Abstract
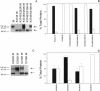
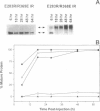
In voltage-dependent Shaker K+ channels, charged residues E293 in transmembrane segment S2 and R365, R368, and R371 in S4 contribute significantly to the gating charge movement that accompanies activation. Using an intragenic suppression strategy, we have now probed for structural interaction between transmembrane segments S2, S3, and S4 in Shaker channels. Charge reversal mutations of E283 in S2 and K374 in S4 disrupt maturation of the protein. Maturation was specifically and efficiently rescued by second-site charge reversal mutations, indicating that electrostatic interactions exist between E283 in S2 and R368 and R371 in S4, and between K374 in S4 and E293 in S2 and D316 in S3. Rescued subunits were incorporated into functional channels, demonstrating that a native structure was restored. Our data indicate that K374 interacts with E293 and D316 within the same subunit. These electrostatic interactions mediate the proper folding of the protein and are likely to persist in the native structure. Our results raise the possibility that the S4 segment is tilted relative to S2 and S3 in the voltage-sensing domain of Shaker channels. Such an arrangement might provide solvent access to voltage-sensing residues, which we find to be highly tolerant of mutations.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal S. K., MacKinnon R. Contribution of the S4 segment to gating charge in the Shaker K+ channel. Neuron. 1996 Jun;16(6):1169–1177. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. E., Becktel W. J., Dahlquist F. W. pH-induced denaturation of proteins: a single salt bridge contributes 3-5 kcal/mol to the free energy of folding of T4 lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2403–2408. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Perozo E., Stefani E. Gating of Shaker K+ channels: II. The components of gating currents and a model of channel activation. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1011–1021. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80882-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Molecular properties of voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:953–985. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosson P., Lankford S. P., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Membrane protein association by potential intramembrane charge pairs. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):414–416. doi: 10.1038/351414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demo S. D., Yellen G. The inactivation gate of the Shaker K+ channel behaves like an open-channel blocker. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):743–753. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durell S. R., Guy H. R. Atomic scale structure and functional models of voltage-gated potassium channels. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):238–250. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81809-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fersht A. R. Conformational equilibria in -and -chymotrypsin. The energetics and importance of the salt bridge. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(2):497–509. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. A. A structural vignette common to voltage sensors and conduction pores: canaliculi. Neuron. 1996 Apr;16(4):717–722. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Conti F. Pursuing the structure and function of voltage-gated channels. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jun;13(6):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90160-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzog P. E., Cain B. D. Second-site suppressor mutations at glycine 218 and histidine 245 in the alpha subunit of F1F0 ATP synthase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32313–32317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendsch Z. S., Jonsson T., Sauer R. T., Tidor B. Protein stabilization by removal of unsatisfied polar groups: computational approaches and experimental tests. Biochemistry. 1996 Jun 18;35(24):7621–7625. doi: 10.1021/bi9605191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendsch Z. S., Tidor B. Do salt bridges stabilize proteins? A continuum electrostatic analysis. Protein Sci. 1994 Feb;3(2):211–226. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Biophysical and molecular mechanisms of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):533–538. doi: 10.1126/science.2122519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacoff E. Y., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Putative receptor for the cytoplasmic inactivation gate in the Shaker K+ channel. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):86–90. doi: 10.1038/353086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. C., Hansen C. L., Wilson T. H. The interaction between aspartic acid 237 and lysine 358 in the lactose carrier of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 25;1062(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90390-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landt O., Grunert H. P., Hahn U. A general method for rapid site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1990 Nov 30;96(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90351-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson H. P., Baker O. S., Dhillon D. S., Isacoff E. Y. Transmembrane movement of the shaker K+ channel S4. Neuron. 1996 Feb;16(2):387–397. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. I., Hwang P. P., Hansen C., Wilson T. H. Possible salt bridges between transmembrane alpha-helices of the lactose carrier of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20758–20764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Engelman D. M. Specificity and promiscuity in membrane helix interactions. Q Rev Biophys. 1994 May;27(2):157–218. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Flanagan J. M., Hunt J. F., Adair B. D., Bormann B. J., Dempsey C. E., Engelman D. M. Glycophorin A dimerization is driven by specific interactions between transmembrane alpha-helices. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7683–7689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Flanagan J. M., Treutlein H. R., Zhang J., Engelman D. M. Sequence specificity in the dimerization of transmembrane alpha-helices. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 29;31(51):12719–12725. doi: 10.1021/bi00166a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Treutlein H. R., Adams P. D., Brünger A. T., Engelman D. M. A dimerization motif for transmembrane alpha-helices. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Mar;1(3):157–163. doi: 10.1038/nsb0394-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Unwin N., Stauffer K. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Images of purified Shaker potassium channels. Curr Biol. 1994 Feb 1;4(2):110–115. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(94)00026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Mathias N., Steussy C. N., Goebl M. G. Intragenic suppression among CDC34 (UBC3) mutations defines a class of ubiquitin-conjugating catalytic domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;15(10):5635–5644. