Abstract
In biology, molecular linkages at, within, and beneath cell interfaces arise mainly from weak noncovalent interactions. These bonds will fail under any level of pulling force if held for sufficient time. Thus, when tested with ultrasensitive force probes, we expect cohesive material strength and strength of adhesion at interfaces to be time- and loading rate-dependent properties. To examine what can be learned from measurements of bond strength, we have extended Kramers' theory for reaction kinetics in liquids to bond dissociation under force and tested the predictions by smart Monte Carlo (Brownian dynamics) simulations of bond rupture. By definition, bond strength is the force that produces the most frequent failure in repeated tests of breakage, i.e., the peak in the distribution of rupture forces. As verified by the simulations, theory shows that bond strength progresses through three dynamic regimes of loading rate. First, bond strength emerges at a critical rate of loading (> or = 0) at which spontaneous dissociation is just frequent enough to keep the distribution peak at zero force. In the slow-loading regime immediately above the critical rate, strength grows as a weak power of loading rate and reflects initial coupling of force to the bonding potential. At higher rates, there is crossover to a fast regime in which strength continues to increase as the logarithm of the loading rate over many decades independent of the type of attraction. Finally, at ultrafast loading rates approaching the domain of molecular dynamics simulations, the bonding potential is quickly overwhelmed by the rapidly increasing force, so that only naked frictional drag on the structure remains to retard separation. Hence, to expose the energy landscape that governs bond strength, molecular adhesion forces must be examined over an enormous span of time scales. However, a significant gap exists between the time domain of force measurements in the laboratory and the extremely fast scale of molecular motions. Using results from a simulation of biotin-avidin bonds (Izrailev, S., S. Stepaniants, M. Balsera, Y. Oono, and K. Schulten. 1997. Molecular dynamics study of unbinding of the avidin-biotin complex. Biophys. J., this issue), we describe how Brownian dynamics can help bridge the gap between molecular dynamics and probe tests.
Full text
PDF

