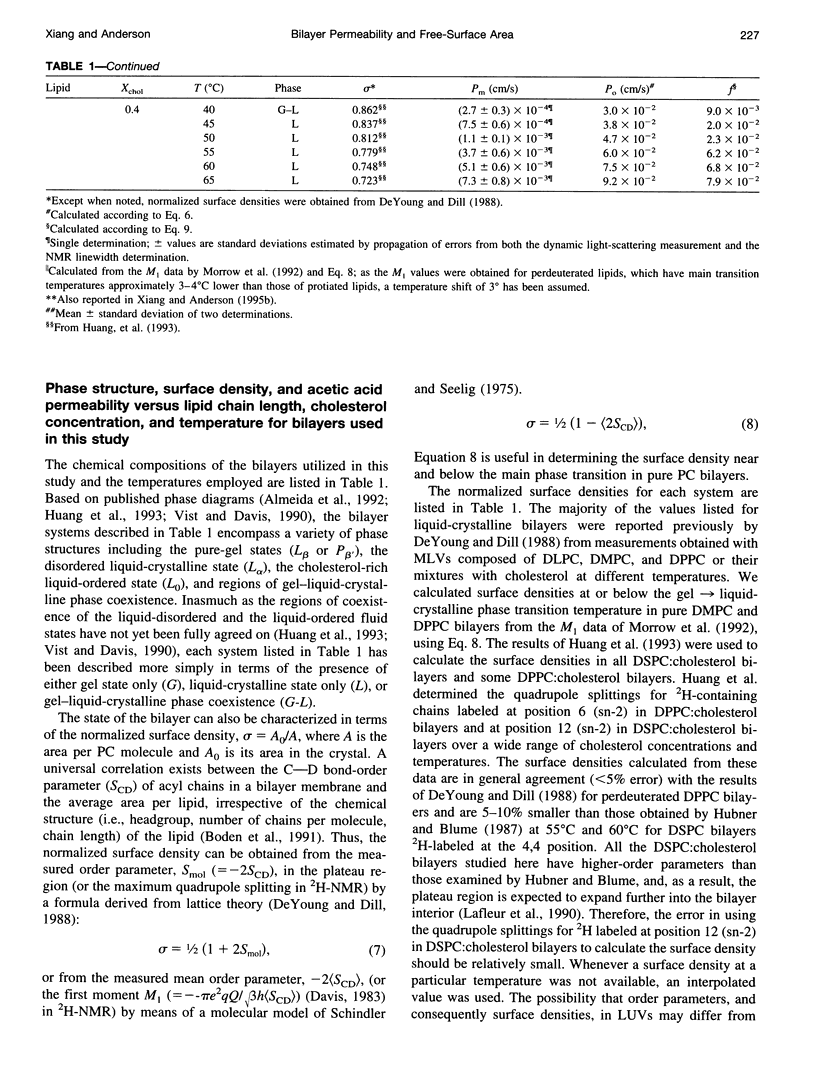
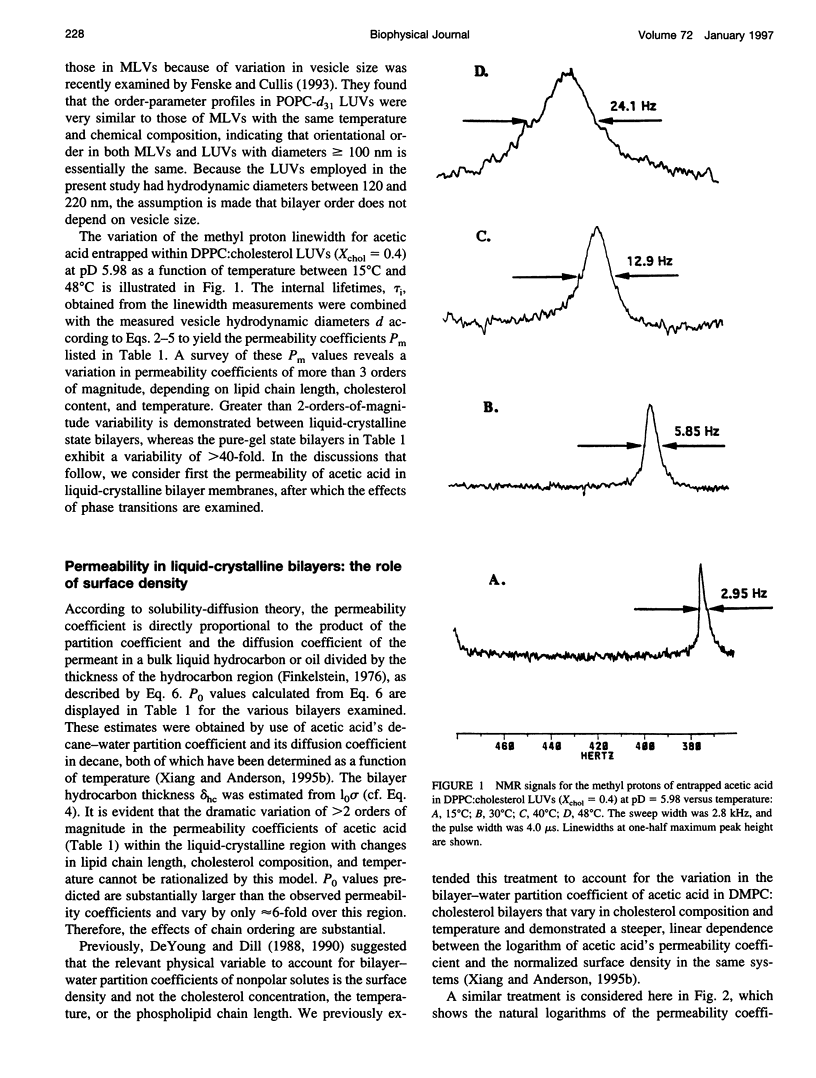
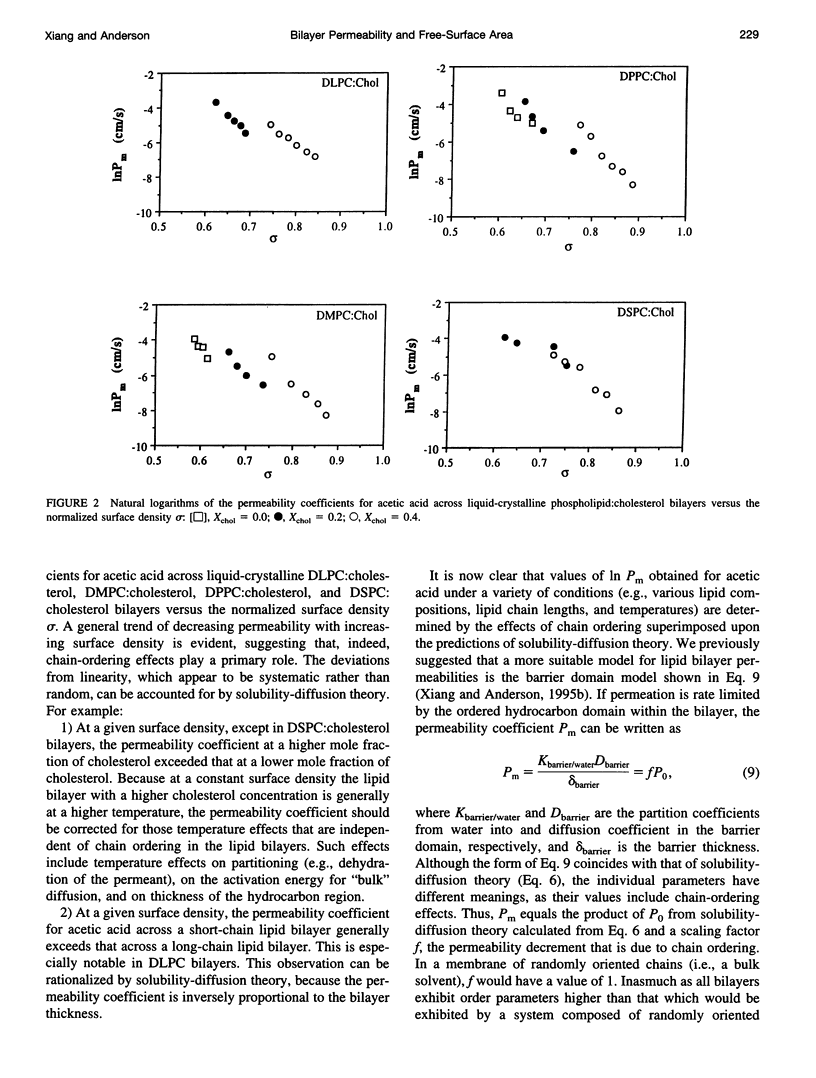
Abstract
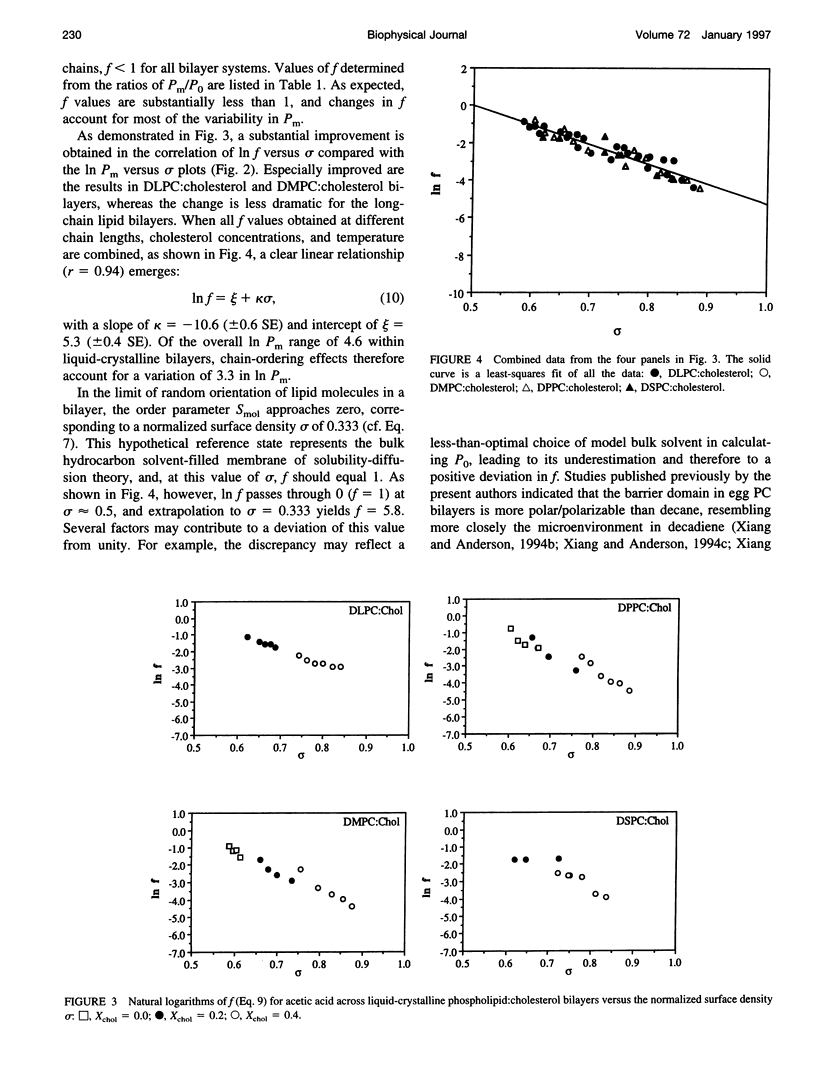
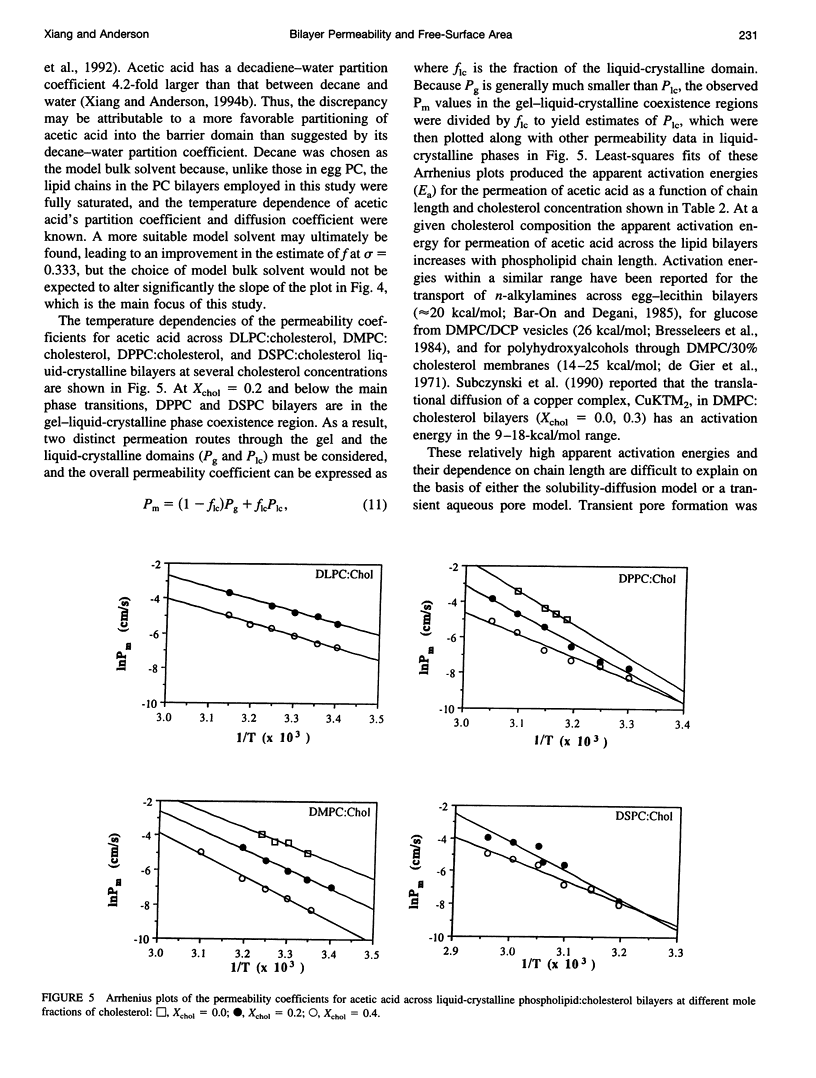
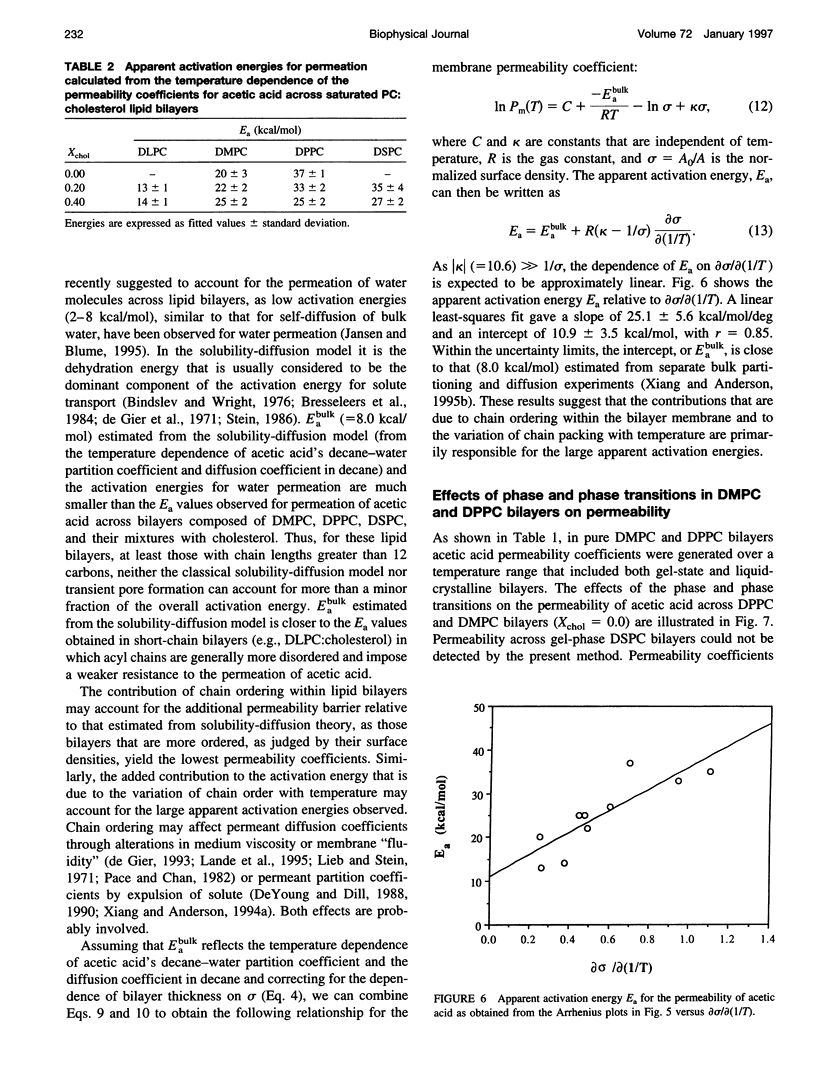
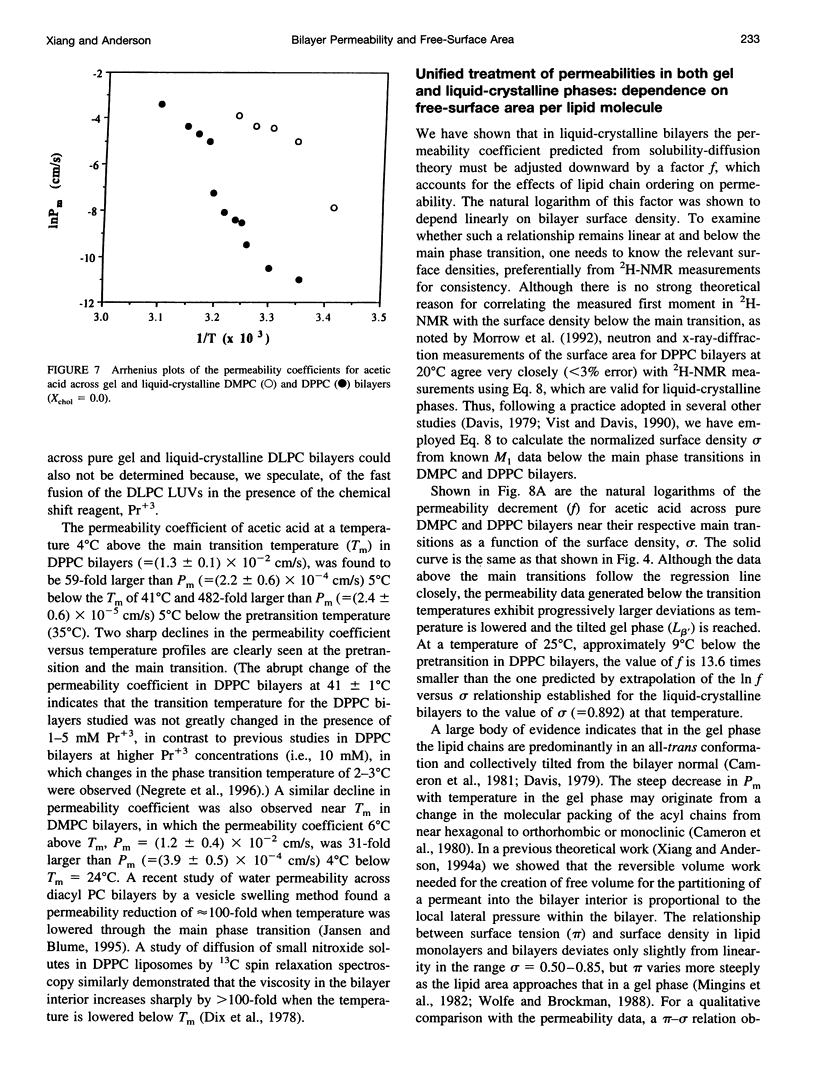
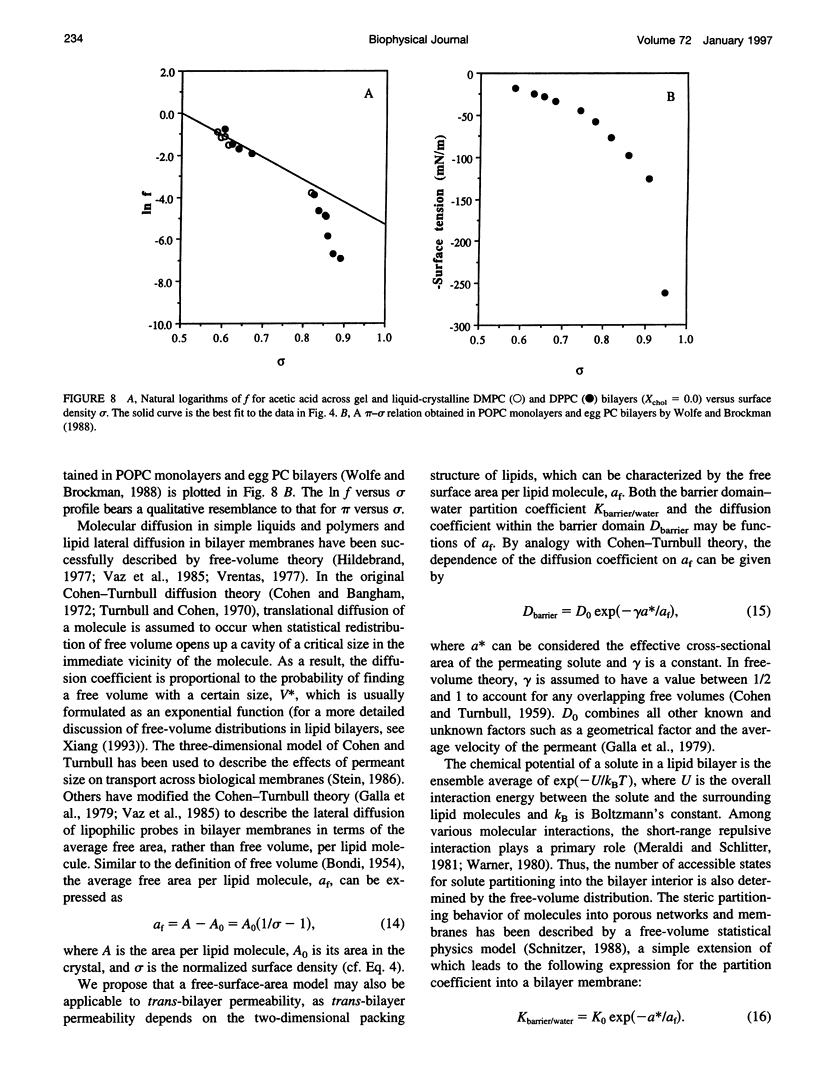
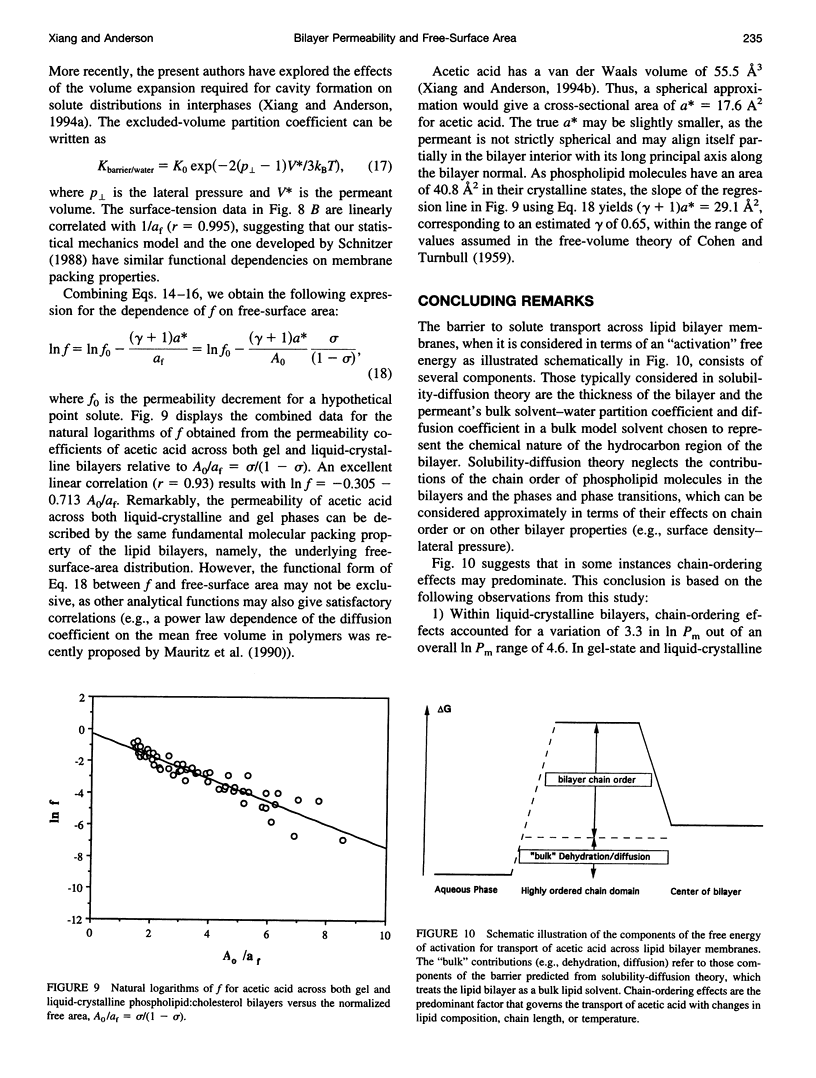
Solubility-diffusion theory, which treats the lipid bilayer membrane as a bulk lipid solvent into which permeants must partition and diffuse across, fails to account for the effects of lipid bilayer chain order on the permeability coefficient of any given permeant. This study addresses the scaling factor that must be applied to predictions from solubility-diffusion theory to correct for chain ordering. The effects of bilayer chemical composition, temperature, and phase structure on the permeability coefficient (Pm) of acetic acid were investigated in large unilamellar vesicles by a combined method of NMR line broadening and dynamic light scattering. Permeability values were obtained in distearoylphosphatidylcholine, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine, and dilauroylphosphatidylcholine bilayers, and their mixtures with cholesterol, at various temperatures both above and below the gel-->liquid-crystalline phase transition temperatures (Tm). A new scaling factor, the permeability decrement f, is introduced to account for the decrease in permeability coefficient from that predicted by solubility-diffusion theory owing to chain ordering in lipid bilayers. Values of f were obtained by division of the observed Pm by the permeability coefficient predicted from a bulk solubility-diffusion model. In liquid-crystalline phases, a strong correlation (r = 0.94) between f and the normalized surface density sigma was obtained: in f = 5.3 - 10.6 sigma. Activation energies (Ea) for the permeability of acetic acid decreased with decreasing phospholipid chain length and correlated with the sensitivity of chain ordering to temperature, [symbol: see text] sigma/[symbol: see text](1/T), as chain length was varied. Pm values decreased