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.10.5635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Aldrich R. W., Lee A. W. Functional stoichiometry of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):757–759. doi: 10.1126/science.7694359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R. Determination of the subunit stoichiometry of a voltage-activated potassium channel. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):232–235. doi: 10.1038/350232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Yellen G. Mutations affecting TEA blockade and ion permeation in voltage-activated K+ channels. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):276–279. doi: 10.1126/science.2218530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannuzzu L. M., Moronne M. M., Isacoff E. Y. Direct physical measure of conformational rearrangement underlying potassium channel gating. Science. 1996 Jan 12;271(5246):213–216. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5246.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeker A. K., Garcia-Moreno B., Shortle D. Contributions of the ionizable amino acids to the stability of staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1996 May 21;35(20):6443–6449. doi: 10.1021/bi960171+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H. Roles of electrostatic interaction in proteins. Q Rev Biophys. 1996 Feb;29(1):1–90. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveberg M., Fersht A. R. New approach to the study of transient protein conformations: the formation of a semiburied salt link in the folding pathway of barnase. Biochemistry. 1996 May 28;35(21):6795–6805. doi: 10.1021/bi9529317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papazian D. M., Shao X. M., Seoh S. A., Mock A. F., Huang Y., Wainstock D. H. Electrostatic interactions of S4 voltage sensor in Shaker K+ channel. Neuron. 1995 Jun;14(6):1293–1301. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papazian D. M., Timpe L. C., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Alteration of voltage-dependence of Shaker potassium channel by mutations in the S4 sequence. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):305–310. doi: 10.1038/349305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peled-Zehavi H., Arkin I. T., Engelman D. M., Shai Y. Coassembly of synthetic segments of shaker K+ channel within phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1996 May 28;35(21):6828–6838. doi: 10.1021/bi952988t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perozo E., Santacruz-Toloza L., Stefani E., Bezanilla F., Papazian D. M. S4 mutations alter gating currents of Shaker K channels. Biophys J. 1994 Feb;66(2 Pt 1):345–354. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80783-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin-Tóth M., Kaback H. R. Properties of interacting aspartic acid and lysine residues in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 28;32(38):10027–10035. doi: 10.1021/bi00089a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santacruz-Toloza L., Huang Y., John S. A., Papazian D. M. Glycosylation of shaker potassium channel protein in insect cell culture and in Xenopus oocytes. Biochemistry. 1994 May 10;33(18):5607–5613. doi: 10.1021/bi00184a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoppa N. E., McCormack K., Tanouye M. A., Sigworth F. J. The size of gating charge in wild-type and mutant Shaker potassium channels. Science. 1992 Mar 27;255(5052):1712–1715. doi: 10.1126/science.1553560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulteis C. T., John S. A., Huang Y., Tang C. Y., Papazian D. M. Conserved cysteine residues in the shaker K+ channel are not linked by a disulfide bond. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 7;34(5):1725–1733. doi: 10.1021/bi00005a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulteis C. T., Nagaya N., Papazian D. M. Intersubunit interaction between amino- and carboxyl-terminal cysteine residues in tetrameric shaker K+ channels. Biochemistry. 1996 Sep 17;35(37):12133–12140. doi: 10.1021/bi961083s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Multiple potassium-channel components are produced by alternative splicing at the Shaker locus in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):137–142. doi: 10.1038/331137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seoh S. A., Sigg D., Papazian D. M., Bezanilla F. Voltage-sensing residues in the S2 and S4 segments of the Shaker K+ channel. Neuron. 1996 Jun;16(6):1159–1167. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Lin B. Genetic analysis of staphylococcal nuclease: identification of three intragenic "global" suppressors of nuclease-minus mutations. Genetics. 1985 Aug;110(4):539–555. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Voltage gating of ion channels. Q Rev Biophys. 1994 Feb;27(1):1–40. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpe L. C., Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Expression of functional potassium channels from Shaker cDNA in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):143–145. doi: 10.1038/331143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissot A. C., Vuilleumier S., Fersht A. R. Importance of two buried salt bridges in the stability and folding pathway of barnase. Biochemistry. 1996 May 28;35(21):6786–6794. doi: 10.1021/bi952930e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldburger C. D., Schildbach J. F., Sauer R. T. Are buried salt bridges important for protein stability and conformational specificity? Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Feb;2(2):122–128. doi: 10.1038/nsb0295-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N., George A. L., Jr, Horn R. Molecular basis of charge movement in voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 1996 Jan;16(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N., Horn R. Evidence for voltage-dependent S4 movement in sodium channels. Neuron. 1995 Jul;15(1):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G., Jurman M. E., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. Mutations affecting internal TEA blockade identify the probable pore-forming region of a K+ channel. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):939–942. doi: 10.1126/science.2000494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., Aldrich R. W. Restoration of inactivation in mutants of Shaker potassium channels by a peptide derived from ShB. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):568–571. doi: 10.1126/science.2122520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., Aldrich R. W. Shaker potassium channel gating. III: Evaluation of kinetic models for activation. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Feb;103(2):321–362. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Rago J. P., Hermann-Le Denmat S., Pâques F., Risler F. P., Netter P., Slonimski P. P. Genetic analysis of the folded structure of yeast mitochondrial cytochrome b by selection of intragenic second-site revertants. J Mol Biol. 1995 May 12;248(4):804–811. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Rago J. P., Netter P., Slonimski P. P. Intragenic suppressors reveal long distance interactions between inactivating and reactivating amino acid replacements generating three-dimensional constraints in the structure of mitochondrial cytochrome b. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15750–15757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]