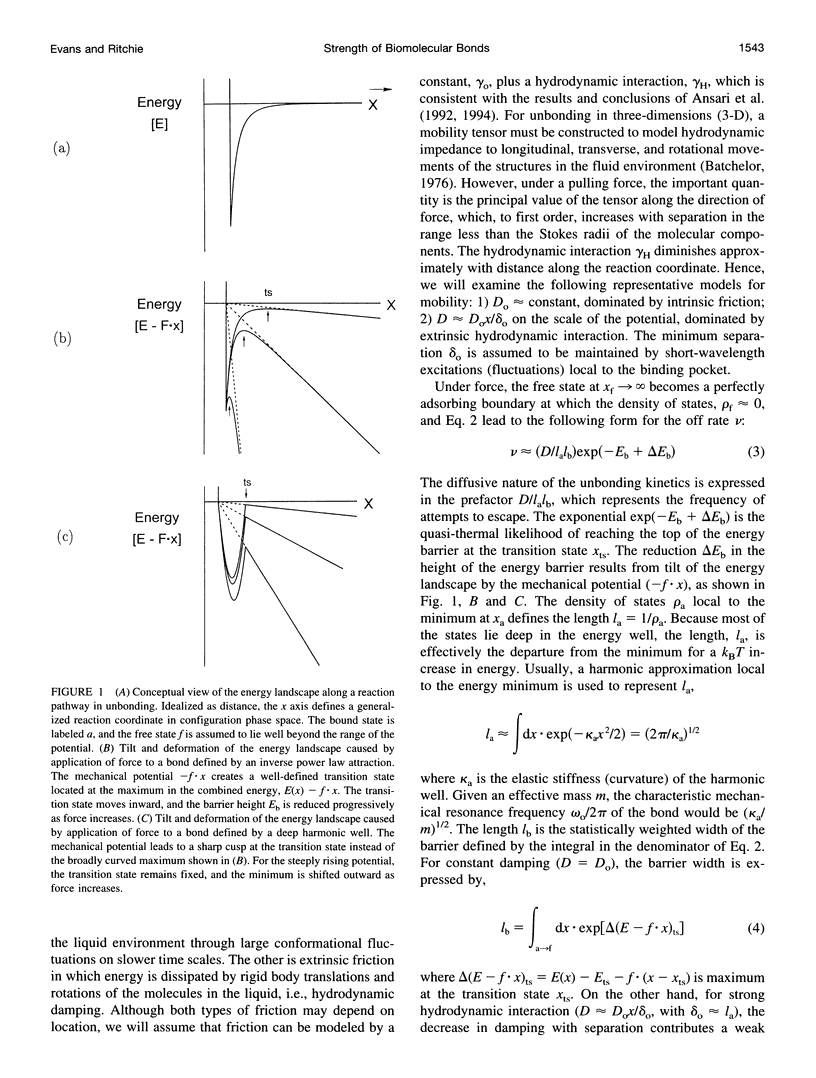







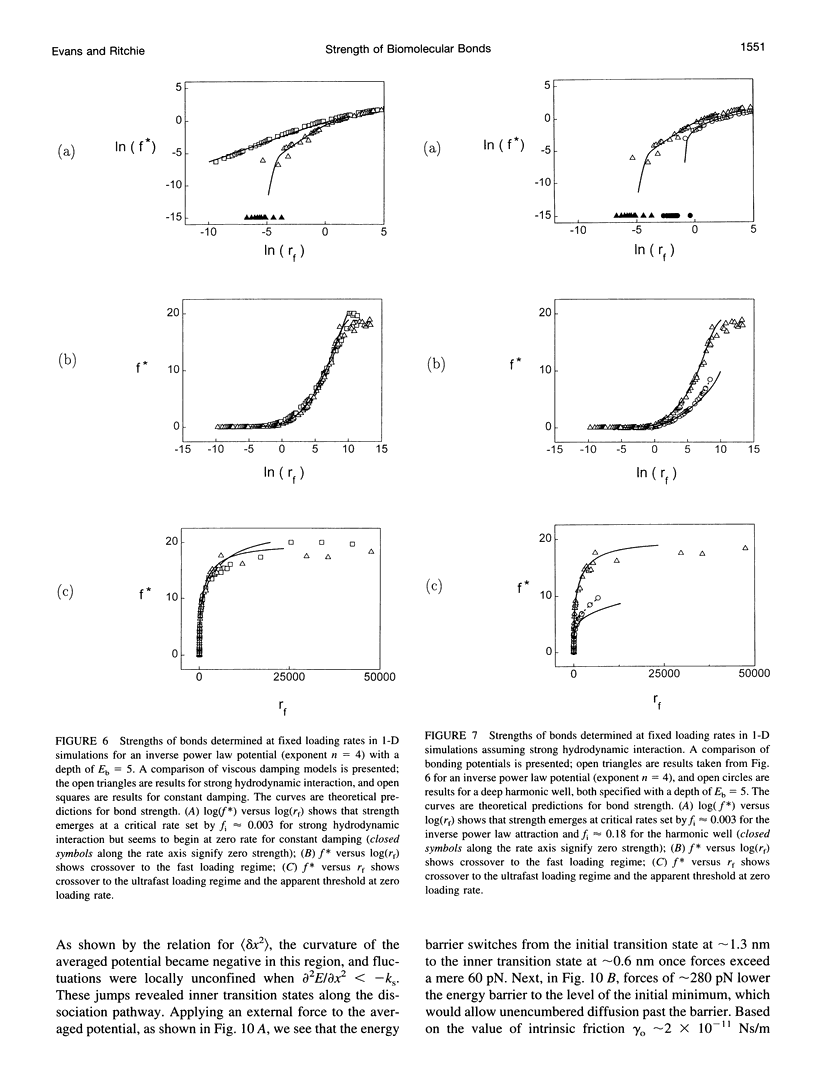




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alon R., Hammer D. A., Springer T. A. Lifetime of the P-selectin-carbohydrate bond and its response to tensile force in hydrodynamic flow. Nature. 1995 Apr 6;374(6522):539–542. doi: 10.1038/374539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari A., Jones C. M., Henry E. R., Hofrichter J., Eaton W. A. Conformational relaxation and ligand binding in myoglobin. Biochemistry. 1994 May 3;33(17):5128–5145. doi: 10.1021/bi00183a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari A., Jones C. M., Henry E. R., Hofrichter J., Eaton W. A. The role of solvent viscosity in the dynamics of protein conformational changes. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1796–1798. doi: 10.1126/science.1615323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkin A., Schütze K., Dziedzic J. M., Euteneuer U., Schliwa M. Force generation of organelle transport measured in vivo by an infrared laser trap. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):346–348. doi: 10.1038/348346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science. 1978 May 12;200(4342):618–627. doi: 10.1126/science.347575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembo M., Torney D. C., Saxman K., Hammer D. The reaction-limited kinetics of membrane-to-surface adhesion and detachment. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jun 22;234(1274):55–83. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Berk D., Leung A. Detachment of agglutinin-bonded red blood cells. I. Forces to rupture molecular-point attachments. Biophys J. 1991 Apr;59(4):838–848. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82296-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Ritchie K., Merkel R. Sensitive force technique to probe molecular adhesion and structural linkages at biological interfaces. Biophys J. 1995 Jun;68(6):2580–2587. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80441-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florin E. L., Moy V. T., Gaub H. E. Adhesion forces between individual ligand-receptor pairs. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.8153628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubmüller H., Heymann B., Tavan P. Ligand binding: molecular mechanics calculation of the streptavidin-biotin rupture force. Science. 1996 Feb 16;271(5251):997–999. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5251.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izrailev S., Stepaniants S., Balsera M., Oono Y., Schulten K. Molecular dynamics study of unbinding of the avidin-biotin complex. Biophys J. 1997 Apr;72(4):1568–1581. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78804-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Sheetz M. P. Force of single kinesin molecules measured with optical tweezers. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):232–234. doi: 10.1126/science.8469975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moy V. T., Florin E. L., Gaub H. E. Intermolecular forces and energies between ligands and receptors. Science. 1994 Oct 14;266(5183):257–259. doi: 10.1126/science.7939660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmacher M., Tillamnn R. W., Fritz M., Gaub H. E. From molecules to cells: imaging soft samples with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1900–1905. doi: 10.1126/science.1411505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tees D. F., Coenen O., Goldsmith H. L. Interaction forces between red cells agglutinated by antibody. IV. Time and force dependence of break-up. Biophys J. 1993 Sep;65(3):1318–1334. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81180-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