abruptly at temperatures below the main phase transition temperatures in pure dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine and dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers (30-60-fold) and below the pretransition in dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers (8-fold), and the linear relationship between in f and sigma established for liquid-crystalline bilayers was no longer followed. However, in both gel and liquid-crystalline phases in f was found to exhibit an inverse correlation with free surface area (in f = -0.31 - 29.1/af, where af is the average free area (in square angstroms) per lipid molecule). Thus, the lipid bilayer permeability of acetic acid can be predicted from the relevant chain-packing properties in the bilayer (free surface area), regardless of whether chain ordering is varied by changes in temperature, lipid chain length, cholesterol concentration, or bilayer phase structure, provided that temperature effects on permeant dehydration and diffusion and the chain-length effects on bilayer barrier thickness are properly taken into account.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alger J. R., Prestegard J. H. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of acetic acid permeation of large unilamellar vesicle membranes. Biophys J. 1979 Oct;28(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85154-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida P. F., Vaz W. L., Thompson T. E. Lateral diffusion in the liquid phases of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine/cholesterol lipid bilayers: a free volume analysis. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 28;31(29):6739–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00144a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangham A. D., Standish M. M., Watkins J. C. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):238–252. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-On Z., Degani H. Permeability of alkylamines across phosphatidylcholine vesicles as studied by 1H-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 14;813(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindslev N., Wright E. M. Effect of temperature on nonelectrolyte permeation across the toad urinary bladder. J Membr Biol. 1976 Nov 22;29(3):265–288. doi: 10.1007/BF01868966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden N., Jones S. A., Sixl F. On the use of deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance as a probe of chain packing in lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2146–2155. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresseleers G. J., Goderis H. L., Tobback P. P. Measurement of the glucose permeation rate across phospholipid bilayers using small unilamellar vesicles. Effect of membrane composition and temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 30;772(3):374–382. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. G., Casal H. L., Gudgin E. F., Mantsch H. H. The gel phase of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine. An infrared characterization of the acyl chain packing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 13;596(3):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. G., Casal H. L., Mantsch H. H., Boulanger Y., Smith I. C. The thermotropic behavior of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine bilayers. A Fourier transform infrared study of specifically labeled lipids. Biophys J. 1981 Jul;35(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84769-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. E., Bangham A. D. Diffusion of small non-electrolytes across liposome membranes. Nature. 1972 Mar 24;236(5343):173–174. doi: 10.1038/236173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. H. Deuterium magnetic resonance study of the gel and liquid crystalline phases of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biophys J. 1979 Sep;27(3):339–358. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85222-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. H. The description of membrane lipid conformation, order and dynamics by 2H-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):117–171. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Gier J., Mandersloot J. G., Hupkes J. V., McElhaney R. N., Van Beek W. P. On the mechanism of non-electrolyte permeation through lipid bilayers and through biomembranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 1;233(3):610–618. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90160-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Young L. R., Dill K. A. Solute partitioning into lipid bilayer membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5281–5289. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix J. A., Kivelson D., Diamond J. M. Molecular motion of small nonelectrolyte molecules in lecithin bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1978 Jun 9;40(4):315–342. doi: 10.1007/BF01874162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenske D. B., Cullis P. R. Acyl chain orientational order in large unilamellar vesicles: comparison with multilamellar liposomes: a 2H and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biophys J. 1993 May;64(5):1482–1491. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81515-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A. Water and nonelectrolyte permeability of lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Aug;68(2):127–135. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.2.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Hartmann W., Theilen U., Sackmann E. On two-dimensional passive random walk in lipid bilayers and fluid pathways in biomembranes. J Membr Biol. 1979 Jul 31;48(3):215–236. doi: 10.1007/BF01872892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. H., Lee C. W., Das Gupta S. K., Blume A., Griffin R. G. A 13C and 2H nuclear magnetic resonance study of phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol interactions: characterization of liquid-gel phases. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 7;32(48):13277–13287. doi: 10.1021/bi00211a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen M., Blume A. A comparative study of diffusive and osmotic water permeation across bilayers composed of phospholipids with different head groups and fatty acyl chains. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):997–1008. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80275-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafleur M., Cullis P. R., Bloom M. Modulation of the orientational order profile of the lipid acyl chain in the L alpha phase. Eur Biophys J. 1990;19(2):55–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00185086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe M. A., Williams M. L., Elias P. M. Human epidermal lipids: characterization and modulations during differentiation. J Lipid Res. 1983 Feb;24(2):131–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lande M. B., Donovan J. M., Zeidel M. L. The relationship between membrane fluidity and permeabilities to water, solutes, ammonia, and protons. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Jul;106(1):67–84. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magin R. L., Niesman M. R. Temperature-dependent permeability of large unilamellar liposomes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1984 Mar;34(3):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(84)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meraldi J. P., Schlitter J. A statistical mechanical treatment of fatty acyl chain order in phospholipid bilayers and correlation with experimental data. A. Theory. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 20;645(2):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow M. R., Whitehead J. P., Lu D. Chain-length dependence of lipid bilayer properties near the liquid crystal to gel phase transition. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):18–27. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81579-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wilkinson D. A. Lecithin bilayers. Density measurement and molecular interactions. Biophys J. 1978 Aug;23(2):159–175. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85441-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson F., Hunt C. A., Szoka F. C., Vail W. J., Papahadjopoulos D. Preparation of liposomes of defined size distribution by extrusion through polycarbonate membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):9–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paula S., Volkov A. G., Van Hoek A. N., Haines T. H., Deamer D. W. Permeation of protons, potassium ions, and small polar molecules through phospholipid bilayers as a function of membrane thickness. Biophys J. 1996 Jan;70(1):339–348. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79575-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Beck K. Translational diffusion in phospholipid monolayers measured by fluorescence microphotolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7183–7187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sada E., Katoh S., Terashima M., Kawahara H., Katoh M. Effects of surface charges and cholesterol content on amino acid permeabilities of small unilamellar vesicles. J Pharm Sci. 1990 Mar;79(3):232–235. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600790311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Seelig J. Deuterium order parameters in relation to thermodynamic properties of a phospholiped bilayer. A statistical mechanical interpretation. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2283–2287. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J. E. Analysis of steric partition behavior of molecules in membranes using statistical physics. Application to gel chromatography and electrophoresis. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1065–1076. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83043-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4839–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., McIntosh T. J. Interdigitated hydrocarbon chain packing causes the biphasic transition behavior in lipid/alcohol suspensions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 13;773(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90562-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subczynski W. K., Antholine W. E., Hyde J. S., Kusumi A. Microimmiscibility and three-dimensional dynamic structures of phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol membranes: translational diffusion of a copper complex in the membrane. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7936–7945. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subczynski W. K., Hyde J. S. Concentration of oxygen in lipid bilayers using a spin-label method. Biophys J. 1983 Mar;41(3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84439-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd A. P., Mehlhorn R. J., Macey R. I. Amine and carboxylate spin probe permeability in red cells. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):41–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01870789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd A. P., Mehlhorn R. J., Macey R. I. Amine spin probe permeability in sonicated liposomes. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):53–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01870790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Clegg R. M., Hallmann D. Translational diffusion of lipids in liquid crystalline phase phosphatidylcholine multibilayers. A comparison of experiment with theory. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):781–786. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vist M. R., Davis J. H. Phase equilibria of cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures: 2H nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):451–464. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter A., Gutknecht J. Permeability of small nonelectrolytes through lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(3):207–217. doi: 10.1007/BF01870127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe D. H., Brockman H. L. Regulation of the surface pressure of lipid monolayers and bilayers by the activity of water: derivation and application of an equation of state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4285–4289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang T. X. A computer simulation of free-volume distributions and related structural properties in a model lipid bilayer. Biophys J. 1993 Sep;65(3):1108–1120. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81156-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang T. X., Anderson B. D. Development of a combined NMR paramagnetic ion-induced line-broadening/dynamic light scattering method for permeability measurements across lipid bilayer membranes. J Pharm Sci. 1995 Nov;84(11):1308–1315. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600841110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang T. X., Anderson B. D. Molecular distributions in interphases: statistical mechanical theory combined with molecular dynamics simulation of a model lipid bilayer. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):561–572. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80833-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang T. X., Anderson B. D. Phospholipid surface density determines the partitioning and permeability of acetic acid in DMPC:cholesterol bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1995 Nov;148(2):157–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00207271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang T. X., Anderson B. D. Substituent contributions to the transport of substituted p-toluic acids across lipid bilayer membranes. J Pharm Sci. 1994 Oct;83(10):1511–1518. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600831027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang T. X., Anderson B. D. The relationship between permeant size and permeability in lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1994 Jun;140(2):111–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00232899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang T. X., Chen X., Anderson B. D. Transport methods for probing the barrier domain of lipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):78–88. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81581-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gier J. Osmotic behaviour and permeability properties of liposomes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1993 Sep;64(1-3):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(93)90065-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


